45a7a5f3d286630742146997efe6e099.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Telemedicine : A low cost solution Anunay Nayak Jayanta Mukherjee Arun Kumar Majumdar Department of Computer Science and & Engineering IIT Kharagpur
Telemedicine : A low cost solution Anunay Nayak Jayanta Mukherjee Arun Kumar Majumdar Department of Computer Science and & Engineering IIT Kharagpur
 A brief sketch of our journey • May 1997 : Invitation for a proposal by MCIT (then DOE) on Telemedicine over ordinary telephone lines. • March 1998 : Submission of a Draft proposal in collaboration with School of Tropical Medicine and WECS (WEBEL). • Jan 1999 : Starting of Project Work. • Aug 2000 : A Prototype system developed (Telemedi. K Software Version 1. 0) • Nov 2000 : Installed in STM for in house training and demonstration. • Feb 2001 : First beta test between STM Kolkata and IIT Kharagpur. • Feb 2002 : Inauguration of Telemedicine between School of Tropical Medicine, Kolkata and Habra State General Hospital. • April 2002 : Inauguration of the second nodal center at Cooch Bihar. • May 2002 : Project involving connections of six hospitals of Government of West Bengal is taken by WEBEL (IIT Kharagpur being the consultant). • Nov 2002 : Telemedi. K version 3. 0 with a better front end and flexibilities in users operations.
A brief sketch of our journey • May 1997 : Invitation for a proposal by MCIT (then DOE) on Telemedicine over ordinary telephone lines. • March 1998 : Submission of a Draft proposal in collaboration with School of Tropical Medicine and WECS (WEBEL). • Jan 1999 : Starting of Project Work. • Aug 2000 : A Prototype system developed (Telemedi. K Software Version 1. 0) • Nov 2000 : Installed in STM for in house training and demonstration. • Feb 2001 : First beta test between STM Kolkata and IIT Kharagpur. • Feb 2002 : Inauguration of Telemedicine between School of Tropical Medicine, Kolkata and Habra State General Hospital. • April 2002 : Inauguration of the second nodal center at Cooch Bihar. • May 2002 : Project involving connections of six hospitals of Government of West Bengal is taken by WEBEL (IIT Kharagpur being the consultant). • Nov 2002 : Telemedi. K version 3. 0 with a better front end and flexibilities in users operations.
 Field trials and demonstrations –Between West Bank Hospital, Mourigram and B. C. Roy Hospital, IIT Kharagpur –Between IIT Extn. Center Bhubaneswar and IIT Kharagpur –CMC Vellore. –Chittaranjan Cancer Research Center, Kolkata. –National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases, Kolkata. –ELITEX’ 2001 and ELITEX’ 2002, New Delhi. -Sikkim Manipal Institute of Medical Sciences, Sikkim -Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Sevagram, Wardha
Field trials and demonstrations –Between West Bank Hospital, Mourigram and B. C. Roy Hospital, IIT Kharagpur –Between IIT Extn. Center Bhubaneswar and IIT Kharagpur –CMC Vellore. –Chittaranjan Cancer Research Center, Kolkata. –National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases, Kolkata. –ELITEX’ 2001 and ELITEX’ 2002, New Delhi. -Sikkim Manipal Institute of Medical Sciences, Sikkim -Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Sevagram, Wardha
 What is Telemedicine • Telemedicine may be defined as the use of computers and telecommunication technologies to provide medical information and services from distant locations
What is Telemedicine • Telemedicine may be defined as the use of computers and telecommunication technologies to provide medical information and services from distant locations
 Different types of services è Telecardiology è Teleradiology è Telepathology è Telepsychiatry è Early Warning System [ Prevention and control of endemic and infectious diseases ]
Different types of services è Telecardiology è Teleradiology è Telepathology è Telepsychiatry è Early Warning System [ Prevention and control of endemic and infectious diseases ]
 Telemedicine in India • Existing system limited only to private hospital • APPOLO Group of Hospitals. • RN Tagore Cardiac Hospital, Calcutta. (Asia Heart Foundation) • No Telemedicine system for public health care • Corporate Sectors Offering Telemedicine Systems • APPOLO Group • Online Telemedicine System, Ahmedabad. • WIPRO GE • SIEMENS
Telemedicine in India • Existing system limited only to private hospital • APPOLO Group of Hospitals. • RN Tagore Cardiac Hospital, Calcutta. (Asia Heart Foundation) • No Telemedicine system for public health care • Corporate Sectors Offering Telemedicine Systems • APPOLO Group • Online Telemedicine System, Ahmedabad. • WIPRO GE • SIEMENS
 Government Efforts • MCIT • IIT Kharagpur • CDAC • ISRO
Government Efforts • MCIT • IIT Kharagpur • CDAC • ISRO
 Why it is relevant to our society Poor infrastructure Non-availability of experts (disparate distribution) Low doctor-patient ratio (large population) Lack of proper medical education Special attention required for Public Health Care System
Why it is relevant to our society Poor infrastructure Non-availability of experts (disparate distribution) Low doctor-patient ratio (large population) Lack of proper medical education Special attention required for Public Health Care System
 Major Challenges • Poor Data Communication Infrastructure. • A Large Population Catered by Government Hospitals. • System Features should be scalable. • Cost of the system should be scalable.
Major Challenges • Poor Data Communication Infrastructure. • A Large Population Catered by Government Hospitals. • System Features should be scalable. • Cost of the system should be scalable.
 Aim of the Telemedik System • Information management – – Patient information Medical data (signs, symptoms, test reports, etc. . ) Appointment scheduling Archival and retrieval of patient records • Low cost solution – Using ordinary telephone line • Service to large population – Through public health care delivery systems • Development of knowledge-based system – For decision support – For training and education
Aim of the Telemedik System • Information management – – Patient information Medical data (signs, symptoms, test reports, etc. . ) Appointment scheduling Archival and retrieval of patient records • Low cost solution – Using ordinary telephone line • Service to large population – Through public health care delivery systems • Development of knowledge-based system – For decision support – For training and education
 Key Principles • Avoid Adhocism : Preorganisation of Patient Data • Minimize online data transfer • Patient Management with Database support
Key Principles • Avoid Adhocism : Preorganisation of Patient Data • Minimize online data transfer • Patient Management with Database support
 Technical issues over Low Bandwidth Problem • Longer time for data transfer • Poor video quality Solution Store and forward policy Transferring sequence of still images
Technical issues over Low Bandwidth Problem • Longer time for data transfer • Poor video quality Solution Store and forward policy Transferring sequence of still images
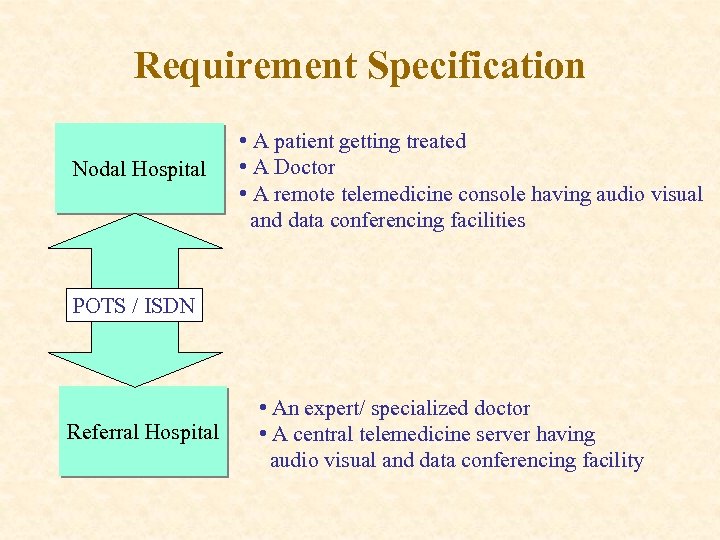 Requirement Specification Nodal Hospital • A patient getting treated • A Doctor • A remote telemedicine console having audio visual and data conferencing facilities POTS / ISDN Referral Hospital • An expert/ specialized doctor • A central telemedicine server having audio visual and data conferencing facility
Requirement Specification Nodal Hospital • A patient getting treated • A Doctor • A remote telemedicine console having audio visual and data conferencing facilities POTS / ISDN Referral Hospital • An expert/ specialized doctor • A central telemedicine server having audio visual and data conferencing facility
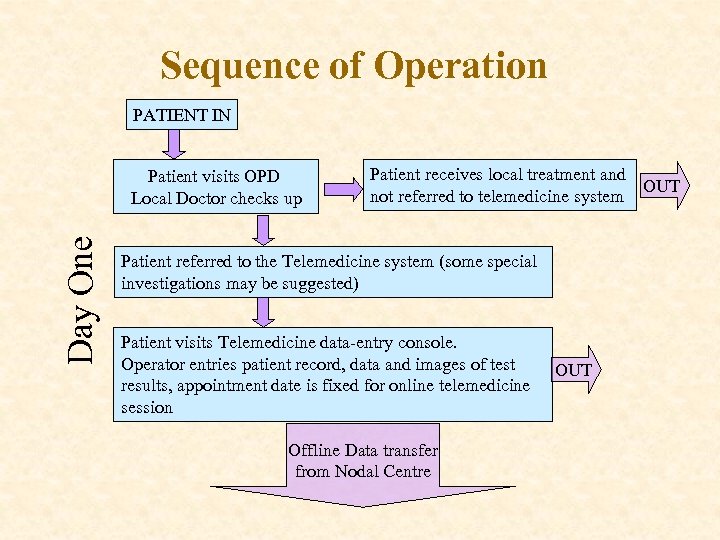 Sequence of Operation PATIENT IN Day One Patient visits OPD Local Doctor checks up Patient receives local treatment and OUT not referred to telemedicine system Patient referred to the Telemedicine system (some special investigations may be suggested) Patient visits Telemedicine data-entry console. Operator entries patient record, data and images of test results, appointment date is fixed for online telemedicine session Offline Data transfer from Nodal Centre OUT
Sequence of Operation PATIENT IN Day One Patient visits OPD Local Doctor checks up Patient receives local treatment and OUT not referred to telemedicine system Patient referred to the Telemedicine system (some special investigations may be suggested) Patient visits Telemedicine data-entry console. Operator entries patient record, data and images of test results, appointment date is fixed for online telemedicine session Offline Data transfer from Nodal Centre OUT
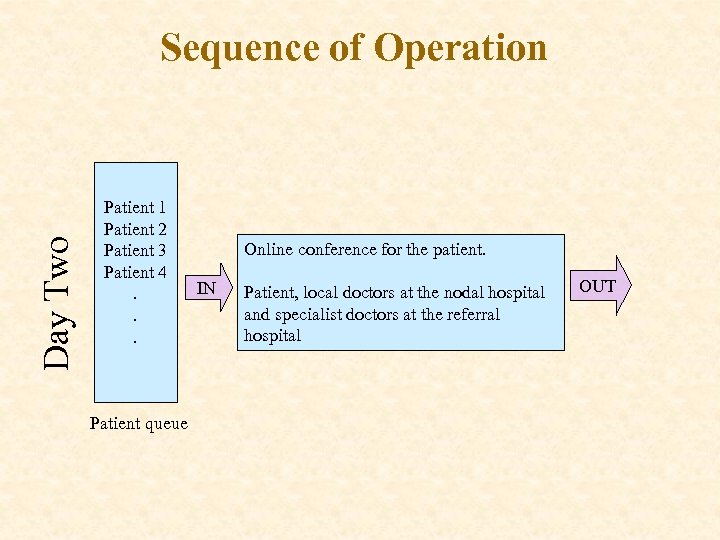 Day Two Sequence of Operation Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4. . . Patient queue Online conference for the patient. IN Patient, local doctors at the nodal hospital and specialist doctors at the referral hospital OUT
Day Two Sequence of Operation Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4. . . Patient queue Online conference for the patient. IN Patient, local doctors at the nodal hospital and specialist doctors at the referral hospital OUT
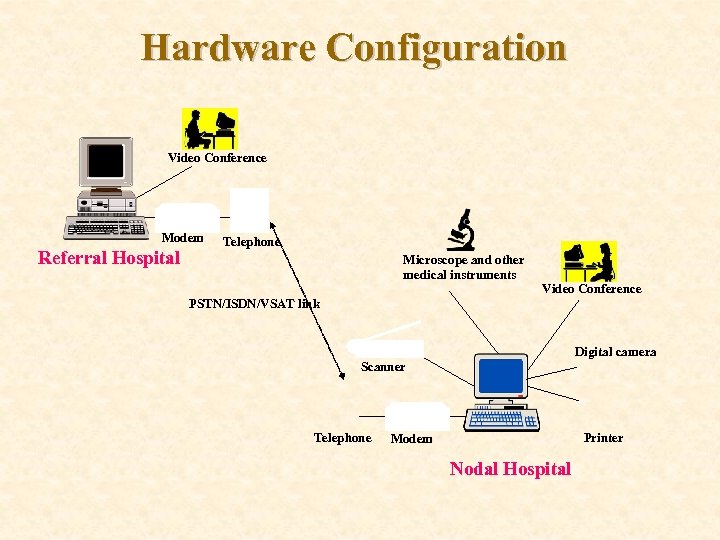 Hardware Configuration Video Conference Modem Referral Hospital Telephone Microscope and other medical instruments Video Conference PSTN/ISDN/VSAT link Digital camera Scanner Telephone Printer Modem Nodal Hospital
Hardware Configuration Video Conference Modem Referral Hospital Telephone Microscope and other medical instruments Video Conference PSTN/ISDN/VSAT link Digital camera Scanner Telephone Printer Modem Nodal Hospital
 Software Modules Offline Activities Online Activities
Software Modules Offline Activities Online Activities
 The Data • • • Data related to a patient’s personal information Data related to a patients medical information Data for patient management in Telemedicine Data related to the doctors Data for system management
The Data • • • Data related to a patient’s personal information Data related to a patients medical information Data for patient management in Telemedicine Data related to the doctors Data for system management
 Employment Generation • Extension of existing services. • Personals involved.
Employment Generation • Extension of existing services. • Personals involved.
 Other Issues • Incorporation of Standard. • Health Level Seven (HL 7) • Digital Imaging Communication in Medicine (DICOM) • Data Security. • Legal & Ethical Issue
Other Issues • Incorporation of Standard. • Health Level Seven (HL 7) • Digital Imaging Communication in Medicine (DICOM) • Data Security. • Legal & Ethical Issue



