0d6fb8b04fae135610119d02c7d62b99.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 87
 Technical Reference Model ( Information Technology Standards ) July 2004
Technical Reference Model ( Information Technology Standards ) July 2004
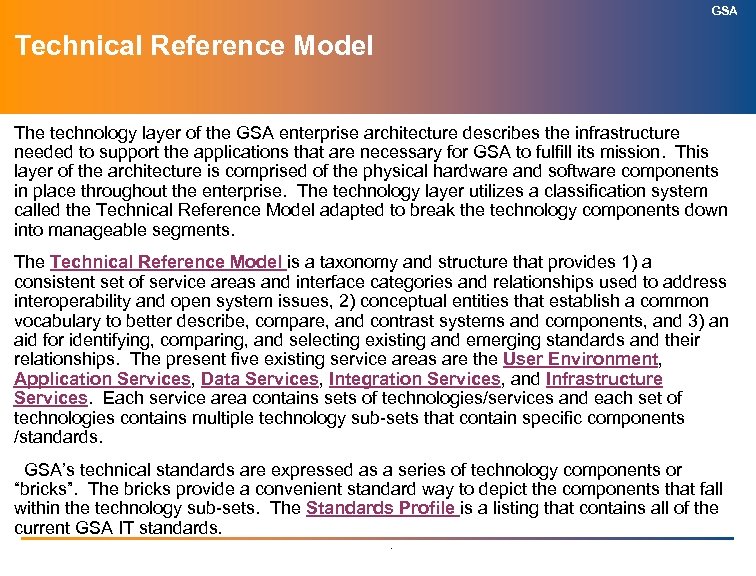 GSA Technical Reference Model The technology layer of the GSA enterprise architecture describes the infrastructure needed to support the applications that are necessary for GSA to fulfill its mission. This layer of the architecture is comprised of the physical hardware and software components in place throughout the enterprise. The technology layer utilizes a classification system called the Technical Reference Model adapted to break the technology components down into manageable segments. The Technical Reference Model is a taxonomy and structure that provides 1) a consistent set of service areas and interface categories and relationships used to address interoperability and open system issues, 2) conceptual entities that establish a common vocabulary to better describe, compare, and contrast systems and components, and 3) an aid for identifying, comparing, and selecting existing and emerging standards and their relationships. The present five existing service areas are the User Environment, Application Services, Data Services, Integration Services, and Infrastructure Services. Each service area contains sets of technologies/services and each set of technologies contains multiple technology sub-sets that contain specific components /standards. GSA’s technical standards are expressed as a series of technology components or “bricks”. The bricks provide a convenient standard way to depict the components that fall within the technology sub-sets. The Standards Profile is a listing that contains all of the current GSA IT standards. .
GSA Technical Reference Model The technology layer of the GSA enterprise architecture describes the infrastructure needed to support the applications that are necessary for GSA to fulfill its mission. This layer of the architecture is comprised of the physical hardware and software components in place throughout the enterprise. The technology layer utilizes a classification system called the Technical Reference Model adapted to break the technology components down into manageable segments. The Technical Reference Model is a taxonomy and structure that provides 1) a consistent set of service areas and interface categories and relationships used to address interoperability and open system issues, 2) conceptual entities that establish a common vocabulary to better describe, compare, and contrast systems and components, and 3) an aid for identifying, comparing, and selecting existing and emerging standards and their relationships. The present five existing service areas are the User Environment, Application Services, Data Services, Integration Services, and Infrastructure Services. Each service area contains sets of technologies/services and each set of technologies contains multiple technology sub-sets that contain specific components /standards. GSA’s technical standards are expressed as a series of technology components or “bricks”. The bricks provide a convenient standard way to depict the components that fall within the technology sub-sets. The Standards Profile is a listing that contains all of the current GSA IT standards. .
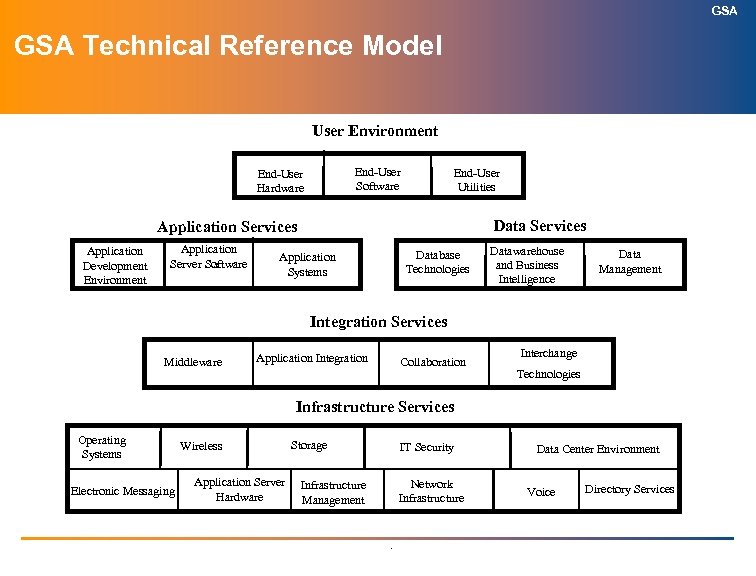 GSA Technical Reference Model User Environment End-User Software End-User Hardware End-User Utilities Data Services Application Development Environment Application Server Software s Database Technologies Application Systems Datawarehouse and Business Intelligence Data Management Integration Services Middleware Application Integration Collaboration Interchange Technologies Infrastructure Services Operating Systems Electronic Messaging Wireless Application Server Hardware Storage IT Security Network Infrastructure Management . Data Center Environment Voice Directory Services
GSA Technical Reference Model User Environment End-User Software End-User Hardware End-User Utilities Data Services Application Development Environment Application Server Software s Database Technologies Application Systems Datawarehouse and Business Intelligence Data Management Integration Services Middleware Application Integration Collaboration Interchange Technologies Infrastructure Services Operating Systems Electronic Messaging Wireless Application Server Hardware Storage IT Security Network Infrastructure Management . Data Center Environment Voice Directory Services
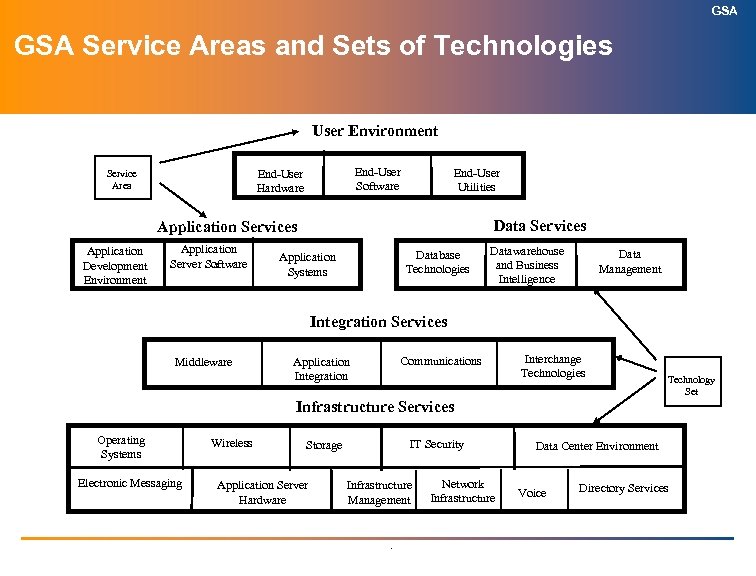 GSA Service Areas and Sets of Technologies User Environment End-User Software End-User Hardware Service Area End-User Utilities Data Services Application Development Environment Application Server Software s Database Technologies Application Systems Datawarehouse and Business Intelligence Data Management Integration Services Middleware Communications Application Integration Interchange Technologies Technology Set Infrastructure Services Operating Systems Electronic Messaging Wireless IT Security Storage Application Server Hardware Infrastructure Management . Network Infrastructure Data Center Environment Voice Directory Services
GSA Service Areas and Sets of Technologies User Environment End-User Software End-User Hardware Service Area End-User Utilities Data Services Application Development Environment Application Server Software s Database Technologies Application Systems Datawarehouse and Business Intelligence Data Management Integration Services Middleware Communications Application Integration Interchange Technologies Technology Set Infrastructure Services Operating Systems Electronic Messaging Wireless IT Security Storage Application Server Hardware Infrastructure Management . Network Infrastructure Data Center Environment Voice Directory Services
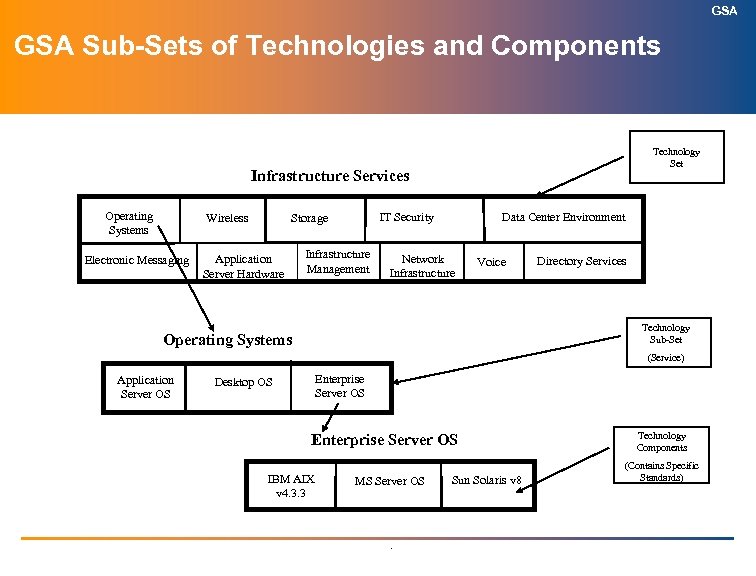 GSA Sub-Sets of Technologies and Components Technology Set Infrastructure Services Operating Systems Electronic Messaging IT Security Storage Wireless Application Server Hardware Infrastructure Management Data Center Environment Network Infrastructure Voice Directory Services Technology Sub-Set Operating Systems (Service) Application Server OS Enterprise Server OS Desktop OS Enterprise Server OS IBM AIX v 4. 3. 3 MS Server OS . Sun Solaris v 8 Technology Components (Contains Specific Standards)
GSA Sub-Sets of Technologies and Components Technology Set Infrastructure Services Operating Systems Electronic Messaging IT Security Storage Wireless Application Server Hardware Infrastructure Management Data Center Environment Network Infrastructure Voice Directory Services Technology Sub-Set Operating Systems (Service) Application Server OS Enterprise Server OS Desktop OS Enterprise Server OS IBM AIX v 4. 3. 3 MS Server OS . Sun Solaris v 8 Technology Components (Contains Specific Standards)
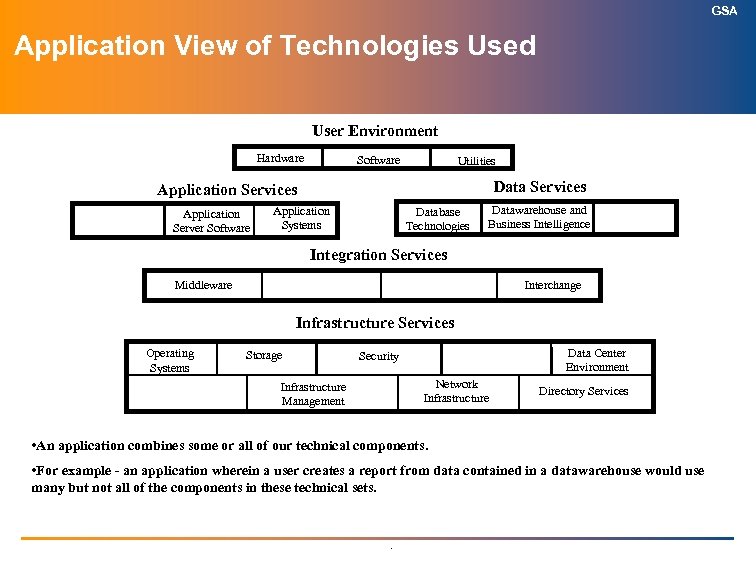 GSA Application View of Technologies Used User Environment Hardware Software Utilities Data Services Application Server Software Application Systems Database Technologies Datawarehouse and Business Intelligence Integration Services Middleware Interchange Infrastructure Services Operating Systems Storage Data Center Environment Security Network Infrastructure Management Directory Services • An application combines some or all of our technical components. • For example - an application wherein a user creates a report from data contained in a datawarehouse would use many but not all of the components in these technical sets. .
GSA Application View of Technologies Used User Environment Hardware Software Utilities Data Services Application Server Software Application Systems Database Technologies Datawarehouse and Business Intelligence Integration Services Middleware Interchange Infrastructure Services Operating Systems Storage Data Center Environment Security Network Infrastructure Management Directory Services • An application combines some or all of our technical components. • For example - an application wherein a user creates a report from data contained in a datawarehouse would use many but not all of the components in these technical sets. .
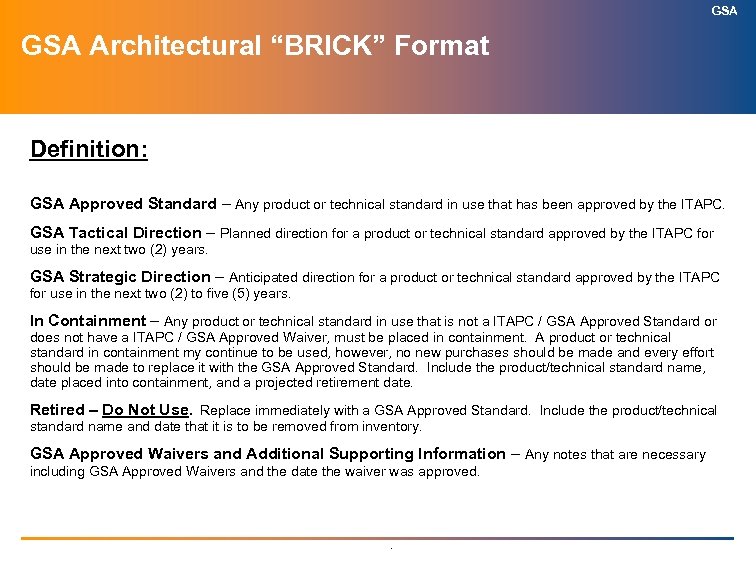 GSA Architectural “BRICK” Format Definition: GSA Approved Standard – Any product or technical standard in use that has been approved by the ITAPC. GSA Tactical Direction – Planned direction for a product or technical standard approved by the ITAPC for use in the next two (2) years. GSA Strategic Direction – Anticipated direction for a product or technical standard approved by the ITAPC for use in the next two (2) to five (5) years. In Containment – Any product or technical standard in use that is not a ITAPC / GSA Approved Standard or does not have a ITAPC / GSA Approved Waiver, must be placed in containment. A product or technical standard in containment my continue to be used, however, no new purchases should be made and every effort should be made to replace it with the GSA Approved Standard. Include the product/technical standard name, date placed into containment, and a projected retirement date. Retired – Do Not Use. Replace immediately with a GSA Approved Standard. Include the product/technical standard name and date that it is to be removed from inventory. GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information – Any notes that are necessary including GSA Approved Waivers and the date the waiver was approved. .
GSA Architectural “BRICK” Format Definition: GSA Approved Standard – Any product or technical standard in use that has been approved by the ITAPC. GSA Tactical Direction – Planned direction for a product or technical standard approved by the ITAPC for use in the next two (2) years. GSA Strategic Direction – Anticipated direction for a product or technical standard approved by the ITAPC for use in the next two (2) to five (5) years. In Containment – Any product or technical standard in use that is not a ITAPC / GSA Approved Standard or does not have a ITAPC / GSA Approved Waiver, must be placed in containment. A product or technical standard in containment my continue to be used, however, no new purchases should be made and every effort should be made to replace it with the GSA Approved Standard. Include the product/technical standard name, date placed into containment, and a projected retirement date. Retired – Do Not Use. Replace immediately with a GSA Approved Standard. Include the product/technical standard name and date that it is to be removed from inventory. GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information – Any notes that are necessary including GSA Approved Waivers and the date the waiver was approved. .
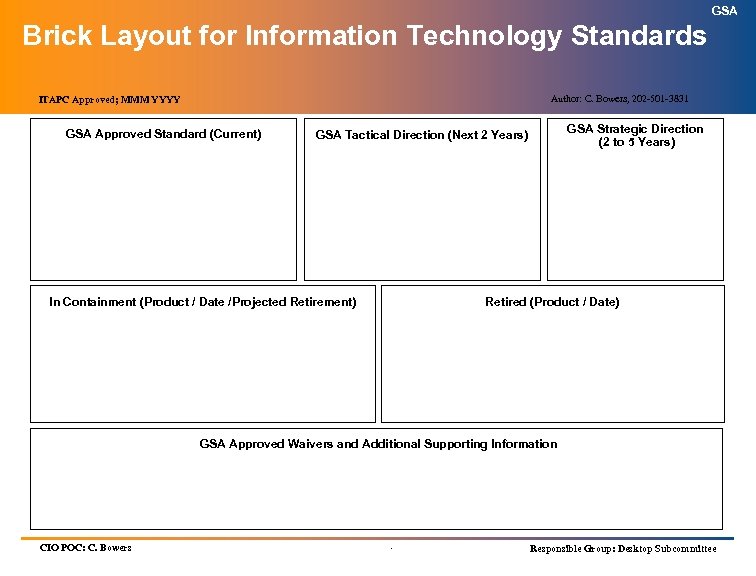 GSA Brick Layout for Information Technology Standards Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved; MMM YYYY GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
GSA Brick Layout for Information Technology Standards Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved; MMM YYYY GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
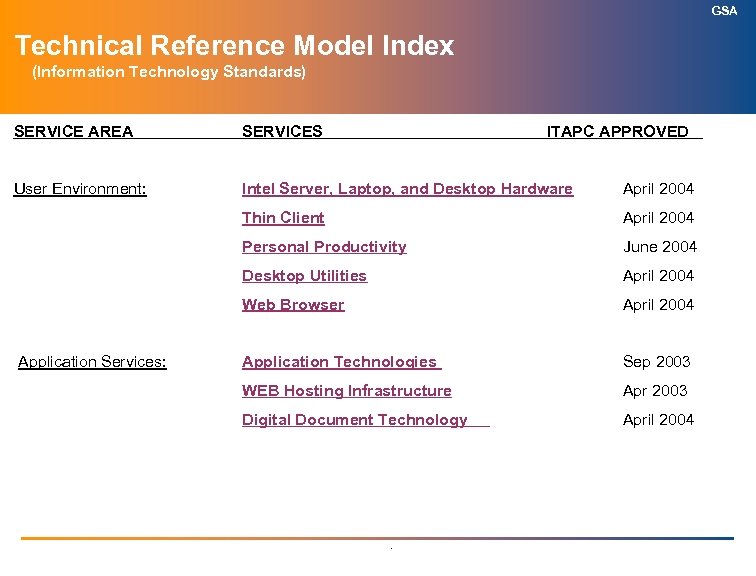 GSA Technical Reference Model Index (Information Technology Standards) SERVICE AREA SERVICES User Environment: Intel Server, Laptop, and Desktop Hardware April 2004 Thin Client April 2004 Personal Productivity June 2004 Desktop Utilities April 2004 Web Browser April 2004 Application Technologies Sep 2003 WEB Hosting Infrastructure Apr 2003 Digital Document Technology April 2004 Application Services: ITAPC APPROVED .
GSA Technical Reference Model Index (Information Technology Standards) SERVICE AREA SERVICES User Environment: Intel Server, Laptop, and Desktop Hardware April 2004 Thin Client April 2004 Personal Productivity June 2004 Desktop Utilities April 2004 Web Browser April 2004 Application Technologies Sep 2003 WEB Hosting Infrastructure Apr 2003 Digital Document Technology April 2004 Application Services: ITAPC APPROVED .
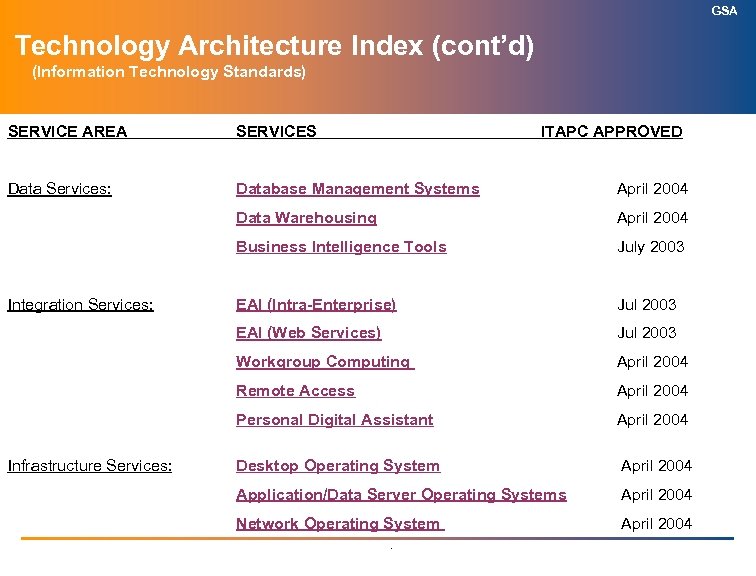 GSA Technology Architecture Index (cont’d) (Information Technology Standards) SERVICE AREA SERVICES ITAPC APPROVED Data Services: Database Management Systems April 2004 Data Warehousing April 2004 Business Intelligence Tools July 2003 Integration Services: EAI (Intra-Enterprise) EAI (Web Services) Jul 2003 Workgroup Computing April 2004 Remote Access April 2004 Personal Digital Assistant April 2004 Desktop Operating System April 2004 Application/Data Server Operating Systems April 2004 Network Operating System April 2004 Infrastructure Services: . Jul 2003
GSA Technology Architecture Index (cont’d) (Information Technology Standards) SERVICE AREA SERVICES ITAPC APPROVED Data Services: Database Management Systems April 2004 Data Warehousing April 2004 Business Intelligence Tools July 2003 Integration Services: EAI (Intra-Enterprise) EAI (Web Services) Jul 2003 Workgroup Computing April 2004 Remote Access April 2004 Personal Digital Assistant April 2004 Desktop Operating System April 2004 Application/Data Server Operating Systems April 2004 Network Operating System April 2004 Infrastructure Services: . Jul 2003
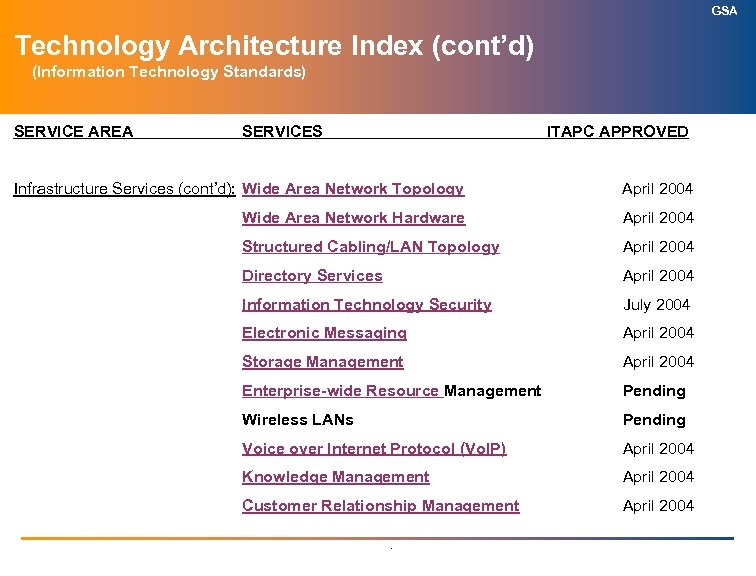 GSA Technology Architecture Index (cont’d) (Information Technology Standards) SERVICE AREA SERVICES ITAPC APPROVED Infrastructure Services (cont’d): Wide Area Network Topology April 2004 Wide Area Network Hardware April 2004 Structured Cabling/LAN Topology April 2004 Directory Services April 2004 Information Technology Security July 2004 Electronic Messaging April 2004 Storage Management April 2004 Enterprise-wide Resource Management Pending Wireless LANs Pending Voice over Internet Protocol (Vo. IP) April 2004 Knowledge Management April 2004 Customer Relationship Management April 2004 .
GSA Technology Architecture Index (cont’d) (Information Technology Standards) SERVICE AREA SERVICES ITAPC APPROVED Infrastructure Services (cont’d): Wide Area Network Topology April 2004 Wide Area Network Hardware April 2004 Structured Cabling/LAN Topology April 2004 Directory Services April 2004 Information Technology Security July 2004 Electronic Messaging April 2004 Storage Management April 2004 Enterprise-wide Resource Management Pending Wireless LANs Pending Voice over Internet Protocol (Vo. IP) April 2004 Knowledge Management April 2004 Customer Relationship Management April 2004 .
 GSA Intel Server, Laptop, and Desktop Hardware Definition: · Machinery and equipment associated with application servers, laptop and desktop personal computing devices. A server or personal computer is composed of both hardware and software. The software provides the instructions, and the hardware performs the processing. · GSA has an agency-wide Blanket Purchase Agreement (BPA) for purchase of computer hardware. The goal of the BPA is to remain current with the needs of the agency. In GSA all server, laptop, and desktop personal computers are to be procured from the BPA unless an exception is specifically granted. · Any exception to procuring servers, laptops, and desktop personal computers outside of the BPA requires a waiver from the OCIO before procurement. .
GSA Intel Server, Laptop, and Desktop Hardware Definition: · Machinery and equipment associated with application servers, laptop and desktop personal computing devices. A server or personal computer is composed of both hardware and software. The software provides the instructions, and the hardware performs the processing. · GSA has an agency-wide Blanket Purchase Agreement (BPA) for purchase of computer hardware. The goal of the BPA is to remain current with the needs of the agency. In GSA all server, laptop, and desktop personal computers are to be procured from the BPA unless an exception is specifically granted. · Any exception to procuring servers, laptops, and desktop personal computers outside of the BPA requires a waiver from the OCIO before procurement. .
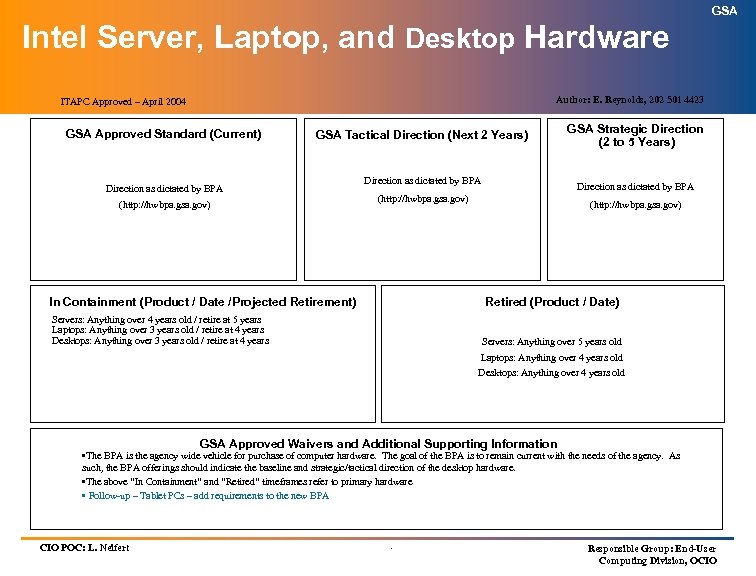 GSA Intel Server, Laptop, and Desktop Hardware Author: E. Reynolds, 202 501 4423 ITAPC Approved – April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Direction as dictated by BPA (http: //hwbpa. gsa. gov) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) (http: //hwbpa. gsa. gov) Retired (Product / Date) Servers: Anything over 4 years old / retire at 5 years Laptops: Anything over 3 years old / retire at 4 years Desktops: Anything over 3 years old / retire at 4 years Servers: Anything over 5 years old Laptops: Anything over 4 years old Desktops: Anything over 4 years old GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • The BPA is the agency wide vehicle for purchase of computer hardware. The goal of the BPA is to remain current with the needs of the agency. As such, the BPA offerings should indicate the baseline and strategic/tactical direction of the desktop hardware. • The above “In Containment” and “Retired” timeframes refer to primary hardware • Follow-up – Tablet PCs – add requirements to the new BPA CIO POC: L. Neifert . Responsible Group: End-User Computing Division, OCIO
GSA Intel Server, Laptop, and Desktop Hardware Author: E. Reynolds, 202 501 4423 ITAPC Approved – April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Direction as dictated by BPA (http: //hwbpa. gsa. gov) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) (http: //hwbpa. gsa. gov) Retired (Product / Date) Servers: Anything over 4 years old / retire at 5 years Laptops: Anything over 3 years old / retire at 4 years Desktops: Anything over 3 years old / retire at 4 years Servers: Anything over 5 years old Laptops: Anything over 4 years old Desktops: Anything over 4 years old GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • The BPA is the agency wide vehicle for purchase of computer hardware. The goal of the BPA is to remain current with the needs of the agency. As such, the BPA offerings should indicate the baseline and strategic/tactical direction of the desktop hardware. • The above “In Containment” and “Retired” timeframes refer to primary hardware • Follow-up – Tablet PCs – add requirements to the new BPA CIO POC: L. Neifert . Responsible Group: End-User Computing Division, OCIO
 GSA Thin Client Definition: Server-centric, not device-centric · Thin Client: What It Is – A thin-client application is a logical construct, not a physical one. Thin-client desktop computing is server-centric. The applications are executed on the server and do not require client-resident installation; the graphical user interface and some application logic may be rendered to the client. · Thin-client desktop computing also includes browser and Java-based applications where the applications are centralized on servers, but some of the presentation logic and some application logic may be distributed to the client. · Thin Client: What It Is Not – A common misperception is that a thin-client application is device-centric and requires a thin-client device, like a Windows terminal. Thin-client applications do not require a thinclient device. Choice of desktop device is secondary. The typical thin-client device is a PC configured with “fat client” applications and with access to thin-client applications. If enterprises are deploying a true thin-client device, all the applications must be deployed as thin-client applications. .
GSA Thin Client Definition: Server-centric, not device-centric · Thin Client: What It Is – A thin-client application is a logical construct, not a physical one. Thin-client desktop computing is server-centric. The applications are executed on the server and do not require client-resident installation; the graphical user interface and some application logic may be rendered to the client. · Thin-client desktop computing also includes browser and Java-based applications where the applications are centralized on servers, but some of the presentation logic and some application logic may be distributed to the client. · Thin Client: What It Is Not – A common misperception is that a thin-client application is device-centric and requires a thin-client device, like a Windows terminal. Thin-client applications do not require a thinclient device. Choice of desktop device is secondary. The typical thin-client device is a PC configured with “fat client” applications and with access to thin-client applications. If enterprises are deploying a true thin-client device, all the applications must be deployed as thin-client applications. .
 GSA Thin Client ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: K. Rice, 202 -501 -0496 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Windows 2000 Terminal Services Windows 2003 Terminal Services Metaframe Presentation Server GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Metaframe Presentation Server In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Metaframe Presentation Server Longhorn Terminal Services Retired (Product / Date) Metaframe 1. 8 – June 2005 (retirement) Windows NT 4 TSE (as of January 2004) / June 2005 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Some GSA organizations are not interested in upgrading beyond Metaframe 1. 8 but concur in placing it in containment. NT 4 TSE is no longer sold, and support stopped in January 2004 from Microsoft. Metaframe 1. 8 is no longer sold but LIMITED support still exists. CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
GSA Thin Client ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: K. Rice, 202 -501 -0496 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Windows 2000 Terminal Services Windows 2003 Terminal Services Metaframe Presentation Server GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Metaframe Presentation Server In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Metaframe Presentation Server Longhorn Terminal Services Retired (Product / Date) Metaframe 1. 8 – June 2005 (retirement) Windows NT 4 TSE (as of January 2004) / June 2005 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Some GSA organizations are not interested in upgrading beyond Metaframe 1. 8 but concur in placing it in containment. NT 4 TSE is no longer sold, and support stopped in January 2004 from Microsoft. Metaframe 1. 8 is no longer sold but LIMITED support still exists. CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
 GSA Personal Productivity Definition: Technology for enabling personal productivity, such as the desktop Office Suite including word processing, spreadsheets, and presentation preparation. This also includes all other personal productivity software that the ITAPC has approved as GSA Standards and is included on the official GSA Desktop Image. .
GSA Personal Productivity Definition: Technology for enabling personal productivity, such as the desktop Office Suite including word processing, spreadsheets, and presentation preparation. This also includes all other personal productivity software that the ITAPC has approved as GSA Standards and is included on the official GSA Desktop Image. .
 GSA Personal Productivity Author: K. Rice 202 501 0496 ITAPC Approved: June 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Microsoft Office 2003 GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Microsoft Office 2003 MS Project X; Visio 2003; Microsoft Office X MS Project 2003; Visio X; In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) Office 2000 to be placed in containment on 9/13/04 All earlier versions of MS Office, except MS Access 97 are retired as of 10/01/01. Access 97 retired as of 1/1/03 MS Project 97 and any earlier MS Project applications as of 10/1/01. GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • The personal productivity suite has long been connected with the current desktop operating system. As such, the personal productivity suite closely mirrors the desktop operating brick. • An approved exception is the use of Word. Perfect and Lotus 1 -2 -3 for communication with certain external agencies. CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
GSA Personal Productivity Author: K. Rice 202 501 0496 ITAPC Approved: June 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Microsoft Office 2003 GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Microsoft Office 2003 MS Project X; Visio 2003; Microsoft Office X MS Project 2003; Visio X; In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) Office 2000 to be placed in containment on 9/13/04 All earlier versions of MS Office, except MS Access 97 are retired as of 10/01/01. Access 97 retired as of 1/1/03 MS Project 97 and any earlier MS Project applications as of 10/1/01. GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • The personal productivity suite has long been connected with the current desktop operating system. As such, the personal productivity suite closely mirrors the desktop operating brick. • An approved exception is the use of Word. Perfect and Lotus 1 -2 -3 for communication with certain external agencies. CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
 GSA Desktop Utilities Definition: Technology for enabling personal productivity besides the desktop Office Suite. This includes all other personal productivity software that the ITAPC has approved as GSA Standards. It also contains the standards for handheld devices. .
GSA Desktop Utilities Definition: Technology for enabling personal productivity besides the desktop Office Suite. This includes all other personal productivity software that the ITAPC has approved as GSA Standards. It also contains the standards for handheld devices. .
 GSA Desktop Utilities Author: K. Rice 202 501 0496 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Misc: Real Player G 2; Win Zip 9. 0; Windows Media Player Handheld Synchronization: Palm Pilot (Palm Desktop, Easy. Sync, Intellisync) ; Windows CE (Active. Sync); Blackberry (Blackberry Desktop Software, WIC); Lotus Easy. Sync Misc: Real Player X; Win Zip X ; Windows Media Handheld Synchronization: : Palm Pilot (Palm Desktop, Easy. Sync, Intellisync) ; Windows CE (Active. Sync); Blackberry (Blackberry Desktop Software, WIC) ; Lotus Easy. Sync Document Viewer: Auto. Cad Volo. Viewer, Visio Viewer 2003, Adobe Acrobat Reader 6. x Windows Media Player Handheld Synchronization: : Palm Pilot (Palm Desktop, Easy. Sync, Intellisync) ; Windows CE (Active. Sync); Blackberry (Blackberry Desktop Software, WIC) ; Lotus Easy. Sync Document Viewer: Auto. Cad Volo. Viewer, Visio Viewer 2003, Adobe Acrobat Reader 6. x In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Document Viewer: Auto. Cad Volo. Viewer, Visio Viewer X, Adobe Acrobat Reader X Retired (Product / Date) All previous versions of Real Player, Win Zip, and Visio as of 1/01/03. Inovie Team Center as of 10/1/01; GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Desktop utilities were previously shown as part of the Personal Productivity “brick”, they are ITAPC approved GSA Standards. Inclusion of Visio and Project Management on this brick will be revisited in the next FY. Follow-up – research FTP capabilities and utilities – Possible solution: WS FTP CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
GSA Desktop Utilities Author: K. Rice 202 501 0496 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Misc: Real Player G 2; Win Zip 9. 0; Windows Media Player Handheld Synchronization: Palm Pilot (Palm Desktop, Easy. Sync, Intellisync) ; Windows CE (Active. Sync); Blackberry (Blackberry Desktop Software, WIC); Lotus Easy. Sync Misc: Real Player X; Win Zip X ; Windows Media Handheld Synchronization: : Palm Pilot (Palm Desktop, Easy. Sync, Intellisync) ; Windows CE (Active. Sync); Blackberry (Blackberry Desktop Software, WIC) ; Lotus Easy. Sync Document Viewer: Auto. Cad Volo. Viewer, Visio Viewer 2003, Adobe Acrobat Reader 6. x Windows Media Player Handheld Synchronization: : Palm Pilot (Palm Desktop, Easy. Sync, Intellisync) ; Windows CE (Active. Sync); Blackberry (Blackberry Desktop Software, WIC) ; Lotus Easy. Sync Document Viewer: Auto. Cad Volo. Viewer, Visio Viewer 2003, Adobe Acrobat Reader 6. x In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Document Viewer: Auto. Cad Volo. Viewer, Visio Viewer X, Adobe Acrobat Reader X Retired (Product / Date) All previous versions of Real Player, Win Zip, and Visio as of 1/01/03. Inovie Team Center as of 10/1/01; GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Desktop utilities were previously shown as part of the Personal Productivity “brick”, they are ITAPC approved GSA Standards. Inclusion of Visio and Project Management on this brick will be revisited in the next FY. Follow-up – research FTP capabilities and utilities – Possible solution: WS FTP CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
 GSA Web Browser Definition: A software program on a client system used to locate and display Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) documents on an intranet or the Internet. Browsers are most often used to access World Wide Web pages. Most browsers can display graphics and photographs as well as text, and can present multi-media information, including sound and video, which may require additional applets called plug-ins. Netscape Navigator and Microsoft Internet Explorer are examples of browsers. .
GSA Web Browser Definition: A software program on a client system used to locate and display Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) documents on an intranet or the Internet. Browsers are most often used to access World Wide Web pages. Most browsers can display graphics and photographs as well as text, and can present multi-media information, including sound and video, which may require additional applets called plug-ins. Netscape Navigator and Microsoft Internet Explorer are examples of browsers. .
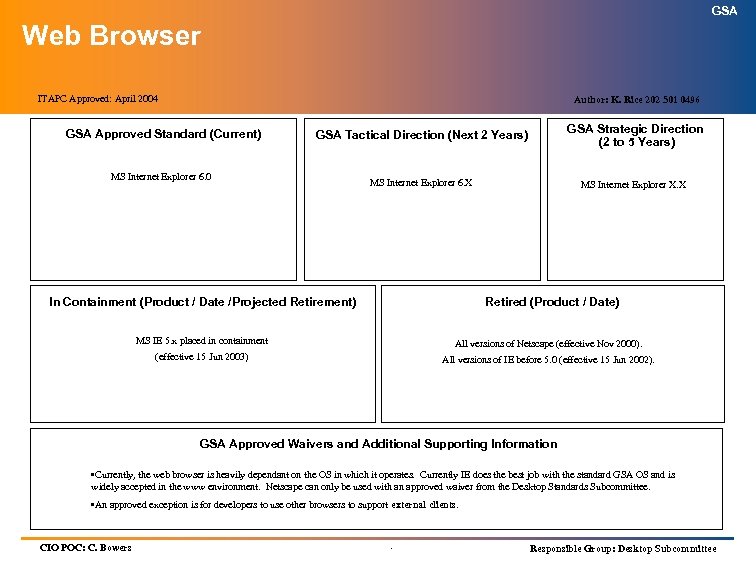 GSA Web Browser ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: K. Rice 202 501 0496 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) MS Internet Explorer 6. X MS Internet Explorer X. X MS Internet Explorer 6. 0 In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) MS IE 5. x placed in containment All versions of Netscape (effective Nov 2000). (effective 15 Jun 2003) All versions of IE before 5. 0 (effective 15 Jun 2002). GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Currently, the web browser is heavily dependant on the OS in which it operates. Currently IE does the best job with the standard GSA OS and is widely accepted in the www environment. Netscape can only be used with an approved waiver from the Desktop Standards Subcommittee. • An approved exception is for developers to use other browsers to support external clients. CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
GSA Web Browser ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: K. Rice 202 501 0496 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) MS Internet Explorer 6. X MS Internet Explorer X. X MS Internet Explorer 6. 0 In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) MS IE 5. x placed in containment All versions of Netscape (effective Nov 2000). (effective 15 Jun 2003) All versions of IE before 5. 0 (effective 15 Jun 2002). GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Currently, the web browser is heavily dependant on the OS in which it operates. Currently IE does the best job with the standard GSA OS and is widely accepted in the www environment. Netscape can only be used with an approved waiver from the Desktop Standards Subcommittee. • An approved exception is for developers to use other browsers to support external clients. CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
 GSA Application Technologies Definition: This element focuses on the specification for the tools and languages associated with the development of new applications, both large (enterprise) and smaller (workgroup). Such applications may or may not involve WEB access. .
GSA Application Technologies Definition: This element focuses on the specification for the tools and languages associated with the development of new applications, both large (enterprise) and smaller (workgroup). Such applications may or may not involve WEB access. .
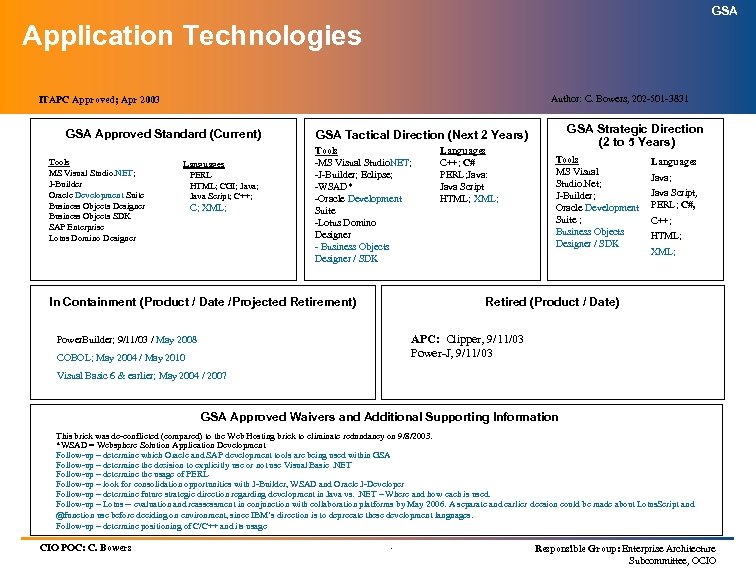 GSA Application Technologies Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved; Apr 2003 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Tools MS Visual Studio. NET; J-Builder Oracle Development Suite Business Objects Designer Business Objects SDK SAP Enterprise Lotus Domino Designer Languages PERL HTML; CGI; Java Script; C++; C; XML; GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Tools -MS Visual Studio. NET; -J-Builder; Eclipse; -WSAD* -Oracle Development Suite -Lotus Domino Designer - Business Objects Designer / SDK In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Languages C++; C# PERL; Java: Java Script HTML; XML; Tools MS Visual Studio. Net; J-Builder; Oracle Development Suite ; Business Objects Designer / SDK Languages Java; Java Script, PERL; C#, C++; HTML; XML; Retired (Product / Date) APC: Clipper, 9/11/03 Power-J, 9/11/03 Power. Builder; 9/11/03 / May 2008 COBOL; May 2004 / May 2010 Visual Basic 6 & earlier; May 2004 / 2007 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information This brick was de-conflicted (compared) to the Web Hosting brick to eliminate redundancy on 9/8/2003. *WSAD = Websphere Solution Application Development Follow-up – determine which Oracle and SAP development tools are being used within GSA Follow-up – determine the decision to explicitly use or not use Visual Basic. NET Follow-up – determine the usage of PERL Follow-up – look for consolidation opportunities with J-Builder, WSAD and Oracle J-Developer Follow-up – determine future strategic direction regarding development in Java vs. . NET – Where and how each is used. Follow-up – Lotus -- evaluation and reassessment in conjunction with collaboration platforms by May 2006. A separate and earlier decsion could be made about Lotus. Script and @function use before deciding on environment, since IBM’s direction is to deprecate these development languages. Follow-up – determine positioning of C/C++ and its usage CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Subcommittee, OCIO
GSA Application Technologies Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved; Apr 2003 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Tools MS Visual Studio. NET; J-Builder Oracle Development Suite Business Objects Designer Business Objects SDK SAP Enterprise Lotus Domino Designer Languages PERL HTML; CGI; Java Script; C++; C; XML; GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Tools -MS Visual Studio. NET; -J-Builder; Eclipse; -WSAD* -Oracle Development Suite -Lotus Domino Designer - Business Objects Designer / SDK In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Languages C++; C# PERL; Java: Java Script HTML; XML; Tools MS Visual Studio. Net; J-Builder; Oracle Development Suite ; Business Objects Designer / SDK Languages Java; Java Script, PERL; C#, C++; HTML; XML; Retired (Product / Date) APC: Clipper, 9/11/03 Power-J, 9/11/03 Power. Builder; 9/11/03 / May 2008 COBOL; May 2004 / May 2010 Visual Basic 6 & earlier; May 2004 / 2007 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information This brick was de-conflicted (compared) to the Web Hosting brick to eliminate redundancy on 9/8/2003. *WSAD = Websphere Solution Application Development Follow-up – determine which Oracle and SAP development tools are being used within GSA Follow-up – determine the decision to explicitly use or not use Visual Basic. NET Follow-up – determine the usage of PERL Follow-up – look for consolidation opportunities with J-Builder, WSAD and Oracle J-Developer Follow-up – determine future strategic direction regarding development in Java vs. . NET – Where and how each is used. Follow-up – Lotus -- evaluation and reassessment in conjunction with collaboration platforms by May 2006. A separate and earlier decsion could be made about Lotus. Script and @function use before deciding on environment, since IBM’s direction is to deprecate these development languages. Follow-up – determine positioning of C/C++ and its usage CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Subcommittee, OCIO
 GSA Web Hosting Infrastructure Definition: Technologies and infrastructure elements associated with development and support of web-based applications and electronic commerce as it pertains to web server and application server capabilities. Examples include Web Hosting Services, Enterprise Information Portals, Application servers. Web content management (WCM) infrastructure is the core platform for enabling related technologies such as personalization, multi-channel output, and e-commerce. Adoption of WCM is a prerequisite for a competitive global Web site and enterprise portals for all but trailing-edge enterprises. .
GSA Web Hosting Infrastructure Definition: Technologies and infrastructure elements associated with development and support of web-based applications and electronic commerce as it pertains to web server and application server capabilities. Examples include Web Hosting Services, Enterprise Information Portals, Application servers. Web content management (WCM) infrastructure is the core platform for enabling related technologies such as personalization, multi-channel output, and e-commerce. Adoption of WCM is a prerequisite for a competitive global Web site and enterprise portals for all but trailing-edge enterprises. .
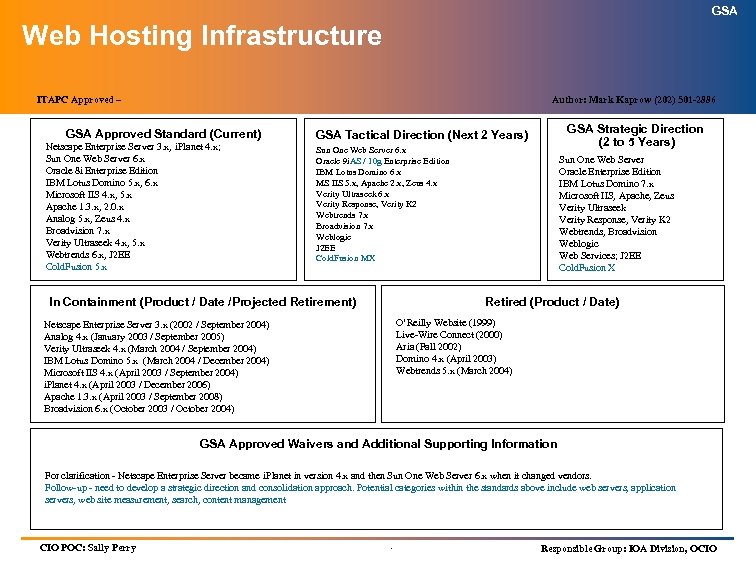 GSA Web Hosting Infrastructure ITAPC Approved – Author: Mark Kaprow (202) 501 -2886 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Netscape Enterprise Server 3. x, i. Planet 4. x; Sun One Web Server 6. x Oracle 8 i Enterprise Edition IBM Lotus Domino 5. x, 6. x Microsoft IIS 4. x, 5. x Apache 1. 3. x, 2. 0. x Analog 5. x, Zeus 4. x Broadvision 7. x Verity Ultraseek 4. x, 5. x Webtrends 6. x, J 2 EE Cold. Fusion 5. x GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Sun One Web Server 6. x Oracle 9 i. AS / 10 g Enterprise Edition IBM Lotus Domino 6. x MS IIS 5. x, Apache 2. x, Zeus 4. x Verity Ultraseek 6. x Verity Response, Verity K 2 Webtrends 7. x Broadvision 7. x Weblogic J 2 EE Cold. Fusion MX In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Sun One Web Server Oracle Enterprise Edition IBM Lotus Domino 7. x Microsoft IIS, Apache, Zeus Verity Ultraseek Verity Response, Verity K 2 Webtrends, Broadvision Weblogic Web Services; J 2 EE Cold. Fusion X Retired (Product / Date) O’Reilly Website (1999) Live-Wire Connect (2000) Aria (Fall 2002) Domino 4. x (April 2003) Webtrends 5. x (March 2004) Netscape Enterprise Server 3. x (2002 / September 2004) Analog 4. x (January 2003 / September 2005) Verity Ultraseek 4. x (March 2004 / September 2004) IBM Lotus Domino 5. x (March 2004 / December 2004) Microsoft IIS 4. x (April 2003 / September 2004) i. Planet 4. x (April 2003 / December 2006) Apache 1. 3. x (April 2003 / September 2008) Broadvision 6. x (October 2003 / October 2004) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information For clarification - Netscape Enterprise Server became i. Planet in version 4. x and then Sun One Web Server 6. x when it changed vendors. Follow-up - need to develop a strategic direction and consolidation approach. Potential categories within the standards above include web servers, application servers, web site measurement, search, content management CIO POC: Sally Perry . Responsible Group: IOA Division, OCIO
GSA Web Hosting Infrastructure ITAPC Approved – Author: Mark Kaprow (202) 501 -2886 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Netscape Enterprise Server 3. x, i. Planet 4. x; Sun One Web Server 6. x Oracle 8 i Enterprise Edition IBM Lotus Domino 5. x, 6. x Microsoft IIS 4. x, 5. x Apache 1. 3. x, 2. 0. x Analog 5. x, Zeus 4. x Broadvision 7. x Verity Ultraseek 4. x, 5. x Webtrends 6. x, J 2 EE Cold. Fusion 5. x GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Sun One Web Server 6. x Oracle 9 i. AS / 10 g Enterprise Edition IBM Lotus Domino 6. x MS IIS 5. x, Apache 2. x, Zeus 4. x Verity Ultraseek 6. x Verity Response, Verity K 2 Webtrends 7. x Broadvision 7. x Weblogic J 2 EE Cold. Fusion MX In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Sun One Web Server Oracle Enterprise Edition IBM Lotus Domino 7. x Microsoft IIS, Apache, Zeus Verity Ultraseek Verity Response, Verity K 2 Webtrends, Broadvision Weblogic Web Services; J 2 EE Cold. Fusion X Retired (Product / Date) O’Reilly Website (1999) Live-Wire Connect (2000) Aria (Fall 2002) Domino 4. x (April 2003) Webtrends 5. x (March 2004) Netscape Enterprise Server 3. x (2002 / September 2004) Analog 4. x (January 2003 / September 2005) Verity Ultraseek 4. x (March 2004 / September 2004) IBM Lotus Domino 5. x (March 2004 / December 2004) Microsoft IIS 4. x (April 2003 / September 2004) i. Planet 4. x (April 2003 / December 2006) Apache 1. 3. x (April 2003 / September 2008) Broadvision 6. x (October 2003 / October 2004) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information For clarification - Netscape Enterprise Server became i. Planet in version 4. x and then Sun One Web Server 6. x when it changed vendors. Follow-up - need to develop a strategic direction and consolidation approach. Potential categories within the standards above include web servers, application servers, web site measurement, search, content management CIO POC: Sally Perry . Responsible Group: IOA Division, OCIO
 GSA Digital Document Technology Definition: This element has evolved into Integrated Document Management (IDM) software. It is a type of middleware for organizing electronic documents; managing content; enabling secure access to documents and unstructured data; routing documents and automating related tasks; and facilitating document distribution. IDM products provide functionality for storing, locating, and retrieving information throughout the document's life cycle; i. e. , from the time it is created to the time it is archived to offline storage media. Many current IDM vendors and products take this life-cycle approach by addressing the following processes: authoring/creation, review and approval, distribution, and archiving. .
GSA Digital Document Technology Definition: This element has evolved into Integrated Document Management (IDM) software. It is a type of middleware for organizing electronic documents; managing content; enabling secure access to documents and unstructured data; routing documents and automating related tasks; and facilitating document distribution. IDM products provide functionality for storing, locating, and retrieving information throughout the document's life cycle; i. e. , from the time it is created to the time it is archived to offline storage media. Many current IDM vendors and products take this life-cycle approach by addressing the following processes: authoring/creation, review and approval, distribution, and archiving. .
 GSA Digital Document Technology Author: K. Rice, 202 -501 -0496 ITAPC Approved; April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Documentum; Adobe Acrobat Lotus Notes (. nsf); Internet Quorum (Correspondence Tracking) Lasherfishe GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Documentum; Adobe Acrobat Lotus Notes (. nsf); Internet Quorum (Correspondence Tracking) Lasherfishe In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Documentum; Adobe Acrobat Lotus Notes (. nsf); Internet Quorum (Correspondence Tracking) Lasherfishe Retired (Product / Date) Adobe Acrobat 5. x / May 2004 / May 2005 Adobe Acrobat 4. x as of 10/01/01 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Requirement of the Paperwork Elimination Act. File formats are governed by Draft OAD 1820. 2 “Managing Electronic Records. ” • As the need arises – determine specific GSA requirements for specifying standards for content management and records management • Follow-up – Notes/. nsf evaluation and reassessment in conjunction with collaboration platforms by May 2006 CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
GSA Digital Document Technology Author: K. Rice, 202 -501 -0496 ITAPC Approved; April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Documentum; Adobe Acrobat Lotus Notes (. nsf); Internet Quorum (Correspondence Tracking) Lasherfishe GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Documentum; Adobe Acrobat Lotus Notes (. nsf); Internet Quorum (Correspondence Tracking) Lasherfishe In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Documentum; Adobe Acrobat Lotus Notes (. nsf); Internet Quorum (Correspondence Tracking) Lasherfishe Retired (Product / Date) Adobe Acrobat 5. x / May 2004 / May 2005 Adobe Acrobat 4. x as of 10/01/01 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Requirement of the Paperwork Elimination Act. File formats are governed by Draft OAD 1820. 2 “Managing Electronic Records. ” • As the need arises – determine specific GSA requirements for specifying standards for content management and records management • Follow-up – Notes/. nsf evaluation and reassessment in conjunction with collaboration platforms by May 2006 CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
 GSA Knowledge Management Definition: A discipline that promotes a collaborative and integrated approach to the creation, capture, organization, access and use of an enterprise’s information assets. This includes databases, documents and, most important, the un-captured, tacit expertise and experience of individual workers. · The Gartner KM Process Framework defines five KM activities: – Create: The activities that result in new knowledge. – Capture: The activities that enable capture and representation of tacit knowledge in explicit form, thereby moving knowledge from the individual and making it available across the enterprise. – Organize: The activities that classify and categorize knowledge for storage and retrieval purposes. This includes maintenance of knowledge data as well as the indices, maps and processes that manage it. – Access: The activities through which knowledge is disseminated to or requested by users – Use: The application of knowledge to work activities, decisions and opportunities. Use is recursive, i. e. , it generates feedback that affects the other activities, and this feedback may be injected into the KM process through any of the other four activities. .
GSA Knowledge Management Definition: A discipline that promotes a collaborative and integrated approach to the creation, capture, organization, access and use of an enterprise’s information assets. This includes databases, documents and, most important, the un-captured, tacit expertise and experience of individual workers. · The Gartner KM Process Framework defines five KM activities: – Create: The activities that result in new knowledge. – Capture: The activities that enable capture and representation of tacit knowledge in explicit form, thereby moving knowledge from the individual and making it available across the enterprise. – Organize: The activities that classify and categorize knowledge for storage and retrieval purposes. This includes maintenance of knowledge data as well as the indices, maps and processes that manage it. – Access: The activities through which knowledge is disseminated to or requested by users – Use: The application of knowledge to work activities, decisions and opportunities. Use is recursive, i. e. , it generates feedback that affects the other activities, and this feedback may be injected into the KM process through any of the other four activities. .
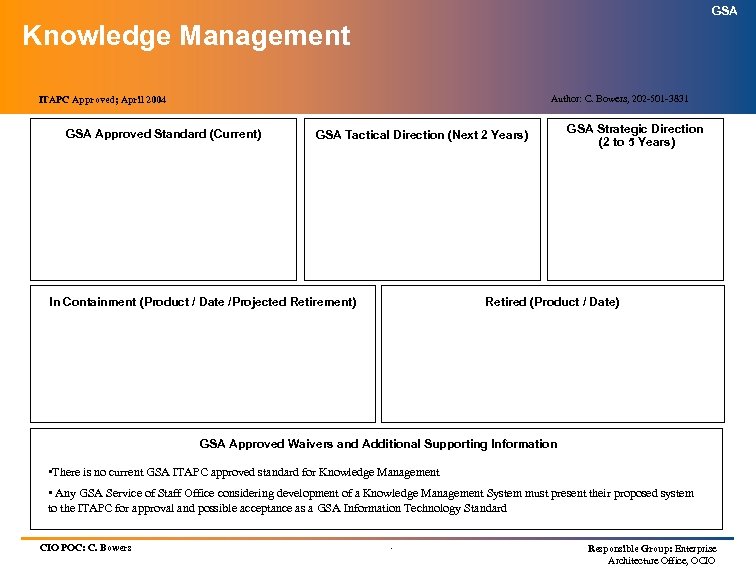 GSA Knowledge Management Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved; April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • There is no current GSA ITAPC approved standard for Knowledge Management • Any GSA Service of Staff Office considering development of a Knowledge Management System must present their proposed system to the ITAPC for approval and possible acceptance as a GSA Information Technology Standard CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Office, OCIO
GSA Knowledge Management Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved; April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • There is no current GSA ITAPC approved standard for Knowledge Management • Any GSA Service of Staff Office considering development of a Knowledge Management System must present their proposed system to the ITAPC for approval and possible acceptance as a GSA Information Technology Standard CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Office, OCIO
 GSA Customer Relationship Management Definition: · Customer Relationship Management - CRM refers to the concept of moving ownership of the customer up to the enterprise level and away from individual departments and/or lines of business (LOBs). These departments/LOBs are still responsible for customer interactions, but the enterprise is responsible for the customer. · To accomplish CRM, the enterprise brings automation to each customer touch point (i. e. , initiatives in sales force automation, the Internet, point of sale, and call/contact centers are all pieces of CRM, but they are not substitutes for it). CRM is: – composed of tactics, processes and behaviors; – not a technology; technology is the enabler of strategy, tactics, processes, and skill sets. » the technology is implemented tactically. – an initiative that causes fundamental changes in the organizational structure — from departmental/LOB (internal) to functional (customer) view. – very public: it is centered around your customer and anything that “goes wrong” becomes visible very quickly. .
GSA Customer Relationship Management Definition: · Customer Relationship Management - CRM refers to the concept of moving ownership of the customer up to the enterprise level and away from individual departments and/or lines of business (LOBs). These departments/LOBs are still responsible for customer interactions, but the enterprise is responsible for the customer. · To accomplish CRM, the enterprise brings automation to each customer touch point (i. e. , initiatives in sales force automation, the Internet, point of sale, and call/contact centers are all pieces of CRM, but they are not substitutes for it). CRM is: – composed of tactics, processes and behaviors; – not a technology; technology is the enabler of strategy, tactics, processes, and skill sets. » the technology is implemented tactically. – an initiative that causes fundamental changes in the organizational structure — from departmental/LOB (internal) to functional (customer) view. – very public: it is centered around your customer and anything that “goes wrong” becomes visible very quickly. .
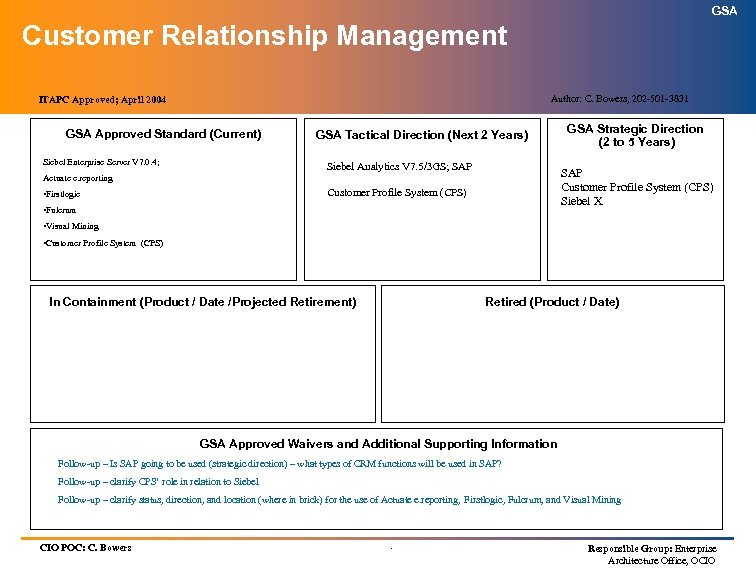 GSA Customer Relationship Management Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved; April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Siebel Enterprise Server V 7. 0. 4; GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Siebel Analytics V 7. 5/3 GS; SAP Customer Profile System (CPS) Siebel X Actuate e. reporting Customer Profile System (CPS) • Firstlogic GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) • Fulcrum • Visual Mining • Customer Profile System (CPS) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Follow-up – Is SAP going to be used (strategic direction) – what types of CRM functions will be used in SAP? Follow-up – clarify CPS’ role in relation to Siebel Follow-up – clarify status, direction, and location (where in brick) for the use of Actuate e. reporting, Firstlogic, Fulcrum, and Visual Mining CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Office, OCIO
GSA Customer Relationship Management Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved; April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Siebel Enterprise Server V 7. 0. 4; GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Siebel Analytics V 7. 5/3 GS; SAP Customer Profile System (CPS) Siebel X Actuate e. reporting Customer Profile System (CPS) • Firstlogic GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) • Fulcrum • Visual Mining • Customer Profile System (CPS) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Follow-up – Is SAP going to be used (strategic direction) – what types of CRM functions will be used in SAP? Follow-up – clarify CPS’ role in relation to Siebel Follow-up – clarify status, direction, and location (where in brick) for the use of Actuate e. reporting, Firstlogic, Fulcrum, and Visual Mining CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Office, OCIO
 GSA Database Management Systems Definition: A Database Management System (DBMS) is a program (software package) that enables end-users or application programmers to create and access data in a database. The DBMS manages user requests (and requests from other programs) so that users and other programs are free from having to understand where the data is physically located on storage media and, in a multi-user system, who else may also be accessing the data. In handling user requests, the DBMS ensures the integrity of the data (that is, making sure it continues to be accessible and is consistently organized as intended) and security (making sure only those with access privileges can access the data). A DBMS manages data in databases rather than files in file systems. .
GSA Database Management Systems Definition: A Database Management System (DBMS) is a program (software package) that enables end-users or application programmers to create and access data in a database. The DBMS manages user requests (and requests from other programs) so that users and other programs are free from having to understand where the data is physically located on storage media and, in a multi-user system, who else may also be accessing the data. In handling user requests, the DBMS ensures the integrity of the data (that is, making sure it continues to be accessible and is consistently organized as intended) and security (making sure only those with access privileges can access the data). A DBMS manages data in databases rather than files in file systems. .
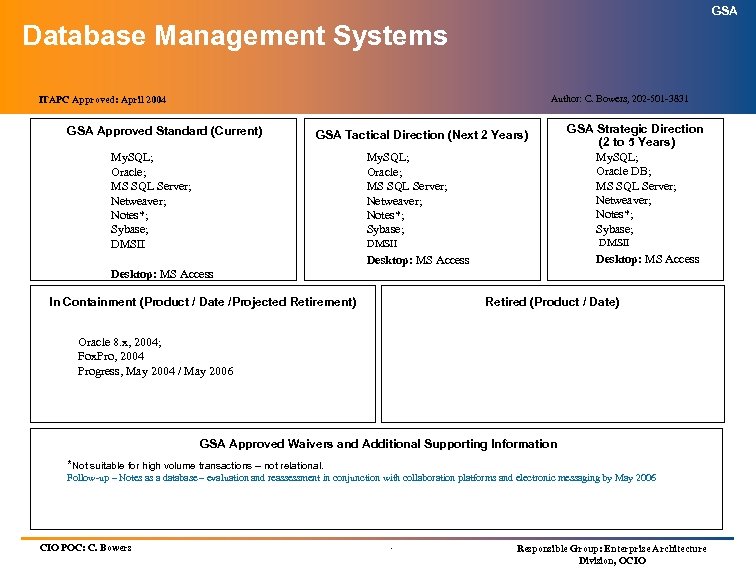 GSA Database Management Systems Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) My. SQL; Oracle; MS SQL Server; Netweaver; Notes*; Sybase; DMSII GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) My. SQL; Oracle DB; MS SQL Server; Netweaver; Notes*; Sybase; DMSII Desktop: MS Access In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) Oracle 8. x, 2004; Fox. Pro, 2004 Progress, May 2004 / May 2006 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information *Not suitable for high volume transactions – not relational. Follow-up – Notes as a database – evaluation and reassessment in conjunction with collaboration platforms and electronic messaging by May 2006 CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Division, OCIO
GSA Database Management Systems Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) My. SQL; Oracle; MS SQL Server; Netweaver; Notes*; Sybase; DMSII GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) My. SQL; Oracle DB; MS SQL Server; Netweaver; Notes*; Sybase; DMSII Desktop: MS Access In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) Oracle 8. x, 2004; Fox. Pro, 2004 Progress, May 2004 / May 2006 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information *Not suitable for high volume transactions – not relational. Follow-up – Notes as a database – evaluation and reassessment in conjunction with collaboration platforms and electronic messaging by May 2006 CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Division, OCIO
 GSA Data Warehousing Definition: A storage architecture designed to hold data extracted from transaction systems, operational data stores and external sources. The warehouse then combines that data in an aggregate, summary form suitable for enterprise-wide data analysis and reporting for predefined business needs. The five components of a data warehouse are production data sources, data extraction and conversion, the data warehouse database management system, and data warehouse administration. Note: for our purposes, Business Intelligence is treated as a separate architecture element. .
GSA Data Warehousing Definition: A storage architecture designed to hold data extracted from transaction systems, operational data stores and external sources. The warehouse then combines that data in an aggregate, summary form suitable for enterprise-wide data analysis and reporting for predefined business needs. The five components of a data warehouse are production data sources, data extraction and conversion, the data warehouse database management system, and data warehouse administration. Note: for our purposes, Business Intelligence is treated as a separate architecture element. .
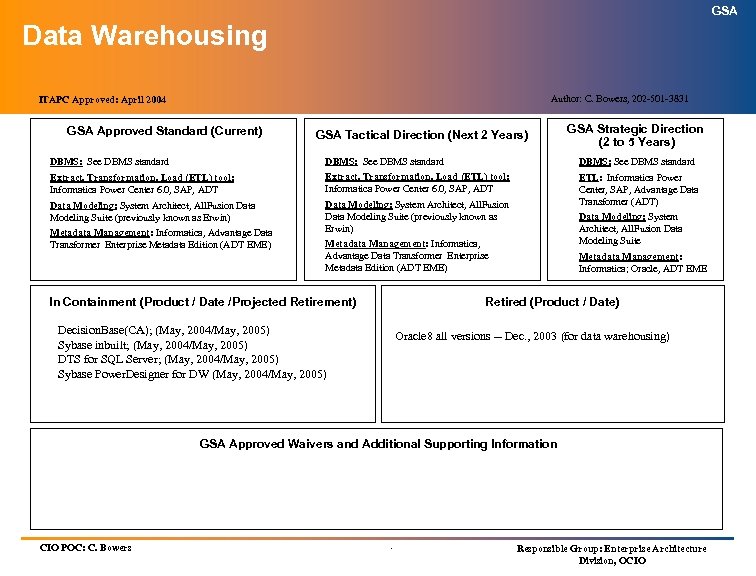 GSA Data Warehousing Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) DBMS: See DBMS standard Extract, Transformation, Load (ETL) tool: Informatica Power Center 6. 0, SAP, ADT Data Modeling: System Architect, All. Fusion Data Modeling Suite (previously known as Erwin) ETL: Informatica Power Center, SAP, Advantage Data Transformer (ADT) Metadata Management: Informatica, Advantage Data Transformer Enterprise Metadata Edition (ADT EME) Data Modeling: System Architect, All. Fusion Data Modeling Suite Metadata Management: Informatica, Advantage Data Transformer Enterprise Metadata Edition (ADT EME) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Metadata Management: Informatica; Oracle, ADT EME Retired (Product / Date) Decision. Base(CA); (May, 2004/May, 2005) Sybase inbuilt; (May, 2004/May, 2005) DTS for SQL Server; (May, 2004/May, 2005) Sybase Power. Designer for DW (May, 2004/May, 2005) Oracle 8 all versions -- Dec. , 2003 (for data warehousing) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Division, OCIO
GSA Data Warehousing Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) DBMS: See DBMS standard Extract, Transformation, Load (ETL) tool: Informatica Power Center 6. 0, SAP, ADT Data Modeling: System Architect, All. Fusion Data Modeling Suite (previously known as Erwin) ETL: Informatica Power Center, SAP, Advantage Data Transformer (ADT) Metadata Management: Informatica, Advantage Data Transformer Enterprise Metadata Edition (ADT EME) Data Modeling: System Architect, All. Fusion Data Modeling Suite Metadata Management: Informatica, Advantage Data Transformer Enterprise Metadata Edition (ADT EME) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Metadata Management: Informatica; Oracle, ADT EME Retired (Product / Date) Decision. Base(CA); (May, 2004/May, 2005) Sybase inbuilt; (May, 2004/May, 2005) DTS for SQL Server; (May, 2004/May, 2005) Sybase Power. Designer for DW (May, 2004/May, 2005) Oracle 8 all versions -- Dec. , 2003 (for data warehousing) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Division, OCIO
 GSA Business Intelligence Tools Definition: An interactive process for exploring and analyzing structured, domain-specific information (often stored in data warehouses) to discern trends or patterns, thereby deriving insights and drawing conclusions. The BI process includes communicating findings and effecting change. Domains include customers, suppliers, products, services and competitors. Has the following attributes: web-enabled multidimensional analysis; data transformation capability; data integration capability; support Oracle & Access & SQL Server; provide ODBC & SQL & DB 2 interfaces; suited to both Windows and UNIX environments; provide download capability to Excel. .
GSA Business Intelligence Tools Definition: An interactive process for exploring and analyzing structured, domain-specific information (often stored in data warehouses) to discern trends or patterns, thereby deriving insights and drawing conclusions. The BI process includes communicating findings and effecting change. Domains include customers, suppliers, products, services and competitors. Has the following attributes: web-enabled multidimensional analysis; data transformation capability; data integration capability; support Oracle & Access & SQL Server; provide ODBC & SQL & DB 2 interfaces; suited to both Windows and UNIX environments; provide download capability to Excel. .
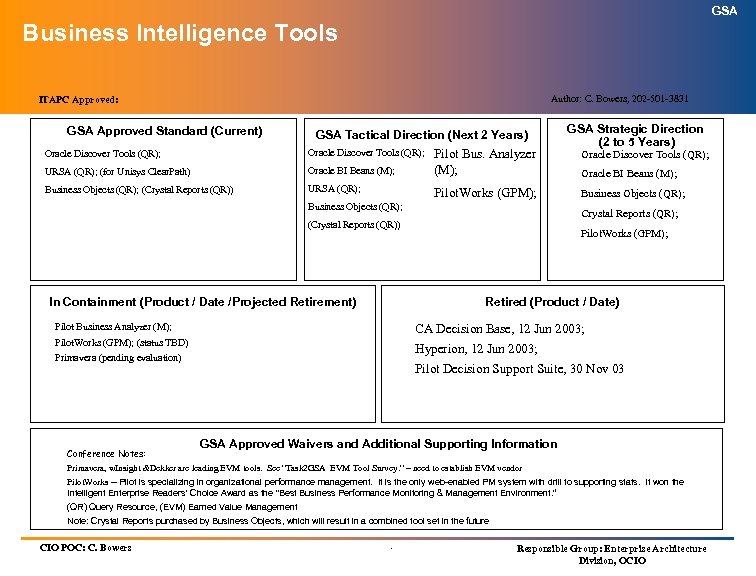 GSA Business Intelligence Tools Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved: GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Oracle Discover Tools (QR); URSA (QR); (for Unisys Clear. Path) Oracle BI Beans (M); Business Objects (QR); (Crystal Reports (QR)) URSA (QR); Pilot Bus. Analyzer (M); Pilot. Works (GPM); Business Objects (QR); Oracle Discover Tools (QR); Oracle BI Beans (M); Business Objects (QR); Crystal Reports (QR); (Crystal Reports (QR)) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Pilot. Works (GPM); Retired (Product / Date) Pilot Business Analyzer (M); CA Decision Base, 12 Jun 2003; Pilot. Works (GPM); (status TBD) Hyperion, 12 Jun 2003; Primavera (pending evaluation) Conference Notes: Pilot Decision Support Suite, 30 Nov 03 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Primavera, w. Insight &Dekker are leading EVM tools. See “Task 2 GSA EVM Tool Survey. ” – need to establish EVM vendor Pilot. Works -- Pilot is specializing in organizational performance management. It is the only web-enabled PM system with drill to supporting stats. It won the Intelligent Enterprise Readers' Choice Award as the "Best Business Performance Monitoring & Management Environment. “ (QR) Query Resource, (EVM) Earned Value Management Note: Crystal Reports purchased by Business Objects, which will result in a combined tool set in the future CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Division, OCIO
GSA Business Intelligence Tools Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved: GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Oracle Discover Tools (QR); URSA (QR); (for Unisys Clear. Path) Oracle BI Beans (M); Business Objects (QR); (Crystal Reports (QR)) URSA (QR); Pilot Bus. Analyzer (M); Pilot. Works (GPM); Business Objects (QR); Oracle Discover Tools (QR); Oracle BI Beans (M); Business Objects (QR); Crystal Reports (QR); (Crystal Reports (QR)) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Pilot. Works (GPM); Retired (Product / Date) Pilot Business Analyzer (M); CA Decision Base, 12 Jun 2003; Pilot. Works (GPM); (status TBD) Hyperion, 12 Jun 2003; Primavera (pending evaluation) Conference Notes: Pilot Decision Support Suite, 30 Nov 03 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Primavera, w. Insight &Dekker are leading EVM tools. See “Task 2 GSA EVM Tool Survey. ” – need to establish EVM vendor Pilot. Works -- Pilot is specializing in organizational performance management. It is the only web-enabled PM system with drill to supporting stats. It won the Intelligent Enterprise Readers' Choice Award as the "Best Business Performance Monitoring & Management Environment. “ (QR) Query Resource, (EVM) Earned Value Management Note: Crystal Reports purchased by Business Objects, which will result in a combined tool set in the future CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Division, OCIO
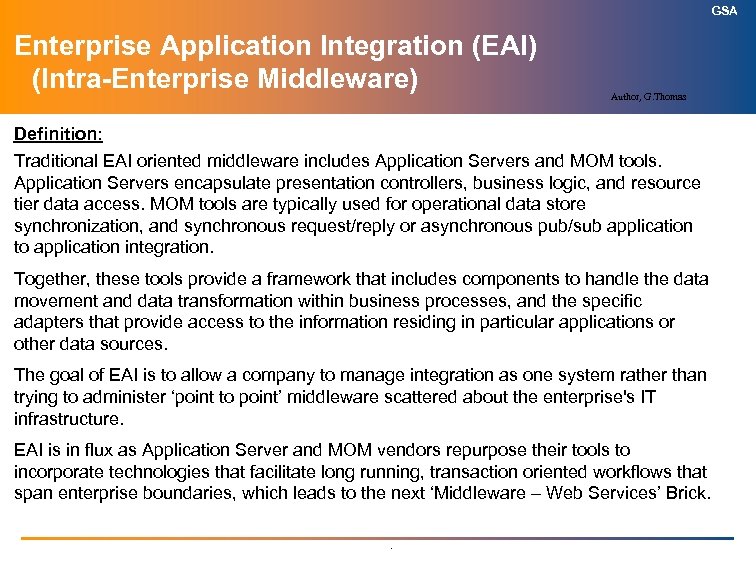 GSA Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) (Intra-Enterprise Middleware) Author, G. Thomas Definition: Traditional EAI oriented middleware includes Application Servers and MOM tools. Application Servers encapsulate presentation controllers, business logic, and resource tier data access. MOM tools are typically used for operational data store synchronization, and synchronous request/reply or asynchronous pub/sub application to application integration. Together, these tools provide a framework that includes components to handle the data movement and data transformation within business processes, and the specific adapters that provide access to the information residing in particular applications or other data sources. The goal of EAI is to allow a company to manage integration as one system rather than trying to administer ‘point to point’ middleware scattered about the enterprise's IT infrastructure. EAI is in flux as Application Server and MOM vendors repurpose their tools to incorporate technologies that facilitate long running, transaction oriented workflows that span enterprise boundaries, which leads to the next ‘Middleware – Web Services’ Brick. .
GSA Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) (Intra-Enterprise Middleware) Author, G. Thomas Definition: Traditional EAI oriented middleware includes Application Servers and MOM tools. Application Servers encapsulate presentation controllers, business logic, and resource tier data access. MOM tools are typically used for operational data store synchronization, and synchronous request/reply or asynchronous pub/sub application to application integration. Together, these tools provide a framework that includes components to handle the data movement and data transformation within business processes, and the specific adapters that provide access to the information residing in particular applications or other data sources. The goal of EAI is to allow a company to manage integration as one system rather than trying to administer ‘point to point’ middleware scattered about the enterprise's IT infrastructure. EAI is in flux as Application Server and MOM vendors repurpose their tools to incorporate technologies that facilitate long running, transaction oriented workflows that span enterprise boundaries, which leads to the next ‘Middleware – Web Services’ Brick. .
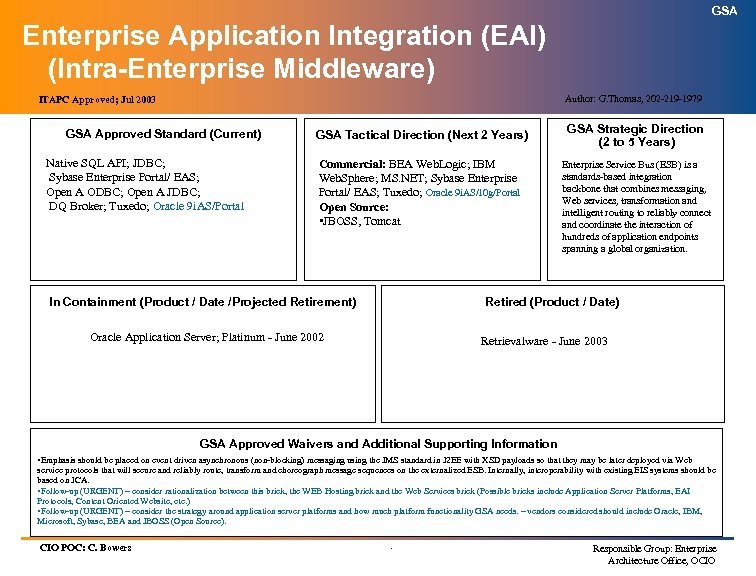 GSA Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) (Intra-Enterprise Middleware) Author: G. Thomas, 202 -219 -1979 ITAPC Approved; Jul 2003 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Native SQL API; JDBC; Sybase Enterprise Portal/ EAS; Open A ODBC; Open A JDBC; DQ Broker; Tuxedo; Oracle 9 i. AS/Portal GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Commercial: BEA Web. Logic; IBM Web. Sphere; MS. NET; Sybase Enterprise Portal/ EAS; Tuxedo; Oracle 9 i. AS/10 g/Portal Open Source: • JBOSS, Tomcat In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) is a standards-based integration backbone that combines messaging, Web services, transformation and intelligent routing to reliably connect and coordinate the interaction of hundreds of application endpoints spanning a global organization. Retired (Product / Date) Oracle Application Server; Platinum - June 2002 Retrievalware - June 2003 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Emphasis should be placed on event driven asynchronous (non-blocking) messaging using the JMS standard in J 2 EE with XSD payloads so that they may be later deployed via Web service protocols that will secure and reliably route, transform and choreograph message sequences on the externalized ESB. Internally, interoperability with existing EIS systems should be based on JCA. • Follow-up (URGENT) – consider rationalization between this brick, the WEB Hosting brick and the Web Services brick (Possible bricks include Application Server Platforms, EAI Protocols, Content Oriented Website, etc. ) • Follow-up (URGENT) – consider the strategy around application server platforms and how much platform functionality GSA needs. – vendors considered should include Oracle, IBM, Microsoft, Sybase, BEA and JBOSS (Open Source). CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Office, OCIO
GSA Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) (Intra-Enterprise Middleware) Author: G. Thomas, 202 -219 -1979 ITAPC Approved; Jul 2003 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Native SQL API; JDBC; Sybase Enterprise Portal/ EAS; Open A ODBC; Open A JDBC; DQ Broker; Tuxedo; Oracle 9 i. AS/Portal GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Commercial: BEA Web. Logic; IBM Web. Sphere; MS. NET; Sybase Enterprise Portal/ EAS; Tuxedo; Oracle 9 i. AS/10 g/Portal Open Source: • JBOSS, Tomcat In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) is a standards-based integration backbone that combines messaging, Web services, transformation and intelligent routing to reliably connect and coordinate the interaction of hundreds of application endpoints spanning a global organization. Retired (Product / Date) Oracle Application Server; Platinum - June 2002 Retrievalware - June 2003 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Emphasis should be placed on event driven asynchronous (non-blocking) messaging using the JMS standard in J 2 EE with XSD payloads so that they may be later deployed via Web service protocols that will secure and reliably route, transform and choreograph message sequences on the externalized ESB. Internally, interoperability with existing EIS systems should be based on JCA. • Follow-up (URGENT) – consider rationalization between this brick, the WEB Hosting brick and the Web Services brick (Possible bricks include Application Server Platforms, EAI Protocols, Content Oriented Website, etc. ) • Follow-up (URGENT) – consider the strategy around application server platforms and how much platform functionality GSA needs. – vendors considered should include Oracle, IBM, Microsoft, Sybase, BEA and JBOSS (Open Source). CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Office, OCIO
 GSA Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) (Web Services) Author, G. Thomas Definition: Web Services support the extension of traditional EAI Application Servers and MOM queues as Enterprise Service Bus technologies, which implements a Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) that is the foundation for an IT infrastructure framework based on a logical Publish/Find/Bind/Execute processing model. SOA emphasizes trans-enterprise interoperability of loosely coupled distributed components whose orchestrated XML message choreographies use open Internet standard transports and protocols. Web Services open standards are the foundation for SOA, moving the focus of IT interoperability from applications to message streams. The WS-I standards (also part of the TRM) include the basic Web Service standards that make the ‘publish-find-bind’ paradigm possible. Publishers are providers who expose application component interfaces to be discovered or found by component consumers via a component registry, whereupon they can bind to and execute the services listed based on establishing a contractual agreement of their roles in the message sequencing. OASIS and IBM/MS are driving the set of specifications that are emerging as the SOA/ESB Platform, based on Web Services technologies. Web Service deployment gives rise to a complementary set of Orchestration and Qo. S Management tools for ESB technologies, which is an emerging and rapidly evolving market space. .
GSA Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) (Web Services) Author, G. Thomas Definition: Web Services support the extension of traditional EAI Application Servers and MOM queues as Enterprise Service Bus technologies, which implements a Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) that is the foundation for an IT infrastructure framework based on a logical Publish/Find/Bind/Execute processing model. SOA emphasizes trans-enterprise interoperability of loosely coupled distributed components whose orchestrated XML message choreographies use open Internet standard transports and protocols. Web Services open standards are the foundation for SOA, moving the focus of IT interoperability from applications to message streams. The WS-I standards (also part of the TRM) include the basic Web Service standards that make the ‘publish-find-bind’ paradigm possible. Publishers are providers who expose application component interfaces to be discovered or found by component consumers via a component registry, whereupon they can bind to and execute the services listed based on establishing a contractual agreement of their roles in the message sequencing. OASIS and IBM/MS are driving the set of specifications that are emerging as the SOA/ESB Platform, based on Web Services technologies. Web Service deployment gives rise to a complementary set of Orchestration and Qo. S Management tools for ESB technologies, which is an emerging and rapidly evolving market space. .
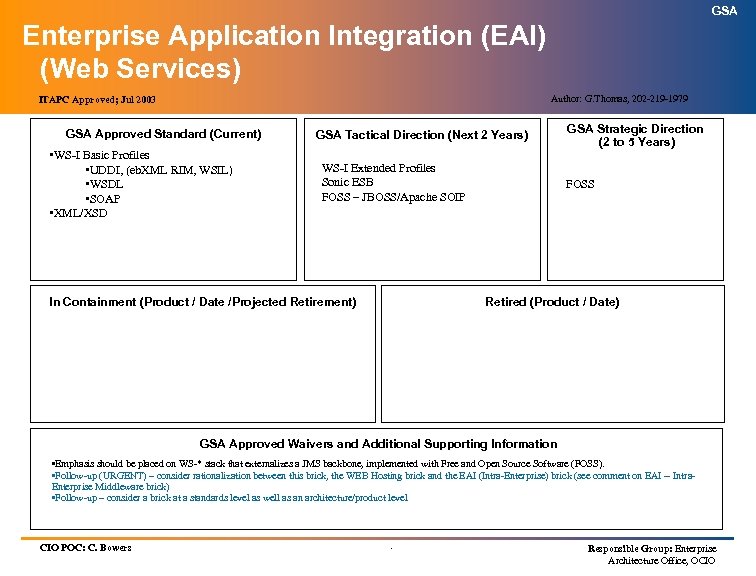 GSA Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) (Web Services) Author: G. Thomas, 202 -219 -1979 ITAPC Approved; Jul 2003 GSA Approved Standard (Current) • WS-I Basic Profiles • UDDI, (eb. XML RIM, WSIL) • WSDL • SOAP • XML/XSD GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) WS-I Extended Profiles Sonic ESB FOSS – JBOSS/Apache SOIP In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) FOSS Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Emphasis should be placed on WS-* stack that externalizes a JMS backbone, implemented with Free and Open Source Software (FOSS). • Follow-up (URGENT) – consider rationalization between this brick, the WEB Hosting brick and the EAI (Intra-Enterprise) brick (see comment on EAI -- Intra. Enterprise Middleware brick) • Follow-up – consider a brick at a standards level as well as an architecture/product level CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Office, OCIO
GSA Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) (Web Services) Author: G. Thomas, 202 -219 -1979 ITAPC Approved; Jul 2003 GSA Approved Standard (Current) • WS-I Basic Profiles • UDDI, (eb. XML RIM, WSIL) • WSDL • SOAP • XML/XSD GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) WS-I Extended Profiles Sonic ESB FOSS – JBOSS/Apache SOIP In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) FOSS Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Emphasis should be placed on WS-* stack that externalizes a JMS backbone, implemented with Free and Open Source Software (FOSS). • Follow-up (URGENT) – consider rationalization between this brick, the WEB Hosting brick and the EAI (Intra-Enterprise) brick (see comment on EAI -- Intra. Enterprise Middleware brick) • Follow-up – consider a brick at a standards level as well as an architecture/product level CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Office, OCIO
 GSA Workgroup Computing Definition: This element is a broad one that encompasses applications that deliver capability for group collaboration and light workflow. Much of this functionality (e. g. , message transfer agents, directory, gateways, e-mail clients, collaborative tasks, scheduling) is now combined in comprehensive “Group. Ware” packages like Microsoft Exchange or Lotus Notes Domino. Another way to think of this is to roll up to a higher level category: collaborative computing. This generally includes the four elements of: Group. Ware/Collaboration tools Messaging/directory services Electronic document management/workflow E-mail/calendaring/scheduling Because document management, e-mail/calendar/schedule have been covered elsewhere, this brick will cover only workflow and groupware/collaboration. .
GSA Workgroup Computing Definition: This element is a broad one that encompasses applications that deliver capability for group collaboration and light workflow. Much of this functionality (e. g. , message transfer agents, directory, gateways, e-mail clients, collaborative tasks, scheduling) is now combined in comprehensive “Group. Ware” packages like Microsoft Exchange or Lotus Notes Domino. Another way to think of this is to roll up to a higher level category: collaborative computing. This generally includes the four elements of: Group. Ware/Collaboration tools Messaging/directory services Electronic document management/workflow E-mail/calendaring/scheduling Because document management, e-mail/calendar/schedule have been covered elsewhere, this brick will cover only workflow and groupware/collaboration. .
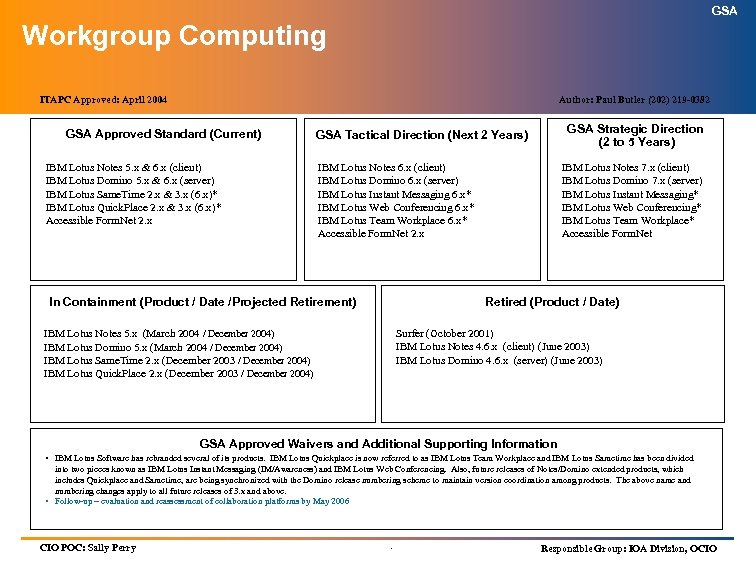 GSA Workgroup Computing ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: Paul Butler (202) 219 -0382 GSA Approved Standard (Current) IBM Lotus Notes 5. x & 6. x (client) IBM Lotus Domino 5. x & 6. x (server) IBM Lotus Same. Time 2. x & 3. x (6. x)* IBM Lotus Quick. Place 2. x & 3. x (6. x)* Accessible Form. Net 2. x GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) IBM Lotus Notes 6. x (client) IBM Lotus Domino 6. x (server) IBM Lotus Instant Messaging 6. x* IBM Lotus Web Conferencing 6. x* IBM Lotus Team Workplace 6. x* Accessible Form. Net 2. x In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) IBM Lotus Notes 7. x (client) IBM Lotus Domino 7. x (server) IBM Lotus Instant Messaging* IBM Lotus Web Conferencing* IBM Lotus Team Workplace* Accessible Form. Net Retired (Product / Date) Surfer (October 2001) IBM Lotus Notes 4. 6. x (client) (June 2003) IBM Lotus Domino 4. 6. x (server) (June 2003) IBM Lotus Notes 5. x (March 2004 / December 2004) IBM Lotus Domino 5. x (March 2004 / December 2004) IBM Lotus Same. Time 2. x (December 2003 / December 2004) IBM Lotus Quick. Place 2. x (December 2003 / December 2004) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • IBM Lotus Software has rebranded several of its products. IBM Lotus Quickplace is now referred to as IBM Lotus Team Workplace and IBM Lotus Sametime has been divided into two pieces known as IBM Lotus Instant Messaging (IM/Awareness) and IBM Lotus Web Conferencing. Also, future releases of Notes/Domino extended products, which includes Quickplace and Sametime, are being synchronized with the Domino release numbering scheme to maintain version coordination among products. The above name and numbering changes apply to all future releases of 3. x and above. • Follow-up – evaluation and reassessment of collaboration platforms by May 2006 CIO POC: Sally Perry . Responsible Group: IOA Division, OCIO
GSA Workgroup Computing ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: Paul Butler (202) 219 -0382 GSA Approved Standard (Current) IBM Lotus Notes 5. x & 6. x (client) IBM Lotus Domino 5. x & 6. x (server) IBM Lotus Same. Time 2. x & 3. x (6. x)* IBM Lotus Quick. Place 2. x & 3. x (6. x)* Accessible Form. Net 2. x GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) IBM Lotus Notes 6. x (client) IBM Lotus Domino 6. x (server) IBM Lotus Instant Messaging 6. x* IBM Lotus Web Conferencing 6. x* IBM Lotus Team Workplace 6. x* Accessible Form. Net 2. x In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) IBM Lotus Notes 7. x (client) IBM Lotus Domino 7. x (server) IBM Lotus Instant Messaging* IBM Lotus Web Conferencing* IBM Lotus Team Workplace* Accessible Form. Net Retired (Product / Date) Surfer (October 2001) IBM Lotus Notes 4. 6. x (client) (June 2003) IBM Lotus Domino 4. 6. x (server) (June 2003) IBM Lotus Notes 5. x (March 2004 / December 2004) IBM Lotus Domino 5. x (March 2004 / December 2004) IBM Lotus Same. Time 2. x (December 2003 / December 2004) IBM Lotus Quick. Place 2. x (December 2003 / December 2004) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • IBM Lotus Software has rebranded several of its products. IBM Lotus Quickplace is now referred to as IBM Lotus Team Workplace and IBM Lotus Sametime has been divided into two pieces known as IBM Lotus Instant Messaging (IM/Awareness) and IBM Lotus Web Conferencing. Also, future releases of Notes/Domino extended products, which includes Quickplace and Sametime, are being synchronized with the Domino release numbering scheme to maintain version coordination among products. The above name and numbering changes apply to all future releases of 3. x and above. • Follow-up – evaluation and reassessment of collaboration platforms by May 2006 CIO POC: Sally Perry . Responsible Group: IOA Division, OCIO
 GSA Remote Access Definition: · Remote access is the ability to log on to a network from a distant location. Generally, this requires a computer, a modem and remote access software to allow the computer to dial into the network over a telephone line. Remote access can promote productivity and cut costs. , employees can retrieve corporate information and use E-mail when they are traveling. · Any employee that works outside the office and uses wide-area networks (WANs) to connect back to a business office to coexist with office counterparts, is also engaged in remote access. The definition applies regardless of the type of network and end connection used, i. e. , public switched telephone network, ISDN, valueadded network, generic digital subscriber line (x. DSL), frame relay, asynchronous transfer mode (ATM), cable modem, private circuit, public Internet, or partner extranet. The definition applies to anyone who formally works in the enterprise supply chain, including employees, partners, customers, suppliers and contractors. .
GSA Remote Access Definition: · Remote access is the ability to log on to a network from a distant location. Generally, this requires a computer, a modem and remote access software to allow the computer to dial into the network over a telephone line. Remote access can promote productivity and cut costs. , employees can retrieve corporate information and use E-mail when they are traveling. · Any employee that works outside the office and uses wide-area networks (WANs) to connect back to a business office to coexist with office counterparts, is also engaged in remote access. The definition applies regardless of the type of network and end connection used, i. e. , public switched telephone network, ISDN, valueadded network, generic digital subscriber line (x. DSL), frame relay, asynchronous transfer mode (ATM), cable modem, private circuit, public Internet, or partner extranet. The definition applies to anyone who formally works in the enterprise supply chain, including employees, partners, customers, suppliers and contractors. .
 GSA Remote Access ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: Dianne Phillips, 202, 219 -2114 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Cisco AS 5350; Virtual Private Network (VPN) Next Generation (NG ) FP 3. VPN/ NG FP 3; GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Cisco AS 5350; VPN NG , Application Intelligence (AI) R 55; In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) VPN/NG/AI R 55; Retired (Product / Date) VPN NG / September 2004 /Retirement is dependant on Testing , LAN Admin and end-user migration. GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Follow-up – VPN Smart Gate used by the local area backbone network (discussion/additional detail to be reviewed) • This brick is focused on remote access security • Follow-up – consider expanding standards to include policy or other standards to address other hardware and connectivity. For example, it could set preferred connectivity service providers. CIO POC: G. Mc. Nerney . Responsible Group: Internetworking Division OCIO
GSA Remote Access ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: Dianne Phillips, 202, 219 -2114 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Cisco AS 5350; Virtual Private Network (VPN) Next Generation (NG ) FP 3. VPN/ NG FP 3; GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Cisco AS 5350; VPN NG , Application Intelligence (AI) R 55; In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) VPN/NG/AI R 55; Retired (Product / Date) VPN NG / September 2004 /Retirement is dependant on Testing , LAN Admin and end-user migration. GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Follow-up – VPN Smart Gate used by the local area backbone network (discussion/additional detail to be reviewed) • This brick is focused on remote access security • Follow-up – consider expanding standards to include policy or other standards to address other hardware and connectivity. For example, it could set preferred connectivity service providers. CIO POC: G. Mc. Nerney . Responsible Group: Internetworking Division OCIO
 GSA Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) Devices Definition: Wireless PDA -- devices that synchronize wirelessly via the cellular network or other wireless networks. Wired PDA – devices that synchronize via desktop or laptop computer .
GSA Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) Devices Definition: Wireless PDA -- devices that synchronize wirelessly via the cellular network or other wireless networks. Wired PDA – devices that synchronize via desktop or laptop computer .
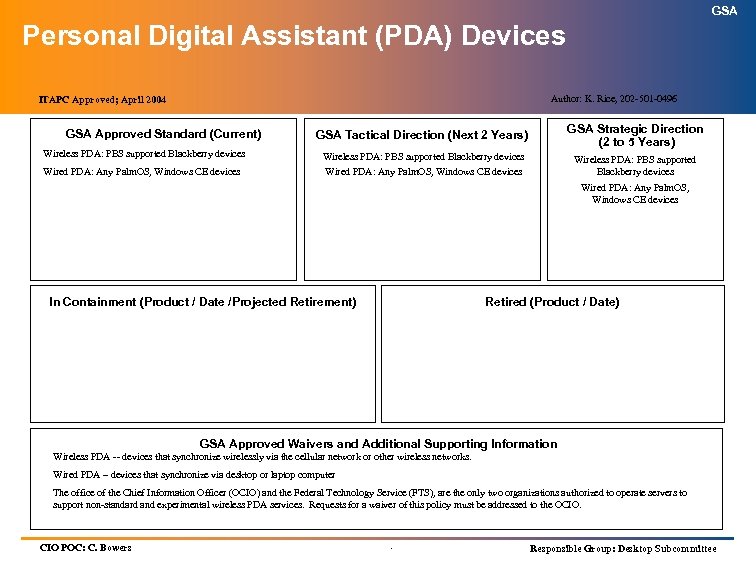 GSA Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) Devices Author: K. Rice, 202 -501 -0496 ITAPC Approved; April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Wireless PDA: PBS supported Blackberry devices Wired PDA: Any Palm. OS, Windows CE devices In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Wireless PDA -- devices that synchronize wirelessly via the cellular network or other wireless networks. Wired PDA – devices that synchronize via desktop or laptop computer The office of the Chief Information Officer (OCIO) and the Federal Technology Service (FTS), are the only two organizations authorized to operate servers to support non-standard and experimental wireless PDA services. Requests for a waiver of this policy must be addressed to the OCIO. CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
GSA Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) Devices Author: K. Rice, 202 -501 -0496 ITAPC Approved; April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Wireless PDA: PBS supported Blackberry devices Wired PDA: Any Palm. OS, Windows CE devices In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Wireless PDA -- devices that synchronize wirelessly via the cellular network or other wireless networks. Wired PDA – devices that synchronize via desktop or laptop computer The office of the Chief Information Officer (OCIO) and the Federal Technology Service (FTS), are the only two organizations authorized to operate servers to support non-standard and experimental wireless PDA services. Requests for a waiver of this policy must be addressed to the OCIO. CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
 GSA Desktop Operating Systems Definition: The main control program that runs a “normal office desktop computer” and sets the standard for running desktop application programs. It is the first program loaded when the computer is turned on, and it resides in memory at all times. An operating system is responsible for functions such as memory allocation, managing programs and errors, and directing input and output. It may be developed by the computer vendor or by a third-party independent software vendor. .
GSA Desktop Operating Systems Definition: The main control program that runs a “normal office desktop computer” and sets the standard for running desktop application programs. It is the first program loaded when the computer is turned on, and it resides in memory at all times. An operating system is responsible for functions such as memory allocation, managing programs and errors, and directing input and output. It may be developed by the computer vendor or by a third-party independent software vendor. .
 GSA Desktop Operating System Author: K. Rice 202 501 0496 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Windows XP GSA Approved Standard (Current) Future versions of Microsoft (Longhorn) Windows 2000 and Windows XP In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) Windows ME, Windows 98, MS NT 4. 0 are retired effective 1 Oct 2001 Windows 2000 / 13 Sept 2004 / End of product support GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Other platforms such as MAC OS should only be deployed with a waiver from the Desktop Standards Subcommittee. • This brick applies to GFE including GFE home use. • Follow-up -- set projected retirement for Windows 2000. CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
GSA Desktop Operating System Author: K. Rice 202 501 0496 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Windows XP GSA Approved Standard (Current) Future versions of Microsoft (Longhorn) Windows 2000 and Windows XP In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) Windows ME, Windows 98, MS NT 4. 0 are retired effective 1 Oct 2001 Windows 2000 / 13 Sept 2004 / End of product support GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Other platforms such as MAC OS should only be deployed with a waiver from the Desktop Standards Subcommittee. • This brick applies to GFE including GFE home use. • Follow-up -- set projected retirement for Windows 2000. CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
 GSA Application/Data Server Operating System Definition: The main control program running on an Application Server or Data Server that sets the standard for running application programs or DBMSs. It is the first program loaded when the server is turned on, and it resides in memory at all times. The operating system is responsible for functions such as memory allocation, managing programs and errors, and directing input and output. It may be developed by the server vendor or by a third-party independent software vendor. .
GSA Application/Data Server Operating System Definition: The main control program running on an Application Server or Data Server that sets the standard for running application programs or DBMSs. It is the first program loaded when the server is turned on, and it resides in memory at all times. The operating system is responsible for functions such as memory allocation, managing programs and errors, and directing input and output. It may be developed by the server vendor or by a third-party independent software vendor. .
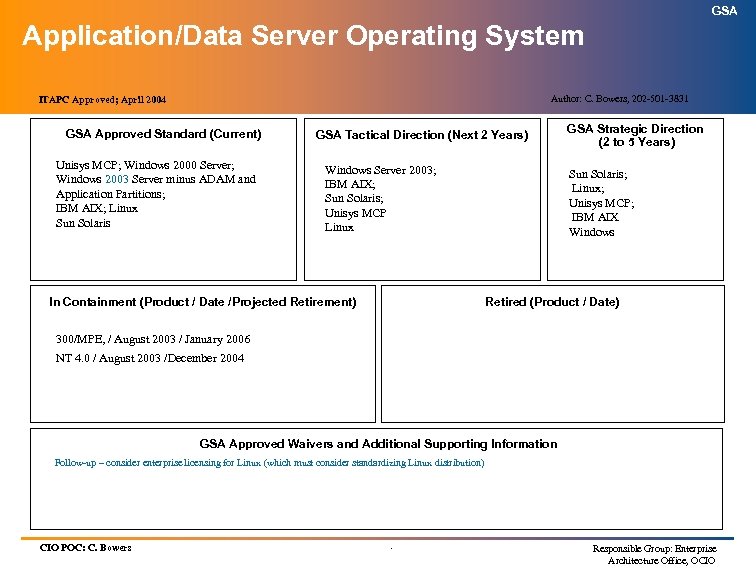 GSA Application/Data Server Operating System Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved; April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Unisys MCP; Windows 2000 Server; Windows 2003 Server minus ADAM and Application Partitions; IBM AIX; Linux Sun Solaris GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Windows Server 2003; IBM AIX; Sun Solaris; Unisys MCP Linux In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Sun Solaris; Linux; Unisys MCP; IBM AIX Windows Retired (Product / Date) 300/MPE, / August 2003 / January 2006 NT 4. 0 / August 2003 /December 2004 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Follow-up – consider enterprise licensing for Linux (which must consider standardizing Linux distribution) CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Office, OCIO
GSA Application/Data Server Operating System Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved; April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Unisys MCP; Windows 2000 Server; Windows 2003 Server minus ADAM and Application Partitions; IBM AIX; Linux Sun Solaris GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Windows Server 2003; IBM AIX; Sun Solaris; Unisys MCP Linux In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Sun Solaris; Linux; Unisys MCP; IBM AIX Windows Retired (Product / Date) 300/MPE, / August 2003 / January 2006 NT 4. 0 / August 2003 /December 2004 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Follow-up – consider enterprise licensing for Linux (which must consider standardizing Linux distribution) CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Enterprise Architecture Office, OCIO
 GSA Network Operating System Definition: · The main control program for managing and administering local area network resources. The program runs on domain controller servers. It is the first program loaded when the server is turned on, and it resides in memory at all times. The main functions of the network operating system are user authentication and authorization, application access, and printer and data sharing. .
GSA Network Operating System Definition: · The main control program for managing and administering local area network resources. The program runs on domain controller servers. It is the first program loaded when the server is turned on, and it resides in memory at all times. The main functions of the network operating system are user authentication and authorization, application access, and printer and data sharing. .
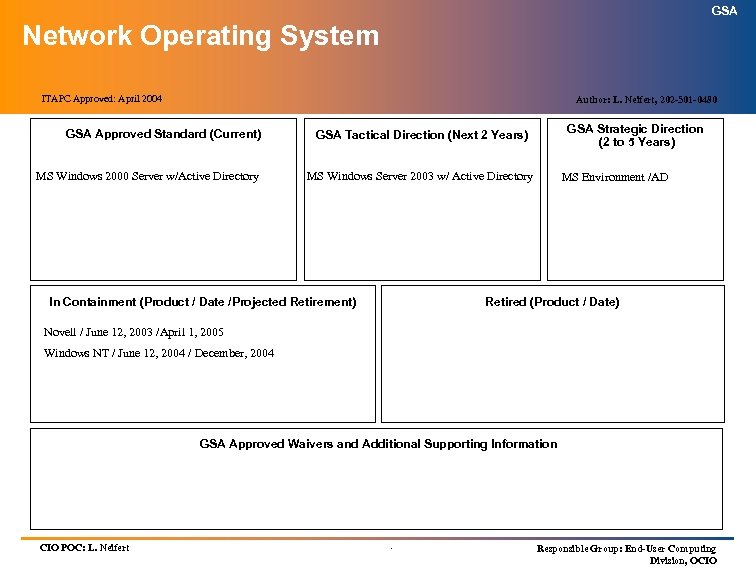 GSA Network Operating System ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: L. Neifert, 202 -501 -0480 GSA Approved Standard (Current) MS Windows 2000 Server w/Active Directory GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) MS Windows Server 2003 w/ Active Directory In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) MS Environment /AD Retired (Product / Date) Novell / June 12, 2003 /April 1, 2005 Windows NT / June 12, 2004 / December, 2004 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CIO POC: L. Neifert . Responsible Group: End-User Computing Division, OCIO
GSA Network Operating System ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: L. Neifert, 202 -501 -0480 GSA Approved Standard (Current) MS Windows 2000 Server w/Active Directory GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) MS Windows Server 2003 w/ Active Directory In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) MS Environment /AD Retired (Product / Date) Novell / June 12, 2003 /April 1, 2005 Windows NT / June 12, 2004 / December, 2004 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CIO POC: L. Neifert . Responsible Group: End-User Computing Division, OCIO
 GSA Storage Management Definitions: · DAS (direct attached storage) – Traditional, disks directly attached to the hardware platform that utilizes them, can include RAID technology. · NAS (network attached storage) – A NAS product combines a file server with storage and networking technologies. Hardware issues touch upon processors, disk drives, RAID controllers, and network ports, while software includes the embedded operating system, file system and storage management. Networking technology involves network protocols such as the Ethernet and Fibre Channel. · SAN (storage or server area network) – SAN consists of two tiers: The first tier - the storage plumbing tier - provides connectivity between nodes in a network and transports device-oriented commands and status. At least one storage node must be connected to this network. The second tier - the software tier - uses software to provide value-added services that operate over the first tier. Thus a simple Fibre Channel installation does not constitute a SAN by itself. .
GSA Storage Management Definitions: · DAS (direct attached storage) – Traditional, disks directly attached to the hardware platform that utilizes them, can include RAID technology. · NAS (network attached storage) – A NAS product combines a file server with storage and networking technologies. Hardware issues touch upon processors, disk drives, RAID controllers, and network ports, while software includes the embedded operating system, file system and storage management. Networking technology involves network protocols such as the Ethernet and Fibre Channel. · SAN (storage or server area network) – SAN consists of two tiers: The first tier - the storage plumbing tier - provides connectivity between nodes in a network and transports device-oriented commands and status. At least one storage node must be connected to this network. The second tier - the software tier - uses software to provide value-added services that operate over the first tier. Thus a simple Fibre Channel installation does not constitute a SAN by itself. .
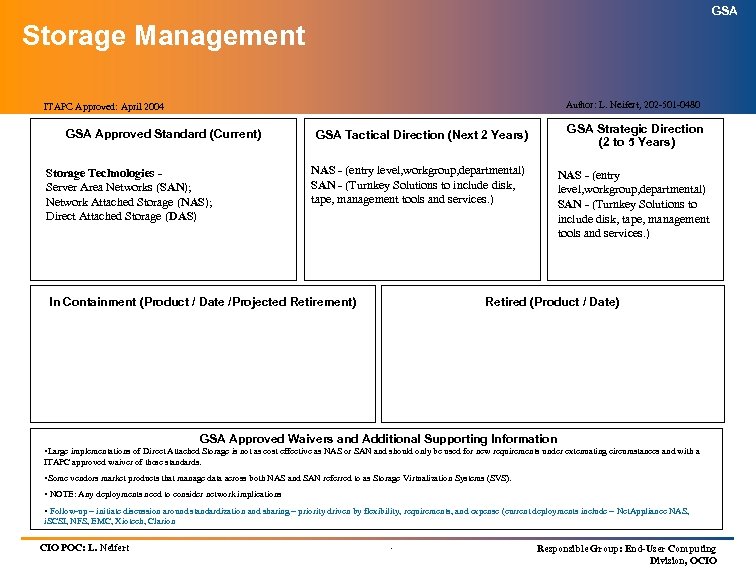 GSA Storage Management Author: L. Neifert, 202 -501 -0480 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Storage Technologies Server Area Networks (SAN); Network Attached Storage (NAS); Direct Attached Storage (DAS) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) NAS - (entry level, workgroup, departmental) SAN - (Turnkey Solutions to include disk, tape, management tools and services. ) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) NAS - (entry level, workgroup, departmental) SAN - (Turnkey Solutions to include disk, tape, management tools and services. ) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Large implementations of Direct Attached Storage is not as cost effective as NAS or SAN and should only be used for new requirements under extenuating circumstances and with a ITAPC approved waiver of these standards. • Some vendors market products that manage data across both NAS and SAN referred to as Storage Virtualization Systems (SVS). • NOTE: Any deployments need to consider network implications • Follow-up – initiate discussion around standardization and sharing – priority driven by flexibility, requirements, and expense (current deployments include – Net. Appliance NAS, i. SCSI, NFS, EMC, Xiotech, Clarion CIO POC: L. Neifert . Responsible Group: End-User Computing Division, OCIO
GSA Storage Management Author: L. Neifert, 202 -501 -0480 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Storage Technologies Server Area Networks (SAN); Network Attached Storage (NAS); Direct Attached Storage (DAS) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) NAS - (entry level, workgroup, departmental) SAN - (Turnkey Solutions to include disk, tape, management tools and services. ) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) NAS - (entry level, workgroup, departmental) SAN - (Turnkey Solutions to include disk, tape, management tools and services. ) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Large implementations of Direct Attached Storage is not as cost effective as NAS or SAN and should only be used for new requirements under extenuating circumstances and with a ITAPC approved waiver of these standards. • Some vendors market products that manage data across both NAS and SAN referred to as Storage Virtualization Systems (SVS). • NOTE: Any deployments need to consider network implications • Follow-up – initiate discussion around standardization and sharing – priority driven by flexibility, requirements, and expense (current deployments include – Net. Appliance NAS, i. SCSI, NFS, EMC, Xiotech, Clarion CIO POC: L. Neifert . Responsible Group: End-User Computing Division, OCIO
 GSA Wireless LAN Definition: .
GSA Wireless LAN Definition: .
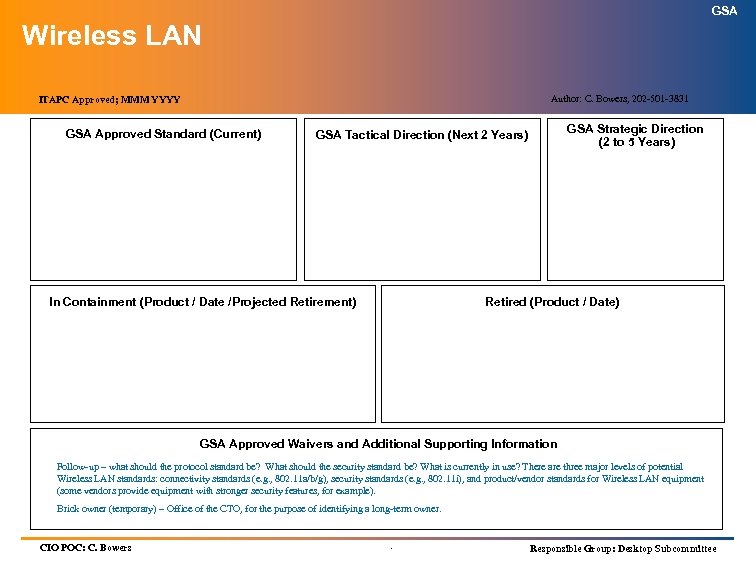 GSA Wireless LAN Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved; MMM YYYY GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Follow-up – what should the protocol standard be? What should the security standard be? What is currently in use? There are three major levels of potential Wireless LAN standards: connectivity standards (e. g. , 802. 11 a/b/g), security standards (e. g. , 802. 11 i), and product/vendor standards for Wireless LAN equipment (some vendors provide equipment with stronger security features, for example). Brick owner (temporary) – Office of the CTO, for the purpose of identifying a long-term owner. CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
GSA Wireless LAN Author: C. Bowers, 202 -501 -3831 ITAPC Approved; MMM YYYY GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Follow-up – what should the protocol standard be? What should the security standard be? What is currently in use? There are three major levels of potential Wireless LAN standards: connectivity standards (e. g. , 802. 11 a/b/g), security standards (e. g. , 802. 11 i), and product/vendor standards for Wireless LAN equipment (some vendors provide equipment with stronger security features, for example). Brick owner (temporary) – Office of the CTO, for the purpose of identifying a long-term owner. CIO POC: C. Bowers . Responsible Group: Desktop Subcommittee
 GSA Information Technology Security Definition: Enterprise-wide IT security consists of policies, standards, architecture, processes, education, products and monitoring that all work together making up a comprehensive but sound solution to achieve Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Enterprises lacking a comprehensive approach will incur large, unwarranted costs and ineffective results. The foundation for an enterprise-wide security initiative rests with a clearly defined set of technology-independent standards. These typically consist of a definition of roles and responsibilities, baseline controls, risk management requirements, and escalation and incident-response standards. All security technology falls into one of the four following categories of processes: · AUTHENTICATION · AUTHORIZATION · ADMINISTRATION · AUDIT .
GSA Information Technology Security Definition: Enterprise-wide IT security consists of policies, standards, architecture, processes, education, products and monitoring that all work together making up a comprehensive but sound solution to achieve Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Enterprises lacking a comprehensive approach will incur large, unwarranted costs and ineffective results. The foundation for an enterprise-wide security initiative rests with a clearly defined set of technology-independent standards. These typically consist of a definition of roles and responsibilities, baseline controls, risk management requirements, and escalation and incident-response standards. All security technology falls into one of the four following categories of processes: · AUTHENTICATION · AUTHORIZATION · ADMINISTRATION · AUDIT .
 GSA Information Technology Security - Authentication Definition: Authentication is the process by which the network or system validates the identity of a user’s logon information or verifies the integrity of a transmitted message from it’s source. A user’s name and password are compared against an authorized list, and if the system detects a match, access is granted to the extent specified in the permission list for that user. With a transmitted message, encryption procedures check to ensure it is from a trusted source using both hardware and software tools. IT Security Authentication components include: · Password Management · Single Sign-on · Smart Cards/Tokens/Certificates · Biometrics · Firewalls and Firewall Appliances · Remote Access · Encryption · DDo. S Protection .
GSA Information Technology Security - Authentication Definition: Authentication is the process by which the network or system validates the identity of a user’s logon information or verifies the integrity of a transmitted message from it’s source. A user’s name and password are compared against an authorized list, and if the system detects a match, access is granted to the extent specified in the permission list for that user. With a transmitted message, encryption procedures check to ensure it is from a trusted source using both hardware and software tools. IT Security Authentication components include: · Password Management · Single Sign-on · Smart Cards/Tokens/Certificates · Biometrics · Firewalls and Firewall Appliances · Remote Access · Encryption · DDo. S Protection .
 GSA Information Technology Security - Authentication ITAPC Approved – July 2004 Author: Kurt Garbars, 202: 208 -7485 GSA Approved Standard (Current) LAN/WAN FW: Check. Point FW NG, Cisco PIX (LAN and site-to-site WAN bridging only) VPN: Check. Point VPN NG, Smartgate VPN, Secure Client, and Cisco PIX for site-to-site WAN bridging Encryption: PGP, SSH, SFTP, SSL GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) LAN/WAN FW: Check. Point FW NG, Cisco PIX(LAN and site-to-site WAN bridging only) VPN: , Check. Point VPN NG, Smartgate VPN, Secure Client, and Cisco PIX for site-to-site WAN bridging Encryption: PGP, SSH, SFTP, SSL E-authentication Infrastructure In Containment (Product/Date/Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Reduced Sign-on and VPN solutions LAN/WAN FW enhancements Retired (Product / Date) Check. Point FW 4. 1(July 04 /September 04) OPIE (Onetime Password System) (July 04/December 04) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CIO POC: K. Garbars . Responsible Group: IT Security Subcommittee
GSA Information Technology Security - Authentication ITAPC Approved – July 2004 Author: Kurt Garbars, 202: 208 -7485 GSA Approved Standard (Current) LAN/WAN FW: Check. Point FW NG, Cisco PIX (LAN and site-to-site WAN bridging only) VPN: Check. Point VPN NG, Smartgate VPN, Secure Client, and Cisco PIX for site-to-site WAN bridging Encryption: PGP, SSH, SFTP, SSL GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) LAN/WAN FW: Check. Point FW NG, Cisco PIX(LAN and site-to-site WAN bridging only) VPN: , Check. Point VPN NG, Smartgate VPN, Secure Client, and Cisco PIX for site-to-site WAN bridging Encryption: PGP, SSH, SFTP, SSL E-authentication Infrastructure In Containment (Product/Date/Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Reduced Sign-on and VPN solutions LAN/WAN FW enhancements Retired (Product / Date) Check. Point FW 4. 1(July 04 /September 04) OPIE (Onetime Password System) (July 04/December 04) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CIO POC: K. Garbars . Responsible Group: IT Security Subcommittee
 GSA Information Technology Security - Authorization Definition: Authorization is the right granted to an individual or system to access a networked system and the data stored on it. Authorization is typically set up by a system administrator and verified by the computer based on some form of user identification, such as a code number or password for local and remote access. Based upon authorization rights, the user can perform only certain procedures that are granted by the system administrator. IT Security Authorization components include: · Application Protection · Operating System Protection (Hardening) · Resource (Data) Access Control · Antivirus/Behavior Blocking · Secure E-mail · Web/Content/Spam Filtering · Wireless Access Control · Provisioning · Identity Management · Configuration Management · Compliance Management .
GSA Information Technology Security - Authorization Definition: Authorization is the right granted to an individual or system to access a networked system and the data stored on it. Authorization is typically set up by a system administrator and verified by the computer based on some form of user identification, such as a code number or password for local and remote access. Based upon authorization rights, the user can perform only certain procedures that are granted by the system administrator. IT Security Authorization components include: · Application Protection · Operating System Protection (Hardening) · Resource (Data) Access Control · Antivirus/Behavior Blocking · Secure E-mail · Web/Content/Spam Filtering · Wireless Access Control · Provisioning · Identity Management · Configuration Management · Compliance Management .
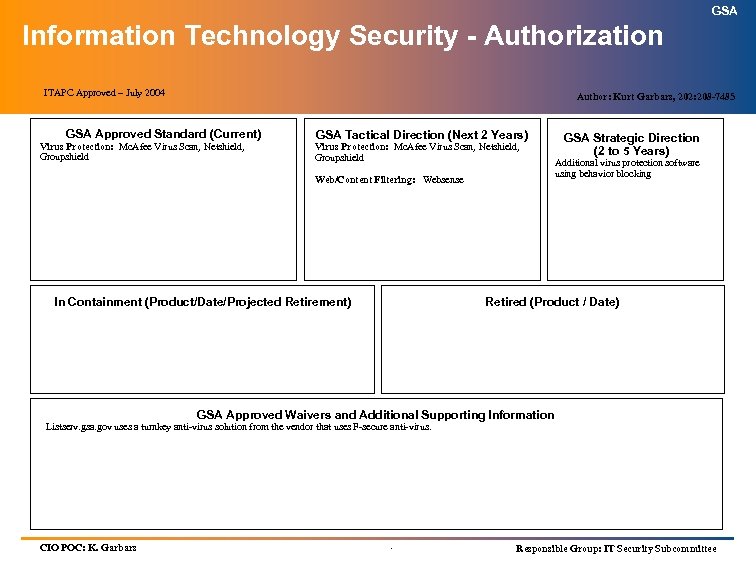 GSA Information Technology Security - Authorization ITAPC Approved – July 2004 Author: Kurt Garbars, 202: 208 -7485 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Virus Protection: Mc. Afee Virus Scan, Netshield, Groupshield GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Virus Protection: Mc. Afee Virus Scan, Netshield, Groupshield Web/Content Filtering: Websense In Containment (Product/Date/Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Additional virus protection software using behavior blocking Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Listserv. gsa. gov uses a turnkey anti-virus solution from the vendor that uses F-secure anti-virus. CIO POC: K. Garbars . Responsible Group: IT Security Subcommittee
GSA Information Technology Security - Authorization ITAPC Approved – July 2004 Author: Kurt Garbars, 202: 208 -7485 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Virus Protection: Mc. Afee Virus Scan, Netshield, Groupshield GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Virus Protection: Mc. Afee Virus Scan, Netshield, Groupshield Web/Content Filtering: Websense In Containment (Product/Date/Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Additional virus protection software using behavior blocking Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Listserv. gsa. gov uses a turnkey anti-virus solution from the vendor that uses F-secure anti-virus. CIO POC: K. Garbars . Responsible Group: IT Security Subcommittee
 GSA Information Technology Security - Administration Definition: Administration is the process in which those who are in charge of operations of a network or system, assisted by automated tools, make decisions on and maintain enforcement of rules and regulations of system use, install new workstations and other devices, add and remove individuals from the list of authorized users, archive files, oversee password protection and other security measures, monitor and analyze the usage of shared resources, ensure continuity of operations, handle malfunctioning equipment, and diagnose network problems. IT Security Administration components include: · Bandwidth Management · Backup · Security Intelligence Consoles and Web Sites · Event Management Consoles and Tools · Intrusion Management Consoles and Aggregation · Host-Based Intrusion Detection .
GSA Information Technology Security - Administration Definition: Administration is the process in which those who are in charge of operations of a network or system, assisted by automated tools, make decisions on and maintain enforcement of rules and regulations of system use, install new workstations and other devices, add and remove individuals from the list of authorized users, archive files, oversee password protection and other security measures, monitor and analyze the usage of shared resources, ensure continuity of operations, handle malfunctioning equipment, and diagnose network problems. IT Security Administration components include: · Bandwidth Management · Backup · Security Intelligence Consoles and Web Sites · Event Management Consoles and Tools · Intrusion Management Consoles and Aggregation · Host-Based Intrusion Detection .
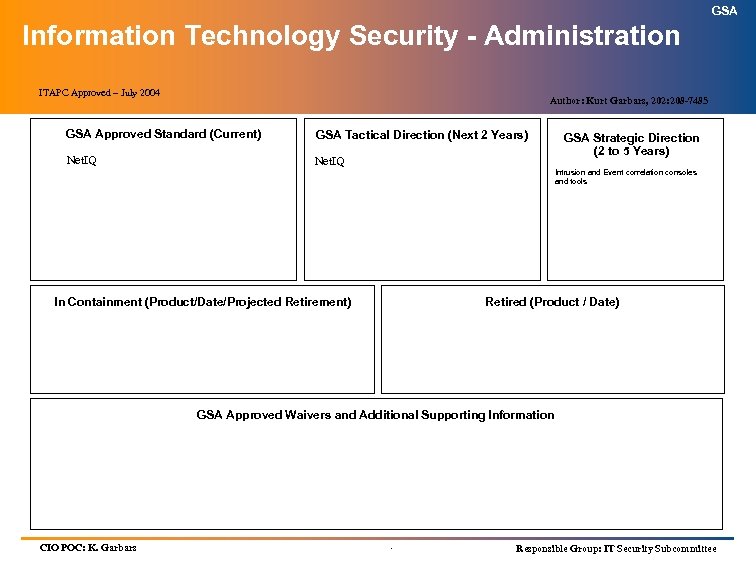 GSA Information Technology Security - Administration ITAPC Approved – July 2004 Author: Kurt Garbars, 202: 208 -7485 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Net. IQ GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Net. IQ GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Intrusion and Event correlation consoles and tools In Containment (Product/Date/Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CIO POC: K. Garbars . Responsible Group: IT Security Subcommittee
GSA Information Technology Security - Administration ITAPC Approved – July 2004 Author: Kurt Garbars, 202: 208 -7485 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Net. IQ GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Net. IQ GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Intrusion and Event correlation consoles and tools In Containment (Product/Date/Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CIO POC: K. Garbars . Responsible Group: IT Security Subcommittee
 GSA Information Technology Security - Audit Definition: The audit process is an examination of equipment, programs, activities, and procedures to determine how efficiently the overall system or network is performing, especially in terms of ensuring the integrity and security of data. In the auditing process, an operating system uses a variety of procedures, such as database sampling and generating confirmation, to detect and record security-related events, such as an attempt to create, to access, or to delete objects such as files and directories. The record of each event is stored in a file known as the security log, whose contents are available only to those with the proper clearance. IT Security Audit components include: · Network-Based Intrusion Detection · Wireless Detection Tools · Vulnerability Testing Tools · Remote Perimeter Management (FW/IDS/Access Control) · Managed Security Monitoring · Vulnerability/Penetration Testing · General Consulting .
GSA Information Technology Security - Audit Definition: The audit process is an examination of equipment, programs, activities, and procedures to determine how efficiently the overall system or network is performing, especially in terms of ensuring the integrity and security of data. In the auditing process, an operating system uses a variety of procedures, such as database sampling and generating confirmation, to detect and record security-related events, such as an attempt to create, to access, or to delete objects such as files and directories. The record of each event is stored in a file known as the security log, whose contents are available only to those with the proper clearance. IT Security Audit components include: · Network-Based Intrusion Detection · Wireless Detection Tools · Vulnerability Testing Tools · Remote Perimeter Management (FW/IDS/Access Control) · Managed Security Monitoring · Vulnerability/Penetration Testing · General Consulting .
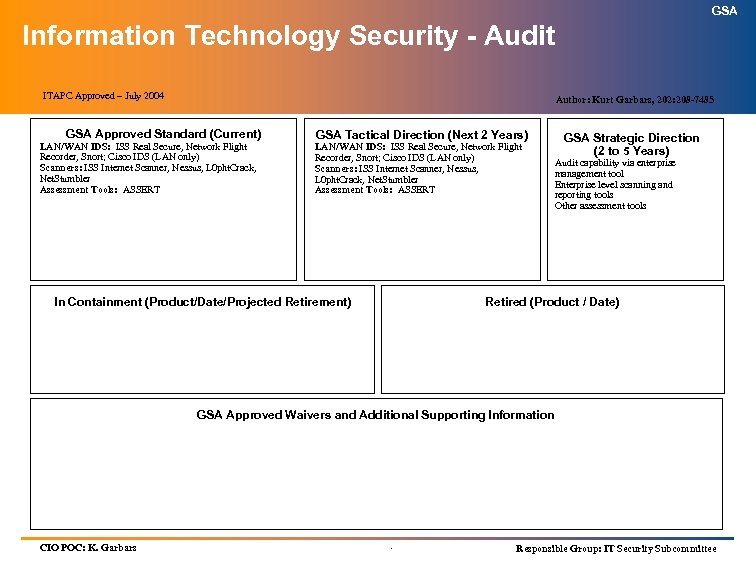 GSA Information Technology Security - Audit ITAPC Approved – July 2004 Author: Kurt Garbars, 202: 208 -7485 GSA Approved Standard (Current) LAN/WAN IDS: ISS Real Secure, Network Flight Recorder, Snort; Cisco IDS (LAN only) Scanners: ISS Internet Scanner, Nessus, L 0 pht. Crack, Net. Stumbler Assessment Tools: ASSERT GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) LAN/WAN IDS: ISS Real Secure, Network Flight Recorder, Snort; Cisco IDS (LAN only) Scanners: ISS Internet Scanner, Nessus, L 0 pht. Crack, Net. Stumbler Assessment Tools: ASSERT In Containment (Product/Date/Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Audit capability via enterprise management tool Enterprise level scanning and reporting tools Other assessment tools Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CIO POC: K. Garbars . Responsible Group: IT Security Subcommittee
GSA Information Technology Security - Audit ITAPC Approved – July 2004 Author: Kurt Garbars, 202: 208 -7485 GSA Approved Standard (Current) LAN/WAN IDS: ISS Real Secure, Network Flight Recorder, Snort; Cisco IDS (LAN only) Scanners: ISS Internet Scanner, Nessus, L 0 pht. Crack, Net. Stumbler Assessment Tools: ASSERT GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) LAN/WAN IDS: ISS Real Secure, Network Flight Recorder, Snort; Cisco IDS (LAN only) Scanners: ISS Internet Scanner, Nessus, L 0 pht. Crack, Net. Stumbler Assessment Tools: ASSERT In Containment (Product/Date/Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Audit capability via enterprise management tool Enterprise level scanning and reporting tools Other assessment tools Retired (Product / Date) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CIO POC: K. Garbars . Responsible Group: IT Security Subcommittee
 GSA Electronic Messaging Definition: Electronic messaging includes the combination of hardware (i. e. server), protocols utilized, and software (i. e. electronic messaging) capabilities that permit the electronic transmission and storage of messages (generally text or graphics) and attached or enclosed files. It also includes an E-mail application system that interfaces with the endusers. Some E-mail systems are limited to communication between end-users on the same network; others have gateways that allow end users to send messages to other designated computer systems or worldwide over the Internet. Once sent, the messages (also called E-mail) are stored in electronic mailboxes until the recipient retrieves them. .
GSA Electronic Messaging Definition: Electronic messaging includes the combination of hardware (i. e. server), protocols utilized, and software (i. e. electronic messaging) capabilities that permit the electronic transmission and storage of messages (generally text or graphics) and attached or enclosed files. It also includes an E-mail application system that interfaces with the endusers. Some E-mail systems are limited to communication between end-users on the same network; others have gateways that allow end users to send messages to other designated computer systems or worldwide over the Internet. Once sent, the messages (also called E-mail) are stored in electronic mailboxes until the recipient retrieves them. .
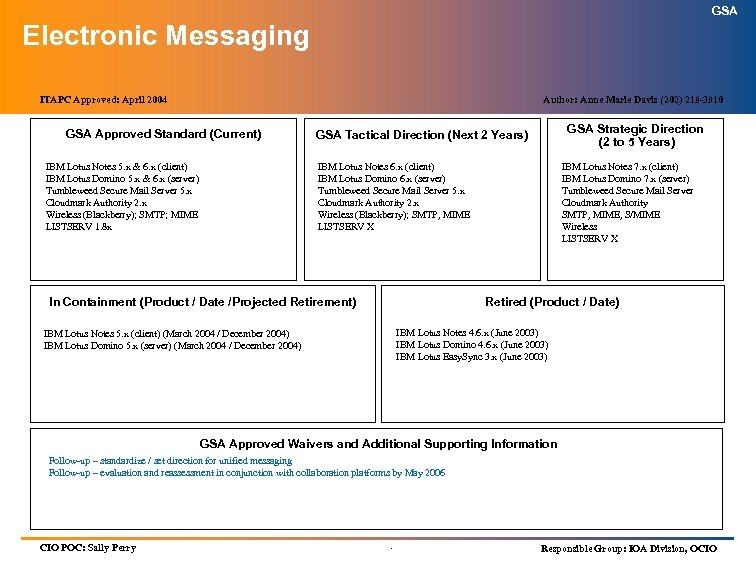 GSA Electronic Messaging ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: Anne Marie Davis (202) 219 -3910 GSA Approved Standard (Current) IBM Lotus Notes 5. x & 6. x (client) IBM Lotus Domino 5. x & 6. x (server) Tumbleweed Secure Mail Server 5. x Cloudmark Authority 2. x Wireless (Blackberry); SMTP; MIME LISTSERV 1. 8 x GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) IBM Lotus Notes 6. x (client) IBM Lotus Domino 6. x (server) Tumbleweed Secure Mail Server 5. x Cloudmark Authority 2. x Wireless (Blackberry); SMTP, MIME LISTSERV X In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) IBM Lotus Notes 7. x (client) IBM Lotus Domino 7. x (server) Tumbleweed Secure Mail Server Cloudmark Authority SMTP, MIME, S/MIME Wireless LISTSERV X Retired (Product / Date) IBM Lotus Notes 4. 6. x (June 2003) IBM Lotus Domino 4. 6. x (June 2003) IBM Lotus Easy. Sync 3. x (June 2003) IBM Lotus Notes 5. x (client) (March 2004 / December 2004) IBM Lotus Domino 5. x (server) (March 2004 / December 2004) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Follow-up – standardize / set direction for unified messaging Follow-up – evaluation and reassessment in conjunction with collaboration platforms by May 2006 CIO POC: Sally Perry . Responsible Group: IOA Division, OCIO
GSA Electronic Messaging ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: Anne Marie Davis (202) 219 -3910 GSA Approved Standard (Current) IBM Lotus Notes 5. x & 6. x (client) IBM Lotus Domino 5. x & 6. x (server) Tumbleweed Secure Mail Server 5. x Cloudmark Authority 2. x Wireless (Blackberry); SMTP; MIME LISTSERV 1. 8 x GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) IBM Lotus Notes 6. x (client) IBM Lotus Domino 6. x (server) Tumbleweed Secure Mail Server 5. x Cloudmark Authority 2. x Wireless (Blackberry); SMTP, MIME LISTSERV X In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) IBM Lotus Notes 7. x (client) IBM Lotus Domino 7. x (server) Tumbleweed Secure Mail Server Cloudmark Authority SMTP, MIME, S/MIME Wireless LISTSERV X Retired (Product / Date) IBM Lotus Notes 4. 6. x (June 2003) IBM Lotus Domino 4. 6. x (June 2003) IBM Lotus Easy. Sync 3. x (June 2003) IBM Lotus Notes 5. x (client) (March 2004 / December 2004) IBM Lotus Domino 5. x (server) (March 2004 / December 2004) GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information Follow-up – standardize / set direction for unified messaging Follow-up – evaluation and reassessment in conjunction with collaboration platforms by May 2006 CIO POC: Sally Perry . Responsible Group: IOA Division, OCIO
 GSA Enterprise-wide Resource Management Definition: Acquisition, maintenance and ongoing management and support of hardware and software assets. .
GSA Enterprise-wide Resource Management Definition: Acquisition, maintenance and ongoing management and support of hardware and software assets. .
 GSA Enterprise-wide Resource Management ITAPC Approved: Author: J. Donow, 202 -219 -0886 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Help Desk: Support Magic, Remedy, Unicenter AHD Help Desk: CA Unicenter AHD, Remedy Push: SMS, On. Demand Wininstall, Unicenter SDO Push: CA Unicenter SDO, On. Demand Wininstall Remote Control: SMS, Proxy, Unicenter RCO, PC Telecommute (server management) Remote Control: CA Unicenter RCO, Proxy Asset Management: CA Unicenter AMO, Computrace, CA Unicenter TND (single product) On. Demand Wininstall Asset Management: Support Magic, SMS, Computrace, Unicenter AMO, Dell Open Manage Client In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) PC Telecommute / ? ? ? ? ? (desktop) PC Anywhere / ? ? ? ? ? (desktop) Zen Works / ? ? ? ? ? Netwizard GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Unicenter TND’s time dimension, neural network agent, enterprise management portal, and advanced user interface technology capabilities will further support the strategic direction. • Follow Up -- Look for a better solution for distributed updates and patch management (push, distributed updates), which is particularly important for teleworkers and for home GFE. Possible solutions include Patch. Link and Mobile Automation, as well as other vendors/categories. • Follow-up – consider taking a broader view of how GSA defines/approaches enterprise resource management – rather than desktop centric, it can include the broader picture of IT infrastructure management and Forrester’s vision of Organic IT. This follow-up items should include CIOs. • Follow-up – close loop on Unicenter standardization -- what should be the scope of Unicenter usage and deployment? • Follow-up – consider adding Windows Terminal Server and VNC as standards specifically for server management, as well as allowing contained usage of PC Anywhere. CIO POC: L. Neifert . Responsible Group: End-User Computing Division, OCIO
GSA Enterprise-wide Resource Management ITAPC Approved: Author: J. Donow, 202 -219 -0886 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Help Desk: Support Magic, Remedy, Unicenter AHD Help Desk: CA Unicenter AHD, Remedy Push: SMS, On. Demand Wininstall, Unicenter SDO Push: CA Unicenter SDO, On. Demand Wininstall Remote Control: SMS, Proxy, Unicenter RCO, PC Telecommute (server management) Remote Control: CA Unicenter RCO, Proxy Asset Management: CA Unicenter AMO, Computrace, CA Unicenter TND (single product) On. Demand Wininstall Asset Management: Support Magic, SMS, Computrace, Unicenter AMO, Dell Open Manage Client In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) PC Telecommute / ? ? ? ? ? (desktop) PC Anywhere / ? ? ? ? ? (desktop) Zen Works / ? ? ? ? ? Netwizard GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Unicenter TND’s time dimension, neural network agent, enterprise management portal, and advanced user interface technology capabilities will further support the strategic direction. • Follow Up -- Look for a better solution for distributed updates and patch management (push, distributed updates), which is particularly important for teleworkers and for home GFE. Possible solutions include Patch. Link and Mobile Automation, as well as other vendors/categories. • Follow-up – consider taking a broader view of how GSA defines/approaches enterprise resource management – rather than desktop centric, it can include the broader picture of IT infrastructure management and Forrester’s vision of Organic IT. This follow-up items should include CIOs. • Follow-up – close loop on Unicenter standardization -- what should be the scope of Unicenter usage and deployment? • Follow-up – consider adding Windows Terminal Server and VNC as standards specifically for server management, as well as allowing contained usage of PC Anywhere. CIO POC: L. Neifert . Responsible Group: End-User Computing Division, OCIO
 GSA Wide Area Network Topology Definition: · A communications network that connects computing devices over geographically dispersed locations. While a local-area network (LAN) typically services a single building or location, a WAN covers a much larger area such as a city, state or country. WANs can use either phone lines or dedicated communication lines. Transmission speeds are typically slower than those of LANs. .
GSA Wide Area Network Topology Definition: · A communications network that connects computing devices over geographically dispersed locations. While a local-area network (LAN) typically services a single building or location, a WAN covers a much larger area such as a city, state or country. WANs can use either phone lines or dedicated communication lines. Transmission speeds are typically slower than those of LANs. .
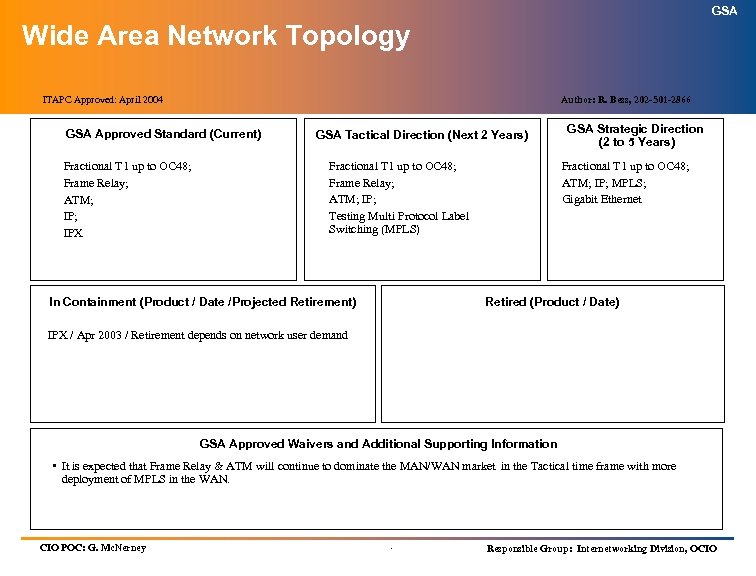 GSA Wide Area Network Topology ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: R. Bess, 202 -501 -2866 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Fractional T 1 up to OC 48; Frame Relay; ATM; IPX GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Fractional T 1 up to OC 48; Frame Relay; ATM; IP; Testing Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Fractional T 1 up to OC 48; ATM; IP; MPLS; Gigabit Ethernet Retired (Product / Date) IPX / Apr 2003 / Retirement depends on network user demand GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • It is expected that Frame Relay & ATM will continue to dominate the MAN/WAN market in the Tactical time frame with more deployment of MPLS in the WAN. CIO POC: G. Mc. Nerney . Responsible Group: Internetworking Division, OCIO
GSA Wide Area Network Topology ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: R. Bess, 202 -501 -2866 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Fractional T 1 up to OC 48; Frame Relay; ATM; IPX GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Fractional T 1 up to OC 48; Frame Relay; ATM; IP; Testing Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Fractional T 1 up to OC 48; ATM; IP; MPLS; Gigabit Ethernet Retired (Product / Date) IPX / Apr 2003 / Retirement depends on network user demand GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • It is expected that Frame Relay & ATM will continue to dominate the MAN/WAN market in the Tactical time frame with more deployment of MPLS in the WAN. CIO POC: G. Mc. Nerney . Responsible Group: Internetworking Division, OCIO
 GSA Wide Area Network Hardware Definition: · A router is a device that connects two networks. Routers receive packets of information from computers or other routers on the network; they then send these packets to their destinations based on addresses at the beginning of the packets and a road map of the other computers and peripherals on the network and related networks. · A switch is a network device that filters, forwards, frames based on the destination address of each frame. The switch operates at the data link layer of the OSI model. .
GSA Wide Area Network Hardware Definition: · A router is a device that connects two networks. Routers receive packets of information from computers or other routers on the network; they then send these packets to their destinations based on addresses at the beginning of the packets and a road map of the other computers and peripherals on the network and related networks. · A switch is a network device that filters, forwards, frames based on the destination address of each frame. The switch operates at the data link layer of the OSI model. .
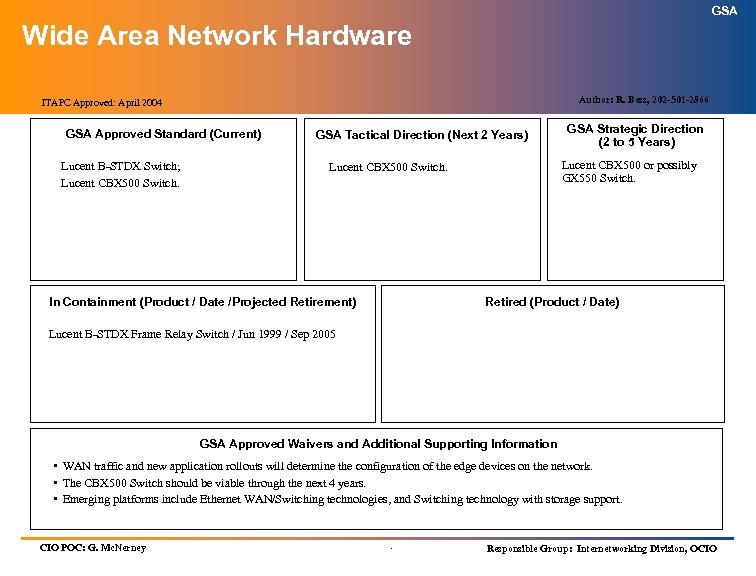 GSA Wide Area Network Hardware Author: R. Bess, 202 -501 -2866 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Lucent B-STDX Switch; Lucent CBX 500 Switch. GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Lucent CBX 500 or possibly GX 550 Switch. Lucent CBX 500 Switch. In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Retired (Product / Date) Lucent B-STDX Frame Relay Switch / Jun 1999 / Sep 2005 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • WAN traffic and new application rollouts will determine the configuration of the edge devices on the network. • The CBX 500 Switch should be viable through the next 4 years. • Emerging platforms include Ethernet WAN/Switching technologies, and Switching technology with storage support. CIO POC: G. Mc. Nerney . Responsible Group: Internetworking Division, OCIO
GSA Wide Area Network Hardware Author: R. Bess, 202 -501 -2866 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Lucent B-STDX Switch; Lucent CBX 500 Switch. GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Lucent CBX 500 or possibly GX 550 Switch. Lucent CBX 500 Switch. In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) Retired (Product / Date) Lucent B-STDX Frame Relay Switch / Jun 1999 / Sep 2005 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • WAN traffic and new application rollouts will determine the configuration of the edge devices on the network. • The CBX 500 Switch should be viable through the next 4 years. • Emerging platforms include Ethernet WAN/Switching technologies, and Switching technology with storage support. CIO POC: G. Mc. Nerney . Responsible Group: Internetworking Division, OCIO
 GSA Structured Cabling /LAN Topology Definition: · A geographically limited communication network that connects users within a defined area. A LAN is generally within a building or small group of buildings and is managed and owned by a single enterprise. The shorter distances within a building or campus enable faster communications at a lower cost than wide-area networks (WANs). Although an increasing number of LANs use Internet standards and protocols, they are normally protected from the public Internet by firewalls. LANs are generally used to perform the following functions: – – Print on printers attached to the network. Transfer data or software to or from other systems attached to the network. Send e-mail to other users on the network. Access wider-area networks, including the Internet, via a direct connection from the network, for external file transfer, e-mail, facsimile, group collaboration and video-conferencing. · Structured cabling is the physical wiring of the environment that allows the interconnections between devices. Lower level (OSI - physical layer) topology of the LAN and how LANs connect to other related resources. · Includes network cabling subsystems: horizontal, backbone, work area, equipment/computer room, telecommunications closet, entrance facilities, and administration. · Cabling standards bodies include National - ANSI/TIA/EIA 568 -A and International - ISO/IEC 11801 .
GSA Structured Cabling /LAN Topology Definition: · A geographically limited communication network that connects users within a defined area. A LAN is generally within a building or small group of buildings and is managed and owned by a single enterprise. The shorter distances within a building or campus enable faster communications at a lower cost than wide-area networks (WANs). Although an increasing number of LANs use Internet standards and protocols, they are normally protected from the public Internet by firewalls. LANs are generally used to perform the following functions: – – Print on printers attached to the network. Transfer data or software to or from other systems attached to the network. Send e-mail to other users on the network. Access wider-area networks, including the Internet, via a direct connection from the network, for external file transfer, e-mail, facsimile, group collaboration and video-conferencing. · Structured cabling is the physical wiring of the environment that allows the interconnections between devices. Lower level (OSI - physical layer) topology of the LAN and how LANs connect to other related resources. · Includes network cabling subsystems: horizontal, backbone, work area, equipment/computer room, telecommunications closet, entrance facilities, and administration. · Cabling standards bodies include National - ANSI/TIA/EIA 568 -A and International - ISO/IEC 11801 .
 GSA Structured Cabling / LAN Topology ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: J. Donow, 202 -219 -0886 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Wiring: Cat 5 e UTP; Multimode Fiber; Data. Link: Ethernet 10/100 Base T Cat 5 e; 100 Mb switched to desktop Ethernet 100 Base T; Gig uplinks in Wire Closets 10/100 to the Ports; 10 Gb between Core, GB Servers Protocol; TCP/IP GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Wiring: Single-mode Fiber; Wireless; Bluetooth Datalink: Ethernet 100; 10 Gigabit Ethernet Wiring: Cat 5 e UTP; Singlemode Fiber; Wireless Datalink: Ethernet/100 Base T; 10 Gigabit Ethernet; Protocol; TCP/IP (must plan for v. 6) Protocol; TCP/IP In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) Wiring: Coax; 100 VG; Anylan, Cat 3 Datalink: 10 Base 2; 10 Base. T; FDDI, FAST Ethernet/110 Base. TX February 2003 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Wireless LAN is transitioning to a standards-based, high-bandwidth, cost-effective solution • It may be possible to squeeze out one more generation of LAN technology on existing MMF fiber to save the costs of SMF electronics, but the end of the road for MMF is in sight. CIO POC: L. Neifert . Responsible Group: End-User Computing Division, OCIO
GSA Structured Cabling / LAN Topology ITAPC Approved: April 2004 Author: J. Donow, 202 -219 -0886 GSA Approved Standard (Current) Wiring: Cat 5 e UTP; Multimode Fiber; Data. Link: Ethernet 10/100 Base T Cat 5 e; 100 Mb switched to desktop Ethernet 100 Base T; Gig uplinks in Wire Closets 10/100 to the Ports; 10 Gb between Core, GB Servers Protocol; TCP/IP GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Wiring: Single-mode Fiber; Wireless; Bluetooth Datalink: Ethernet 100; 10 Gigabit Ethernet Wiring: Cat 5 e UTP; Singlemode Fiber; Wireless Datalink: Ethernet/100 Base T; 10 Gigabit Ethernet; Protocol; TCP/IP (must plan for v. 6) Protocol; TCP/IP In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) Wiring: Coax; 100 VG; Anylan, Cat 3 Datalink: 10 Base 2; 10 Base. T; FDDI, FAST Ethernet/110 Base. TX February 2003 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information • Wireless LAN is transitioning to a standards-based, high-bandwidth, cost-effective solution • It may be possible to squeeze out one more generation of LAN technology on existing MMF fiber to save the costs of SMF electronics, but the end of the road for MMF is in sight. CIO POC: L. Neifert . Responsible Group: End-User Computing Division, OCIO
 GSA Voice Over Internet Protocol (Vo. IP) Definition: Voice, Video, and White Boarding convergence are the technologies that support the transmission of voice, video, and white boarding over data networks. It includes such technologies as Voice Over IP, Voice over ATM, Voice over Frame Relay, Sametime and Quick Place. .
GSA Voice Over Internet Protocol (Vo. IP) Definition: Voice, Video, and White Boarding convergence are the technologies that support the transmission of voice, video, and white boarding over data networks. It includes such technologies as Voice Over IP, Voice over ATM, Voice over Frame Relay, Sametime and Quick Place. .
 GSA Voice Over Internet Protocol (Vo. IP) Author: G. Mc. Nerney, 202 -501 -2812 ITAPC Approved; April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) SIP GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) SIP In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) H 323(voice)/January 8, 2004/12 months following release of CISCO call manager version 5. 0, which is scheduled to be released mid CY 04 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CISCO Call Manager currently implements CISCO’s SCCP (light-weight version of H 323) ITAPC approved waivers on Jan 8 th, 2004 for R 3 and R 6 to deploy SCCP to field offices. Follow-up – review interoperability between various vendor solutions CIO POC: G. Mc. Nerney . Responsible Group: Internetworking Division, OCIO
GSA Voice Over Internet Protocol (Vo. IP) Author: G. Mc. Nerney, 202 -501 -2812 ITAPC Approved; April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) SIP GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) SIP In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Retired (Product / Date) H 323(voice)/January 8, 2004/12 months following release of CISCO call manager version 5. 0, which is scheduled to be released mid CY 04 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information CISCO Call Manager currently implements CISCO’s SCCP (light-weight version of H 323) ITAPC approved waivers on Jan 8 th, 2004 for R 3 and R 6 to deploy SCCP to field offices. Follow-up – review interoperability between various vendor solutions CIO POC: G. Mc. Nerney . Responsible Group: Internetworking Division, OCIO
 GSA Directory Services – Identity Management Definition: A directory service works like a phone book by providing a listing of all named network resources including users, computers, servers, applications, printers and storage devices. It provides a map of the network so that objects can be accessed without end users knowing their exact physical location. A directory service can store any information about a network resource that a network application or network users would find useful. .
GSA Directory Services – Identity Management Definition: A directory service works like a phone book by providing a listing of all named network resources including users, computers, servers, applications, printers and storage devices. It provides a map of the network so that objects can be accessed without end users knowing their exact physical location. A directory service can store any information about a network resource that a network application or network users would find useful. .
 GSA Directory Services – Identity Management Author: L. Neifert, 202 -501 -0480 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Single GSA Enterprise Directory Microsoft Windows 2000 Active Directory (AD) AD integrated or LDAP compliant application directories Microsoft Windows 2003 Active Directory Unified Security Architecture (Authentication/Authorization Web Services) AD integrated applications Federated Identity (SAML x, Liberty, Meta. Directory/Provisioning WS-Federation) LDAP compliant application directories (LDAP 3) Microsoft Windows 2003 Active Directory Core security product (SSO) – (evaluation pending) AD integrated applications Federated Identity (SAML 1. 0) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Meta. Directory/Provisioning LDAP compliant application directories (LDAP 3) Retired (Product / Date) Proprietary directories for specific applications / Nov 2002 Novell NDS / Nov 2002 / April 2005 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information New applications and modifications to legacy applications will be LDAP compliant. NOTE: Various vendor implementations of LDAP may not seamlessly integrate with each other. Oracle Internet Directory and legacy directories should be granted waivers to cover current product implementations Follow-up -- Reconcile authentication architecture, biometric data collection, NIST recommendations with the security elements above Follow-up -- Determine architecture and strategy for metadirectory and provisioning technologies (potentially password management, too) CIO POC: L. Neifert . Responsible Group: End-User Computing Division, OCIO
GSA Directory Services – Identity Management Author: L. Neifert, 202 -501 -0480 ITAPC Approved: April 2004 GSA Approved Standard (Current) GSA Strategic Direction (2 to 5 Years) GSA Tactical Direction (Next 2 Years) Single GSA Enterprise Directory Microsoft Windows 2000 Active Directory (AD) AD integrated or LDAP compliant application directories Microsoft Windows 2003 Active Directory Unified Security Architecture (Authentication/Authorization Web Services) AD integrated applications Federated Identity (SAML x, Liberty, Meta. Directory/Provisioning WS-Federation) LDAP compliant application directories (LDAP 3) Microsoft Windows 2003 Active Directory Core security product (SSO) – (evaluation pending) AD integrated applications Federated Identity (SAML 1. 0) In Containment (Product / Date /Projected Retirement) Meta. Directory/Provisioning LDAP compliant application directories (LDAP 3) Retired (Product / Date) Proprietary directories for specific applications / Nov 2002 Novell NDS / Nov 2002 / April 2005 GSA Approved Waivers and Additional Supporting Information New applications and modifications to legacy applications will be LDAP compliant. NOTE: Various vendor implementations of LDAP may not seamlessly integrate with each other. Oracle Internet Directory and legacy directories should be granted waivers to cover current product implementations Follow-up -- Reconcile authentication architecture, biometric data collection, NIST recommendations with the security elements above Follow-up -- Determine architecture and strategy for metadirectory and provisioning technologies (potentially password management, too) CIO POC: L. Neifert . Responsible Group: End-User Computing Division, OCIO
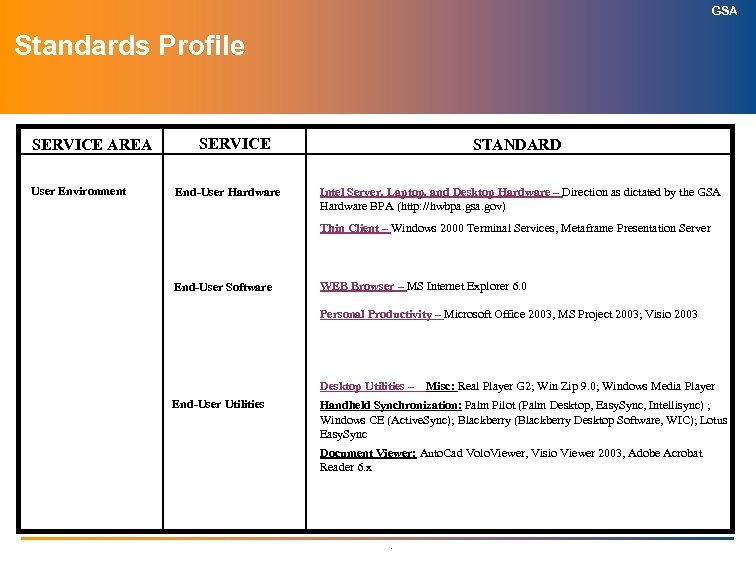 GSA Standards Profile SERVICE AREA User Environment SERVICE End-User Hardware STANDARD Intel Server, Laptop, and Desktop Hardware – Direction as dictated by the GSA Hardware BPA (http: //hwbpa. gsa. gov) Thin Client – Windows 2000 Terminal Services, Metaframe Presentation Server End-User Software WEB Browser – MS Internet Explorer 6. 0 Personal Productivity – Microsoft Office 2003, MS Project 2003; Visio 2003 Desktop Utilities – End-User Utilities Misc: Real Player G 2; Win Zip 9. 0; Windows Media Player Handheld Synchronization: Palm Pilot (Palm Desktop, Easy. Sync, Intellisync) ; Windows CE (Active. Sync); Blackberry (Blackberry Desktop Software, WIC); Lotus Easy. Sync Document Viewer: Auto. Cad Volo. Viewer, Visio Viewer 2003, Adobe Acrobat Reader 6. x .
GSA Standards Profile SERVICE AREA User Environment SERVICE End-User Hardware STANDARD Intel Server, Laptop, and Desktop Hardware – Direction as dictated by the GSA Hardware BPA (http: //hwbpa. gsa. gov) Thin Client – Windows 2000 Terminal Services, Metaframe Presentation Server End-User Software WEB Browser – MS Internet Explorer 6. 0 Personal Productivity – Microsoft Office 2003, MS Project 2003; Visio 2003 Desktop Utilities – End-User Utilities Misc: Real Player G 2; Win Zip 9. 0; Windows Media Player Handheld Synchronization: Palm Pilot (Palm Desktop, Easy. Sync, Intellisync) ; Windows CE (Active. Sync); Blackberry (Blackberry Desktop Software, WIC); Lotus Easy. Sync Document Viewer: Auto. Cad Volo. Viewer, Visio Viewer 2003, Adobe Acrobat Reader 6. x .
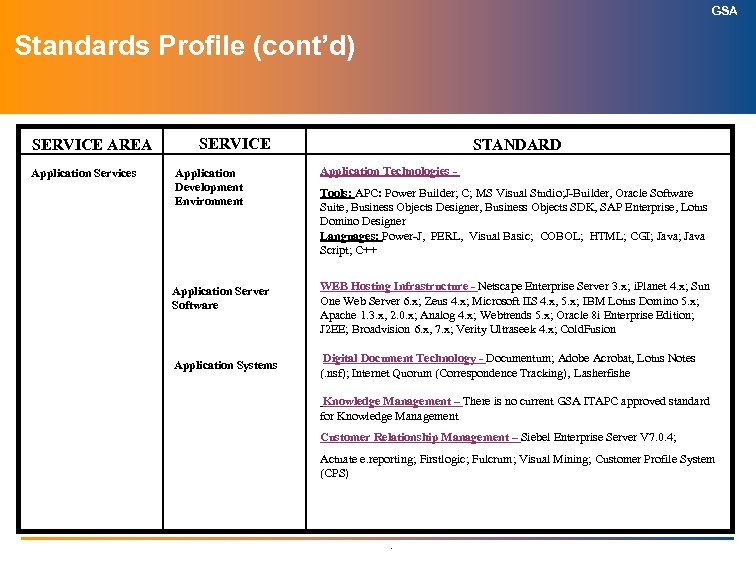 GSA Standards Profile (cont’d) SERVICE AREA Application Services SERVICE STANDARD Application Development Environment Application Technologies - Application Server Software WEB Hosting Infrastructure - Netscape Enterprise Server 3. x; i. Planet 4. x; Sun One Web Server 6. x; Zeus 4. x; Microsoft IIS 4. x, 5. x; IBM Lotus Domino 5. x; Apache 1. 3. x, 2. 0. x; Analog 4. x; Webtrends 5. x; Oracle 8 i Enterprise Edition; J 2 EE; Broadvision 6. x, 7. x; Verity Ultraseek 4. x; Cold. Fusion Application Systems Tools: APC: Power Builder; C; MS Visual Studio; J-Builder, Oracle Software Suite, Business Objects Designer, Business Objects SDK, SAP Enterprise, Lotus Domino Designer Languages: Power-J, PERL, Visual Basic; COBOL; HTML; CGI; Java Script; C++ Digital Document Technology - Documentum; Adobe Acrobat, Lotus Notes (. nsf); Internet Quorum (Correspondence Tracking), Lasherfishe Knowledge Management – There is no current GSA ITAPC approved standard for Knowledge Management Customer Relationship Management – Siebel Enterprise Server V 7. 0. 4; Actuate e. reporting; Firstlogic; Fulcrum; Visual Mining; Customer Profile System (CPS) .
GSA Standards Profile (cont’d) SERVICE AREA Application Services SERVICE STANDARD Application Development Environment Application Technologies - Application Server Software WEB Hosting Infrastructure - Netscape Enterprise Server 3. x; i. Planet 4. x; Sun One Web Server 6. x; Zeus 4. x; Microsoft IIS 4. x, 5. x; IBM Lotus Domino 5. x; Apache 1. 3. x, 2. 0. x; Analog 4. x; Webtrends 5. x; Oracle 8 i Enterprise Edition; J 2 EE; Broadvision 6. x, 7. x; Verity Ultraseek 4. x; Cold. Fusion Application Systems Tools: APC: Power Builder; C; MS Visual Studio; J-Builder, Oracle Software Suite, Business Objects Designer, Business Objects SDK, SAP Enterprise, Lotus Domino Designer Languages: Power-J, PERL, Visual Basic; COBOL; HTML; CGI; Java Script; C++ Digital Document Technology - Documentum; Adobe Acrobat, Lotus Notes (. nsf); Internet Quorum (Correspondence Tracking), Lasherfishe Knowledge Management – There is no current GSA ITAPC approved standard for Knowledge Management Customer Relationship Management – Siebel Enterprise Server V 7. 0. 4; Actuate e. reporting; Firstlogic; Fulcrum; Visual Mining; Customer Profile System (CPS) .
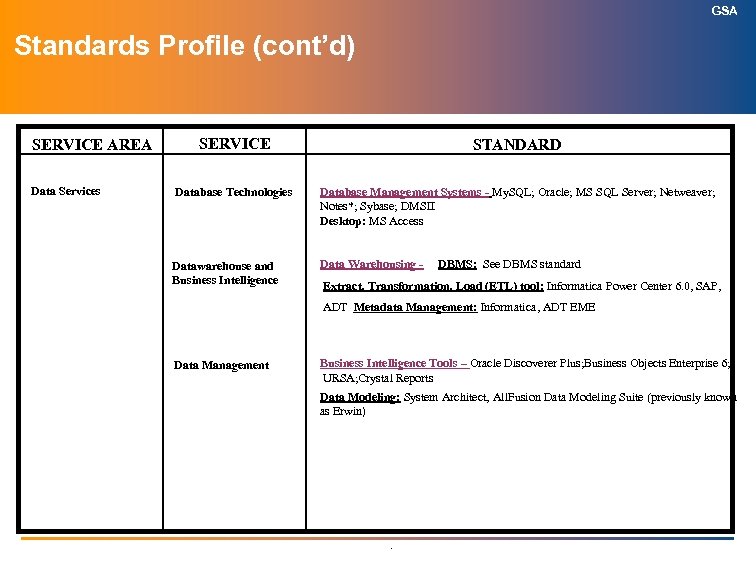 GSA Standards Profile (cont’d) SERVICE AREA Data Services SERVICE STANDARD Database Technologies Database Management Systems - My. SQL; Oracle; MS SQL Server; Netweaver; Notes*; Sybase; DMSII Desktop: MS Access Datawarehouse and Business Intelligence Data Warehousing - DBMS: See DBMS standard Extract, Transformation, Load (ETL) tool: Informatica Power Center 6. 0, SAP, ADT Metadata Management: Informatica, ADT EME Data Management Business Intelligence Tools – Oracle Discoverer Plus; Business Objects Enterprise 6; URSA; Crystal Reports Data Modeling: System Architect, All. Fusion Data Modeling Suite (previously known as Erwin) .
GSA Standards Profile (cont’d) SERVICE AREA Data Services SERVICE STANDARD Database Technologies Database Management Systems - My. SQL; Oracle; MS SQL Server; Netweaver; Notes*; Sybase; DMSII Desktop: MS Access Datawarehouse and Business Intelligence Data Warehousing - DBMS: See DBMS standard Extract, Transformation, Load (ETL) tool: Informatica Power Center 6. 0, SAP, ADT Metadata Management: Informatica, ADT EME Data Management Business Intelligence Tools – Oracle Discoverer Plus; Business Objects Enterprise 6; URSA; Crystal Reports Data Modeling: System Architect, All. Fusion Data Modeling Suite (previously known as Erwin) .
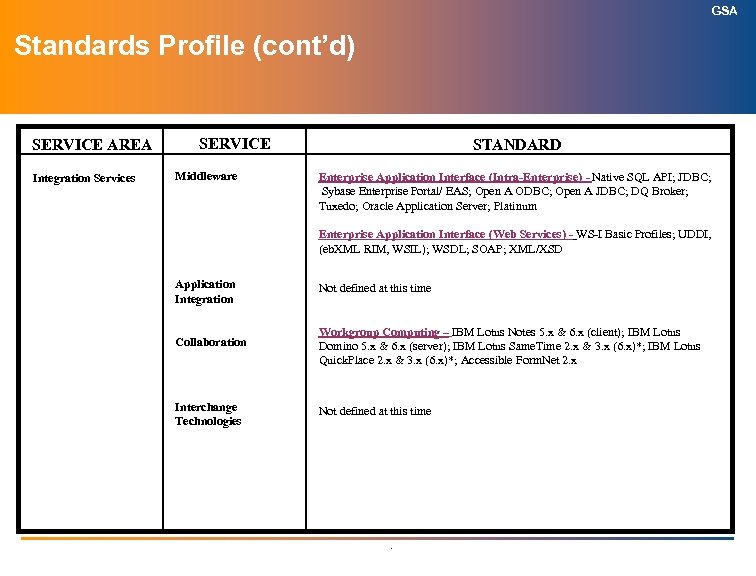 GSA Standards Profile (cont’d) SERVICE AREA Integration Services SERVICE Middleware STANDARD Enterprise Application Interface (Intra-Enterprise) - Native SQL API; JDBC; Sybase Enterprise Portal/ EAS; Open A ODBC; Open A JDBC; DQ Broker; Tuxedo; Oracle Application Server; Platinum Enterprise Application Interface (Web Services) - WS-I Basic Profiles; UDDI, (eb. XML RIM, WSIL); WSDL; SOAP; XML/XSD Application Integration Not defined at this time Collaboration Workgroup Computing – IBM Lotus Notes 5. x & 6. x (client); IBM Lotus Domino 5. x & 6. x (server); IBM Lotus Same. Time 2. x & 3. x (6. x)*; IBM Lotus Quick. Place 2. x & 3. x (6. x)*; Accessible Form. Net 2. x Interchange Technologies Not defined at this time .
GSA Standards Profile (cont’d) SERVICE AREA Integration Services SERVICE Middleware STANDARD Enterprise Application Interface (Intra-Enterprise) - Native SQL API; JDBC; Sybase Enterprise Portal/ EAS; Open A ODBC; Open A JDBC; DQ Broker; Tuxedo; Oracle Application Server; Platinum Enterprise Application Interface (Web Services) - WS-I Basic Profiles; UDDI, (eb. XML RIM, WSIL); WSDL; SOAP; XML/XSD Application Integration Not defined at this time Collaboration Workgroup Computing – IBM Lotus Notes 5. x & 6. x (client); IBM Lotus Domino 5. x & 6. x (server); IBM Lotus Same. Time 2. x & 3. x (6. x)*; IBM Lotus Quick. Place 2. x & 3. x (6. x)*; Accessible Form. Net 2. x Interchange Technologies Not defined at this time .
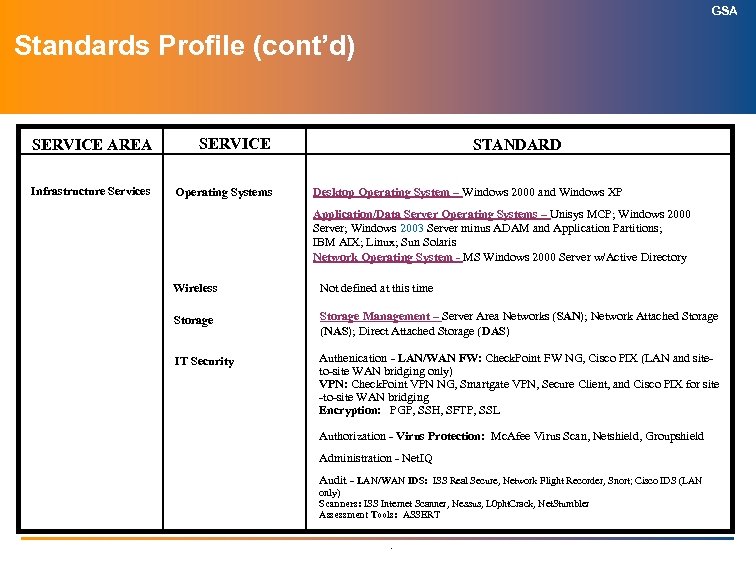 GSA Standards Profile (cont’d) SERVICE AREA SERVICE Infrastructure Services Operating Systems STANDARD Desktop Operating System – Windows 2000 and Windows XP Application/Data Server Operating Systems – Unisys MCP; Windows 2000 Server; Windows 2003 Server minus ADAM and Application Partitions; IBM AIX; Linux; Sun Solaris Network Operating System - MS Windows 2000 Server w/Active Directory Wireless Not defined at this time Storage Management – Server Area Networks (SAN); Network Attached Storage (NAS); Direct Attached Storage (DAS) IT Security Authenication - LAN/WAN FW: Check. Point FW NG, Cisco PIX (LAN and siteto-site WAN bridging only) VPN: Check. Point VPN NG, Smartgate VPN, Secure Client, and Cisco PIX for site -to-site WAN bridging Encryption: PGP, SSH, SFTP, SSL Authorization - Virus Protection: Mc. Afee Virus Scan, Netshield, Groupshield Administration - Net. IQ Audit - LAN/WAN IDS: ISS Real Secure, Network Flight Recorder, Snort; Cisco IDS (LAN only) Scanners: ISS Internet Scanner, Nessus, L 0 pht. Crack, Net. Stumbler Assessment Tools: ASSERT.
GSA Standards Profile (cont’d) SERVICE AREA SERVICE Infrastructure Services Operating Systems STANDARD Desktop Operating System – Windows 2000 and Windows XP Application/Data Server Operating Systems – Unisys MCP; Windows 2000 Server; Windows 2003 Server minus ADAM and Application Partitions; IBM AIX; Linux; Sun Solaris Network Operating System - MS Windows 2000 Server w/Active Directory Wireless Not defined at this time Storage Management – Server Area Networks (SAN); Network Attached Storage (NAS); Direct Attached Storage (DAS) IT Security Authenication - LAN/WAN FW: Check. Point FW NG, Cisco PIX (LAN and siteto-site WAN bridging only) VPN: Check. Point VPN NG, Smartgate VPN, Secure Client, and Cisco PIX for site -to-site WAN bridging Encryption: PGP, SSH, SFTP, SSL Authorization - Virus Protection: Mc. Afee Virus Scan, Netshield, Groupshield Administration - Net. IQ Audit - LAN/WAN IDS: ISS Real Secure, Network Flight Recorder, Snort; Cisco IDS (LAN only) Scanners: ISS Internet Scanner, Nessus, L 0 pht. Crack, Net. Stumbler Assessment Tools: ASSERT.
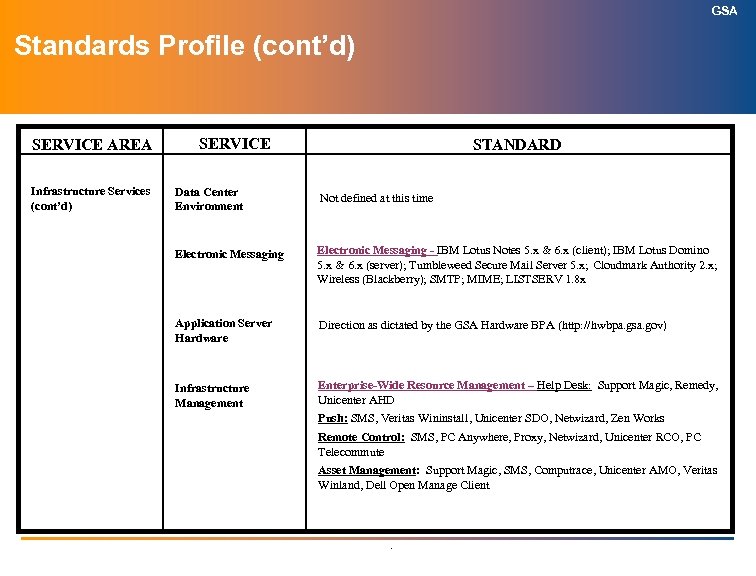 GSA Standards Profile (cont’d) SERVICE AREA Infrastructure Services (cont’d) SERVICE Data Center Environment STANDARD Not defined at this time Electronic Messaging - IBM Lotus Notes 5. x & 6. x (client); IBM Lotus Domino 5. x & 6. x (server); Tumbleweed Secure Mail Server 5. x; Cloudmark Authority 2. x; Wireless (Blackberry); SMTP; MIME; LISTSERV 1. 8 x Application Server Hardware Direction as dictated by the GSA Hardware BPA (http: //hwbpa. gsa. gov) Infrastructure Management Enterprise-Wide Resource Management – Help Desk: Support Magic, Remedy, Unicenter AHD Push: SMS, Veritas Wininstall, Unicenter SDO, Netwizard, Zen Works Remote Control: SMS, PC Anywhere, Proxy, Netwizard, Unicenter RCO, PC Telecommute Asset Management: Support Magic, SMS, Computrace, Unicenter AMO, Veritas Winland, Dell Open Manage Client .
GSA Standards Profile (cont’d) SERVICE AREA Infrastructure Services (cont’d) SERVICE Data Center Environment STANDARD Not defined at this time Electronic Messaging - IBM Lotus Notes 5. x & 6. x (client); IBM Lotus Domino 5. x & 6. x (server); Tumbleweed Secure Mail Server 5. x; Cloudmark Authority 2. x; Wireless (Blackberry); SMTP; MIME; LISTSERV 1. 8 x Application Server Hardware Direction as dictated by the GSA Hardware BPA (http: //hwbpa. gsa. gov) Infrastructure Management Enterprise-Wide Resource Management – Help Desk: Support Magic, Remedy, Unicenter AHD Push: SMS, Veritas Wininstall, Unicenter SDO, Netwizard, Zen Works Remote Control: SMS, PC Anywhere, Proxy, Netwizard, Unicenter RCO, PC Telecommute Asset Management: Support Magic, SMS, Computrace, Unicenter AMO, Veritas Winland, Dell Open Manage Client .
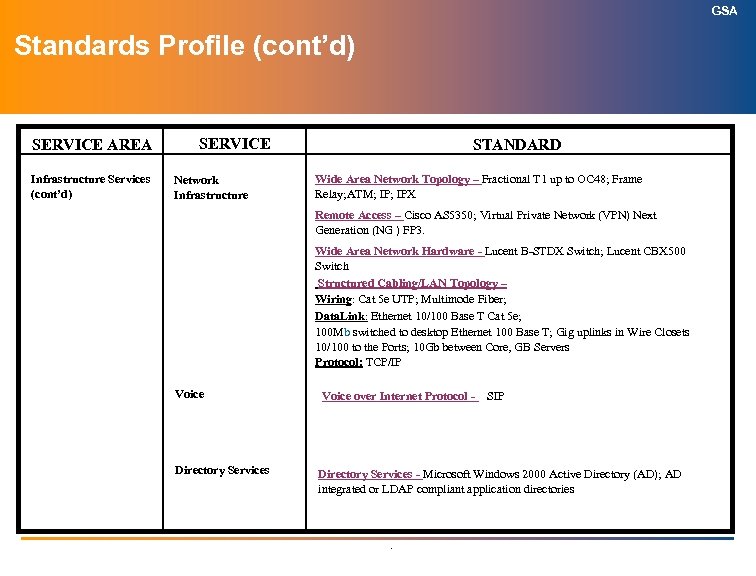 GSA Standards Profile (cont’d) SERVICE AREA Infrastructure Services (cont’d) SERVICE Network Infrastructure STANDARD Wide Area Network Topology – Fractional T 1 up to OC 48; Frame Relay; ATM; IPX Remote Access – Cisco AS 5350; Virtual Private Network (VPN) Next Generation (NG ) FP 3. Wide Area Network Hardware - Lucent B-STDX Switch; Lucent CBX 500 Switch Structured Cabling/LAN Topology – Wiring: Cat 5 e UTP; Multimode Fiber; Data. Link: Ethernet 10/100 Base T Cat 5 e; 100 Mb switched to desktop Ethernet 100 Base T; Gig uplinks in Wire Closets 10/100 to the Ports; 10 Gb between Core, GB Servers Protocol; TCP/IP Voice Directory Services Voice over Internet Protocol - SIP Directory Services - Microsoft Windows 2000 Active Directory (AD); AD integrated or LDAP compliant application directories .
GSA Standards Profile (cont’d) SERVICE AREA Infrastructure Services (cont’d) SERVICE Network Infrastructure STANDARD Wide Area Network Topology – Fractional T 1 up to OC 48; Frame Relay; ATM; IPX Remote Access – Cisco AS 5350; Virtual Private Network (VPN) Next Generation (NG ) FP 3. Wide Area Network Hardware - Lucent B-STDX Switch; Lucent CBX 500 Switch Structured Cabling/LAN Topology – Wiring: Cat 5 e UTP; Multimode Fiber; Data. Link: Ethernet 10/100 Base T Cat 5 e; 100 Mb switched to desktop Ethernet 100 Base T; Gig uplinks in Wire Closets 10/100 to the Ports; 10 Gb between Core, GB Servers Protocol; TCP/IP Voice Directory Services Voice over Internet Protocol - SIP Directory Services - Microsoft Windows 2000 Active Directory (AD); AD integrated or LDAP compliant application directories .


