377a2136c4269dcc1497a8fc6c8c75b5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Technology In Action 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 1
Technology In Action 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 1
 Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating Your System: Understanding and Assessing Hardware 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 2
Technology In Action Chapter 6 Evaluating Your System: Understanding and Assessing Hardware 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 2
 Chapter Topics • To buy or upgrade? • Evaluating your system: – CPU – RAM – Storage devices – Video output – Sound systems – Computer ports • System reliability 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 3
Chapter Topics • To buy or upgrade? • Evaluating your system: – CPU – RAM – Storage devices – Video output – Sound systems – Computer ports • System reliability 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 3
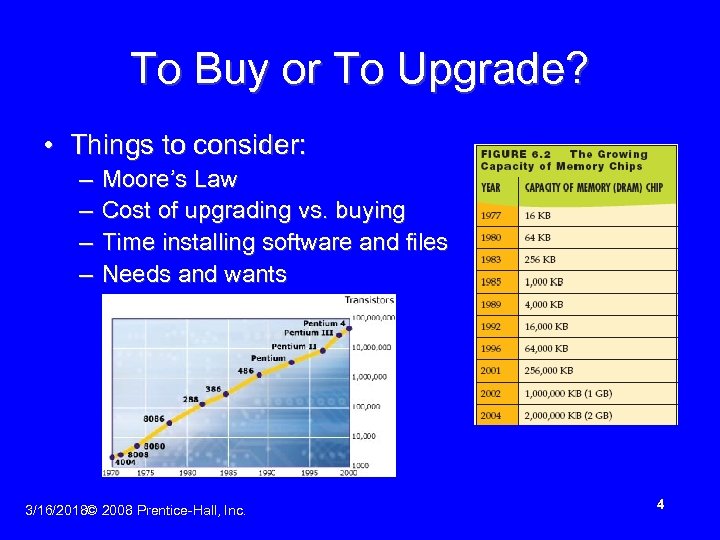 To Buy or To Upgrade? • Things to consider: – – Moore’s Law Cost of upgrading vs. buying Time installing software and files Needs and wants 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 4
To Buy or To Upgrade? • Things to consider: – – Moore’s Law Cost of upgrading vs. buying Time installing software and files Needs and wants 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 4
 Assessing Your Hardware: Evaluating Your System • Assess the computer’s subsystems • The subsystems include – CPU – RAM – Virtual memory – Storage devices – Video – Audio – Ports 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 5
Assessing Your Hardware: Evaluating Your System • Assess the computer’s subsystems • The subsystems include – CPU – RAM – Virtual memory – Storage devices – Video – Audio – Ports 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 5
 Evaluating the CPU • How does the CPU work? – Control unit – Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) – Machine cycle: • Instruction Cycle – Fetch – Decode • Execution Cycle – Execute – Store – Speed: • MHz • GHz 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 6
Evaluating the CPU • How does the CPU work? – Control unit – Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) – Machine cycle: • Instruction Cycle – Fetch – Decode • Execution Cycle – Execute – Store – Speed: • MHz • GHz 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 6
 Evaluating Other CPU Features • Some CPUs are optimized to process multimedia instructions • Intel CPUs called Core Duo processors – Use less power than dual processors – Increase multitasking performance • Intel has more than 17 other designs for chips with more than one core 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 7
Evaluating Other CPU Features • Some CPUs are optimized to process multimedia instructions • Intel CPUs called Core Duo processors – Use less power than dual processors – Increase multitasking performance • Intel has more than 17 other designs for chips with more than one core 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 7
 Upgrading the CPU • Expensive • Easy to install • Motherboard compatibility 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 8
Upgrading the CPU • Expensive • Easy to install • Motherboard compatibility 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 8
 Evaluating RAM • Random access memory (RAM): – Temporary storage (memory) – Volatile • Memory modules: – SIMM – DIMM – RIMM • Types of RAM: – SRAM – DRAM – SDRAM 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 9
Evaluating RAM • Random access memory (RAM): – Temporary storage (memory) – Volatile • Memory modules: – SIMM – DIMM – RIMM • Types of RAM: – SRAM – DRAM – SDRAM 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 9
 How Much Ram is Needed? • • RAM for System Software RAM for Productivity Software RAM for Entertainment RAM for Graphics Programs System Software Windows XP 128 MB Productivity Software MS Office Pro 128 MB Entertainment Software Windows Media Player 64 MB Graphics 128 MB 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. MS Picture It! 10
How Much Ram is Needed? • • RAM for System Software RAM for Productivity Software RAM for Entertainment RAM for Graphics Programs System Software Windows XP 128 MB Productivity Software MS Office Pro 128 MB Entertainment Software Windows Media Player 64 MB Graphics 128 MB 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. MS Picture It! 10
 Adding RAM • Increase system performance • Things to consider: – Type of RAM module – Amount of RAM: • • Maximum limit Number of slots Operating system Applications running at the same time 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 11
Adding RAM • Increase system performance • Things to consider: – Type of RAM module – Amount of RAM: • • Maximum limit Number of slots Operating system Applications running at the same time 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 11
 Evaluating Storage • Types of storage devices: – Hard drive – Floppy drive – Zip disk drive – CD/DVD – Flash memory • Nonvolatile storage 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 12
Evaluating Storage • Types of storage devices: – Hard drive – Floppy drive – Zip disk drive – CD/DVD – Flash memory • Nonvolatile storage 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 12
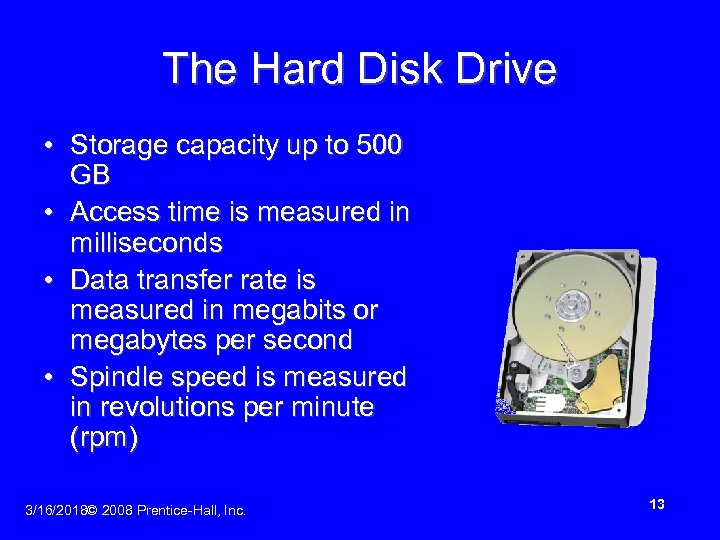 The Hard Disk Drive • Storage capacity up to 500 GB • Access time is measured in milliseconds • Data transfer rate is measured in megabits or megabytes per second • Spindle speed is measured in revolutions per minute (rpm) 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 13
The Hard Disk Drive • Storage capacity up to 500 GB • Access time is measured in milliseconds • Data transfer rate is measured in megabits or megabytes per second • Spindle speed is measured in revolutions per minute (rpm) 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 13
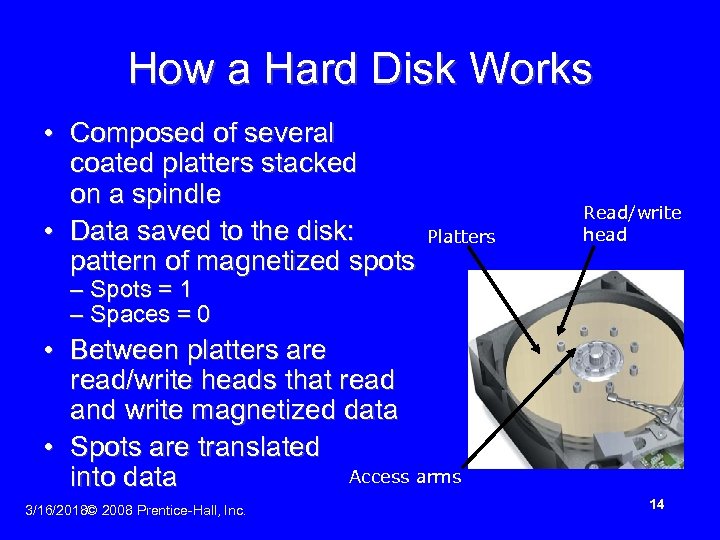 How a Hard Disk Works • Composed of several coated platters stacked on a spindle • Data saved to the disk: pattern of magnetized spots Platters Read/write head – Spots = 1 – Spaces = 0 • Between platters are read/write heads that read and write magnetized data • Spots are translated Access arms into data 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 14
How a Hard Disk Works • Composed of several coated platters stacked on a spindle • Data saved to the disk: pattern of magnetized spots Platters Read/write head – Spots = 1 – Spaces = 0 • Between platters are read/write heads that read and write magnetized data • Spots are translated Access arms into data 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 14
 Portable Storage • Gives us the ability to move data from one computer to another • Types of portable storage devices: – Floppy disk: • Capacity 1. 44 MB – Zip disk: • Capacity 100 MB to 750 MB – CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-RW: • Capacity 700 MB to 9. 4 GB – Flash drive: • Capacity 32 MB to 1 GB – Flash memory Card: • Up to 4 GB 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 15
Portable Storage • Gives us the ability to move data from one computer to another • Types of portable storage devices: – Floppy disk: • Capacity 1. 44 MB – Zip disk: • Capacity 100 MB to 750 MB – CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-RW: • Capacity 700 MB to 9. 4 GB – Flash drive: • Capacity 32 MB to 1 GB – Flash memory Card: • Up to 4 GB 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 15
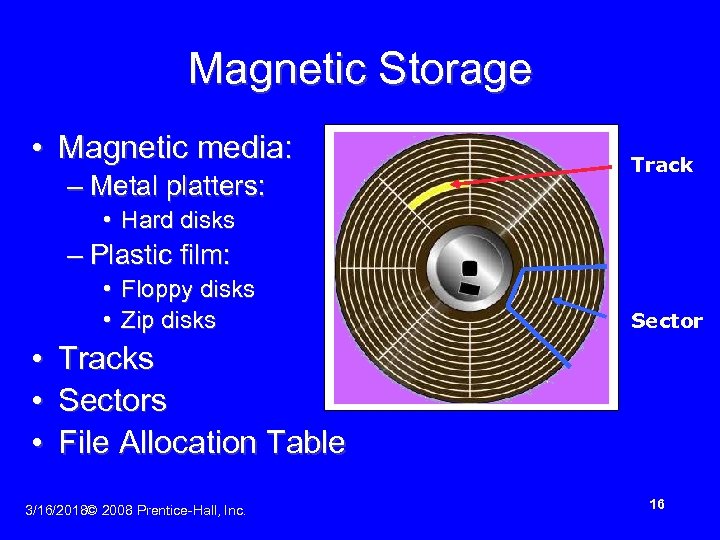 Magnetic Storage • Magnetic media: – Metal platters: Track • Hard disks – Plastic film: • Floppy disks • Zip disks • • • Sector Tracks Sectors File Allocation Table 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 16
Magnetic Storage • Magnetic media: – Metal platters: Track • Hard disks – Plastic film: • Floppy disks • Zip disks • • • Sector Tracks Sectors File Allocation Table 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 16
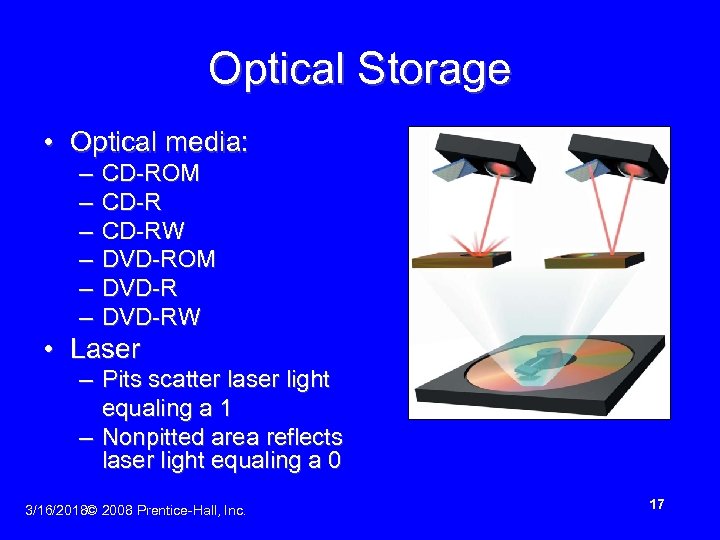 Optical Storage • Optical media: – – – CD-ROM CD-RW DVD-ROM DVD-RW • Laser – Pits scatter laser light equaling a 1 – Nonpitted area reflects laser light equaling a 0 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 17
Optical Storage • Optical media: – – – CD-ROM CD-RW DVD-ROM DVD-RW • Laser – Pits scatter laser light equaling a 1 – Nonpitted area reflects laser light equaling a 0 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 17
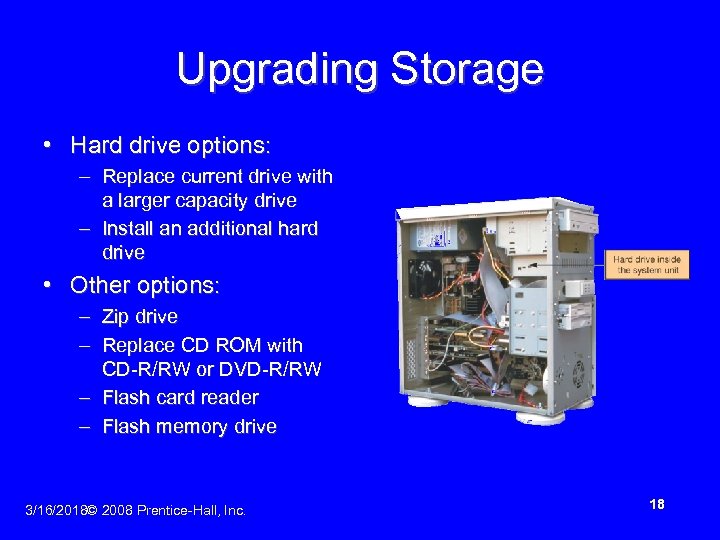 Upgrading Storage • Hard drive options: – Replace current drive with a larger capacity drive – Install an additional hard drive • Other options: – Zip drive – Replace CD ROM with CD-R/RW or DVD-R/RW – Flash card reader – Flash memory drive 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 18
Upgrading Storage • Hard drive options: – Replace current drive with a larger capacity drive – Install an additional hard drive • Other options: – Zip drive – Replace CD ROM with CD-R/RW or DVD-R/RW – Flash card reader – Flash memory drive 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 18
 Evaluating Video • Two components: – Video card (adapter) – Monitor 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 19
Evaluating Video • Two components: – Video card (adapter) – Monitor 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 19
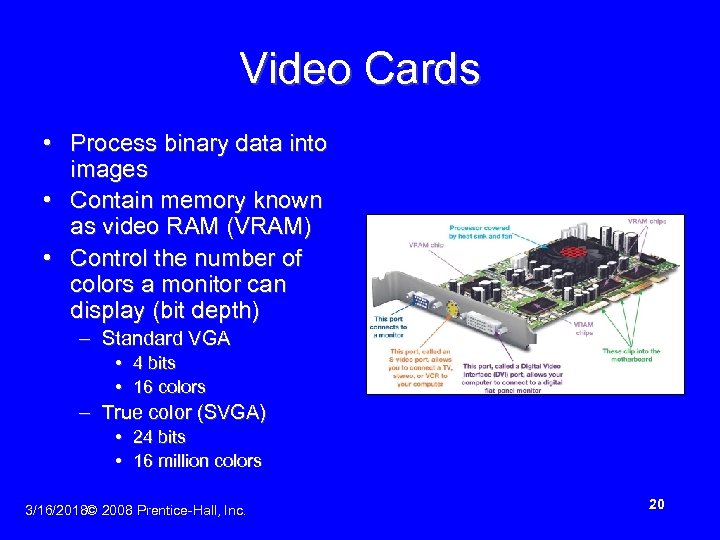 Video Cards • Process binary data into images • Contain memory known as video RAM (VRAM) • Control the number of colors a monitor can display (bit depth) – Standard VGA • 4 bits • 16 colors – True color (SVGA) • 24 bits • 16 million colors 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 20
Video Cards • Process binary data into images • Contain memory known as video RAM (VRAM) • Control the number of colors a monitor can display (bit depth) – Standard VGA • 4 bits • 16 colors – True color (SVGA) • 24 bits • 16 million colors 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 20
 Monitors • Things to consider: – Types: • CRT or LCD – Size: – 15, 17, 19, or 21 inch – Resolution: • Increasing resolution allows more to be displayed – Dot pitch: • . 31 mm or less – Refresh rate: • 75 Hz or higher 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 21
Monitors • Things to consider: – Types: • CRT or LCD – Size: – 15, 17, 19, or 21 inch – Resolution: • Increasing resolution allows more to be displayed – Dot pitch: • . 31 mm or less – Refresh rate: • 75 Hz or higher 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 21
 Evaluating Audio • Sound card: – Process digital data into sounds – 3 D sound cards – Surround sound • Dolby Digital 5. 1 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 22
Evaluating Audio • Sound card: – Process digital data into sounds – 3 D sound cards – Surround sound • Dolby Digital 5. 1 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 22
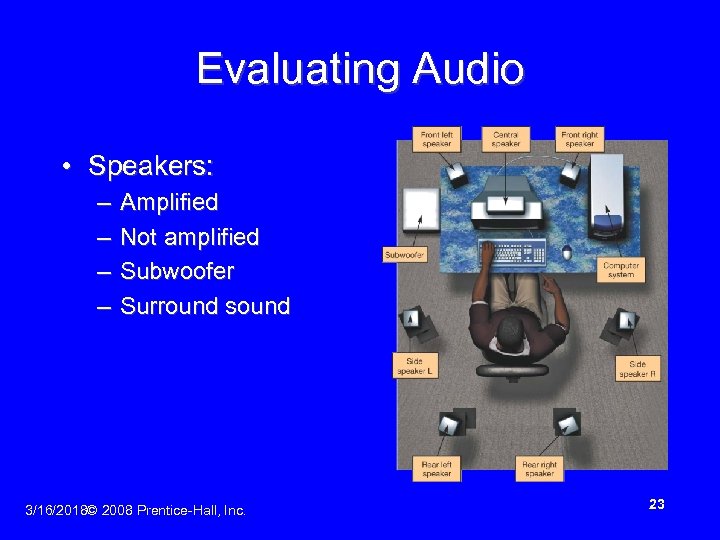 Evaluating Audio • Speakers: – – Amplified Not amplified Subwoofer Surround sound 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 23
Evaluating Audio • Speakers: – – Amplified Not amplified Subwoofer Surround sound 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 23
 Evaluating Ports • Ports are used to connect peripheral devices to the computer • Things to consider: – Devices you want to use – Ports needed for the devices 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 24
Evaluating Ports • Ports are used to connect peripheral devices to the computer • Things to consider: – Devices you want to use – Ports needed for the devices 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 24
 Types of Ports • Serial Port – Transfers data one bit at a time; 56 Kbps PS/2 Port COM 1 Port 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. PS/2 Connectors Serial Connector 25
Types of Ports • Serial Port – Transfers data one bit at a time; 56 Kbps PS/2 Port COM 1 Port 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. PS/2 Connectors Serial Connector 25
 Types of Ports • Parallel – Transfers eight bits of data simultaneously; 12 Mbps 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. LPT 1 Port Printer Cable Connector 26
Types of Ports • Parallel – Transfers eight bits of data simultaneously; 12 Mbps 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. LPT 1 Port Printer Cable Connector 26
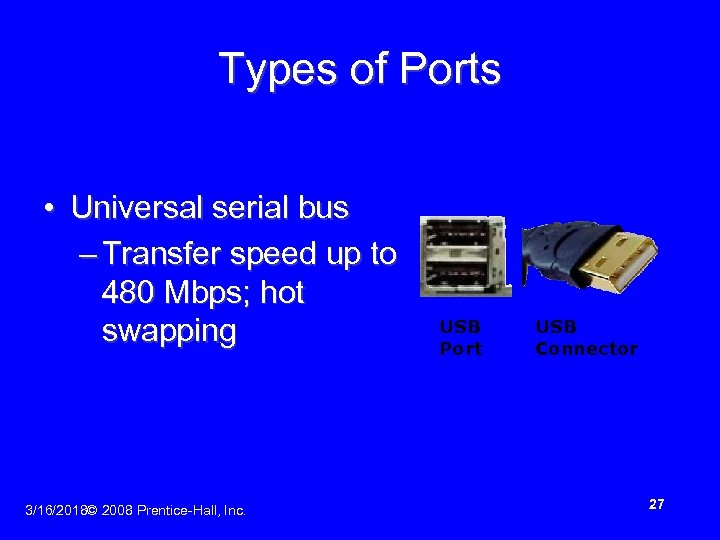 Types of Ports • Universal serial bus – Transfer speed up to 480 Mbps; hot swapping 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. USB Port USB Connector 27
Types of Ports • Universal serial bus – Transfer speed up to 480 Mbps; hot swapping 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. USB Port USB Connector 27
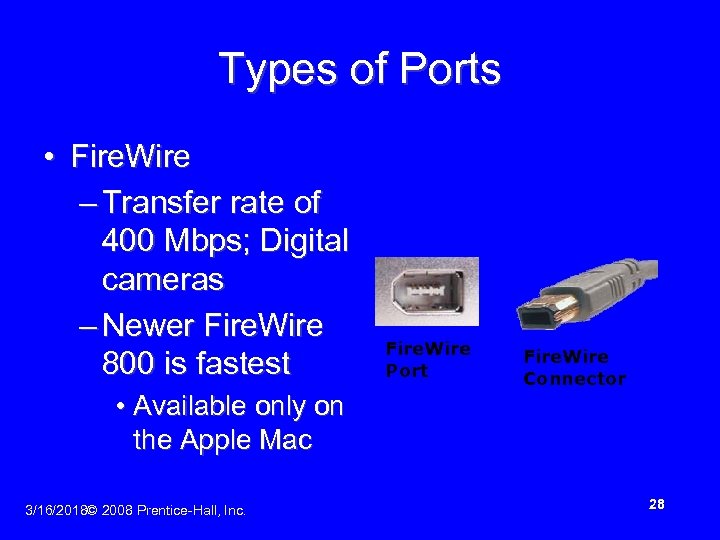 Types of Ports • Fire. Wire – Transfer rate of 400 Mbps; Digital cameras – Newer Fire. Wire 800 is fastest Fire. Wire Port Fire. Wire Connector • Available only on the Apple Mac 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 28
Types of Ports • Fire. Wire – Transfer rate of 400 Mbps; Digital cameras – Newer Fire. Wire 800 is fastest Fire. Wire Port Fire. Wire Connector • Available only on the Apple Mac 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 28
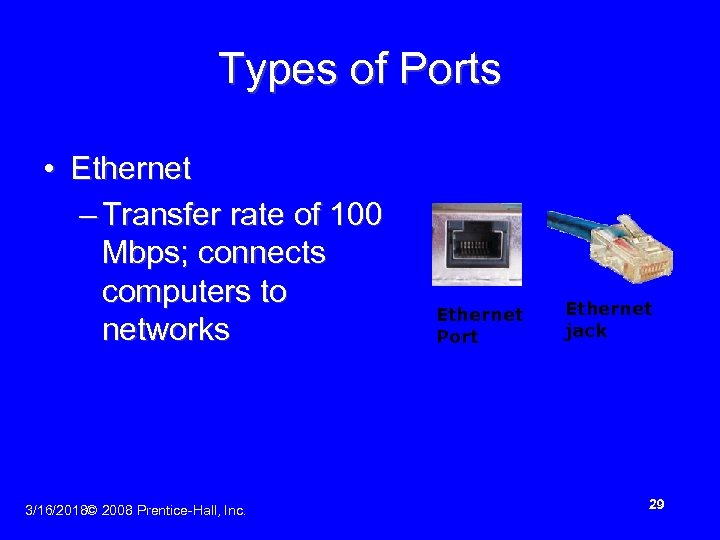 Types of Ports • Ethernet – Transfer rate of 100 Mbps; connects computers to networks 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Ethernet Port Ethernet jack 29
Types of Ports • Ethernet – Transfer rate of 100 Mbps; connects computers to networks 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Ethernet Port Ethernet jack 29
 Types of Ports • Ir. DA – Transfer rate of 4 Mbps; Uses infrared light waves Ir. DA 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 30
Types of Ports • Ir. DA – Transfer rate of 4 Mbps; Uses infrared light waves Ir. DA 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 30
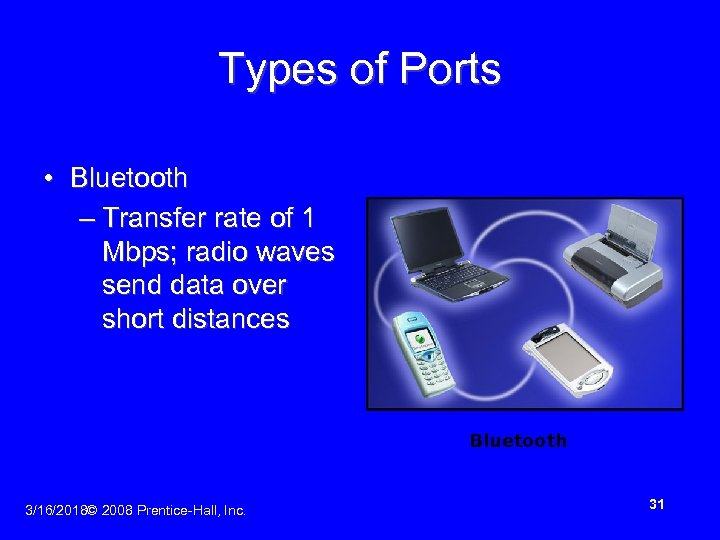 Types of Ports • Bluetooth – Transfer rate of 1 Mbps; radio waves send data over short distances Bluetooth 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 31
Types of Ports • Bluetooth – Transfer rate of 1 Mbps; radio waves send data over short distances Bluetooth 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 31
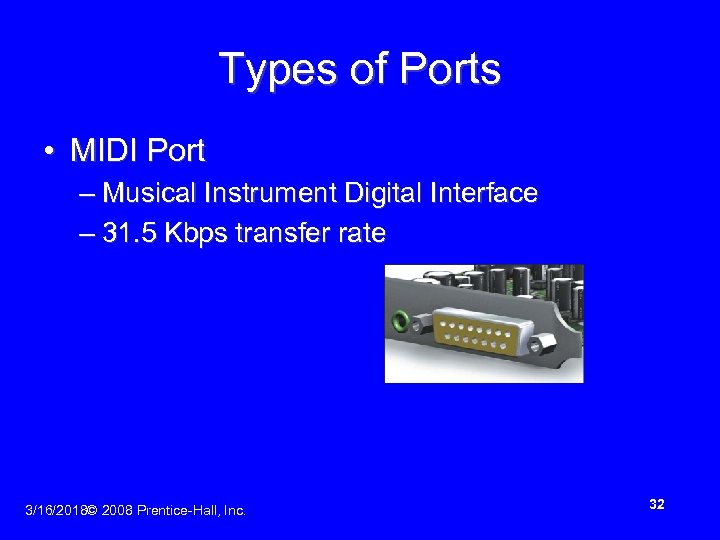 Types of Ports • MIDI Port – Musical Instrument Digital Interface – 31. 5 Kbps transfer rate 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 32
Types of Ports • MIDI Port – Musical Instrument Digital Interface – 31. 5 Kbps transfer rate 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 32
 Adding Ports • Expansion cards: – New port standards • Expansion hubs: – Enables several devices to be connected to a port 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 33
Adding Ports • Expansion cards: – New port standards • Expansion hubs: – Enables several devices to be connected to a port 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 33
 Evaluating System Reliability • Performance: – Slow – Freezes – Crashes • Upkeep and maintenance: – System tools – Control panel – Update software and hardware drivers 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 34
Evaluating System Reliability • Performance: – Slow – Freezes – Crashes • Upkeep and maintenance: – System tools – Control panel – Update software and hardware drivers 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 34
 Upkeep and Maintenance • System tools: – Disk defragmenter – Disk cleanup • Unnecessary files • Control panel: – Add/remove programs – Display – System • Device manager 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 35
Upkeep and Maintenance • System tools: – Disk defragmenter – Disk cleanup • Unnecessary files • Control panel: – Add/remove programs – Display – System • Device manager 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 35
 Update Software and Hardware Drivers • Software: – Automatic updates – Patches • Hardware: – Download updated drivers 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 36
Update Software and Hardware Drivers • Software: – Automatic updates – Patches • Hardware: – Download updated drivers 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 36
 The Last Resort • If problems persist: – Reinstall the operating system – Upgrade the operating system to the latest version 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 37
The Last Resort • If problems persist: – Reinstall the operating system – Upgrade the operating system to the latest version 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 37
 The Final Decision • How closely does your system come to meeting your needs? • How much would it cost to upgrade your system? • How much would it cost to purchase a new system? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 38
The Final Decision • How closely does your system come to meeting your needs? • How much would it cost to upgrade your system? • How much would it cost to purchase a new system? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 38
 Chapter 6 Summary Questions • How can I determine whether I should upgrade my existing computer or buy a new one? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 39
Chapter 6 Summary Questions • How can I determine whether I should upgrade my existing computer or buy a new one? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 39
 Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What does the CPU do and how can I evaluate its performance? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 40
Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What does the CPU do and how can I evaluate its performance? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 40
 Chapter 6 Summary Questions • How does memory work and how can I evaluate how much memory I need? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 41
Chapter 6 Summary Questions • How does memory work and how can I evaluate how much memory I need? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 41
 Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What are the computer’s main storage devices and how can I evaluate whether they match my needs? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 42
Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What are the computer’s main storage devices and how can I evaluate whether they match my needs? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 42
 Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What components affect the output of video and how can I evaluate whether they are meeting my needs? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 43
Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What components affect the output of video and how can I evaluate whether they are meeting my needs? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 43
 Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What components affect the quality of sound and how can I evaluate whether they are meeting my needs? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 44
Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What components affect the quality of sound and how can I evaluate whether they are meeting my needs? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 44
 Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What are the ports available on desktop computers and how can I determine what ports I need? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 45
Chapter 6 Summary Questions • What are the ports available on desktop computers and how can I determine what ports I need? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 45
 Chapter 6 Summary Questions • How can I ensure the reliability of my system? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 46
Chapter 6 Summary Questions • How can I ensure the reliability of my system? 3/16/2018© 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. 46


