9212194d56033a5d4df2dc89b2638a2d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 Terms and Acronyms • To learn Information Technology (IT) is to learn the language of acronyms and terms… • WYSISYG (pronounced WHIZ-zee-wig) “What You See Is What You Get” GUI: Graphical User Interface Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 1
Terms and Acronyms • To learn Information Technology (IT) is to learn the language of acronyms and terms… • WYSISYG (pronounced WHIZ-zee-wig) “What You See Is What You Get” GUI: Graphical User Interface Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 1
 Computer Basics Students and Parents, This is an old computer basics Power. Point that I found on the web which will give you a very basic knowledge of computers and components. You may refer to this at any time except during tests on this material! Please note, this is not original but totally downloaded from the web. You will see the “Cabrillo College” banner throughout and I appreciate those who put this together and their generosity in letting it be used to teach additional students. Johnny Bley, St. Joseph Catholic Unit School Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 2
Computer Basics Students and Parents, This is an old computer basics Power. Point that I found on the web which will give you a very basic knowledge of computers and components. You may refer to this at any time except during tests on this material! Please note, this is not original but totally downloaded from the web. You will see the “Cabrillo College” banner throughout and I appreciate those who put this together and their generosity in letting it be used to teach additional students. Johnny Bley, St. Joseph Catholic Unit School Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 2
 What is a computer? • A computer is a electromechanical device which can be programmed to change (process) information from one form to another. – Do exactly as they are told. – Digital devices: Understand only two different states (OFF and ON) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 3
What is a computer? • A computer is a electromechanical device which can be programmed to change (process) information from one form to another. – Do exactly as they are told. – Digital devices: Understand only two different states (OFF and ON) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 3
 Computers are everywhere Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 4
Computers are everywhere Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 4
 Traditional Types of Computers • General purpose computers – Mainframe – Minicomputer – Microcomputer (Personal Computer) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 5
Traditional Types of Computers • General purpose computers – Mainframe – Minicomputer – Microcomputer (Personal Computer) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 5
 Traditional Types of Computers • Mainframe Computers • • • First computers, introduced in 1950 s Used by large businesses Typically supported 100 to 500 users Very expensive Used for very large processing tasks Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 6
Traditional Types of Computers • Mainframe Computers • • • First computers, introduced in 1950 s Used by large businesses Typically supported 100 to 500 users Very expensive Used for very large processing tasks Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 6
 Traditional Types of Computers • Minicomputers • • • Typically supported 10 to 100 users Smaller and less expensive than mainframes The real difference is relative in terms of price, power, marketing. Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 7
Traditional Types of Computers • Minicomputers • • • Typically supported 10 to 100 users Smaller and less expensive than mainframes The real difference is relative in terms of price, power, marketing. Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 7
 Traditional Types of Computers • Microcomputers (Personal Computer or PC) • Small, self-contained computers with their own CPUs • Used by home and business users • Uses a microprocessor, a CPU (Central Processing Unit) on a single chip. Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 8
Traditional Types of Computers • Microcomputers (Personal Computer or PC) • Small, self-contained computers with their own CPUs • Used by home and business users • Uses a microprocessor, a CPU (Central Processing Unit) on a single chip. Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 8
 Portable Computer • • What are these types of portable computers (a type of personal computer)? Desktop computers Laptop computers Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 9
Portable Computer • • What are these types of portable computers (a type of personal computer)? Desktop computers Laptop computers Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 9
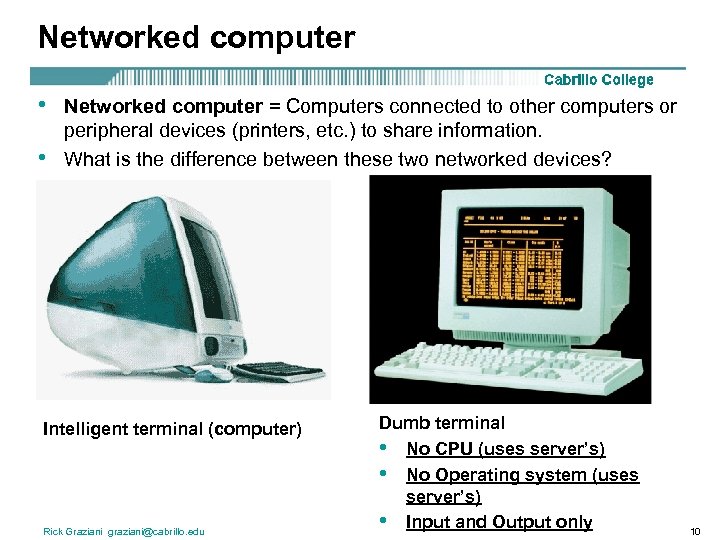 Networked computer • • Networked computer = Computers connected to other computers or peripheral devices (printers, etc. ) to share information. What is the difference between these two networked devices? Intelligent terminal (computer) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu Dumb terminal • No CPU (uses server’s) • No Operating system (uses server’s) • Input and Output only 10
Networked computer • • Networked computer = Computers connected to other computers or peripheral devices (printers, etc. ) to share information. What is the difference between these two networked devices? Intelligent terminal (computer) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu Dumb terminal • No CPU (uses server’s) • No Operating system (uses server’s) • Input and Output only 10
 Embedded Computers • Embedded computers – Computers found in consumer goods in order to enhance their function. Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 11
Embedded Computers • Embedded computers – Computers found in consumer goods in order to enhance their function. Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 11
 Special Purpose Computers • Special purpose or dedicated computers – A device with a specific purpose such as game system or information kiosk. Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 12
Special Purpose Computers • Special purpose or dedicated computers – A device with a specific purpose such as game system or information kiosk. Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 12
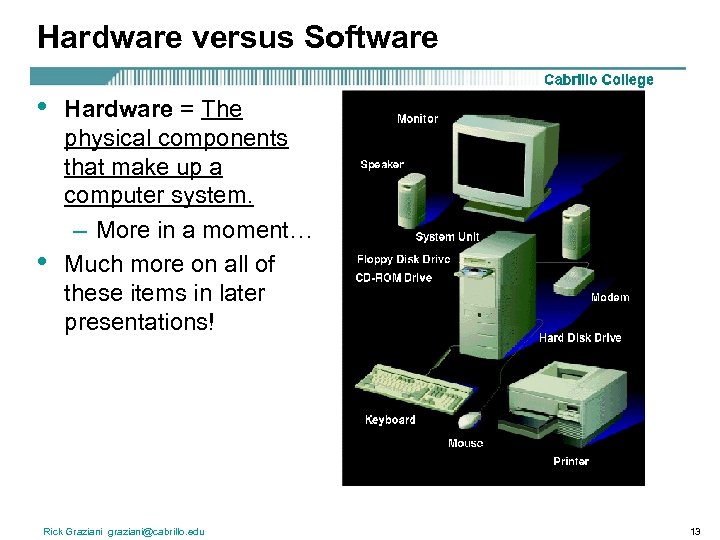 Hardware versus Software • • Hardware = The physical components that make up a computer system. – More in a moment… Much more on all of these items in later presentations! Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 13
Hardware versus Software • • Hardware = The physical components that make up a computer system. – More in a moment… Much more on all of these items in later presentations! Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 13
 Hardware versus Software • Software = The programs (instructions) that tell the computer what to do. – System Software – Application Software – Stored on a storage media such as hard disk, CD-ROM, floppy disk, tape, etc. – More later… Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 14
Hardware versus Software • Software = The programs (instructions) that tell the computer what to do. – System Software – Application Software – Stored on a storage media such as hard disk, CD-ROM, floppy disk, tape, etc. – More later… Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 14
 Hardware Components • This is just an overview, more later… Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 15
Hardware Components • This is just an overview, more later… Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 15
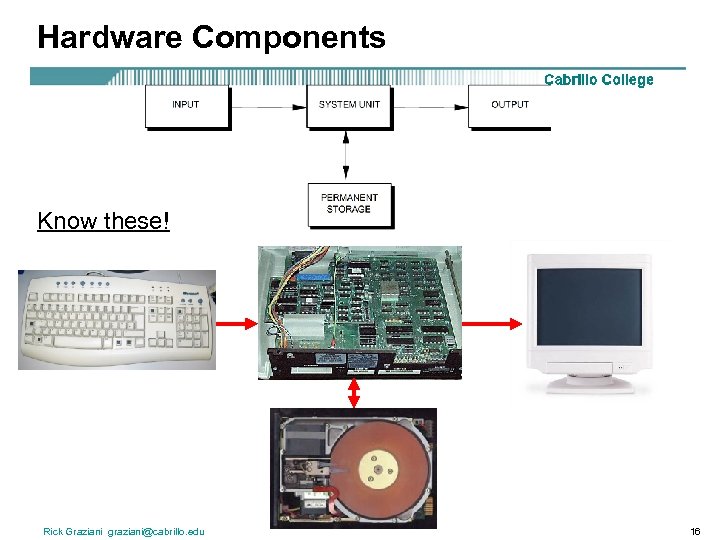 Hardware Components Know these! Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 16
Hardware Components Know these! Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 16
 The Processor Let’s open the box! Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 17
The Processor Let’s open the box! Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 17
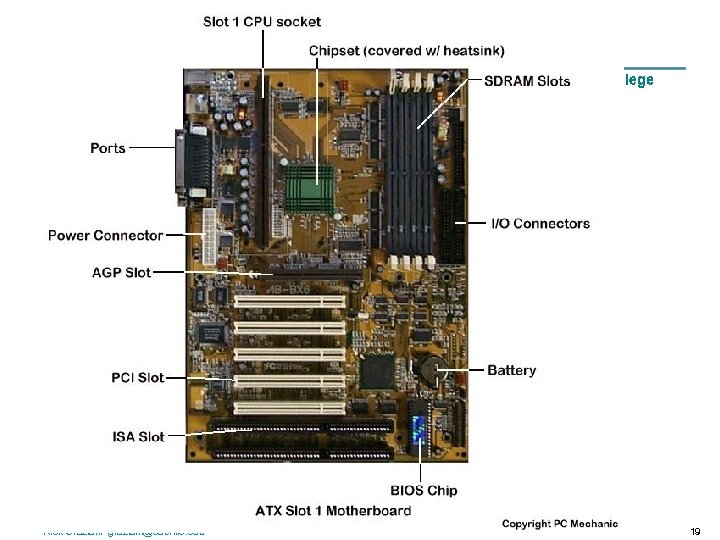
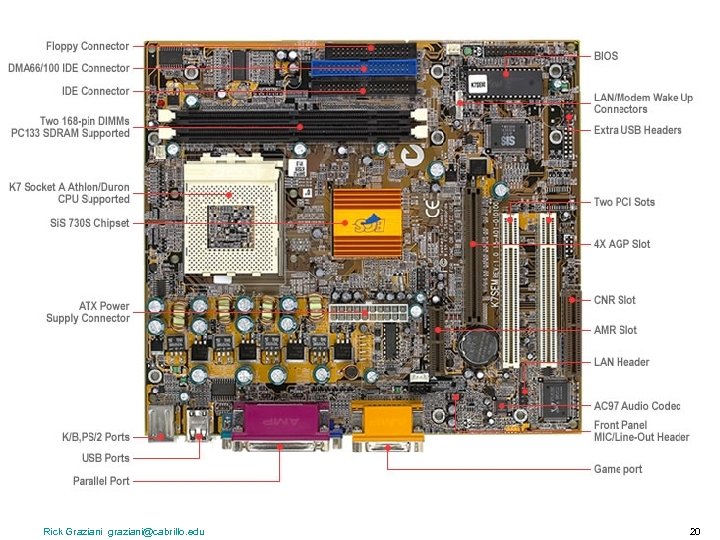
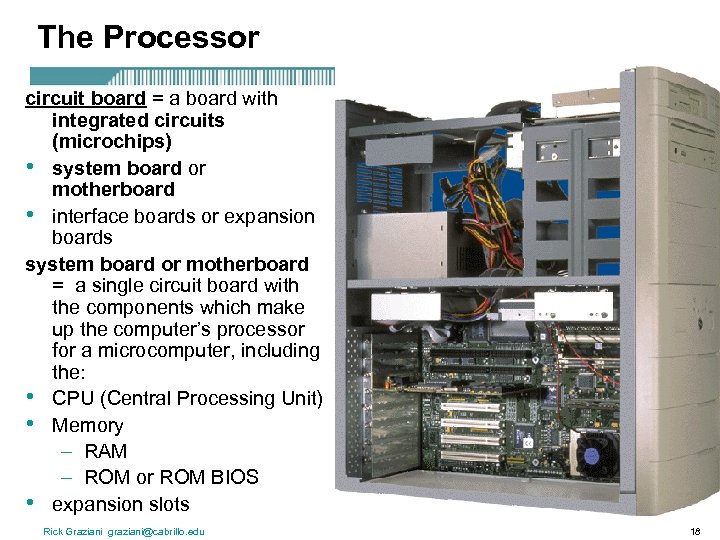 The Processor circuit board = a board with integrated circuits (microchips) • system board or motherboard • interface boards or expansion boards system board or motherboard = a single circuit board with the components which make up the computer’s processor for a microcomputer, including the: • CPU (Central Processing Unit) • Memory – RAM – ROM or ROM BIOS • expansion slots Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 18
The Processor circuit board = a board with integrated circuits (microchips) • system board or motherboard • interface boards or expansion boards system board or motherboard = a single circuit board with the components which make up the computer’s processor for a microcomputer, including the: • CPU (Central Processing Unit) • Memory – RAM – ROM or ROM BIOS • expansion slots Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 18
 Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 19
Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 19
 Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 20
Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 20
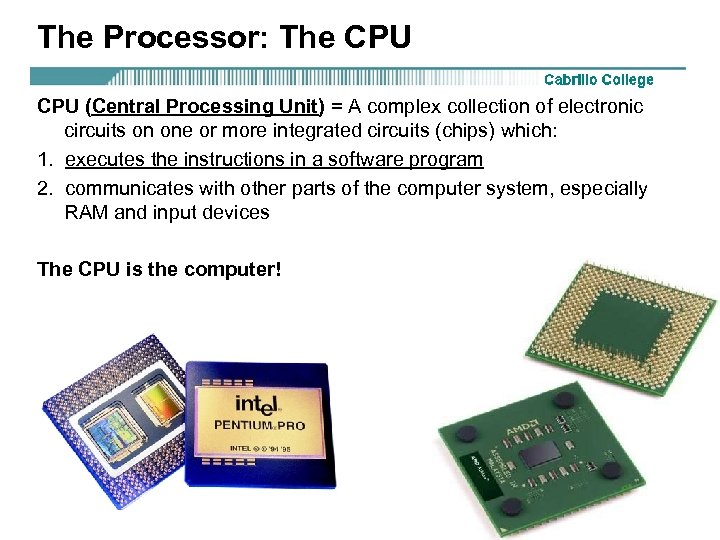 The Processor: The CPU (Central Processing Unit) = A complex collection of electronic circuits on one or more integrated circuits (chips) which: 1. executes the instructions in a software program 2. communicates with other parts of the computer system, especially RAM and input devices The CPU is the computer! Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 21
The Processor: The CPU (Central Processing Unit) = A complex collection of electronic circuits on one or more integrated circuits (chips) which: 1. executes the instructions in a software program 2. communicates with other parts of the computer system, especially RAM and input devices The CPU is the computer! Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 21
 Input and Output Devices Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 22
Input and Output Devices Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 22
 Input Devices • • Enter information into a computer Examples: – – – – – Mouse Keyboard Trackball Touchpad Light pen Joystick Digital camera Microphone Bar code reader Scanner Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 23
Input Devices • • Enter information into a computer Examples: – – – – – Mouse Keyboard Trackball Touchpad Light pen Joystick Digital camera Microphone Bar code reader Scanner Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 23
 Output Devices • • Send information out from a PC Examples: – Speakers – Monitors • Visual Display Unit (VDU), Cathode Ray Tube (CRT), Liquid Crystal Display (LCD), Light-Emitting Diode (LED) – Printers Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 24
Output Devices • • Send information out from a PC Examples: – Speakers – Monitors • Visual Display Unit (VDU), Cathode Ray Tube (CRT), Liquid Crystal Display (LCD), Light-Emitting Diode (LED) – Printers Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 24
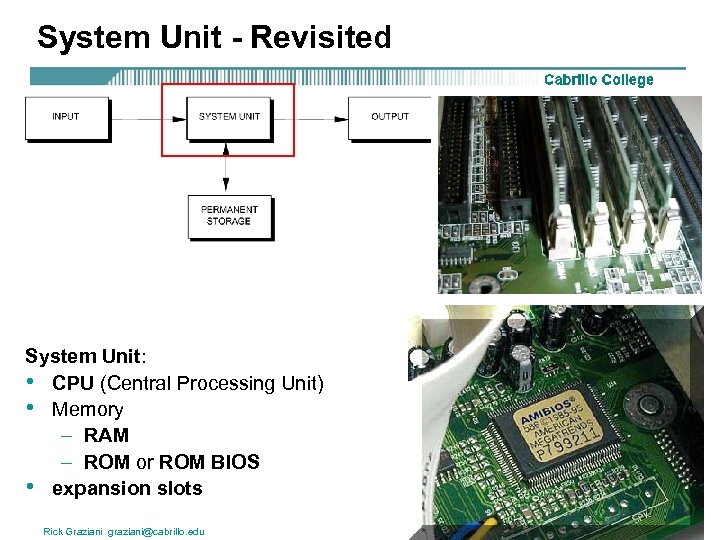 System Unit - Revisited System Unit: • CPU (Central Processing Unit) • Memory – RAM – ROM or ROM BIOS • expansion slots Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 25
System Unit - Revisited System Unit: • CPU (Central Processing Unit) • Memory – RAM – ROM or ROM BIOS • expansion slots Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 25
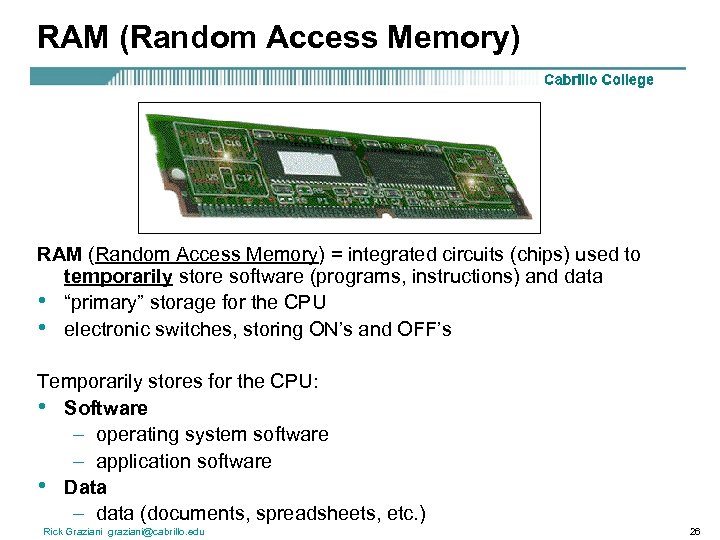 RAM (Random Access Memory) = integrated circuits (chips) used to temporarily store software (programs, instructions) and data • “primary” storage for the CPU • electronic switches, storing ON’s and OFF’s Temporarily stores for the CPU: • Software – operating system software – application software • Data – data (documents, spreadsheets, etc. ) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 26
RAM (Random Access Memory) = integrated circuits (chips) used to temporarily store software (programs, instructions) and data • “primary” storage for the CPU • electronic switches, storing ON’s and OFF’s Temporarily stores for the CPU: • Software – operating system software – application software • Data – data (documents, spreadsheets, etc. ) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 26
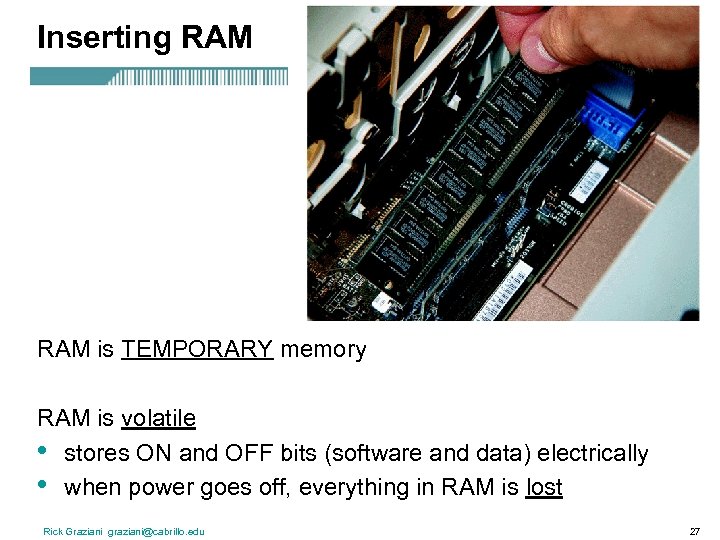 Inserting RAM is TEMPORARY memory RAM is volatile • stores ON and OFF bits (software and data) electrically • when power goes off, everything in RAM is lost Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 27
Inserting RAM is TEMPORARY memory RAM is volatile • stores ON and OFF bits (software and data) electrically • when power goes off, everything in RAM is lost Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 27
 RAM: Speed Why does the CPU use RAM? • The CPU is very FAST! • The CPU needs the instructions (software) and data as quickly as possible • If the CPU has to wait, so does the user Why doesn’t the CPU use permanent storage like disk drives? • Too slow • EXAMPLE: Spellchecker Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 28
RAM: Speed Why does the CPU use RAM? • The CPU is very FAST! • The CPU needs the instructions (software) and data as quickly as possible • If the CPU has to wait, so does the user Why doesn’t the CPU use permanent storage like disk drives? • Too slow • EXAMPLE: Spellchecker Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 28
 RAM: Capacity The amount of RAM determines: • what software and data the user can work on • how much software and data the user can work with • Most computers have at least 256 MB (Megabytes, 256 million bytes) “out of memory” error message from the Operating System The more complex and sophisticated the software, the more instructions that software contains, which means larger software files. Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 29
RAM: Capacity The amount of RAM determines: • what software and data the user can work on • how much software and data the user can work with • Most computers have at least 256 MB (Megabytes, 256 million bytes) “out of memory” error message from the Operating System The more complex and sophisticated the software, the more instructions that software contains, which means larger software files. Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 29
 ROM (Read Only Memory) = integrated circuits (microchips) that are used to permanently store start-up (boot) instructions and other critical information Read Only = information which: • Cannot be changed • Cannot be removed • Cannot be appended (added to) • Fixed by manufacturer Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 30
ROM (Read Only Memory) = integrated circuits (microchips) that are used to permanently store start-up (boot) instructions and other critical information Read Only = information which: • Cannot be changed • Cannot be removed • Cannot be appended (added to) • Fixed by manufacturer Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 30
 ROM (Read Only Memory) ROM is sometimes known as ROM BIOS (Basic Input Output System software) ROM permanently contains: • start-up (boot) instructions • instructions to do “low level” processing of input and output devices, such as the communications with the keyboard and the monitor Firmware = software program which is stored permanently on a microchip, such as the software on the ROM chip Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 31
ROM (Read Only Memory) ROM is sometimes known as ROM BIOS (Basic Input Output System software) ROM permanently contains: • start-up (boot) instructions • instructions to do “low level” processing of input and output devices, such as the communications with the keyboard and the monitor Firmware = software program which is stored permanently on a microchip, such as the software on the ROM chip Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 31
 Looking at your computer Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 32
Looking at your computer Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 32
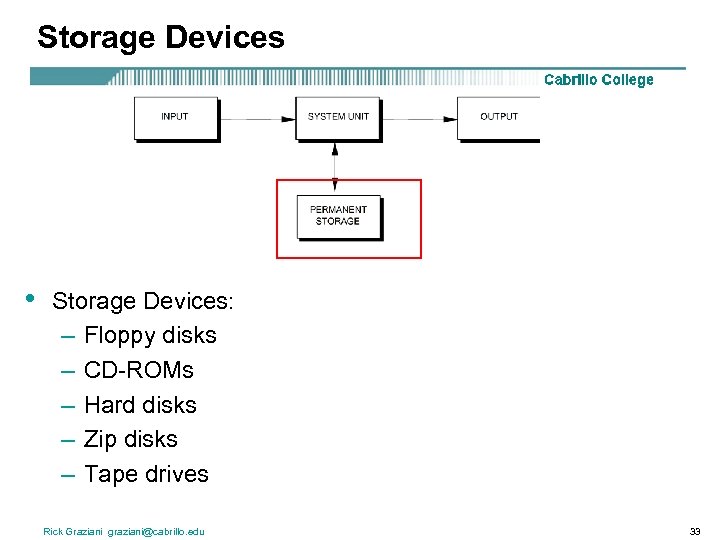 Storage Devices • Storage Devices: – Floppy disks – CD-ROMs – Hard disks – Zip disks – Tape drives Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 33
Storage Devices • Storage Devices: – Floppy disks – CD-ROMs – Hard disks – Zip disks – Tape drives Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 33
 Floppy disks • • • Store up to 1. 44 MB of data Usually 3. 5" square disks Removable Write-Protect tab (Open means “write enabled”) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 34
Floppy disks • • • Store up to 1. 44 MB of data Usually 3. 5" square disks Removable Write-Protect tab (Open means “write enabled”) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 34
 Hard disks • • • Fixed permanently in a hard disk drive inside a system unit Used to store the operating system, applications, and data Can not buy more expansion (easily) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 35
Hard disks • • • Fixed permanently in a hard disk drive inside a system unit Used to store the operating system, applications, and data Can not buy more expansion (easily) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 35
 CD-ROMs • • • Read-only memory devices (but CD-R and CD-RW discs are recordable) Store up to 650 MB of data Portable and can be used on any computer that has a CD-ROM drive CD-R (CD Recordable) CD-RW (CD Rewritable) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 36
CD-ROMs • • • Read-only memory devices (but CD-R and CD-RW discs are recordable) Store up to 650 MB of data Portable and can be used on any computer that has a CD-ROM drive CD-R (CD Recordable) CD-RW (CD Rewritable) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 36
 Flash sticks or memory • • • Storage Digital Player Voice Recorder Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 37
Flash sticks or memory • • • Storage Digital Player Voice Recorder Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 37
 Zip disks • • Store up to 250 MB of data Used for backing up files or transporting large files Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 38
Zip disks • • Store up to 250 MB of data Used for backing up files or transporting large files Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 38
 Tape drives • • • Work like a tape recorder Vary in capacity and access speed Relatively expensive Generally used to back up data Good for “archiving” information Types – Cartridge (slowest) – DAT (Digital Audio Tape) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 39
Tape drives • • • Work like a tape recorder Vary in capacity and access speed Relatively expensive Generally used to back up data Good for “archiving” information Types – Cartridge (slowest) – DAT (Digital Audio Tape) Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 39
 Computer Performance • • • CPU speed (and type) Amount of RAM (and speed) Hard disk capacity Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 40
Computer Performance • • • CPU speed (and type) Amount of RAM (and speed) Hard disk capacity Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 40
 Computer Performance • CPU Speed – Governed by a clock – Measured in millions of cycles per second, or megahertz (MHz) • 700 MHz means 700 million operations per second – Measured in billions of cycles per second, or megahertz (GHz) • 1. 133 MHz means 1 billion, 133 million operations per second Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 41
Computer Performance • CPU Speed – Governed by a clock – Measured in millions of cycles per second, or megahertz (MHz) • 700 MHz means 700 million operations per second – Measured in billions of cycles per second, or megahertz (GHz) • 1. 133 MHz means 1 billion, 133 million operations per second Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 41
 Software • • System Software Application Software Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 42
Software • • System Software Application Software Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 42
 Application Software • • • Performs specific tasks: – Word processing – Calculations – Information storage and retrieval – Accounting Cannot function without the OS (Operating System) Written for a specific operating system and computer hardware. Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 43
Application Software • • • Performs specific tasks: – Word processing – Calculations – Information storage and retrieval – Accounting Cannot function without the OS (Operating System) Written for a specific operating system and computer hardware. Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 43
 Operating System Software • • Loads automatically when you switch on a computer Main roles: – Controls hardware and software – Permits you to manage files – Acts as intermediary between user and applications Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 44
Operating System Software • • Loads automatically when you switch on a computer Main roles: – Controls hardware and software – Permits you to manage files – Acts as intermediary between user and applications Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 44
 Operating System Software which manages the overall operation of the computer system including: • hardware (CPU, RAM, I/O) • security • system interface • application interface Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 45
Operating System Software which manages the overall operation of the computer system including: • hardware (CPU, RAM, I/O) • security • system interface • application interface Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 45
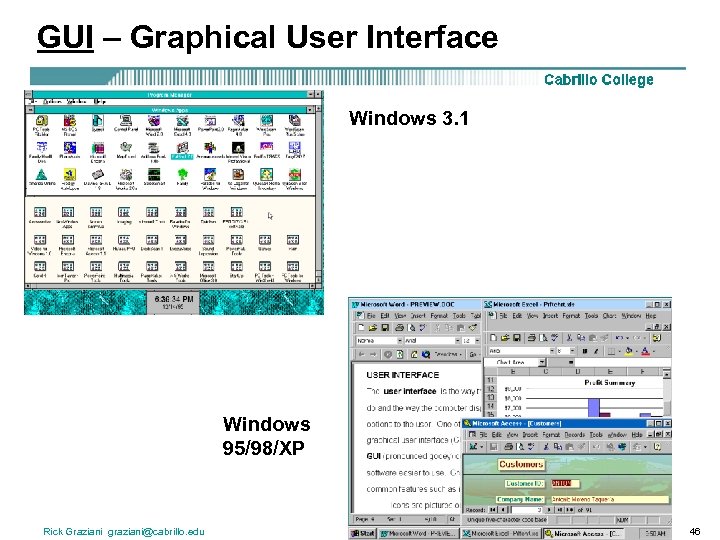 GUI – Graphical User Interface Windows 3. 1 Windows 95/98/XP Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 46
GUI – Graphical User Interface Windows 3. 1 Windows 95/98/XP Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 46
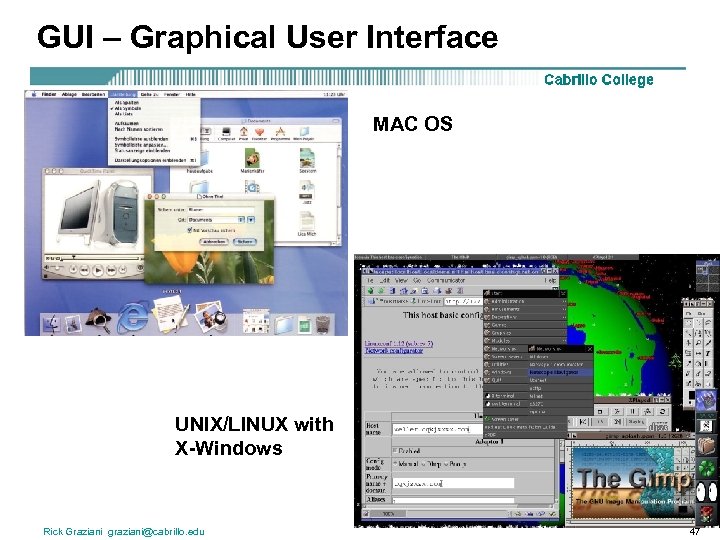 GUI – Graphical User Interface MAC OS UNIX/LINUX with X-Windows Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 47
GUI – Graphical User Interface MAC OS UNIX/LINUX with X-Windows Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 47
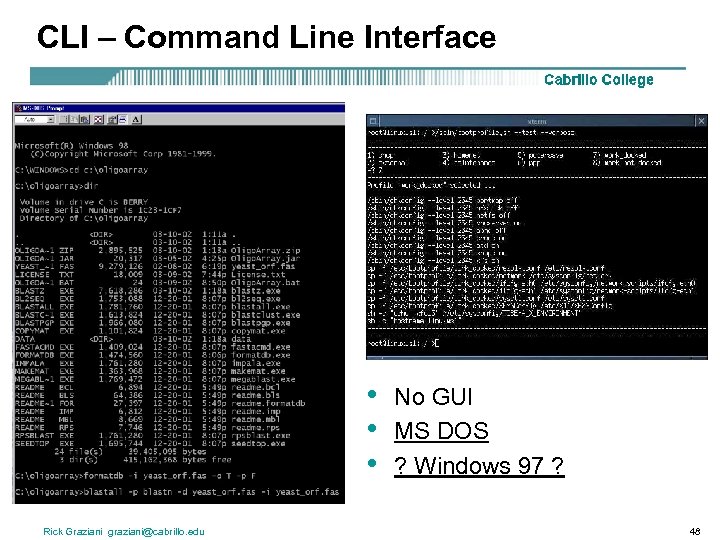 CLI – Command Line Interface • • • Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu No GUI MS DOS ? Windows 97 ? 48
CLI – Command Line Interface • • • Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu No GUI MS DOS ? Windows 97 ? 48
 Putting it altogether! • • • Booting up the computer Creating and saving a word processing document Shutting down the computer Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 49
Putting it altogether! • • • Booting up the computer Creating and saving a word processing document Shutting down the computer Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 49
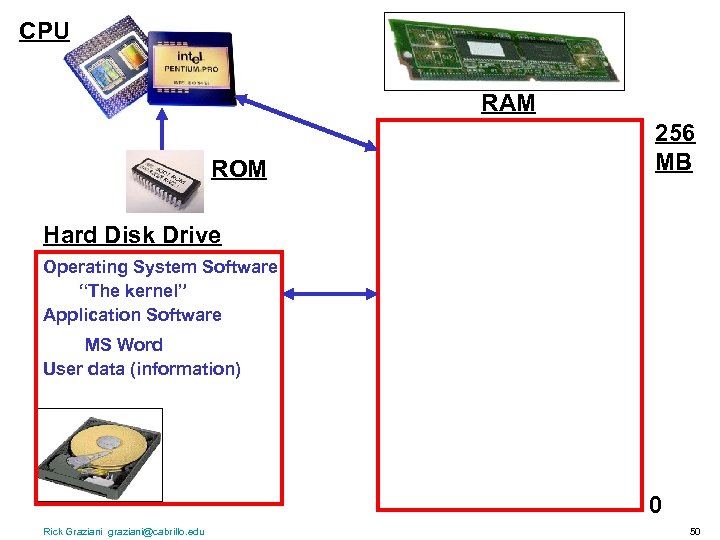 CPU RAM ROM 256 MB Hard Disk Drive Operating System Software “The kernel” Application Software MS Word User data (information) 0 Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 50
CPU RAM ROM 256 MB Hard Disk Drive Operating System Software “The kernel” Application Software MS Word User data (information) 0 Rick Graziani graziani@cabrillo. edu 50


