c4d21ac0f7b0c71205b42e4f1ea5e396.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Technologies for (semi-) automatic metadata creation http: //gate. ac. uk/ http: //nlp. shef. ac. uk/ Diana Maynard University of Sheffield Knowledge. Web WP 1. 3 meeting, Crete, 14 May 2004
Technologies for (semi-) automatic metadata creation http: //gate. ac. uk/ http: //nlp. shef. ac. uk/ Diana Maynard University of Sheffield Knowledge. Web WP 1. 3 meeting, Crete, 14 May 2004
 Overview • USFD is mainly concerned in this WP with best practices and guidelines for ontology-based web applications • State-of-the-art systems and platforms for metadata creation • Metadata is created through semantic tagging • Metadata can be represented as inline (modification of the original document) or standoff (separate storage from the document)
Overview • USFD is mainly concerned in this WP with best practices and guidelines for ontology-based web applications • State-of-the-art systems and platforms for metadata creation • Metadata is created through semantic tagging • Metadata can be represented as inline (modification of the original document) or standoff (separate storage from the document)
 Semi-automatic v automatic metadata creation • Semi-automatic methods are more reliable, but require human intervention – Mn. M: requires initial human annotation; pre-defined ontology – S-CREAM – AERODAML • Automatic methods less reliable, but suitable for large volumes of text, and offer a dynamic view – Sem. Tag: semantic tagging from ontology – KIM: semantic tagging and ontology population – h. Tech. Sight: semantic tagging, ontology population and evolution
Semi-automatic v automatic metadata creation • Semi-automatic methods are more reliable, but require human intervention – Mn. M: requires initial human annotation; pre-defined ontology – S-CREAM – AERODAML • Automatic methods less reliable, but suitable for large volumes of text, and offer a dynamic view – Sem. Tag: semantic tagging from ontology – KIM: semantic tagging and ontology population – h. Tech. Sight: semantic tagging, ontology population and evolution
 Semi-automatic methods • Mn. M • S-CREAM
Semi-automatic methods • Mn. M • S-CREAM
 Mn. M • Semi-automatic in that it requires initial training by user • Uses pre-defined set of concepts in ontology • User browses web and manually annotates his chosen pages • System learns annotation rules, tests them, and takes over annotation, populating ontologies with the instances found • Precision and recall are not perfect, however retraining is possible at any stage
Mn. M • Semi-automatic in that it requires initial training by user • Uses pre-defined set of concepts in ontology • User browses web and manually annotates his chosen pages • System learns annotation rules, tests them, and takes over annotation, populating ontologies with the instances found • Precision and recall are not perfect, however retraining is possible at any stage
 S-CREAM • • Semi-automatic CREAtion of Metadata Uses Onto-O-Mat + Amilcare Trainable for different domains Aligns conceptual markup (which defines relational metadata) provided by e. g. Ont. O-Mat with semantic markup provided by Amilcare
S-CREAM • • Semi-automatic CREAtion of Metadata Uses Onto-O-Mat + Amilcare Trainable for different domains Aligns conceptual markup (which defines relational metadata) provided by e. g. Ont. O-Mat with semantic markup provided by Amilcare
 Annotated data in S-CREAM
Annotated data in S-CREAM
 Amilcare • Amilcare learns IE rules from preannotated data (e. g. using Ont-O-Mat) • Uses GATE (ANNIE) for pre-processing + applies rules learnt in training phase to new documents • Concepts need to be pre-defined, but system can be trained for new domain • Can be tuned towards precision or recall
Amilcare • Amilcare learns IE rules from preannotated data (e. g. using Ont-O-Mat) • Uses GATE (ANNIE) for pre-processing + applies rules learnt in training phase to new documents • Concepts need to be pre-defined, but system can be trained for new domain • Can be tuned towards precision or recall
 Automatic methods • Sem. Tag • KIM • h-Techsight
Automatic methods • Sem. Tag • KIM • h-Techsight
 Sem. Tag and KIM • Sem. Tag and KIM both annotate webpages using instances from an ontology • Main problem is to disambiguate such instances which occur in multiple parts of the ontology • Sem. Tag aims for accuracy of classification, whereas KIM aims more for recall (finding all instances) • KIM also uses IE to find new instances not present in ontology
Sem. Tag and KIM • Sem. Tag and KIM both annotate webpages using instances from an ontology • Main problem is to disambiguate such instances which occur in multiple parts of the ontology • Sem. Tag aims for accuracy of classification, whereas KIM aims more for recall (finding all instances) • KIM also uses IE to find new instances not present in ontology
 Sem. Tag • Automated semantic tagging of large corpora, using TAP ontology (contains 65 K instances) • Largest scale semantic tagging effort to date • Uses concept of Semantic Label Bureau • Annotations are stored separately from web pages (standoff markup) • Uses corpus-wide statistics to improve quality of tagging, e. g. automated alias discovery • Tags can be extracted using a variety of mechanisms, e. g. search for all tags matching a particular object
Sem. Tag • Automated semantic tagging of large corpora, using TAP ontology (contains 65 K instances) • Largest scale semantic tagging effort to date • Uses concept of Semantic Label Bureau • Annotations are stored separately from web pages (standoff markup) • Uses corpus-wide statistics to improve quality of tagging, e. g. automated alias discovery • Tags can be extracted using a variety of mechanisms, e. g. search for all tags matching a particular object
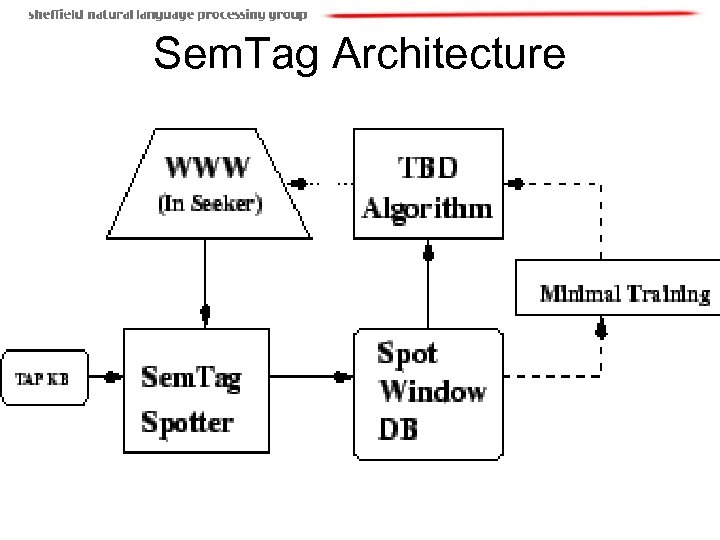 Sem. Tag Architecture
Sem. Tag Architecture
 KIM • Uses an ontology (KIMO) with 86 K/200 K instances • Lookup phase marks instances from the ontology • High ambiguity of instances with the same label (e. g. locations belonging to different countries) • Disambiguation uses an Entity Ranking algorithm, i. e. , priority ordering of entities with the same label based on corpus statistics • Lookup is combined with rule-based IE system (from GATE) to recognise new instances of concepts and relations • Special KB enrichment stage where some of these new instances are added to the KB
KIM • Uses an ontology (KIMO) with 86 K/200 K instances • Lookup phase marks instances from the ontology • High ambiguity of instances with the same label (e. g. locations belonging to different countries) • Disambiguation uses an Entity Ranking algorithm, i. e. , priority ordering of entities with the same label based on corpus statistics • Lookup is combined with rule-based IE system (from GATE) to recognise new instances of concepts and relations • Special KB enrichment stage where some of these new instances are added to the KB
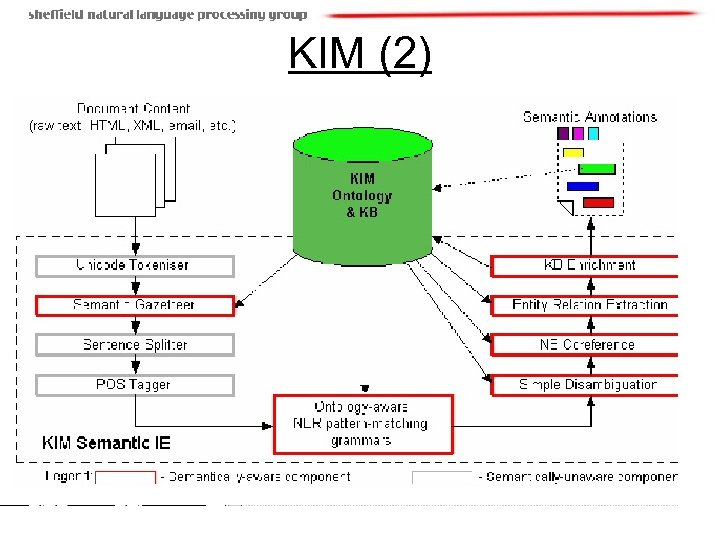 KIM (2)
KIM (2)
 h-Tech. Sight KMP • Knowledge management platform for fully automatic metadata creation and ontology population, and semi-automatic ontology evolution, powered by GATE and Tool. Box. • Data-driven analysis of ontologies enables trends of instances to be monitored • Uses GATE to support the instance-based evolution of ontologies in the Chemical Engineering domain. • Analysis of unrestricted text to extract instances of concepts from such ontologies • Instances populated into a domain-specific ontology and/or exported to an Access / Oracle database
h-Tech. Sight KMP • Knowledge management platform for fully automatic metadata creation and ontology population, and semi-automatic ontology evolution, powered by GATE and Tool. Box. • Data-driven analysis of ontologies enables trends of instances to be monitored • Uses GATE to support the instance-based evolution of ontologies in the Chemical Engineering domain. • Analysis of unrestricted text to extract instances of concepts from such ontologies • Instances populated into a domain-specific ontology and/or exported to an Access / Oracle database
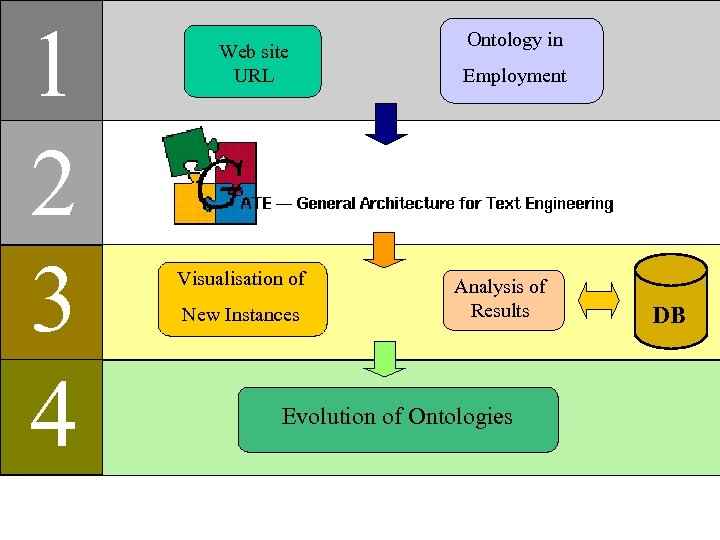 1 2 3 4 Web site URL Visualisation of New Instances Ontology in Employment Analysis of Results Evolution of Ontologies DB
1 2 3 4 Web site URL Visualisation of New Instances Ontology in Employment Analysis of Results Evolution of Ontologies DB
 Ontology-based IE in h-Tech. Sight • Ontology-Based IE for semantic tagging of job adverts, news and reports in chemical engineering domain • Semantic tagging used as input for ontological analysis • Fundamental to the application is a domainspecific ontology • Terminological gazetteer lists are linked to classes in the ontology • Rules classify the mentions in the text wrt the domain ontology • Annotations output into a database or as an ontology
Ontology-based IE in h-Tech. Sight • Ontology-Based IE for semantic tagging of job adverts, news and reports in chemical engineering domain • Semantic tagging used as input for ontological analysis • Fundamental to the application is a domainspecific ontology • Terminological gazetteer lists are linked to classes in the ontology • Rules classify the mentions in the text wrt the domain ontology • Annotations output into a database or as an ontology
 Limitations • h-Techsight uses rule-based IE system • Requires human expert to write rules • Accurate on restricted domains with small ontologies • Adaptation to a new domain / ontology may require some effort
Limitations • h-Techsight uses rule-based IE system • Requires human expert to write rules • Accurate on restricted domains with small ontologies • Adaptation to a new domain / ontology may require some effort
 Summary • Tradeoff between semi-automatic and fully automatic systems, dependent on application, corpus size etc • Tradeoff between rule-based and ML techniques for IE • Tradeoff between dynamic vs static systems
Summary • Tradeoff between semi-automatic and fully automatic systems, dependent on application, corpus size etc • Tradeoff between rule-based and ML techniques for IE • Tradeoff between dynamic vs static systems


