fbbf8aeacb57fbd9667f6e530842c9fe.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 77
 Technological Hazards
Technological Hazards
 Technological Hazards • Smith Ch 13
Technological Hazards • Smith Ch 13
 Technological Hazards • Artificial hazards due to a technological failure – slow-acting – fast-acting
Technological Hazards • Artificial hazards due to a technological failure – slow-acting – fast-acting
 Slow-Acting • • soil and water contamination air pollution occupational disease life-style disease
Slow-Acting • • soil and water contamination air pollution occupational disease life-style disease
 "Smoking is one of the leading causes of all statistics. " -- Liza Minnelli
"Smoking is one of the leading causes of all statistics. " -- Liza Minnelli
 “Smoking kills. If you're killed, you've lost a very important part of your life. ” — Brooke Shields
“Smoking kills. If you're killed, you've lost a very important part of your life. ” — Brooke Shields
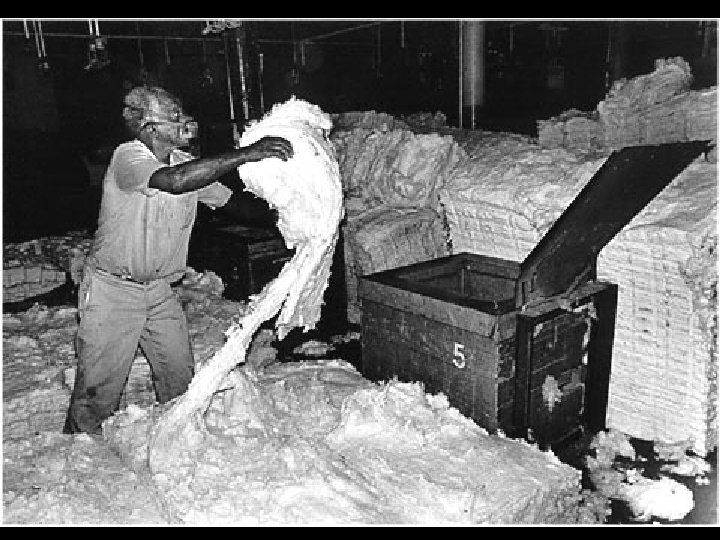
 Byssinosis victim, Greenville SC
Byssinosis victim, Greenville SC




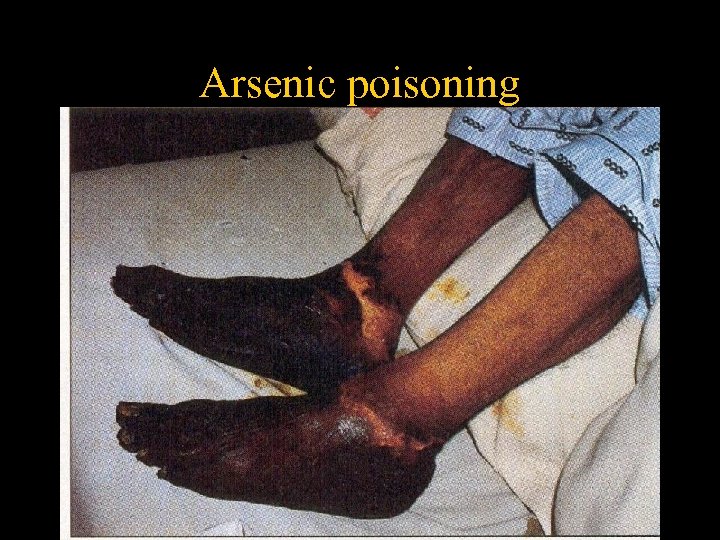 Arsenic poisoning
Arsenic poisoning
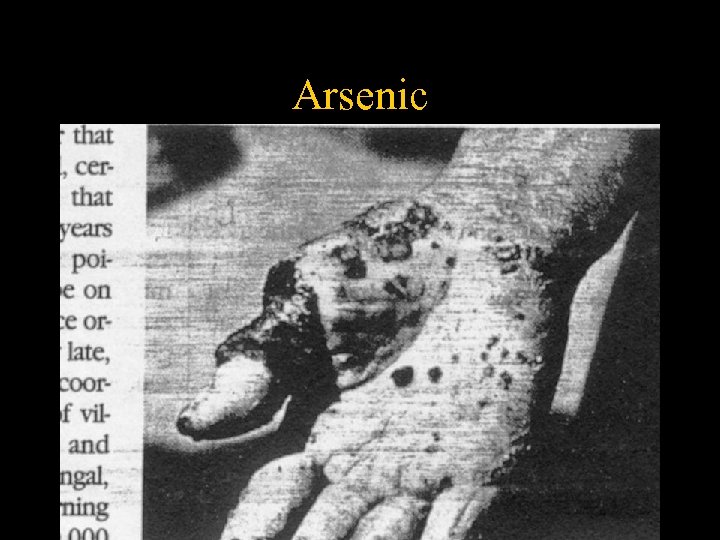 Arsenic
Arsenic
 London Smog Nov 1952
London Smog Nov 1952

 “It isn’t the pollution that’s harming the environment. It’s the impurities in the air and water that are doing it. ” -- Dan Quayle
“It isn’t the pollution that’s harming the environment. It’s the impurities in the air and water that are doing it. ” -- Dan Quayle
 Aral Sea
Aral Sea
 Bangkok
Bangkok
 • Sudbury 1979
• Sudbury 1979
 "Hollywood is the only place where you can wake up in the morning and hear the birds coughing in the trees. " -- Joe Frisco
"Hollywood is the only place where you can wake up in the morning and hear the birds coughing in the trees. " -- Joe Frisco
 Leaking USTs
Leaking USTs
 • British sewage sludge dumped at sea 1980 s
• British sewage sludge dumped at sea 1980 s
 Fast-Acting • • major fires structural failures transportation accidents industrial accident
Fast-Acting • • major fires structural failures transportation accidents industrial accident
 Major conflagrations • 1666 Great Fire of London: 13, 200 houses destroyed • 1871 Great Fire of Chicago: 18, 000 homes destroyed
Major conflagrations • 1666 Great Fire of London: 13, 200 houses destroyed • 1871 Great Fire of Chicago: 18, 000 homes destroyed
 Dutch firework disaster
Dutch firework disaster
 Hagersville ON 1990
Hagersville ON 1990
 London May 10 -11 1941 • Heaviest air raid on London in WW 2 • 35 Weeks into the London “Blitz” • 541 German aircraft involved – 700 tons of high explosive – 86 tons of incendiaries
London May 10 -11 1941 • Heaviest air raid on London in WW 2 • 35 Weeks into the London “Blitz” • 541 German aircraft involved – 700 tons of high explosive – 86 tons of incendiaries
 London May 10 -11 1941 • 1436 Civilians killed • 1800 serious injuries • 2200 fires started, 700 acres burned (bigger than 1666) • 11000 homes destroyed
London May 10 -11 1941 • 1436 Civilians killed • 1800 serious injuries • 2200 fires started, 700 acres burned (bigger than 1666) • 11000 homes destroyed
 Major transport accidents • 1912 Titanic: 1, 500 dead • 1914 Empress of Ireland
Major transport accidents • 1912 Titanic: 1, 500 dead • 1914 Empress of Ireland
 • Empire State crash 1940 s
• Empire State crash 1940 s
 Mississauga Train Derailment • November 1979 train carrying propane & chlorine derails • 250, 000 evacuated
Mississauga Train Derailment • November 1979 train carrying propane & chlorine derails • 250, 000 evacuated

 • Amoco Cadiz 1978
• Amoco Cadiz 1978
 Exxon Valdez • Exxon pays $35 Billion US in compensation for major oil spill in Alaskan waters • Tanker runs aground while captain drunk
Exxon Valdez • Exxon pays $35 Billion US in compensation for major oil spill in Alaskan waters • Tanker runs aground while captain drunk
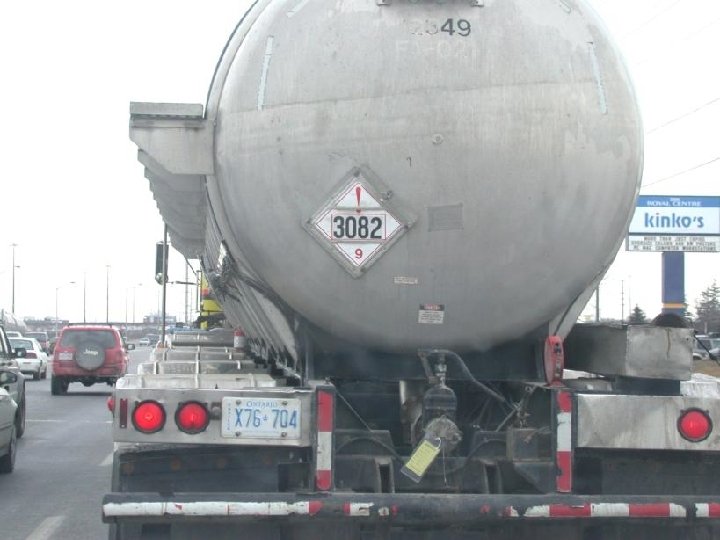

 Major industrial accidents • 1769 San Nazzaro gunpowder explosion: 3, 000 dead • 1858 Boiler explosion, London docks: 2, 000 dead • 1906 Courrieres coal mine explosion: 1, 099 dead • 1917 Halifax Explosion: 1, 200+ dead
Major industrial accidents • 1769 San Nazzaro gunpowder explosion: 3, 000 dead • 1858 Boiler explosion, London docks: 2, 000 dead • 1906 Courrieres coal mine explosion: 1, 099 dead • 1917 Halifax Explosion: 1, 200+ dead
 • Toronto Oil Tank Fire 1911
• Toronto Oil Tank Fire 1911

 Cubatao, Brazil 25 Feb 1984 • 500 squatters die when petroleum spills from industrial plant and ignites shanty community
Cubatao, Brazil 25 Feb 1984 • 500 squatters die when petroleum spills from industrial plant and ignites shanty community
 Mexico City, 19 Nov 1984 • Liquified Petroleum Gas explosions at plant adjoining poor neighbourhood • 452 dead, 31, 000 homeless, 300, 000 evacuated
Mexico City, 19 Nov 1984 • Liquified Petroleum Gas explosions at plant adjoining poor neighbourhood • 452 dead, 31, 000 homeless, 300, 000 evacuated
 Bhopal, India 2 -3 Dec 1984 • India applying modern technology to farming • Leak of toxic Methyl Isocyanate gas from Union Carbide agrochemicals plant • Killed 2000 immediately, 6, 400 total • 34, 000 blinded, 200, 000 injured • 200, 000 refugees
Bhopal, India 2 -3 Dec 1984 • India applying modern technology to farming • Leak of toxic Methyl Isocyanate gas from Union Carbide agrochemicals plant • Killed 2000 immediately, 6, 400 total • 34, 000 blinded, 200, 000 injured • 200, 000 refugees
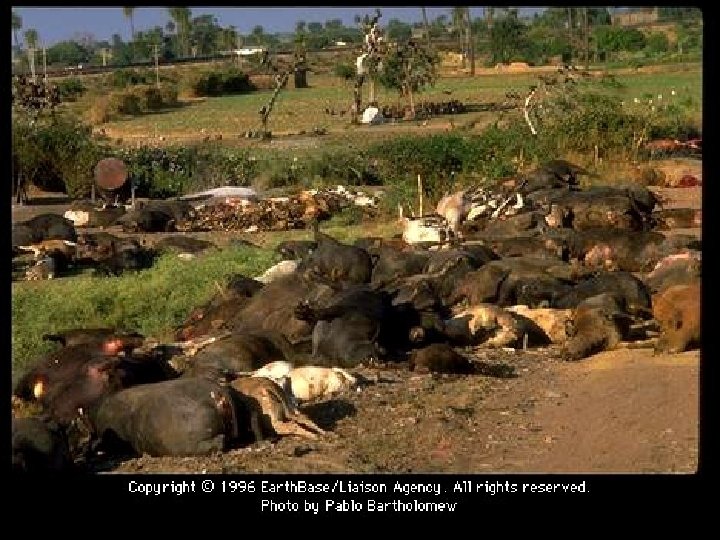
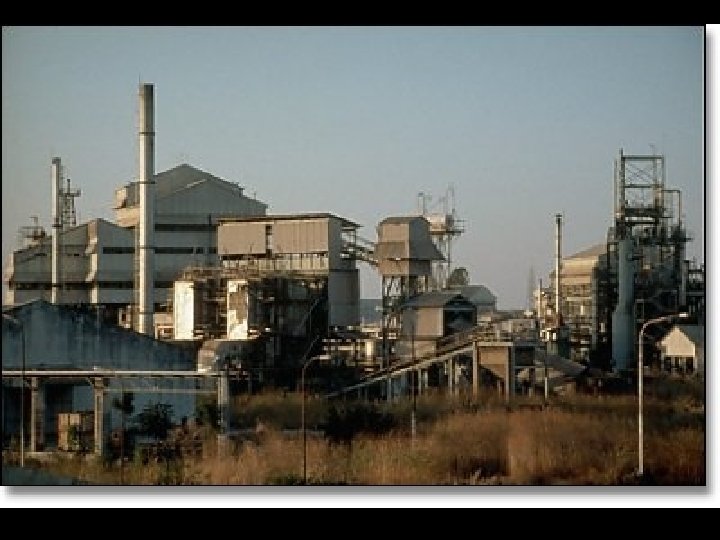
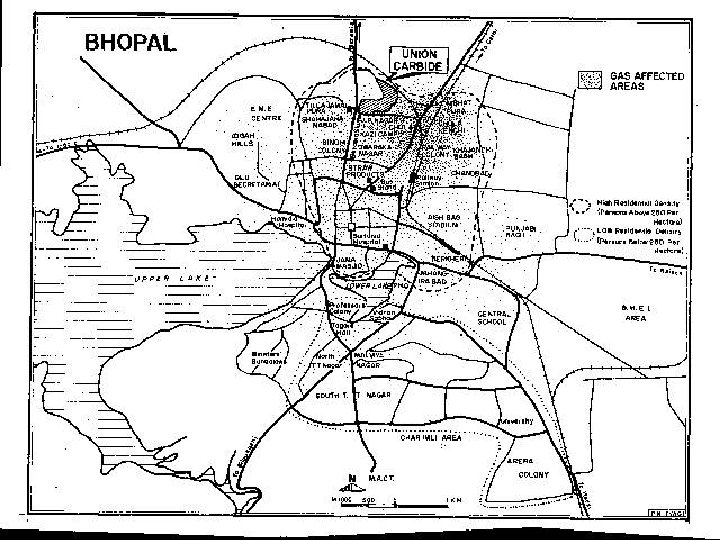


 Bhopal • Factory without US-standard safety measures • Large numbers of vulnerable people living close to the plant • No preparation to evacuate or protect population • Company able to offload much of the responsibility onto India
Bhopal • Factory without US-standard safety measures • Large numbers of vulnerable people living close to the plant • No preparation to evacuate or protect population • Company able to offload much of the responsibility onto India
 Bhopal • Union Carbide eventually pays $470 million US in compensation (1989) • Around $500 per injured person, $2000 per death • Victims face corruption in Indian legal and medical systems
Bhopal • Union Carbide eventually pays $470 million US in compensation (1989) • Around $500 per injured person, $2000 per death • Victims face corruption in Indian legal and medical systems
 Bhopal • Brought tighter controls in USA on chemical companies – US chemical companies shift production to LDCs
Bhopal • Brought tighter controls in USA on chemical companies – US chemical companies shift production to LDCs
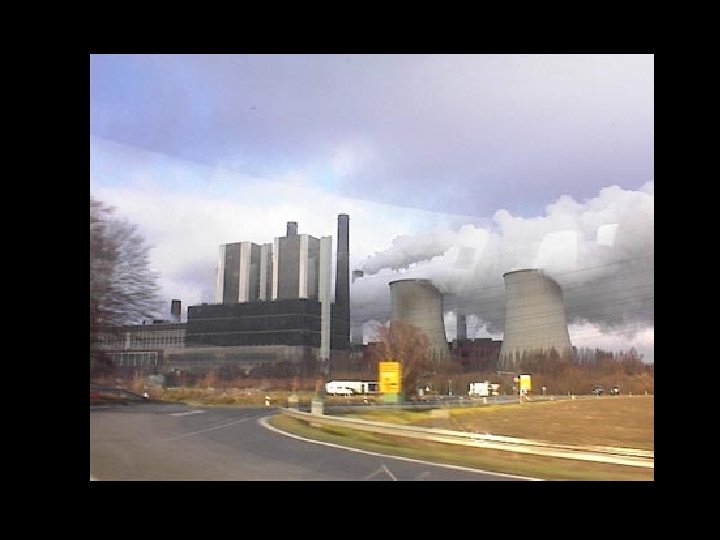


 Exposure increases • More people living in dense urban areas and exposed to risk • More powerful technologies • Rapid pace of technological change: – new hazards in places unfamiliar with them
Exposure increases • More people living in dense urban areas and exposed to risk • More powerful technologies • Rapid pace of technological change: – new hazards in places unfamiliar with them
 Road Deaths • 70% of all road deaths now in LDCs
Road Deaths • 70% of all road deaths now in LDCs
 Dubai
Dubai
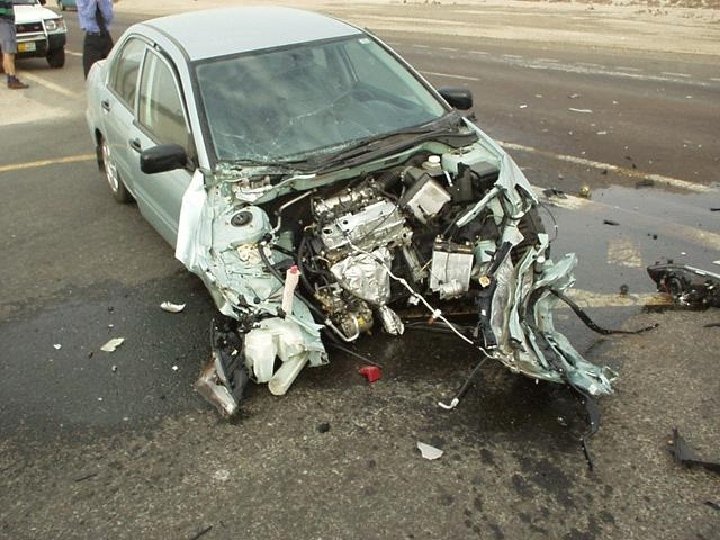
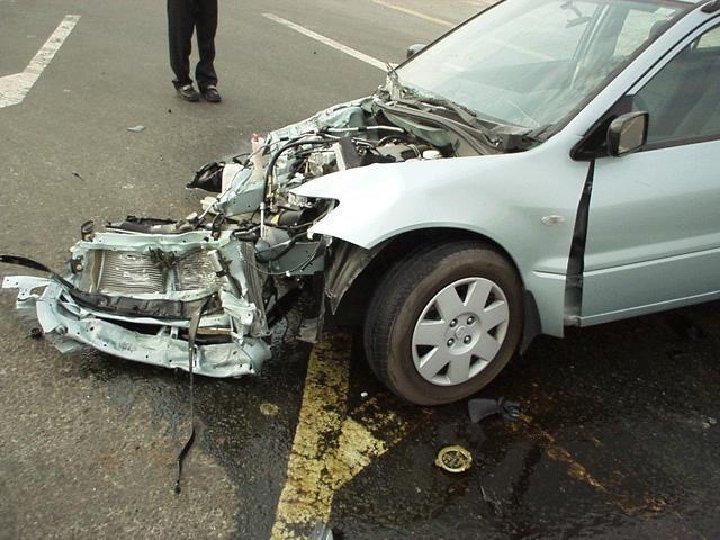
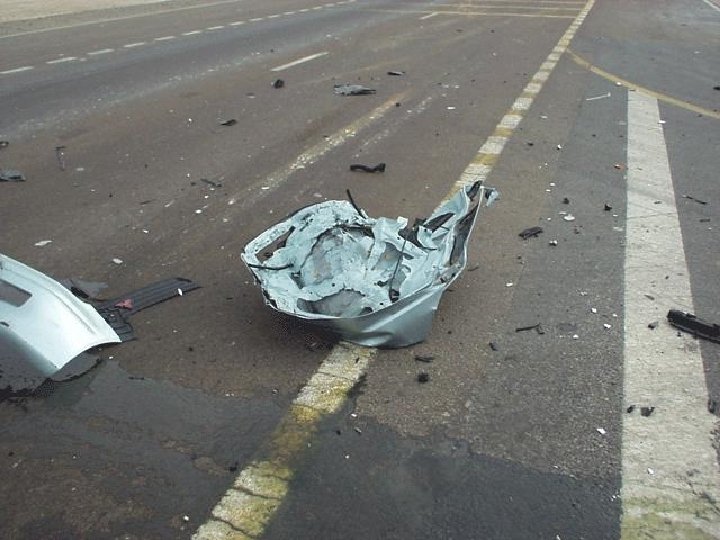
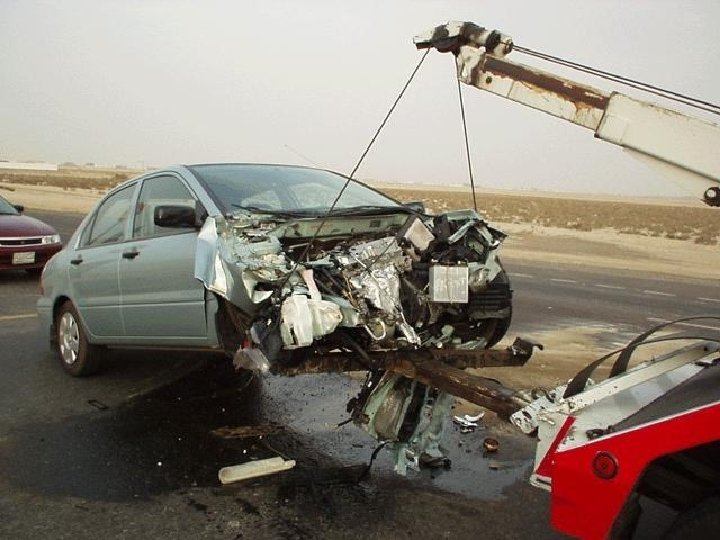




 Globalization of industrial technology • Global spread of industrialization • Globalization of commercial farming – chemicals • From mid 1980 s LDCs enter the big league for industrial accidents
Globalization of industrial technology • Global spread of industrialization • Globalization of commercial farming – chemicals • From mid 1980 s LDCs enter the big league for industrial accidents

 Pesticides in Singapore
Pesticides in Singapore
 Spreading DDT on a Toronto Dump, Spring 1948
Spreading DDT on a Toronto Dump, Spring 1948
 Protection increases • Engineering improves • Safety features improved • Improved safety regulation – Less in LDCs – Eroding in MDCs with reductions in public spending
Protection increases • Engineering improves • Safety features improved • Improved safety regulation – Less in LDCs – Eroding in MDCs with reductions in public spending
 Chernobyl 25 -26 April 1986 • Nuclear reactor accident in Belarus • Flawed plant design plus human incompetence – water-cooled graphite-modified • Radioactive steam blows the 1000 tonne cover off the reactor – fragments flung for 1 km – plume of radioactive gas enters upper atmosphere
Chernobyl 25 -26 April 1986 • Nuclear reactor accident in Belarus • Flawed plant design plus human incompetence – water-cooled graphite-modified • Radioactive steam blows the 1000 tonne cover off the reactor – fragments flung for 1 km – plume of radioactive gas enters upper atmosphere
 Chernobyl 25 -26 April 1986 • US satellite surveillance incomplete – crucial hardware lost on the Space Shuttle Challenger • World has to observe the unfolding disaster on an old LANDSAT satellite – not designed to see things this small – sees two reactors • First western alarm: at a nuke plant in Sweden
Chernobyl 25 -26 April 1986 • US satellite surveillance incomplete – crucial hardware lost on the Space Shuttle Challenger • World has to observe the unfolding disaster on an old LANDSAT satellite – not designed to see things this small – sees two reactors • First western alarm: at a nuke plant in Sweden
 Chernobyl 25 -26 April 1986 • 31+ die from radiation burns – Kamikaze firefighting to bury the reactor • 200+ seriously injured • 135, 000 permanently evacuated within 35 km radius • Abandonment of Pripyat
Chernobyl 25 -26 April 1986 • 31+ die from radiation burns – Kamikaze firefighting to bury the reactor • 200+ seriously injured • 135, 000 permanently evacuated within 35 km radius • Abandonment of Pripyat
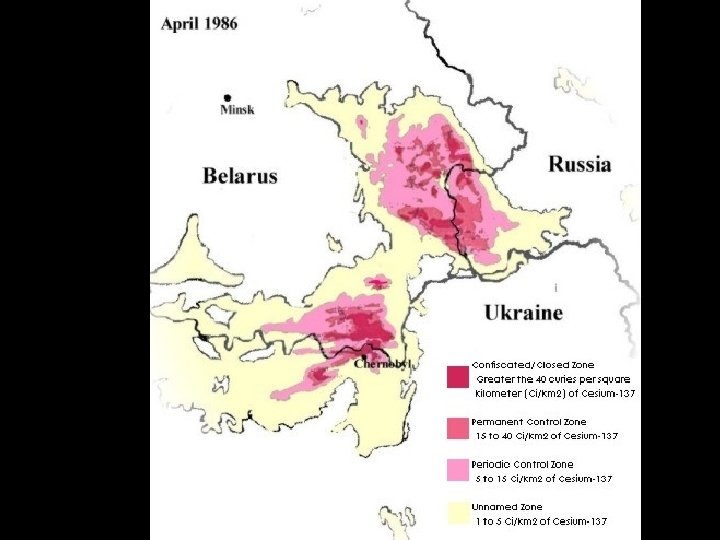
 Chernobyl 25 -26 April 1986 • Radioactive plume circles the globe within 2 weeks • Heaviest fallout in high-rainfall northern hemisphere – contamination of the arctic and subarctic food chains
Chernobyl 25 -26 April 1986 • Radioactive plume circles the globe within 2 weeks • Heaviest fallout in high-rainfall northern hemisphere – contamination of the arctic and subarctic food chains
 Scrapbook of Technological Hazards Historic Waste Disposal
Scrapbook of Technological Hazards Historic Waste Disposal
 Weston Rd & Black Creek • Early C 20 th: flood-liable creek and quarries • Some waste disposal, landfilling, cheap housing • Hurricane Hazel 1954: extensive flooding • Black Creek placed in concrete channel • Metro and York Township landfill the quarries
Weston Rd & Black Creek • Early C 20 th: flood-liable creek and quarries • Some waste disposal, landfilling, cheap housing • Hurricane Hazel 1954: extensive flooding • Black Creek placed in concrete channel • Metro and York Township landfill the quarries
 Weston Rd & Black Creek • Expropriation of Porter Ave homes 1965 – Michael Vukovitz
Weston Rd & Black Creek • Expropriation of Porter Ave homes 1965 – Michael Vukovitz
 Weston Rd & Black Creek • Feb 1965: Landfill-methane explosion on Ave – garage explodes, man becomes human torch • 1969: same garage explodes again – different man becomes human torch • Litigation: Gertson vs Borough of York 1973 – Gertson won
Weston Rd & Black Creek • Feb 1965: Landfill-methane explosion on Ave – garage explodes, man becomes human torch • 1969: same garage explodes again – different man becomes human torch • Litigation: Gertson vs Borough of York 1973 – Gertson won
 Hamilton Waterfront 1970 s • Laidlaw’s Interflow subsidiary treating hazardous liquids on Hamilton waterfront in 1970 s – Thermal treatment – Transfer station – Licensed to send region’s wastes to dump
Hamilton Waterfront 1970 s • Laidlaw’s Interflow subsidiary treating hazardous liquids on Hamilton waterfront in 1970 s – Thermal treatment – Transfer station – Licensed to send region’s wastes to dump
 Upper Ottawa St Dump • Wastes hauled to Upper Ottawa St Landfill – operated by another Laidlaw company: KD Disposals • Upper Ottawa St Landfill leaks – Red Hill Creek contaminated – Region recently fined $500, 000 for this
Upper Ottawa St Dump • Wastes hauled to Upper Ottawa St Landfill – operated by another Laidlaw company: KD Disposals • Upper Ottawa St Landfill leaks – Red Hill Creek contaminated – Region recently fined $500, 000 for this
 Philip Services • 1990 s secured contract to operate Hamilton’s water supply, sewage disposal • 1990 s secured approval for Taro landfill, Stoney Creek
Philip Services • 1990 s secured contract to operate Hamilton’s water supply, sewage disposal • 1990 s secured approval for Taro landfill, Stoney Creek
 Philip Services • Taro Landfill accepts illegal plating wastes from US – Philip forcing city to allow Taro leachate in city sewers • Philip’s spills sewage into Harbour • Philip abandons Hamilton’s blue-box collection programme May 2001 – Leaves City to pick up the pieces • Wonderful corporate behaviour
Philip Services • Taro Landfill accepts illegal plating wastes from US – Philip forcing city to allow Taro leachate in city sewers • Philip’s spills sewage into Harbour • Philip abandons Hamilton’s blue-box collection programme May 2001 – Leaves City to pick up the pieces • Wonderful corporate behaviour
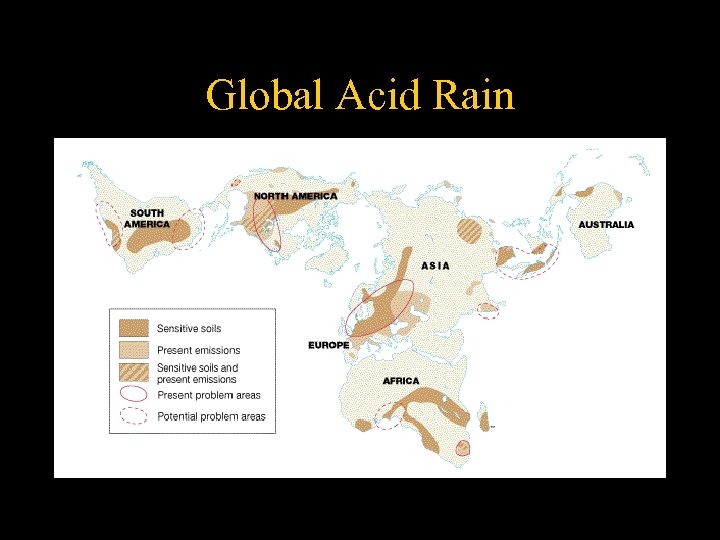 Global Acid Rain
Global Acid Rain
 Technological Hazards • Complex hazard spectrum • Significant role of human factors • Signs that the vulnerability and hazard exposure reflect broad societal changes: – urbanization – global industrialization
Technological Hazards • Complex hazard spectrum • Significant role of human factors • Signs that the vulnerability and hazard exposure reflect broad societal changes: – urbanization – global industrialization



