42e9c4f623533c792a41eb6333709efd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Technologies in ODL: Issues and Implementation Prof Dr Anuwar Ali President/Vice Chancellor Open University Malaysia 14 Sept 2006, Hanoi Vietnam
Technologies in ODL: Issues and Implementation Prof Dr Anuwar Ali President/Vice Chancellor Open University Malaysia 14 Sept 2006, Hanoi Vietnam
 Introduction § OUM was set up as the 7 th private university in Malaysia on August 10, 2000 § It is the first university to practice Open and Distance Learning (ODL) in Malaysia
Introduction § OUM was set up as the 7 th private university in Malaysia on August 10, 2000 § It is the first university to practice Open and Distance Learning (ODL) in Malaysia
 11 Public Universities (IPTA)
11 Public Universities (IPTA)
 Vision To be a leader and innovator in open learning
Vision To be a leader and innovator in open learning
 Mission § To be the leading contributor in democratising education § To develop quality education through multimode learning technologies § To develop and enhance learning experiences towards the development of knowledge-based society
Mission § To be the leading contributor in democratising education § To develop quality education through multimode learning technologies § To develop and enhance learning experiences towards the development of knowledge-based society
 Professionalism Integrity Caring Dedication Shared Values Innovative
Professionalism Integrity Caring Dedication Shared Values Innovative
 LEARNING MATERIALS Our print modules and e-contents are developed in-house by Centre for Instructional Design and Technology (CIDT)
LEARNING MATERIALS Our print modules and e-contents are developed in-house by Centre for Instructional Design and Technology (CIDT)
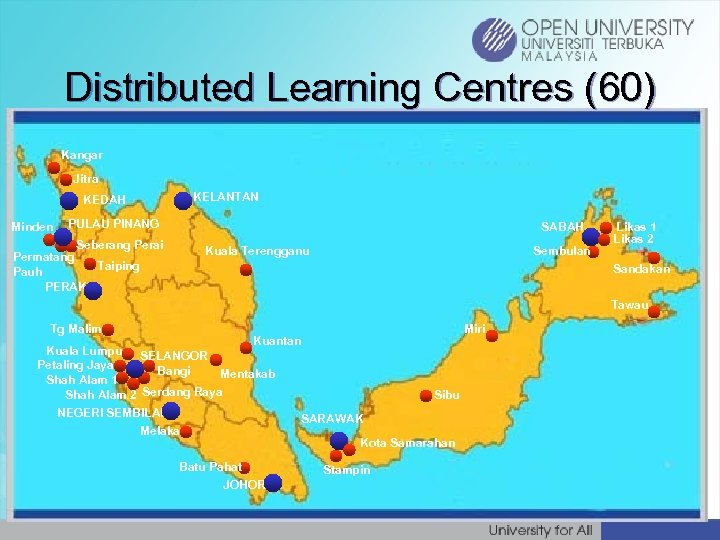 Distributed Learning Centres (60) Kangar Jitra KEDAH Minden KELANTAN PULAU PINANG Seberang Perai Permatang Taiping Pauh PERAK SABAH Kuala Terengganu Sembulan Likas 1 Likas 2 Sandakan Tawau Tg Malim Miri Kuantan Kuala Lumpur SELANGOR Petaling Jaya Bangi Mentakab Shah Alam 1 Shah Alam 2 Serdang Raya NEGERI SEMBILAN Melaka Batu Pahat JOHOR Sibu SARAWAK Kota Samarahan Stampin
Distributed Learning Centres (60) Kangar Jitra KEDAH Minden KELANTAN PULAU PINANG Seberang Perai Permatang Taiping Pauh PERAK SABAH Kuala Terengganu Sembulan Likas 1 Likas 2 Sandakan Tawau Tg Malim Miri Kuantan Kuala Lumpur SELANGOR Petaling Jaya Bangi Mentakab Shah Alam 1 Shah Alam 2 Serdang Raya NEGERI SEMBILAN Melaka Batu Pahat JOHOR Sibu SARAWAK Kota Samarahan Stampin
 Tan Sri Dr. Abdullah Sanusi Digital Library § ISO Certified § Digital Collection: § e-books with over 40, 000 titles § e-journals with over 15, 000 titles and over 1 million articles § Accessible online from anywhere in the world
Tan Sri Dr. Abdullah Sanusi Digital Library § ISO Certified § Digital Collection: § e-books with over 40, 000 titles § e-journals with over 15, 000 titles and over 1 million articles § Accessible online from anywhere in the world
 DELIVERY MODES Online Interactions Face-to-Face Tutorials Self-Managed Learning
DELIVERY MODES Online Interactions Face-to-Face Tutorials Self-Managed Learning
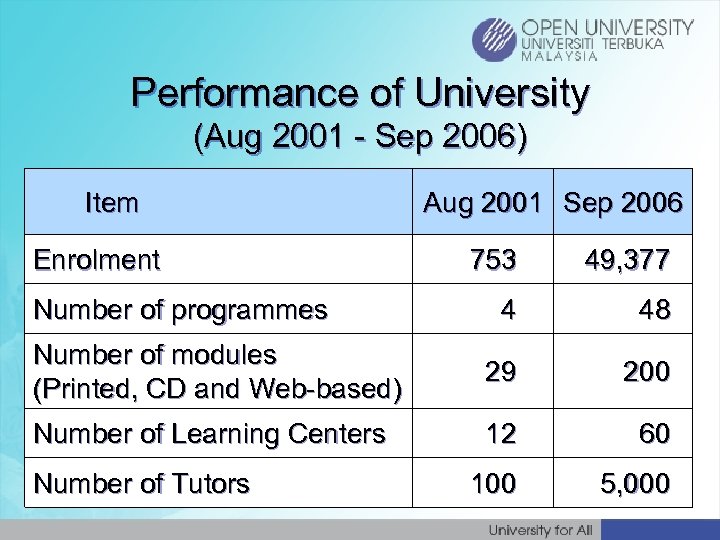 Performance of University (Aug 2001 - Sep 2006) Item Enrolment Aug 2001 Sep 2006 753 49, 377 4 48 Number of modules (Printed, CD and Web-based) 29 200 Number of Learning Centers 12 60 100 5, 000 Number of programmes Number of Tutors
Performance of University (Aug 2001 - Sep 2006) Item Enrolment Aug 2001 Sep 2006 753 49, 377 4 48 Number of modules (Printed, CD and Web-based) 29 200 Number of Learning Centers 12 60 100 5, 000 Number of programmes Number of Tutors
 Quality Assurance At OUM, quality is uppermost in all our endeavours
Quality Assurance At OUM, quality is uppermost in all our endeavours
 Technologies in ODL 1: Learning materials 2: Delivery of learning materials, and 3: Learning management and administration
Technologies in ODL 1: Learning materials 2: Delivery of learning materials, and 3: Learning management and administration
 Selection Criteria Tony Bates (1995), proposes the “ACTIONS’ model as the criteria for selection of technologies: 1: Access- Staff and learners need adequate access to technology 2: Costs-must consider initial and ongoing costs 3: Teaching and learning functions-strengths and weaknesses of different technologies need to be clearly understood
Selection Criteria Tony Bates (1995), proposes the “ACTIONS’ model as the criteria for selection of technologies: 1: Access- Staff and learners need adequate access to technology 2: Costs-must consider initial and ongoing costs 3: Teaching and learning functions-strengths and weaknesses of different technologies need to be clearly understood
 Selection Criteria Tony Bates (1995), proposes the “ACTIONS’ model as the criteria for selection of technologies: 4: Interactivity and user friendliness-interactions are important for the learning process 5: Organisational issues-organisational support is critical for long-term success
Selection Criteria Tony Bates (1995), proposes the “ACTIONS’ model as the criteria for selection of technologies: 4: Interactivity and user friendliness-interactions are important for the learning process 5: Organisational issues-organisational support is critical for long-term success
 Selection Criteria Tony Bates (1995), proposes the “ACTIONS’ model as the criteria for selection of technologies: 6: Novelty-novelty of technology may be important for attracting funding 7: Speed-time required to develop, update and deliver learning materials is an important factor
Selection Criteria Tony Bates (1995), proposes the “ACTIONS’ model as the criteria for selection of technologies: 6: Novelty-novelty of technology may be important for attracting funding 7: Speed-time required to develop, update and deliver learning materials is an important factor
 1 : Learning materials § § Printed modules CDs Audio tapes Web-based
1 : Learning materials § § Printed modules CDs Audio tapes Web-based
 1 : Learning Materials: Issues § Cost § Accessibility § Balance between print content and digital content § Quality and timeliness of raw content § Plagiarism § Availability of skilled manpower
1 : Learning Materials: Issues § Cost § Accessibility § Balance between print content and digital content § Quality and timeliness of raw content § Plagiarism § Availability of skilled manpower
 1 : Learning Materials : Strategies § Establishment of Centre for Instructional Design and Technology (Ci. DT) § Appropriate selection of media for developing content § Adequate compensation to Subject Matter Experts and regular project monitoring § Automatic plagiarism detection system § Continuous upgrading of skills
1 : Learning Materials : Strategies § Establishment of Centre for Instructional Design and Technology (Ci. DT) § Appropriate selection of media for developing content § Adequate compensation to Subject Matter Experts and regular project monitoring § Automatic plagiarism detection system § Continuous upgrading of skills
 2. Delivery of learning materials § § § § Radio Television Audio Conferencing System Video Conferencing System Satellite Broadcasting System Internet Web TV Web Radio
2. Delivery of learning materials § § § § Radio Television Audio Conferencing System Video Conferencing System Satellite Broadcasting System Internet Web TV Web Radio
 2. Delivery of learning materials : Issues § Radio, television and satellite § Costs § Interactivity § Audio and Video-Conferencing System (VCS) § Costs § Readiness of facilitators and learners § Internet, Web TV and Web Radio § Digital divide § High availability
2. Delivery of learning materials : Issues § Radio, television and satellite § Costs § Interactivity § Audio and Video-Conferencing System (VCS) § Costs § Readiness of facilitators and learners § Internet, Web TV and Web Radio § Digital divide § High availability
 2. Delivery of learning materials : Strategies § Radio and television § Adopt web-based radio and television § Use E-mail or forum for interactivity § Audio and Video-Conferencing System (VCS) § Adopt web-based VCS § Awareness and training for facilitators and learners § Internet, web TV and web radio § Introduction of learning skills module § Adopt redundancy and clustering technology
2. Delivery of learning materials : Strategies § Radio and television § Adopt web-based radio and television § Use E-mail or forum for interactivity § Audio and Video-Conferencing System (VCS) § Adopt web-based VCS § Awareness and training for facilitators and learners § Internet, web TV and web radio § Introduction of learning skills module § Adopt redundancy and clustering technology
 3. Learning management and administration • LMS and LCMS • Online and Mobile applications • Push technology
3. Learning management and administration • LMS and LCMS • Online and Mobile applications • Push technology
 3. Learning management and administration: Issues § LMS and LCMS § Cost § Accessibility and availability § Online and mobile applications § Cost § Accessibility and availability § Push technology § Cost § Accessibility
3. Learning management and administration: Issues § LMS and LCMS § Cost § Accessibility and availability § Online and mobile applications § Cost § Accessibility and availability § Push technology § Cost § Accessibility
 3. Learning management and administration: Strategies § LMS and LCMS § Open source § User friendly and ‘light’ § Online and mobile applications § Develop in-house in collaboration with strategic partner § Adopt redundancy and clustering technology § Push technology § Create awareness § Educate users
3. Learning management and administration: Strategies § LMS and LCMS § Open source § User friendly and ‘light’ § Online and mobile applications § Develop in-house in collaboration with strategic partner § Adopt redundancy and clustering technology § Push technology § Create awareness § Educate users
 Conclusions q ODL institutions must leverage on technology in order to effectively and efficiently deliver education to their learners q With appropriate strategies, ODL institutions can reduce costs and yet maintain quality of delivery q ODL institutions need to continuously review usage of technology in line with rapid technological development
Conclusions q ODL institutions must leverage on technology in order to effectively and efficiently deliver education to their learners q With appropriate strategies, ODL institutions can reduce costs and yet maintain quality of delivery q ODL institutions need to continuously review usage of technology in line with rapid technological development
 Thank you
Thank you


