a51a1ce6ea9e5561282771216ba750ac.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Technology in Action Technology in Focus: History of the PC 1
Technology in Action Technology in Focus: History of the PC 1
 Intel 8080 and the Altair 8800 • • • The first microcomputer Sold as a kit Switches for input Lights for output Gates and Allen create a compiler for Basic • MITS receives 4, 000 orders 2
Intel 8080 and the Altair 8800 • • • The first microcomputer Sold as a kit Switches for input Lights for output Gates and Allen create a compiler for Basic • MITS receives 4, 000 orders 2
 Apple I and Apple II • Apple I built by Steve Wozniak in 1976 • Apple II developed by Steve Jobs in 1977 • Uses Motorola processor • First fully contained microcomputer • Highly successful 3
Apple I and Apple II • Apple I built by Steve Wozniak in 1976 • Apple II developed by Steve Jobs in 1977 • Uses Motorola processor • First fully contained microcomputer • Highly successful 3
 Early Competitors • • • Commodore TRS-80 Osborne 4
Early Competitors • • • Commodore TRS-80 Osborne 4
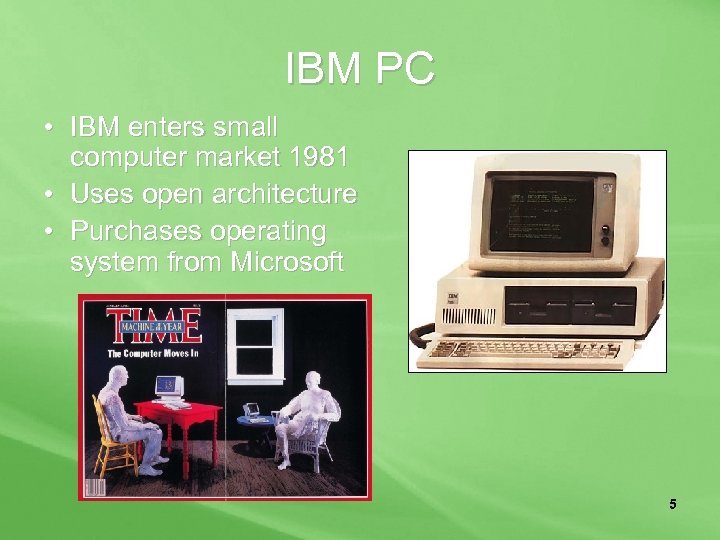 IBM PC • IBM enters small computer market 1981 • Uses open architecture • Purchases operating system from Microsoft 5
IBM PC • IBM enters small computer market 1981 • Uses open architecture • Purchases operating system from Microsoft 5
 Beginners All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code (BASIC) • Revolutionized the software industry • Programming language that beginners could easily learn • Key language of the PC • Bill Gates and Paul Allen used BASIC to write the program for the Altair • Led to the creation of Microsoft 6
Beginners All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code (BASIC) • Revolutionized the software industry • Programming language that beginners could easily learn • Key language of the PC • Bill Gates and Paul Allen used BASIC to write the program for the Altair • Led to the creation of Microsoft 6
 Advent of Operating Systems • Steve Wozniak invents floppy drive • Disk Operating System (DOS): Operating system that controlled the first Apples • Control Program for Microcomputers (CP/M): First operating system for Intel-based PCs • MS-DOS – Operating system for IBM PCs – Based on an operating system called Quick and Dirty Operating System (QDOS) – Created by Bill Gates and Paul Allen – All PCs using the Intel chip used MS-DOS 7
Advent of Operating Systems • Steve Wozniak invents floppy drive • Disk Operating System (DOS): Operating system that controlled the first Apples • Control Program for Microcomputers (CP/M): First operating system for Intel-based PCs • MS-DOS – Operating system for IBM PCs – Based on an operating system called Quick and Dirty Operating System (QDOS) – Created by Bill Gates and Paul Allen – All PCs using the Intel chip used MS-DOS 7
 Software Application Explosion • Electronic Spreadsheets – Visi. Calc – Lotus 1 -2 -3 and Microsoft Excel • Word Processing Bricklin and Frankston – Word. Star – Word for MS-DOS – Word Perfect Visi. Calc screenshot 8
Software Application Explosion • Electronic Spreadsheets – Visi. Calc – Lotus 1 -2 -3 and Microsoft Excel • Word Processing Bricklin and Frankston – Word. Star – Word for MS-DOS – Word Perfect Visi. Calc screenshot 8
 Graphical User Interface • Xerox Alto – Palo Alto Research Center – Alto: 1972 • Apple – Lisa: 1983 – Macintosh: 1984 9
Graphical User Interface • Xerox Alto – Palo Alto Research Center – Alto: 1972 • Apple – Lisa: 1983 – Macintosh: 1984 9
 The Internet Boom • • Mosaic Netscape Internet Explorer Windows 95 10
The Internet Boom • • Mosaic Netscape Internet Explorer Windows 95 10
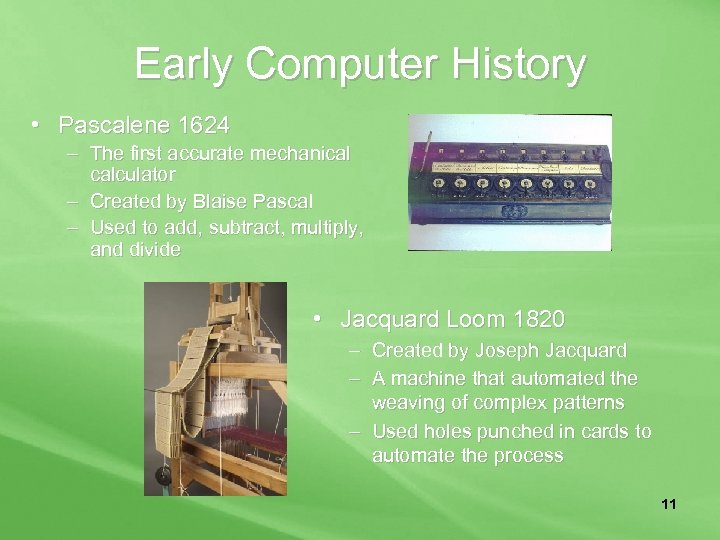 Early Computer History • Pascalene 1624 – The first accurate mechanical calculator – Created by Blaise Pascal – Used to add, subtract, multiply, and divide • Jacquard Loom 1820 – Created by Joseph Jacquard – A machine that automated the weaving of complex patterns – Used holes punched in cards to automate the process 11
Early Computer History • Pascalene 1624 – The first accurate mechanical calculator – Created by Blaise Pascal – Used to add, subtract, multiply, and divide • Jacquard Loom 1820 – Created by Joseph Jacquard – A machine that automated the weaving of complex patterns – Used holes punched in cards to automate the process 11
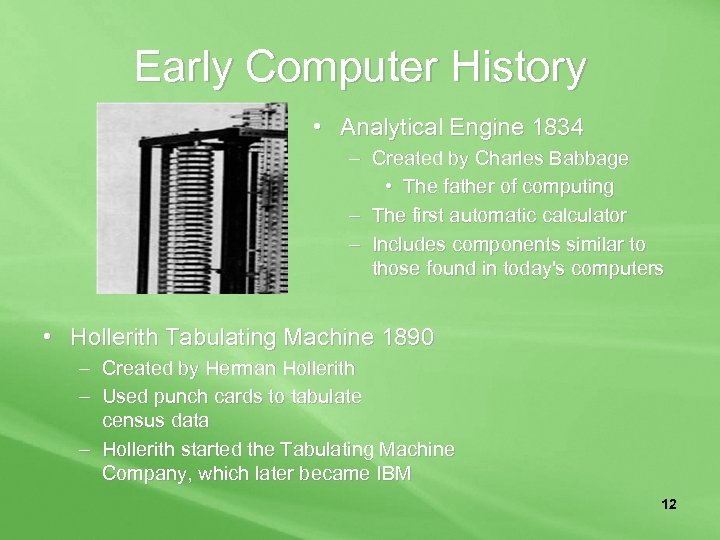 Early Computer History • Analytical Engine 1834 – Created by Charles Babbage • The father of computing – The first automatic calculator – Includes components similar to those found in today's computers • Hollerith Tabulating Machine 1890 – Created by Herman Hollerith – Used punch cards to tabulate census data – Hollerith started the Tabulating Machine Company, which later became IBM 12
Early Computer History • Analytical Engine 1834 – Created by Charles Babbage • The father of computing – The first automatic calculator – Includes components similar to those found in today's computers • Hollerith Tabulating Machine 1890 – Created by Herman Hollerith – Used punch cards to tabulate census data – Hollerith started the Tabulating Machine Company, which later became IBM 12
 Early Computer History • Z 1 1936 – Created by Konrad Zuse – The Z 1 is a mechanical calculator – It included a control unit and memory functions • Atanasoff-Berry Computer 1939 – Created by John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry – The first electrically powered digital computer – Used vacuum tubes to store data – The first computer to use the binary system Atansoff-Berry Computer 13
Early Computer History • Z 1 1936 – Created by Konrad Zuse – The Z 1 is a mechanical calculator – It included a control unit and memory functions • Atanasoff-Berry Computer 1939 – Created by John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry – The first electrically powered digital computer – Used vacuum tubes to store data – The first computer to use the binary system Atansoff-Berry Computer 13
 Early Computer History • Harvard Mark I 1944 – Created by Howard Aiken and Grace Hopper – A computer used by the US Navy for ballistics calculations – Hopper’s contribution to computing was • Invention of the compiler • Coined the term “computer bug” • Turing Machine 1939 – Created by Alan Turing – A hypothetical model that defined a mechanical procedure or algorithm – Concept of an infinite tape that could read, write, and erase was precursor to today’s RAM 1 st use of “computer bug” 14
Early Computer History • Harvard Mark I 1944 – Created by Howard Aiken and Grace Hopper – A computer used by the US Navy for ballistics calculations – Hopper’s contribution to computing was • Invention of the compiler • Coined the term “computer bug” • Turing Machine 1939 – Created by Alan Turing – A hypothetical model that defined a mechanical procedure or algorithm – Concept of an infinite tape that could read, write, and erase was precursor to today’s RAM 1 st use of “computer bug” 14
 Early Computer History • ENIAC 1944 – Created by John W. Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert – The first successful highspeed electronic digital computer ENIAC • UNIVAC 1951 – The first commercially successful electronic digital computer – Used magnetic tape UNIVAC 15
Early Computer History • ENIAC 1944 – Created by John W. Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert – The first successful highspeed electronic digital computer ENIAC • UNIVAC 1951 – The first commercially successful electronic digital computer – Used magnetic tape UNIVAC 15
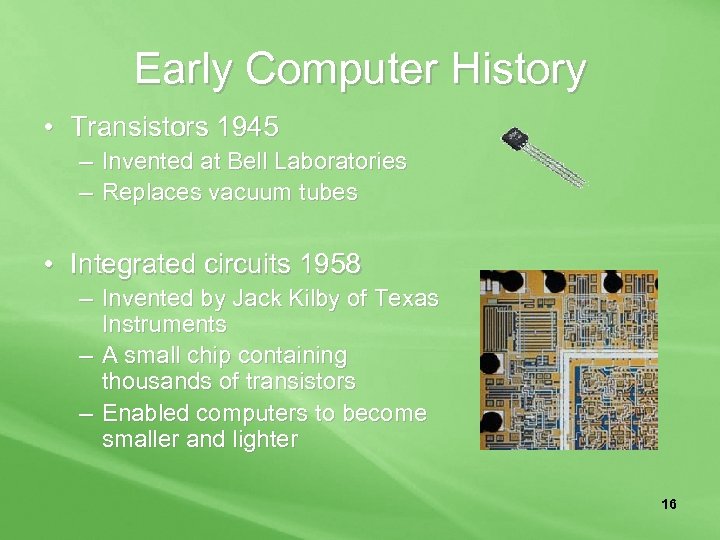 Early Computer History • Transistors 1945 – Invented at Bell Laboratories – Replaces vacuum tubes • Integrated circuits 1958 – Invented by Jack Kilby of Texas Instruments – A small chip containing thousands of transistors – Enabled computers to become smaller and lighter 16
Early Computer History • Transistors 1945 – Invented at Bell Laboratories – Replaces vacuum tubes • Integrated circuits 1958 – Invented by Jack Kilby of Texas Instruments – A small chip containing thousands of transistors – Enabled computers to become smaller and lighter 16
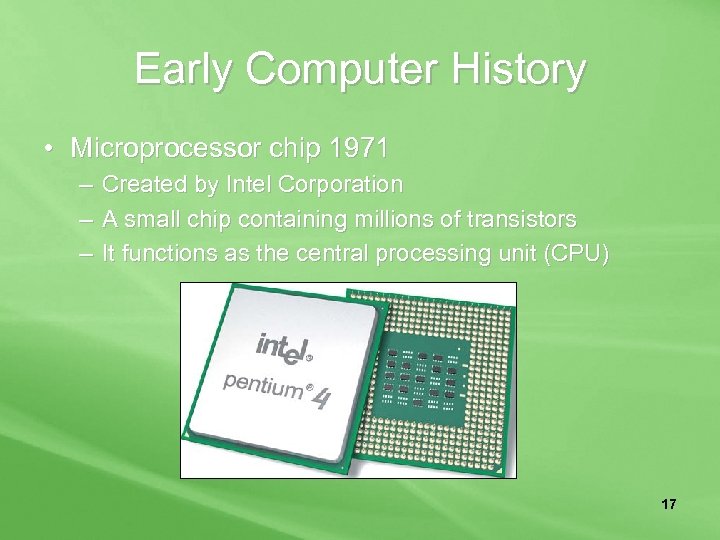 Early Computer History • Microprocessor chip 1971 – Created by Intel Corporation – A small chip containing millions of transistors – It functions as the central processing unit (CPU) 17
Early Computer History • Microprocessor chip 1971 – Created by Intel Corporation – A small chip containing millions of transistors – It functions as the central processing unit (CPU) 17
 Computer Generations • First-generation computers (1946– 1958) – UNIVAC – Use vacuum tubes to store data • Second-generation computers (1959– 1964) – Use transistors to store data • Third-generation computers (1965– 1970) – Use integrated circuits • Fourth-generation computers (1971–Today) – Use a microprocessor chip 18
Computer Generations • First-generation computers (1946– 1958) – UNIVAC – Use vacuum tubes to store data • Second-generation computers (1959– 1964) – Use transistors to store data • Third-generation computers (1965– 1970) – Use integrated circuits • Fourth-generation computers (1971–Today) – Use a microprocessor chip 18


