89026d11c3048771a8d494d3d0c89da5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 System Software • Operating System – – Controls how computer functions Manages hardware Coordinates interaction with application software Provides user interface • Utility Programs – Perform special functions – Perform general housekeeping tasks for the computer ü System maintenance ü File compression – Customize computer to make ur work more pleasant – Improve efficiency © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 1
Technology In Action Chapter 6 System Software • Operating System – – Controls how computer functions Manages hardware Coordinates interaction with application software Provides user interface • Utility Programs – Perform special functions – Perform general housekeeping tasks for the computer ü System maintenance ü File compression – Customize computer to make ur work more pleasant – Improve efficiency © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 1
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Utility programs • • Display utilities Add/remove Programs utility File compression utilities System maintenance utilities – – Disk cleanup Disk defragmenter Scan. Disk Task manager • System restore and backup utilities – System restore – Backup • Task Scheduler utility • Accessibility utilities (Magnifier, Narrator, On-screen keyboard) © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 2
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Utility programs • • Display utilities Add/remove Programs utility File compression utilities System maintenance utilities – – Disk cleanup Disk defragmenter Scan. Disk Task manager • System restore and backup utilities – System restore – Backup • Task Scheduler utility • Accessibility utilities (Magnifier, Narrator, On-screen keyboard) © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 2
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating Your System: Understanding and Assessing Hardware © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 3
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating Your System: Understanding and Assessing Hardware © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 3
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Topics • To buy or upgrade? • Evaluating your system: – – – CPU RAM Storage devices Video output Sound systems Computer ports • System reliability © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 4
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Topics • To buy or upgrade? • Evaluating your system: – – – CPU RAM Storage devices Video output Sound systems Computer ports • System reliability © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 4
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 To Buy or To Upgrade? • Things to consider: – – Moore’s Law Cost of upgrading vs. buying Time installing software and files Needs and wants © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 5
Technology In Action Chapter 6 To Buy or To Upgrade? • Things to consider: – – Moore’s Law Cost of upgrading vs. buying Time installing software and files Needs and wants © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 5
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Assessing Your Hardware: Evaluating Your System • Assess the computer’s subsystems • The subsystems include: – – – – CPU RAM Virtual memory Storage devices Video Audio Ports © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 6
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Assessing Your Hardware: Evaluating Your System • Assess the computer’s subsystems • The subsystems include: – – – – CPU RAM Virtual memory Storage devices Video Audio Ports © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 6
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating the CPU • How does the CPU work? – Two units ü Control unit ü Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) – Machine cycle: ü Fetch ü Decode ü Execute ü Store – Speed: ü Mhz ü Ghz – Intel, AMD, motorola © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 7
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating the CPU • How does the CPU work? – Two units ü Control unit ü Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) – Machine cycle: ü Fetch ü Decode ü Execute ü Store – Speed: ü Mhz ü Ghz – Intel, AMD, motorola © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 7
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Upgrading the CPU • Expensive • Easy to install • Compatibility – Motherboard – Heat sink © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 8
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Upgrading the CPU • Expensive • Easy to install • Compatibility – Motherboard – Heat sink © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 8
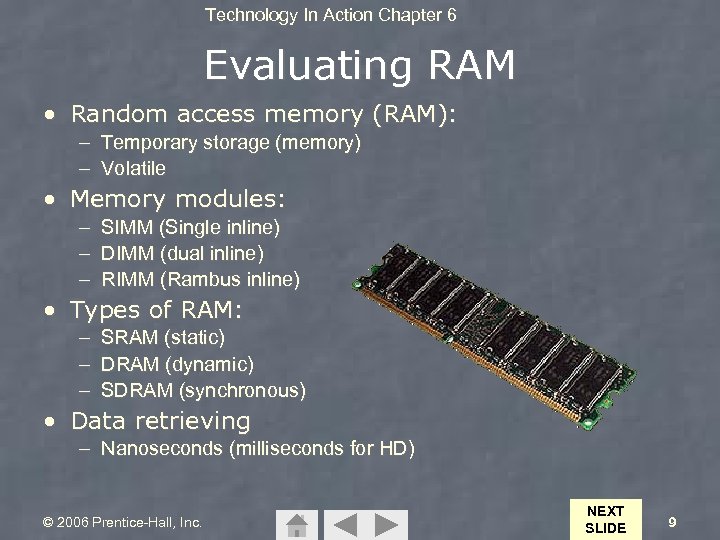 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating RAM • Random access memory (RAM): – Temporary storage (memory) – Volatile • Memory modules: – – – SIMM (Single inline) DIMM (dual inline) RIMM (Rambus inline) • Types of RAM: – SRAM (static) – DRAM (dynamic) – SDRAM (synchronous) • Data retrieving – Nanoseconds (milliseconds for HD) © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 9
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating RAM • Random access memory (RAM): – Temporary storage (memory) – Volatile • Memory modules: – – – SIMM (Single inline) DIMM (dual inline) RIMM (Rambus inline) • Types of RAM: – SRAM (static) – DRAM (dynamic) – SDRAM (synchronous) • Data retrieving – Nanoseconds (milliseconds for HD) © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 9
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Adding RAM • Increase system performance – Memory bound • Things to consider: – Type of RAM module – Amount of RAM: ü Maximum limit ü Number of slots ü Operating system ü Applications running at the same time – Virtual memory ü PF usage © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 10
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Adding RAM • Increase system performance – Memory bound • Things to consider: – Type of RAM module – Amount of RAM: ü Maximum limit ü Number of slots ü Operating system ü Applications running at the same time – Virtual memory ü PF usage © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 10
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating Storage • Types of storage devices: – – – Hard drive Floppy drive Zip disk drive CD/DVD Flash memory • Nonvolatile storage © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 11
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating Storage • Types of storage devices: – – – Hard drive Floppy drive Zip disk drive CD/DVD Flash memory • Nonvolatile storage © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 11
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Storing Data • Magnetic media: Track – Metal platters: ü Hard disks – Plastic film: ü Floppy disks ü Zip disks Sector • Tracks • Sectors • File Allocation Table © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 12
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Storing Data • Magnetic media: Track – Metal platters: ü Hard disks – Plastic film: ü Floppy disks ü Zip disks Sector • Tracks • Sectors • File Allocation Table © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 12
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Storing Data • Optical media: – – – • • • CD ROM CD-RW DVD ROM DVD-RW Laser Pit Land © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 13
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Storing Data • Optical media: – – – • • • CD ROM CD-RW DVD ROM DVD-RW Laser Pit Land © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 13
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 The Hard Disk Drive • Storage capacity up to 400 GB • Access time is measured in milliseconds Platters • Data transfer rate is measured in megabits or megabytes per second • Spindle speed is measured in revolutions per minute (rpm) Read/write head Access arms © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 14
Technology In Action Chapter 6 The Hard Disk Drive • Storage capacity up to 400 GB • Access time is measured in milliseconds Platters • Data transfer rate is measured in megabits or megabytes per second • Spindle speed is measured in revolutions per minute (rpm) Read/write head Access arms © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 14
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 The Hard Disk Drive • SCSI/IDE hard drive – IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) ü 16 to 66 MB per second – SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) ü 40 to 80 MB per second • Sample HD requirements © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 15
Technology In Action Chapter 6 The Hard Disk Drive • SCSI/IDE hard drive – IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) ü 16 to 66 MB per second – SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) ü 40 to 80 MB per second • Sample HD requirements © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 15
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Portable Storage • Gives us the ability to move data from one computer to another • Types of portable storage devices: – Floppy disk: ü Capacity 1. 44 MB – Zip disk: ü Capacity 100 MB to 750 MB – CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-RW: ü Capacity 700 MB to 9. 4 GB – Flash drive: ü Capacity 32 MB to 1 GB © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 16
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Portable Storage • Gives us the ability to move data from one computer to another • Types of portable storage devices: – Floppy disk: ü Capacity 1. 44 MB – Zip disk: ü Capacity 100 MB to 750 MB – CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-RW: ü Capacity 700 MB to 9. 4 GB – Flash drive: ü Capacity 32 MB to 1 GB © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 16
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 CD/DVD • CD – Data Transfer Rate X 150 KB per second – 40 * 12 * 48 (record-rewrite-playback) – CD-ROM, CD-R, CR-RW • DVD – Data Transfer Rate X 1. 3 MB per second – 9 times CD speed – DVD-/+ RW © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 17
Technology In Action Chapter 6 CD/DVD • CD – Data Transfer Rate X 150 KB per second – 40 * 12 * 48 (record-rewrite-playback) – CD-ROM, CD-R, CR-RW • DVD – Data Transfer Rate X 1. 3 MB per second – 9 times CD speed – DVD-/+ RW © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 17
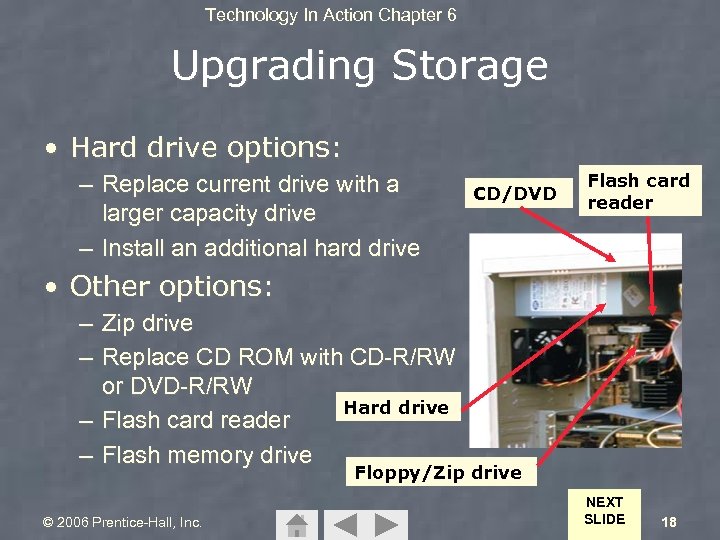 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Upgrading Storage • Hard drive options: – Replace current drive with a larger capacity drive – Install an additional hard drive CD/DVD Flash card reader • Other options: – Zip drive – Replace CD ROM with CD-R/RW or DVD-R/RW Hard drive – Flash card reader – Flash memory drive Floppy/Zip drive © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 18
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Upgrading Storage • Hard drive options: – Replace current drive with a larger capacity drive – Install an additional hard drive CD/DVD Flash card reader • Other options: – Zip drive – Replace CD ROM with CD-R/RW or DVD-R/RW Hard drive – Flash card reader – Flash memory drive Floppy/Zip drive © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 18
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating Video • Two components: – Video card (adapter) – Monitor © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 19
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating Video • Two components: – Video card (adapter) – Monitor © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 19
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Video Cards • Process binary data into images • Contain memory known as video RAM (VRAM) • Control the number of colors a monitor can display (bit depth) – Standard VGA ü 4 bits ü 16 colors – True color (SVGA) ü 24 bits ü 16 million colors © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 20
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Video Cards • Process binary data into images • Contain memory known as video RAM (VRAM) • Control the number of colors a monitor can display (bit depth) – Standard VGA ü 4 bits ü 16 colors – True color (SVGA) ü 24 bits ü 16 million colors © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 20
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Monitors • Things to consider: – Types: ü CRT or LCD – Size: – 15, 17, 19, or 21 inch – Resolution: ü Increasing resolution allows more to be displayed – – – Dot pitch: . 31 mm or less Refresh rate: ü 75 Hz or higher © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 21
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Monitors • Things to consider: – Types: ü CRT or LCD – Size: – 15, 17, 19, or 21 inch – Resolution: ü Increasing resolution allows more to be displayed – – – Dot pitch: . 31 mm or less Refresh rate: ü 75 Hz or higher © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 21
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating Audio • Speakers: – Amplified – Not amplified – Sub-woofer • Sound card: – Process digital data into sounds – 3 D sound cards – Surround sound ü Dolby Digital 5. 1 © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 22
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating Audio • Speakers: – Amplified – Not amplified – Sub-woofer • Sound card: – Process digital data into sounds – 3 D sound cards – Surround sound ü Dolby Digital 5. 1 © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 22
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating Ports • Ports are used to connect peripheral devices to the computer • Things to consider: – Devices you want to use – Ports needed for the devices © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 23
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating Ports • Ports are used to connect peripheral devices to the computer • Things to consider: – Devices you want to use – Ports needed for the devices © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 23
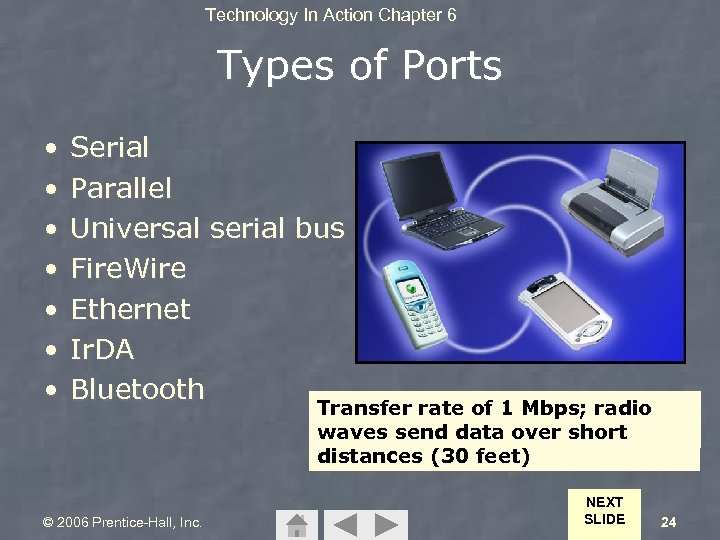 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Types of Ports • • Serial Parallel Universal serial bus Fire. Wire Ethernet Ir. DA Bluetooth © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. LPT 1 Port PS/2 Port Connectors USB Ethernet Fire. Wire Connector Printer Cablejack Connector Port COM 1 Port Serial Connector Transfers 1 Mbps; bit Transfer rate speed Mbps; at a Transfer of data bitsradio 4 of 400 Transfer rate ofeightup toof data Transfers 100 one Mbps; Transfer rate. Mbps; Uses simultaneously; connectslight waves to networks infrared computers 12 Mbps 480 Mbps; Hot wavestime; 56 Kbpsswapping send data over Digital cameras short distances (30 feet) NEXT SLIDE 24
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Types of Ports • • Serial Parallel Universal serial bus Fire. Wire Ethernet Ir. DA Bluetooth © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. LPT 1 Port PS/2 Port Connectors USB Ethernet Fire. Wire Connector Printer Cablejack Connector Port COM 1 Port Serial Connector Transfers 1 Mbps; bit Transfer rate speed Mbps; at a Transfer of data bitsradio 4 of 400 Transfer rate ofeightup toof data Transfers 100 one Mbps; Transfer rate. Mbps; Uses simultaneously; connectslight waves to networks infrared computers 12 Mbps 480 Mbps; Hot wavestime; 56 Kbpsswapping send data over Digital cameras short distances (30 feet) NEXT SLIDE 24
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Adding Ports • Expansion cards: – New port standards • Expansion hubs: – Enables several devices to be connected to a port © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 25
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Adding Ports • Expansion cards: – New port standards • Expansion hubs: – Enables several devices to be connected to a port © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 25
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Summary Questions • How can I determine whether I should upgrade my existing computer or buy a new one? • What does the CPU do and how can I evaluate its performance? • How does memory work and how can I evaluate how much memory I need? • What are the computer’s main storage devices and how can I evaluate whether they match my needs? © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 26
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Summary Questions • How can I determine whether I should upgrade my existing computer or buy a new one? • What does the CPU do and how can I evaluate its performance? • How does memory work and how can I evaluate how much memory I need? • What are the computer’s main storage devices and how can I evaluate whether they match my needs? © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 26
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What components affect the output of video and how can I evaluate whether they are meeting my needs? • What components affect the quality of sound and how can I evaluate whether they are meeting my needs? © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 27
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What components affect the output of video and how can I evaluate whether they are meeting my needs? • What components affect the quality of sound and how can I evaluate whether they are meeting my needs? © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. NEXT SLIDE 27
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What are the ports available on desktop computers and how can I determine what ports I need? • How can I ensure the reliability of my system? © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. LAST SLIDE 28
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What are the ports available on desktop computers and how can I determine what ports I need? • How can I ensure the reliability of my system? © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. LAST SLIDE 28
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Ensure system performs reliably • Run disk defragmenter utility • Check out Startup folder • Clear out unnecessary files – Disk cleanup utility © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 29
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Ensure system performs reliably • Run disk defragmenter utility • Check out Startup folder • Clear out unnecessary files – Disk cleanup utility © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 29
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 In case of Crash • Make sure you have installed any new software or hardware properly – Having latest version of software • If see an error code in Windows, visit http: //support. microsoft. com • Check that you have enough RAM • Reinstall operating system, or upgrade OS to the latest version. © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 30
Technology In Action Chapter 6 In case of Crash • Make sure you have installed any new software or hardware properly – Having latest version of software • If see an error code in Windows, visit http: //support. microsoft. com • Check that you have enough RAM • Reinstall operating system, or upgrade OS to the latest version. © 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 30


