efd920a7348fa411331654d6f63c8e7f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Technion – Israel Institute of Technology MATRICS Research Group ABC Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression Arkadiy Morgenshtein, Avinoam Kolodny, Ran Ginosar MATRICS Research Group, Electrical Engineering Department Technion – Israel Institute of Technology Haifa, Israel 1 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
Technion – Israel Institute of Technology MATRICS Research Group ABC Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression Arkadiy Morgenshtein, Avinoam Kolodny, Ran Ginosar MATRICS Research Group, Electrical Engineering Department Technion – Israel Institute of Technology Haifa, Israel 1 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
 Background & Motivation 2 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
Background & Motivation 2 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
 Synchronous Serial Link Fast Clock generation is problematic Sensitive to timing uncertainty on chip 3 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
Synchronous Serial Link Fast Clock generation is problematic Sensitive to timing uncertainty on chip 3 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
 Asynchronous Serial Link Fast operation No need for clock Insensitive to timing uncertainty 4 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
Asynchronous Serial Link Fast operation No need for clock Insensitive to timing uncertainty 4 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
 Motivation Limited Bandwidth solution Compression Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) 5 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
Motivation Limited Bandwidth solution Compression Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) 5 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
 ABC Concept 6 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC Concept 6 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
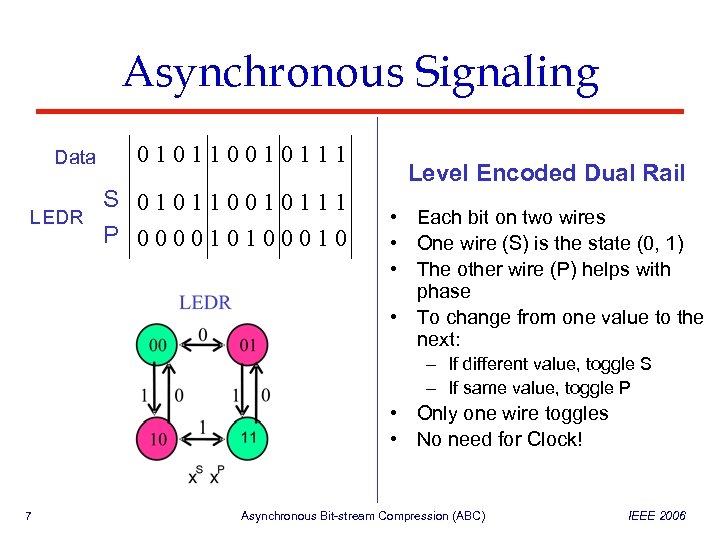 Asynchronous Signaling Data 010110010111 S 010110010111 LEDR P 000010100010 Level Encoded Dual Rail • Each bit on two wires • One wire (S) is the state (0, 1) • The other wire (P) helps with phase • To change from one value to the next: – If different value, toggle S – If same value, toggle P • Only one wire toggles • No need for Clock! 7 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
Asynchronous Signaling Data 010110010111 S 010110010111 LEDR P 000010100010 Level Encoded Dual Rail • Each bit on two wires • One wire (S) is the state (0, 1) • The other wire (P) helps with phase • To change from one value to the next: – If different value, toggle S – If same value, toggle P • Only one wire toggles • No need for Clock! 7 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
 ABC Concept 010110010111 What if… S 010110010111 LEDR both signals would toggle? P 000010100010 Data Level Encoded Dual Rail • Each bit on two wires • One wire (S) is the state (0, 1) • The other wire (P) helps with phase • To change from one value to the next: – If different value, toggle S – If same value, toggle P • Only one wire toggles • No need for Clock! 8 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC Concept 010110010111 What if… S 010110010111 LEDR both signals would toggle? P 000010100010 Data Level Encoded Dual Rail • Each bit on two wires • One wire (S) is the state (0, 1) • The other wire (P) helps with phase • To change from one value to the next: – If different value, toggle S – If same value, toggle P • Only one wire toggles • No need for Clock! 8 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
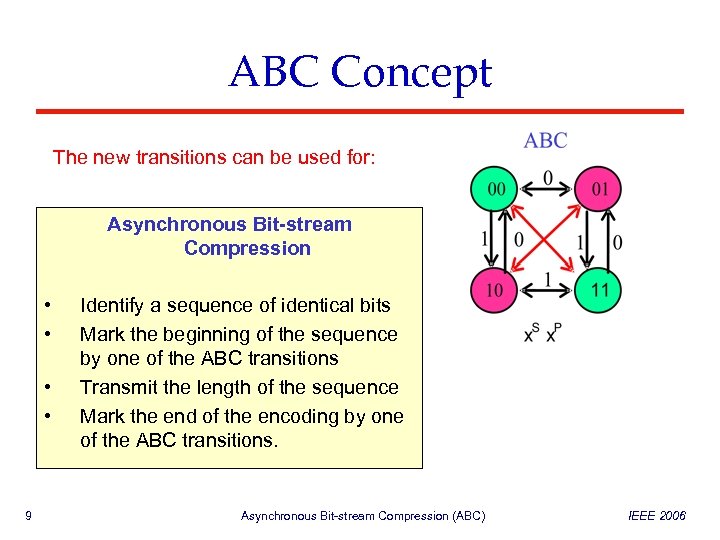 ABC Concept The new transitions can be used for: Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression • • 9 Identify a sequence of identical bits Mark the beginning of the sequence by one of the ABC transitions Transmit the length of the sequence Mark the end of the encoding by one of the ABC transitions. Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC Concept The new transitions can be used for: Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression • • 9 Identify a sequence of identical bits Mark the beginning of the sequence by one of the ABC transitions Transmit the length of the sequence Mark the end of the encoding by one of the ABC transitions. Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
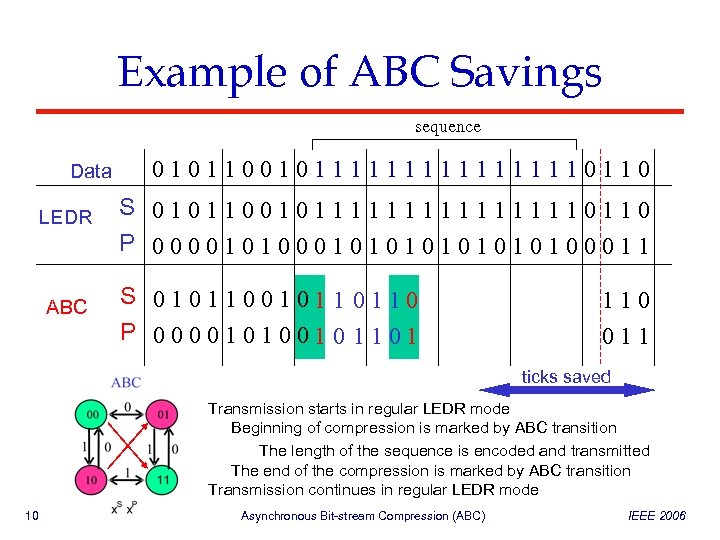 Example of ABC Savings sequence Data LEDR ABC 010110010111111110110 S 010110010111111110110 P 000010101010100011 S 0101100101 1 0110 P 0000101001 0 1101 110 011 ticks saved Transmission starts in regular LEDR mode Beginning of compression is marked by ABC transition The length of the sequence is encoded and transmitted The end of the compression is marked by ABC transition Transmission continues in regular LEDR mode 10 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
Example of ABC Savings sequence Data LEDR ABC 010110010111111110110 S 010110010111111110110 P 000010101010100011 S 0101100101 1 0110 P 0000101001 0 1101 110 011 ticks saved Transmission starts in regular LEDR mode Beginning of compression is marked by ABC transition The length of the sequence is encoded and transmitted The end of the compression is marked by ABC transition Transmission continues in regular LEDR mode 10 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
 ABC Architecture 11 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC Architecture 11 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
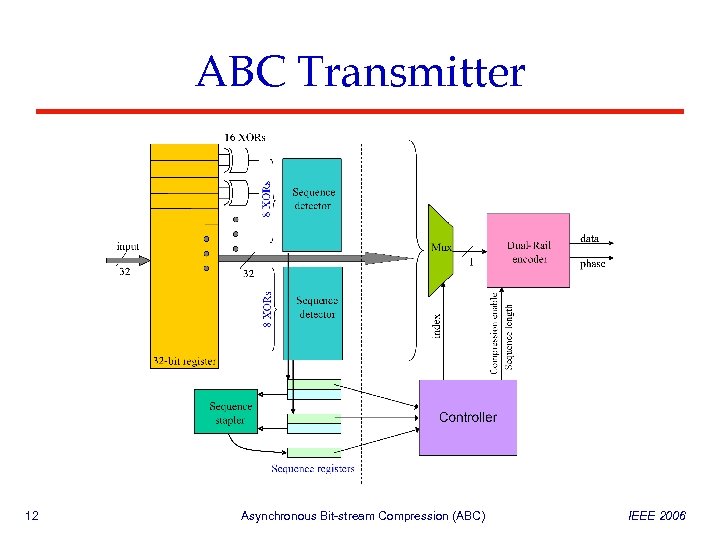 ABC Transmitter 12 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC Transmitter 12 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
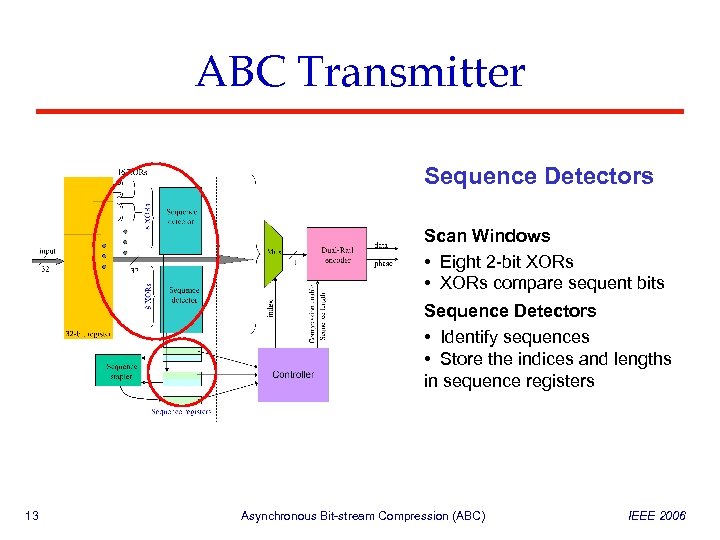 ABC Transmitter Sequence Detectors Scan Windows • Eight 2 -bit XORs • XORs compare sequent bits Sequence Detectors • Identify sequences • Store the indices and lengths in sequence registers 13 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC Transmitter Sequence Detectors Scan Windows • Eight 2 -bit XORs • XORs compare sequent bits Sequence Detectors • Identify sequences • Store the indices and lengths in sequence registers 13 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
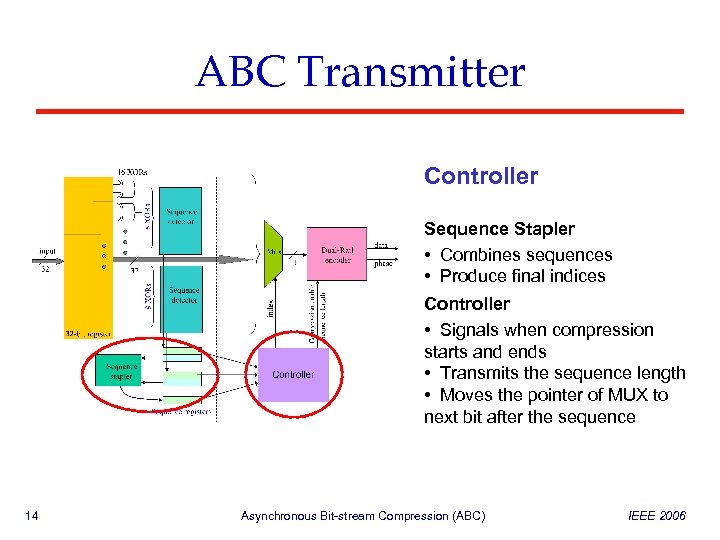 ABC Transmitter Controller Sequence Stapler • Combines sequences • Produce final indices Controller • Signals when compression starts and ends • Transmits the sequence length • Moves the pointer of MUX to next bit after the sequence 14 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC Transmitter Controller Sequence Stapler • Combines sequences • Produce final indices Controller • Signals when compression starts and ends • Transmits the sequence length • Moves the pointer of MUX to next bit after the sequence 14 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
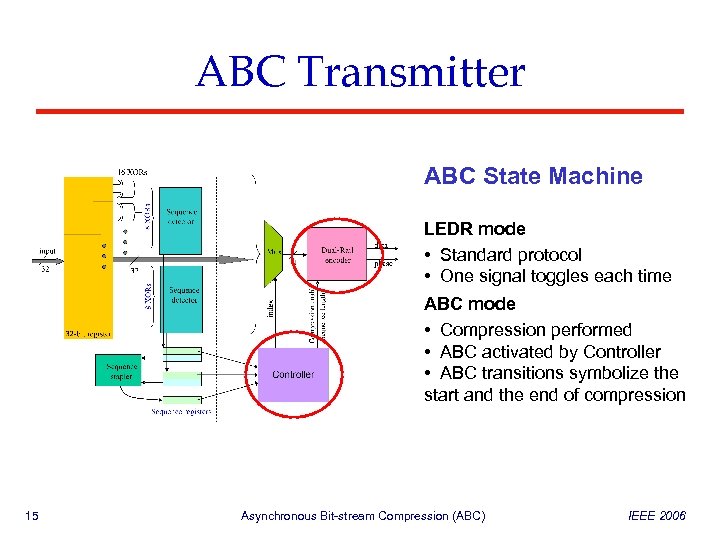 ABC Transmitter ABC State Machine LEDR mode • Standard protocol • One signal toggles each time ABC mode • Compression performed • ABC activated by Controller • ABC transitions symbolize the start and the end of compression 15 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC Transmitter ABC State Machine LEDR mode • Standard protocol • One signal toggles each time ABC mode • Compression performed • ABC activated by Controller • ABC transitions symbolize the start and the end of compression 15 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
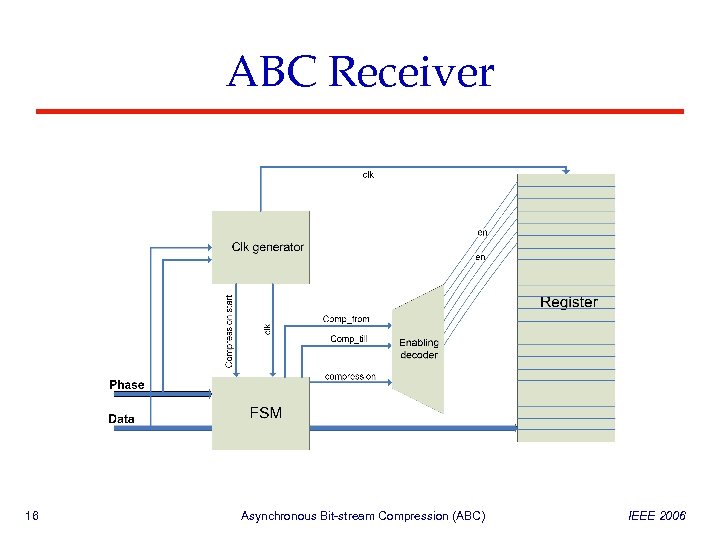 ABC Receiver 16 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC Receiver 16 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
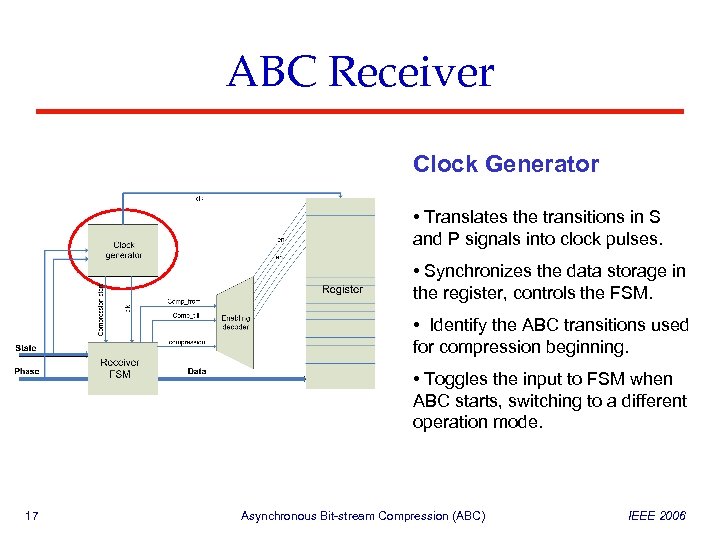 ABC Receiver Clock Generator • Translates the transitions in S and P signals into clock pulses. • Synchronizes the data storage in the register, controls the FSM. • Identify the ABC transitions used for compression beginning. • Toggles the input to FSM when ABC starts, switching to a different operation mode. 17 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC Receiver Clock Generator • Translates the transitions in S and P signals into clock pulses. • Synchronizes the data storage in the register, controls the FSM. • Identify the ABC transitions used for compression beginning. • Toggles the input to FSM when ABC starts, switching to a different operation mode. 17 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
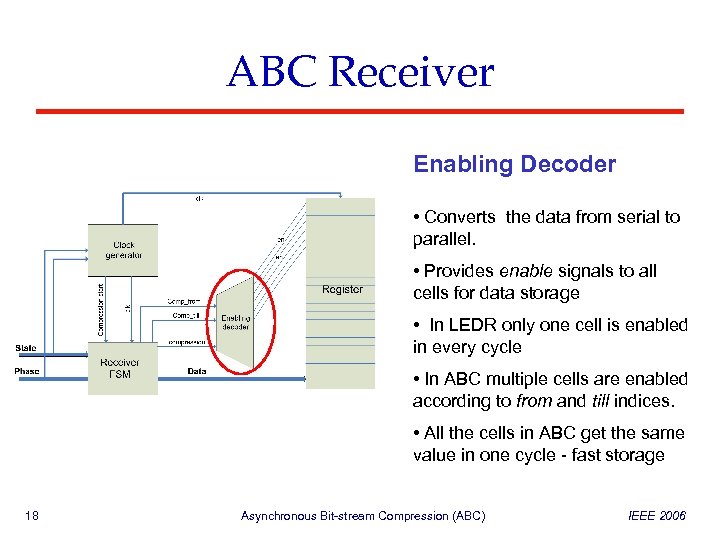 ABC Receiver Enabling Decoder • Converts the data from serial to parallel. • Provides enable signals to all cells for data storage • In LEDR only one cell is enabled in every cycle • In ABC multiple cells are enabled according to from and till indices. • All the cells in ABC get the same value in one cycle - fast storage 18 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC Receiver Enabling Decoder • Converts the data from serial to parallel. • Provides enable signals to all cells for data storage • In LEDR only one cell is enabled in every cycle • In ABC multiple cells are enabled according to from and till indices. • All the cells in ABC get the same value in one cycle - fast storage 18 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
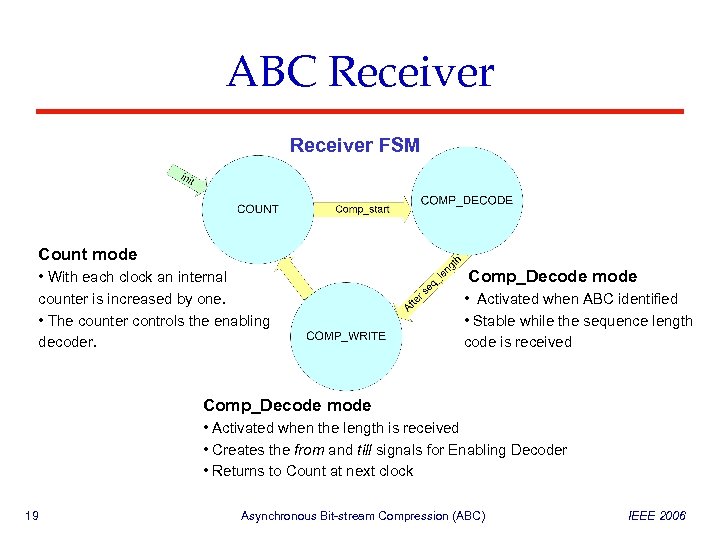 ABC Receiver FSM Count mode • With each clock an internal counter is increased by one. • The counter controls the enabling decoder. Comp_Decode mode • Activated when ABC identified • Stable while the sequence length code is received Comp_Decode mode • Activated when the length is received • Creates the from and till signals for Enabling Decoder • Returns to Count at next clock 19 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC Receiver FSM Count mode • With each clock an internal counter is increased by one. • The counter controls the enabling decoder. Comp_Decode mode • Activated when ABC identified • Stable while the sequence length code is received Comp_Decode mode • Activated when the length is received • Creates the from and till signals for Enabling Decoder • Returns to Count at next clock 19 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
 Design Considerations Alternative Add a register to contain two packets. Detect sequences in one packet while transmitting the other packet. Delaying the transmission by 8 clocks. Allow the scanning of all the bits and detection of the sequences. Transmit the first 8 bits without ABC. Scan and detect sequences in the remaining 24 bits. Trade-offs + Maximal throughput - Increased area and power + No additional register is needed - Increased transmission time + Reduced latency, area and power - Reduced ABC compression efficiency our architecture 20 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
Design Considerations Alternative Add a register to contain two packets. Detect sequences in one packet while transmitting the other packet. Delaying the transmission by 8 clocks. Allow the scanning of all the bits and detection of the sequences. Transmit the first 8 bits without ABC. Scan and detect sequences in the remaining 24 bits. Trade-offs + Maximal throughput - Increased area and power + No additional register is needed - Increased transmission time + Reduced latency, area and power - Reduced ABC compression efficiency our architecture 20 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
 Results 21 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
Results 21 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
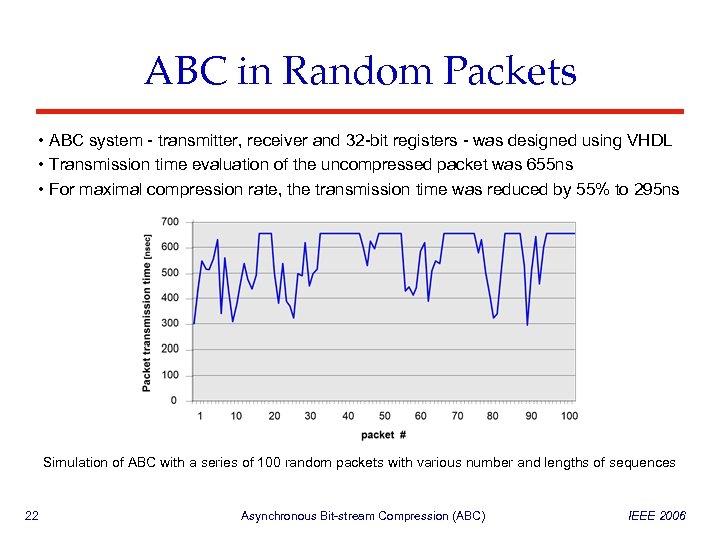 ABC in Random Packets • ABC system - transmitter, receiver and 32 -bit registers - was designed using VHDL • Transmission time evaluation of the uncompressed packet was 655 ns • For maximal compression rate, the transmission time was reduced by 55% to 295 ns Simulation of ABC with a series of 100 random packets with various number and lengths of sequences 22 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
ABC in Random Packets • ABC system - transmitter, receiver and 32 -bit registers - was designed using VHDL • Transmission time evaluation of the uncompressed packet was 655 ns • For maximal compression rate, the transmission time was reduced by 55% to 295 ns Simulation of ABC with a series of 100 random packets with various number and lengths of sequences 22 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
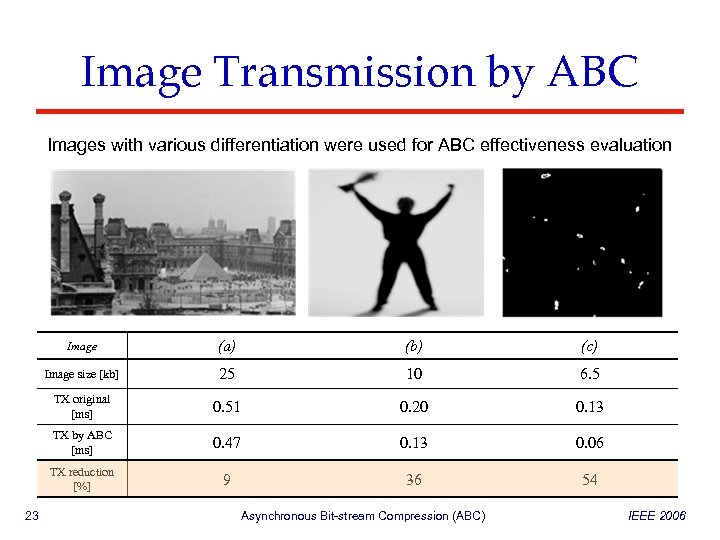 Image Transmission by ABC Images with various differentiation were used for ABC effectiveness evaluation Image (b) (c) Image size [kb] 25 10 6. 5 TX original [ms] 0. 51 0. 20 0. 13 TX by ABC [ms] 0. 47 0. 13 0. 06 TX reduction [%] 23 (a) 9 36 54 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
Image Transmission by ABC Images with various differentiation were used for ABC effectiveness evaluation Image (b) (c) Image size [kb] 25 10 6. 5 TX original [ms] 0. 51 0. 20 0. 13 TX by ABC [ms] 0. 47 0. 13 0. 06 TX reduction [%] 23 (a) 9 36 54 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
 Summary • Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression proposed • ABC targets improvement of BW utilization • Significant saving in transmission time and power • ABC interfaces were implemented and simulated • Number of transitions was reduced by up to 54% 24 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
Summary • Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression proposed • ABC targets improvement of BW utilization • Significant saving in transmission time and power • ABC interfaces were implemented and simulated • Number of transitions was reduced by up to 54% 24 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
 Questions? 25 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006
Questions? 25 Asynchronous Bit-stream Compression (ABC) IEEE 2006


