885108fe8146273240fbea94e6ac26b9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Telecommunication The exchange of information in any form (voice, data, text, images, audio, video) over networks
Telecommunication The exchange of information in any form (voice, data, text, images, audio, video) over networks
 Trends in Telecommunications
Trends in Telecommunications
 Telecom Network Components Terminals – any input/output device that uses telecommunications networks to transmit or receive data Telecommunications Processors – devices that perform control and support functions Telecommunications Channels – media over which data are transmitted and received Computers – all sizes and types Telecommunications Control Software – programs that control telecommunications activities
Telecom Network Components Terminals – any input/output device that uses telecommunications networks to transmit or receive data Telecommunications Processors – devices that perform control and support functions Telecommunications Channels – media over which data are transmitted and received Computers – all sizes and types Telecommunications Control Software – programs that control telecommunications activities
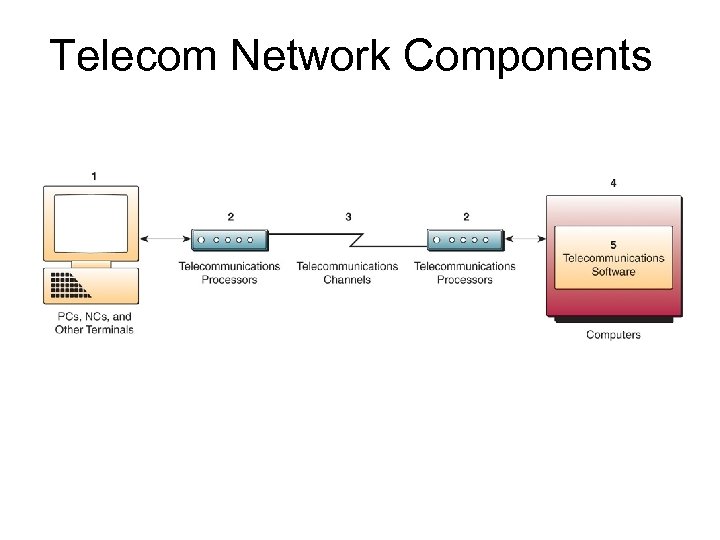 Telecom Network Components
Telecom Network Components
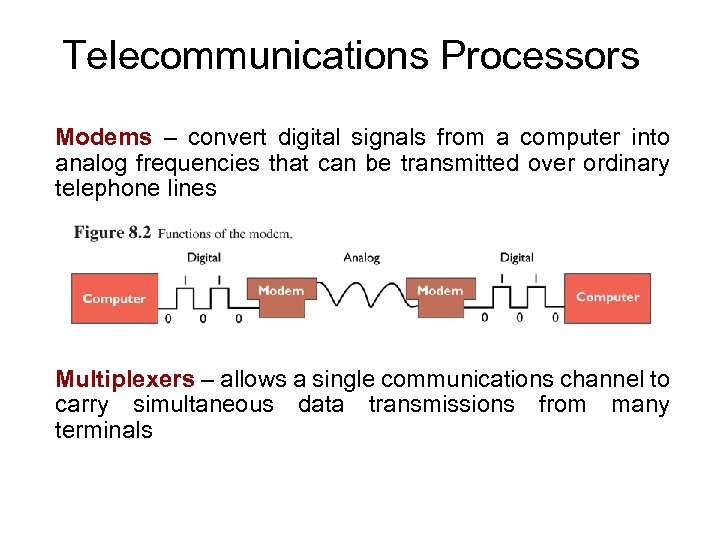 Telecommunications Processors Modems – convert digital signals from a computer into analog frequencies that can be transmitted over ordinary telephone lines Multiplexers – allows a single communications channel to carry simultaneous data transmissions from many terminals
Telecommunications Processors Modems – convert digital signals from a computer into analog frequencies that can be transmitted over ordinary telephone lines Multiplexers – allows a single communications channel to carry simultaneous data transmissions from many terminals
 Bandwidth • Information carrying capacity • Measured in cycles per second/Hz. • Indicates the difference between lowest and highest frequencies. • Higher the bandwidth, greater the volume of data that can be transmitted per unit time. Narrow-band – very low BW; e. g. telegraph links. Voice Band- telephone line with a frequency range of 3003400 Hz. Broadband – high-speed; high capacity. e. g. microwave, cable, fibre optics
Bandwidth • Information carrying capacity • Measured in cycles per second/Hz. • Indicates the difference between lowest and highest frequencies. • Higher the bandwidth, greater the volume of data that can be transmitted per unit time. Narrow-band – very low BW; e. g. telegraph links. Voice Band- telephone line with a frequency range of 3003400 Hz. Broadband – high-speed; high capacity. e. g. microwave, cable, fibre optics
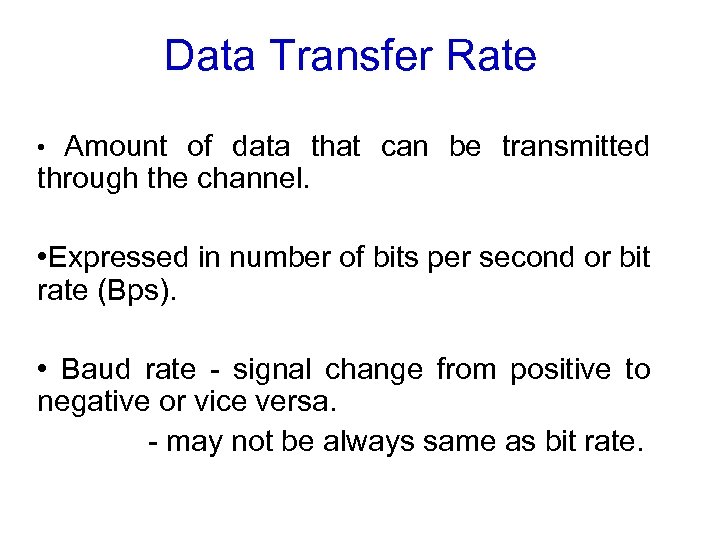 Data Transfer Rate Amount of data that can be transmitted through the channel. • • Expressed in number of bits per second or bit rate (Bps). • Baud rate - signal change from positive to negative or vice versa. - may not be always same as bit rate.
Data Transfer Rate Amount of data that can be transmitted through the channel. • • Expressed in number of bits per second or bit rate (Bps). • Baud rate - signal change from positive to negative or vice versa. - may not be always same as bit rate.
 Types of Signals: Analog and Digital Analog signal • Continuous waveform • Passes through communications medium • Used for voice communications Digital signal • Discrete waveform • Transmits data coded into two discrete states as 1 -bits and 0 -bits • Used for data communications
Types of Signals: Analog and Digital Analog signal • Continuous waveform • Passes through communications medium • Used for voice communications Digital signal • Discrete waveform • Transmits data coded into two discrete states as 1 -bits and 0 -bits • Used for data communications
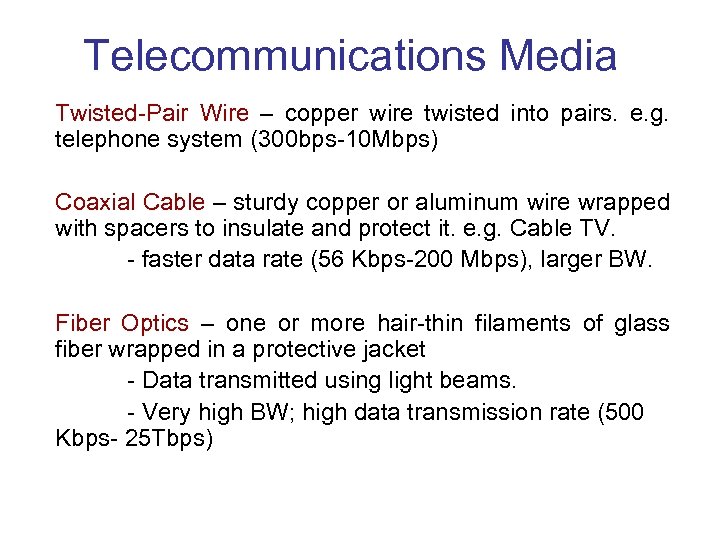 Telecommunications Media Twisted-Pair Wire – copper wire twisted into pairs. e. g. telephone system (300 bps-10 Mbps) Coaxial Cable – sturdy copper or aluminum wire wrapped with spacers to insulate and protect it. e. g. Cable TV. - faster data rate (56 Kbps-200 Mbps), larger BW. Fiber Optics – one or more hair-thin filaments of glass fiber wrapped in a protective jacket - Data transmitted using light beams. - Very high BW; high data transmission rate (500 Kbps- 25 Tbps)
Telecommunications Media Twisted-Pair Wire – copper wire twisted into pairs. e. g. telephone system (300 bps-10 Mbps) Coaxial Cable – sturdy copper or aluminum wire wrapped with spacers to insulate and protect it. e. g. Cable TV. - faster data rate (56 Kbps-200 Mbps), larger BW. Fiber Optics – one or more hair-thin filaments of glass fiber wrapped in a protective jacket - Data transmitted using light beams. - Very high BW; high data transmission rate (500 Kbps- 25 Tbps)
 Telecommunications Media
Telecommunications Media
 Wireless Technologies Terrestrial Microwave – data transmitted with the help of microwaves. Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with frequency in the range of 300, 00 MHz to 3000 MHz. Radio Waves – also electromagnetic waves with low frequency range of 3 KHz to 30 MHz. Communications Satellites - high-earth orbit communications satellites placed in stationary geosynchronous orbits
Wireless Technologies Terrestrial Microwave – data transmitted with the help of microwaves. Microwaves are electromagnetic waves with frequency in the range of 300, 00 MHz to 3000 MHz. Radio Waves – also electromagnetic waves with low frequency range of 3 KHz to 30 MHz. Communications Satellites - high-earth orbit communications satellites placed in stationary geosynchronous orbits
 Wireless Technologies Cellular and PCS Systems – a geographic area divided into cells with one low-power transmitter device per cell used to relay calls from one cell to another Wireless LANs –high- or low-frequency radio technology installed in an office or building Wireless Web – wireless, Web-enabled information appliances accessing the Internet, intranets and extranets
Wireless Technologies Cellular and PCS Systems – a geographic area divided into cells with one low-power transmitter device per cell used to relay calls from one cell to another Wireless LANs –high- or low-frequency radio technology installed in an office or building Wireless Web – wireless, Web-enabled information appliances accessing the Internet, intranets and extranets
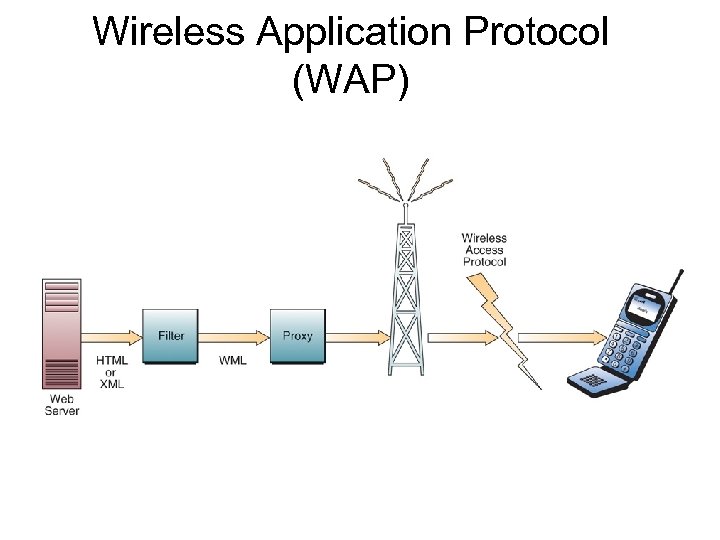 Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)
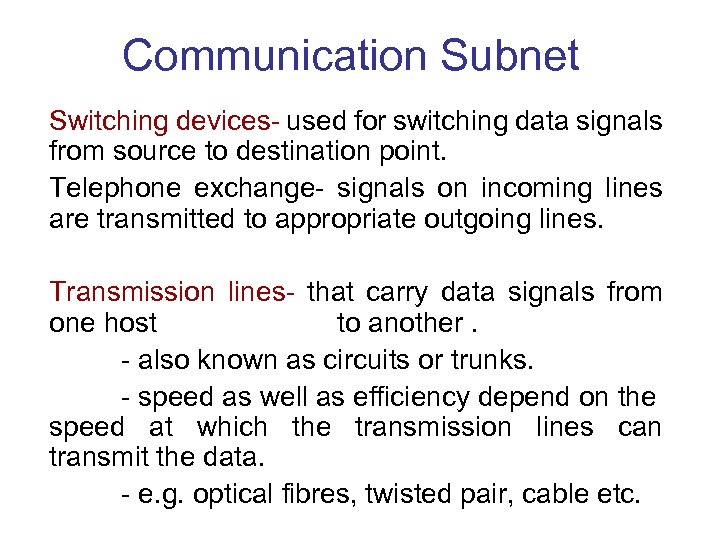 Communication Subnet Switching devices- used for switching data signals from source to destination point. Telephone exchange- signals on incoming lines are transmitted to appropriate outgoing lines. Transmission lines- that carry data signals from one host to another. - also known as circuits or trunks. - speed as well as efficiency depend on the speed at which the transmission lines can transmit the data. - e. g. optical fibres, twisted pair, cable etc.
Communication Subnet Switching devices- used for switching data signals from source to destination point. Telephone exchange- signals on incoming lines are transmitted to appropriate outgoing lines. Transmission lines- that carry data signals from one host to another. - also known as circuits or trunks. - speed as well as efficiency depend on the speed at which the transmission lines can transmit the data. - e. g. optical fibres, twisted pair, cable etc.
 Switching Alternatives Circuit Switching – a switch opens a circuit to establish a link between a sender and receiver; it remains open until the communication session is completed. Packet Switching – messages are divided into fixed or variable length packets, and packets are sent across networks.
Switching Alternatives Circuit Switching – a switch opens a circuit to establish a link between a sender and receiver; it remains open until the communication session is completed. Packet Switching – messages are divided into fixed or variable length packets, and packets are sent across networks.
 Computer Networks • Comprises of communication media, devices, software to connect two or more computer system. • enable the companies to share H/W, computer applications, and databases across the organization. • geographically dispersed employees and workgroups can share documents
Computer Networks • Comprises of communication media, devices, software to connect two or more computer system. • enable the companies to share H/W, computer applications, and databases across the organization. • geographically dispersed employees and workgroups can share documents
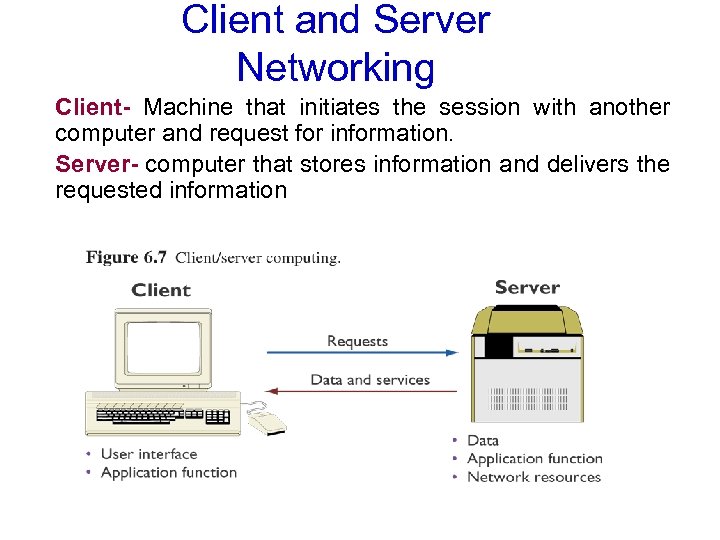 Client and Server Networking Client- Machine that initiates the session with another computer and request for information. Server- computer that stores information and delivers the requested information
Client and Server Networking Client- Machine that initiates the session with another computer and request for information. Server- computer that stores information and delivers the requested information
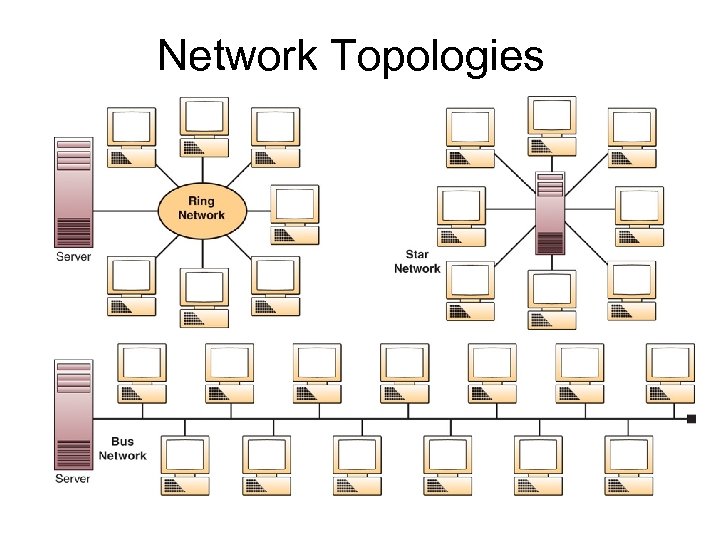
 Network Topologies Bus – all the networked devices share the same communications channel and connected to backbone by transceiver. Ring – Ties local computer processors together in a ring. Star – Ties end user computers to a central computer.
Network Topologies Bus – all the networked devices share the same communications channel and connected to backbone by transceiver. Ring – Ties local computer processors together in a ring. Star – Ties end user computers to a central computer.
 Network Topologies
Network Topologies
 Types of Telecom Networks Point-to-point Communication - point to point communication between two computers for data transmission. - e. g. computer networks in banks Broadcast Communication - All the machines on the network share a single communication channel. - message broadcasted for all receivers. Peer-to-Peer – file-sharing software connects each PC to a central server or to another online user’s PC
Types of Telecom Networks Point-to-point Communication - point to point communication between two computers for data transmission. - e. g. computer networks in banks Broadcast Communication - All the machines on the network share a single communication channel. - message broadcasted for all receivers. Peer-to-Peer – file-sharing software connects each PC to a central server or to another online user’s PC
 Types of Telecom Networks Peer-to-Peer Networks • Type of client/server distributed processing that allows two or more computers to share their resources. • In a standard client/server networks, information stored in centralized file server; Information stored across peer to peer networks is decentralized.
Types of Telecom Networks Peer-to-Peer Networks • Type of client/server distributed processing that allows two or more computers to share their resources. • In a standard client/server networks, information stored in centralized file server; Information stored across peer to peer networks is decentralized.
 Peer to Peer Networks
Peer to Peer Networks
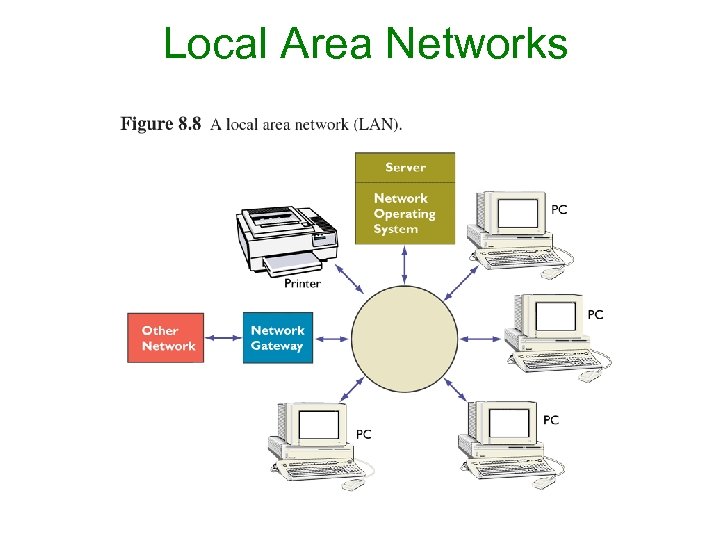
 Types of Telecom Networks Local Area Network (LAN) • Network that connect devices sharing a common communication link and share resources within a limited geographical area. • Serves a local area like floor of a building, college or university campus. • Typical transmission speed is 100 Mbps. • Within the organization, provides fast and efficient access to common bank of information.
Types of Telecom Networks Local Area Network (LAN) • Network that connect devices sharing a common communication link and share resources within a limited geographical area. • Serves a local area like floor of a building, college or university campus. • Typical transmission speed is 100 Mbps. • Within the organization, provides fast and efficient access to common bank of information.
 Local Area Networks
Local Area Networks
 Local Area Networks Wireless LANs Wi-Fi (802. 11 b) standard: Up to 11 Mbps, low cost, high-speed mobile Internet access, links work groups Bluetooth standard: Up to 720 Kbps, small personal area networks
Local Area Networks Wireless LANs Wi-Fi (802. 11 b) standard: Up to 11 Mbps, low cost, high-speed mobile Internet access, links work groups Bluetooth standard: Up to 720 Kbps, small personal area networks
 Types of Telecom Networks Wide Area Network (WAN) –covers a large geographical area such as a state or a country. - May include large corporate networks, military networks, banking networks, airline reservation networks etc. - Typical transmission rates are 2 Mbps, 34 Mbps, 45 Mbps, 625 Mbps etc. - Often implemented in the form of VPN.
Types of Telecom Networks Wide Area Network (WAN) –covers a large geographical area such as a state or a country. - May include large corporate networks, military networks, banking networks, airline reservation networks etc. - Typical transmission rates are 2 Mbps, 34 Mbps, 45 Mbps, 625 Mbps etc. - Often implemented in the form of VPN.
 Types of Telecom Networks Virtual Private Network (VPN) • Secure network that uses the Internet as its main backbone network • Relies on network firewalls, encryption, and other security features. • Effective for extranets and important for international businesses.
Types of Telecom Networks Virtual Private Network (VPN) • Secure network that uses the Internet as its main backbone network • Relies on network firewalls, encryption, and other security features. • Effective for extranets and important for international businesses.
 Types of Telecom Networks Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) Network that interconnects users with computer resources in a geographical area larger than that covered by LAN but smaller than a WAN. • Covers an area between 5 -50 Km diameter. (an area the size of a city). • Generally owned by either group of users or a single network provider
Types of Telecom Networks Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) Network that interconnects users with computer resources in a geographical area larger than that covered by LAN but smaller than a WAN. • Covers an area between 5 -50 Km diameter. (an area the size of a city). • Generally owned by either group of users or a single network provider
 Types of Telecom Networks Value Added Network (VAN) • A private network that can be hired by organization. • Enable the users to more closely tailor communication capabilities to their specific business needs.
Types of Telecom Networks Value Added Network (VAN) • A private network that can be hired by organization. • Enable the users to more closely tailor communication capabilities to their specific business needs.
 Network Architectures & Protocols Protocol – standard set of rules and procedures for the control of communications in a network Network Architecture – the use of standard protocols, standard communications hardware and software interfaces; standard interface between end users and computer systems - the goal of promoting an open, simple, flexible, and efficient telecommunications environment
Network Architectures & Protocols Protocol – standard set of rules and procedures for the control of communications in a network Network Architecture – the use of standard protocols, standard communications hardware and software interfaces; standard interface between end users and computer systems - the goal of promoting an open, simple, flexible, and efficient telecommunications environment
 OSI & TCP/IP Models Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) - model is a seven-layer model that serves as a standard model for network architectures Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) – is a five layer telecommunications protocol used by the Internet
OSI & TCP/IP Models Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) - model is a seven-layer model that serves as a standard model for network architectures Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) – is a five layer telecommunications protocol used by the Internet
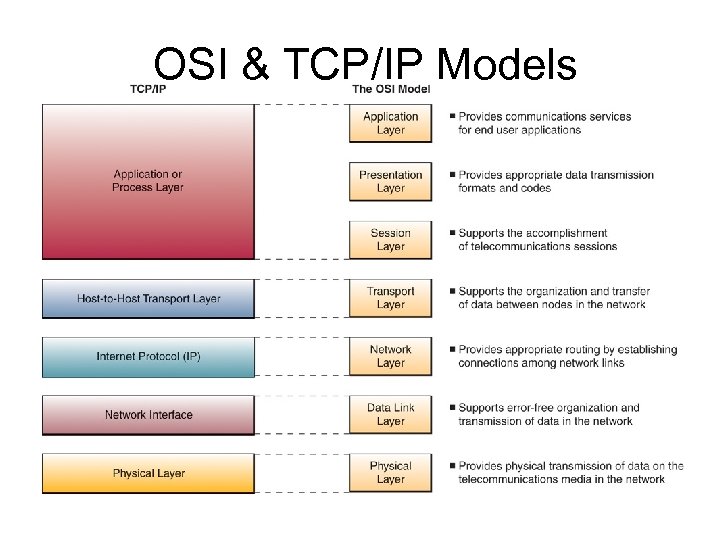 OSI & TCP/IP Models
OSI & TCP/IP Models
 Internet A network made up of millions of smaller private networks, each operate independent of, or in harmony with, all the other millions of networks • Surf • E-mail • Buy and sell • Download • Publish
Internet A network made up of millions of smaller private networks, each operate independent of, or in harmony with, all the other millions of networks • Surf • E-mail • Buy and sell • Download • Publish
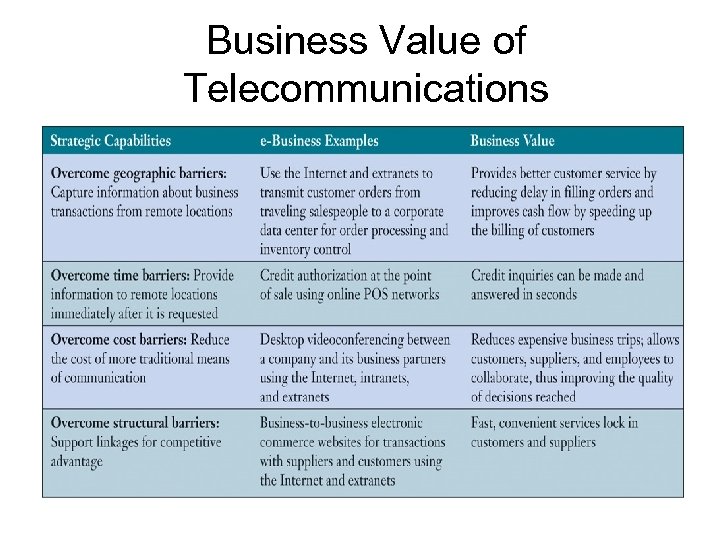 Business Value of Telecommunications
Business Value of Telecommunications
 E- Commerce and E-Business Technologies Teleconferencing: Ability to confer with a group of people simultaneously Data conferencing: Two or more users can edit and modify data files simultaneously Videoconferencing: Participants are able to see each other over video screens
E- Commerce and E-Business Technologies Teleconferencing: Ability to confer with a group of people simultaneously Data conferencing: Two or more users can edit and modify data files simultaneously Videoconferencing: Participants are able to see each other over video screens
 Electronic Commerce and Electronic Business Technologies Distance learning: Education or training delivered over a distance to individuals in one or more locations E-learning: Instruction delivered online using the Internet or private networks
Electronic Commerce and Electronic Business Technologies Distance learning: Education or training delivered over a distance to individuals in one or more locations E-learning: Instruction delivered online using the Internet or private networks
 Summary • Organizations are becoming networked enterprises using the Internet, intranets, and other telecommunications networks to support business operations and collaboration. • Telecom technology is moving toward open, inter-networked digital networks for voice, data, video and multimedia
Summary • Organizations are becoming networked enterprises using the Internet, intranets, and other telecommunications networks to support business operations and collaboration. • Telecom technology is moving toward open, inter-networked digital networks for voice, data, video and multimedia
 Summary • Open systems with unrestricted connectivity using Internet technologies are the primary telecommunications technology drivers in ebusiness systems. • Companies are deriving strategic business value from the Internet, intranets etc. which enables them to disseminate information globally
Summary • Open systems with unrestricted connectivity using Internet technologies are the primary telecommunications technology drivers in ebusiness systems. • Companies are deriving strategic business value from the Internet, intranets etc. which enables them to disseminate information globally
 Summary Businesses are installing and extending intranets throughout their organizations to: – Improve communications and collaboration among individuals and teams within the enterprise –Publish and share valuable business information easily, inexpensively, and effectively via enterprise information portals – Develop and deploy critical applications to support business operations and decision making
Summary Businesses are installing and extending intranets throughout their organizations to: – Improve communications and collaboration among individuals and teams within the enterprise –Publish and share valuable business information easily, inexpensively, and effectively via enterprise information portals – Develop and deploy critical applications to support business operations and decision making
 Summary The major generic components of any telecommunications network are: – Terminals – Telecommunications processors – Communications channels – Computers – Telecommunications software
Summary The major generic components of any telecommunications network are: – Terminals – Telecommunications processors – Communications channels – Computers – Telecommunications software


