6864d2e0a3c2f2db4e7f7a1545850960.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Technical Meeting on Implementation of E-Learning Platforms for Nuclear Education and. Training (ANENT) Nuclear Education and Training in Vietnam - Status and Challenges 13– 17 May 2013, Jakarta, Indonesia Nguyen Thi Yen Ninh Vietnam Atomic Energy Agency (VAEA) Tel: +84 -4 -38263251/+84 -(0)904364715 Fax: +84 -4 -39412970 Emai: ntyninh@most. gov. vn; nguyenthiyenninh@yahoo. com 1
Technical Meeting on Implementation of E-Learning Platforms for Nuclear Education and. Training (ANENT) Nuclear Education and Training in Vietnam - Status and Challenges 13– 17 May 2013, Jakarta, Indonesia Nguyen Thi Yen Ninh Vietnam Atomic Energy Agency (VAEA) Tel: +84 -4 -38263251/+84 -(0)904364715 Fax: +84 -4 -39412970 Emai: ntyninh@most. gov. vn; nguyenthiyenninh@yahoo. com 1
 Outlines 1. Brief Introduction on NPP in Vietnam 2. Education and Training to support NPP in Vietnam 3. Conclusion 2
Outlines 1. Brief Introduction on NPP in Vietnam 2. Education and Training to support NPP in Vietnam 3. Conclusion 2
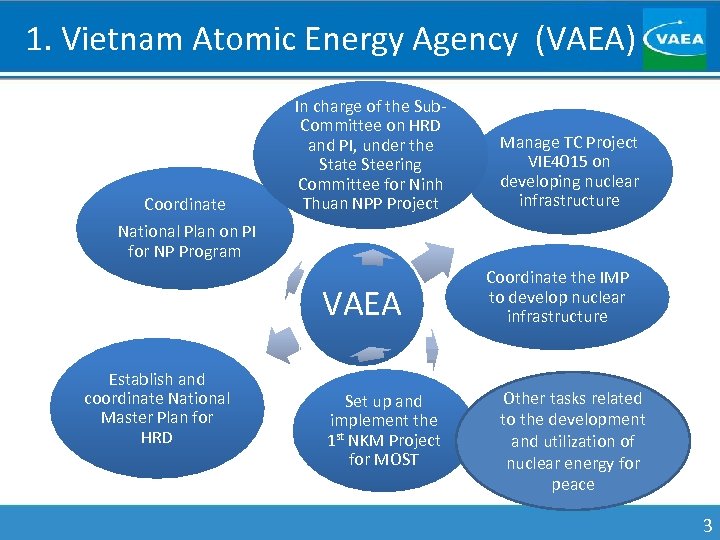 1. Vietnam Atomic Energy Agency (VAEA) Coordinate National Plan on PI for NP Program In charge of the Sub. Committee on HRD and PI, under the State Steering Committee for Ninh Thuan NPP Project VAEA Establish and coordinate National Master Plan for HRD Set up and implement the 1 st NKM Project for MOST Manage TC Project VIE 4015 on developing nuclear infrastructure Coordinate the IMP to develop nuclear infrastructure Other tasks related to the development and utilization of nuclear energy for peace 3
1. Vietnam Atomic Energy Agency (VAEA) Coordinate National Plan on PI for NP Program In charge of the Sub. Committee on HRD and PI, under the State Steering Committee for Ninh Thuan NPP Project VAEA Establish and coordinate National Master Plan for HRD Set up and implement the 1 st NKM Project for MOST Manage TC Project VIE 4015 on developing nuclear infrastructure Coordinate the IMP to develop nuclear infrastructure Other tasks related to the development and utilization of nuclear energy for peace 3
 2. Brief Introduction of Nuclear Power Program in Vietnam 4
2. Brief Introduction of Nuclear Power Program in Vietnam 4
 Overview: Nuclear Option “Development Program Orientation for Nuclear Power in Vietnam up to 2030” Nuclear Power – Solution for – National energy security; – Increasing power demand; – Environmental protection; – For the development of science and technology. 5
Overview: Nuclear Option “Development Program Orientation for Nuclear Power in Vietnam up to 2030” Nuclear Power – Solution for – National energy security; – Increasing power demand; – Environmental protection; – For the development of science and technology. 5
 Ninh Thuan NPP Project • Ninh Thuan: – Area: 3, 360. 1 km 2 – Population: 911, 600 (2004) – Density: 271, 3/km 2 • 1 st Plant: Phuoc Dinh – 2 reactors (2020, 2021) – 2, 000 MW • 2 nd Plant: Vinh Hai – 2 reactors (2021, 2022) – 2, 000 MW 6
Ninh Thuan NPP Project • Ninh Thuan: – Area: 3, 360. 1 km 2 – Population: 911, 600 (2004) – Density: 271, 3/km 2 • 1 st Plant: Phuoc Dinh – 2 reactors (2020, 2021) – 2, 000 MW • 2 nd Plant: Vinh Hai – 2 reactors (2021, 2022) – 2, 000 MW 6
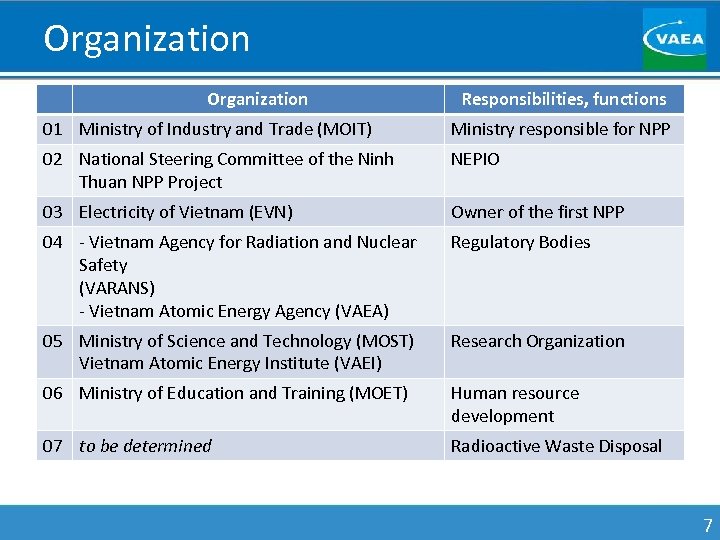 Organization Responsibilities, functions 01 Ministry of Industry and Trade (MOIT) Ministry responsible for NPP 02 National Steering Committee of the Ninh Thuan NPP Project NEPIO 03 Electricity of Vietnam (EVN) Owner of the first NPP 04 - Vietnam Agency for Radiation and Nuclear Safety (VARANS) - Vietnam Atomic Energy Agency (VAEA) Regulatory Bodies 05 Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute (VAEI) Research Organization 06 Ministry of Education and Training (MOET) Human resource development 07 to be determined Radioactive Waste Disposal 7
Organization Responsibilities, functions 01 Ministry of Industry and Trade (MOIT) Ministry responsible for NPP 02 National Steering Committee of the Ninh Thuan NPP Project NEPIO 03 Electricity of Vietnam (EVN) Owner of the first NPP 04 - Vietnam Agency for Radiation and Nuclear Safety (VARANS) - Vietnam Atomic Energy Agency (VAEA) Regulatory Bodies 05 Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute (VAEI) Research Organization 06 Ministry of Education and Training (MOET) Human resource development 07 to be determined Radioactive Waste Disposal 7
 Strategy: Documentation 2006 2007 2008 2010 • Strategy for Peaceful Utilization of Atomic Energy up to 2020 • Master Plan for the Implementation of the Strategy • Strategy for Energy Development up to 2020, with a Vision to 2050 • Atomic Energy Law (Law N° 18/2008/QH-12) • Decree for the Establishment of the National Steering Committee of the Ninh Thuan NPP Project • Development Program Orientation for Nuclear Power in Vietnam up to 2030 • Master Project for the Development and Application of Atomic Energy for Peaceful Use up to 2020 • National Project for the Training and Development of Human Resource for Atomic Energy 8
Strategy: Documentation 2006 2007 2008 2010 • Strategy for Peaceful Utilization of Atomic Energy up to 2020 • Master Plan for the Implementation of the Strategy • Strategy for Energy Development up to 2020, with a Vision to 2050 • Atomic Energy Law (Law N° 18/2008/QH-12) • Decree for the Establishment of the National Steering Committee of the Ninh Thuan NPP Project • Development Program Orientation for Nuclear Power in Vietnam up to 2030 • Master Project for the Development and Application of Atomic Energy for Peaceful Use up to 2020 • National Project for the Training and Development of Human Resource for Atomic Energy 8
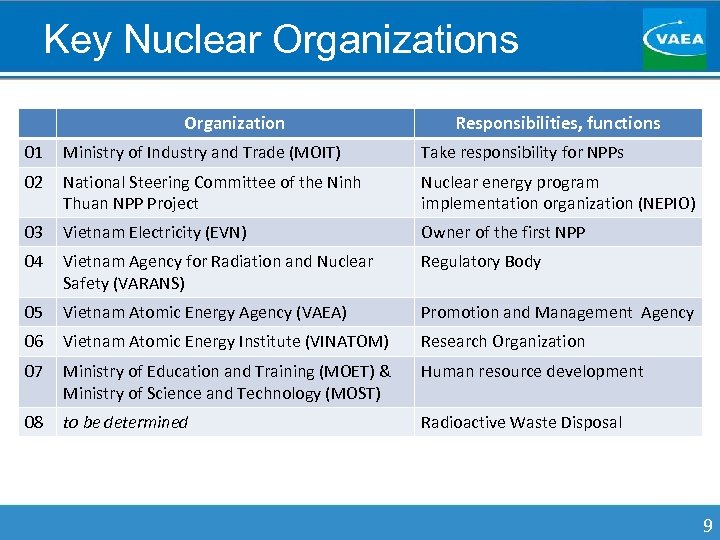 Key Nuclear Organizations Organization Responsibilities, functions 01 Ministry of Industry and Trade (MOIT) Take responsibility for NPPs 02 National Steering Committee of the Ninh Thuan NPP Project Nuclear energy program implementation organization (NEPIO) 03 Vietnam Electricity (EVN) Owner of the first NPP 04 Vietnam Agency for Radiation and Nuclear Safety (VARANS) Regulatory Body 05 Vietnam Atomic Energy Agency (VAEA) Promotion and Management Agency 06 Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute (VINATOM) Research Organization 07 Ministry of Education and Training (MOET) & Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) Human resource development 08 to be determined Radioactive Waste Disposal 9
Key Nuclear Organizations Organization Responsibilities, functions 01 Ministry of Industry and Trade (MOIT) Take responsibility for NPPs 02 National Steering Committee of the Ninh Thuan NPP Project Nuclear energy program implementation organization (NEPIO) 03 Vietnam Electricity (EVN) Owner of the first NPP 04 Vietnam Agency for Radiation and Nuclear Safety (VARANS) Regulatory Body 05 Vietnam Atomic Energy Agency (VAEA) Promotion and Management Agency 06 Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute (VINATOM) Research Organization 07 Ministry of Education and Training (MOET) & Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) Human resource development 08 to be determined Radioactive Waste Disposal 9
 2. Education and Training to Support Nuclear Power Program in Vietnam 10
2. Education and Training to Support Nuclear Power Program in Vietnam 10
 2. Education and Training to Support NP Program in Vietnam • National HRD Scheme in the Field of Atomic Energy up to 2020: • Approved: 16/8/2010 (Prime Minister’s Decision No. 1558/QĐ-TTg) • Total Investment: 3, 000 bil. VND (~150 mil. USD) • For nuclear power projects: • Ø Each year: 240 engineers, bachelors, 35 masters and Ph. Ds (including 20 foreign-trained engineers, bachelors, 15 masters and Ph. Ds) Ø Up to 2020: 2, 400 engineers, 350 masters and Ph. D specialized in nuclear power (including 200 engineers, 150 masters and Ph. D trained abroad) For other applications of atomic energy: Ø Each year: 65 engineers and bachelors, 35 masters and Ph. Ds (including 30 foreign-trained engineers, bachelors, 17 masters and Ph. Ds) Ø Up to 2020: 650 engineers, 250 masters, Ph. Ds (including 150 engineers, 100 masters and Ph. Ds trained abroad) 11
2. Education and Training to Support NP Program in Vietnam • National HRD Scheme in the Field of Atomic Energy up to 2020: • Approved: 16/8/2010 (Prime Minister’s Decision No. 1558/QĐ-TTg) • Total Investment: 3, 000 bil. VND (~150 mil. USD) • For nuclear power projects: • Ø Each year: 240 engineers, bachelors, 35 masters and Ph. Ds (including 20 foreign-trained engineers, bachelors, 15 masters and Ph. Ds) Ø Up to 2020: 2, 400 engineers, 350 masters and Ph. D specialized in nuclear power (including 200 engineers, 150 masters and Ph. D trained abroad) For other applications of atomic energy: Ø Each year: 65 engineers and bachelors, 35 masters and Ph. Ds (including 30 foreign-trained engineers, bachelors, 17 masters and Ph. Ds) Ø Up to 2020: 650 engineers, 250 masters, Ph. Ds (including 150 engineers, 100 masters and Ph. Ds trained abroad) 11
 National Steering Committee for HRD Ø Chairman: Deputy Prime Minister Ø Permanent Deputy Chairman: Minister of Education and Training Ø Members: – Deputy Ministers of Science and Technology; Industry and Trade; Agriculture and Rural Development; Health; Finance; Planning and Investment; Internal Affairs – CEO of EVN Ø Direction Board of the National Planning (established: 8/2011) – Head: Deputy Minister of Education and Training 12
National Steering Committee for HRD Ø Chairman: Deputy Prime Minister Ø Permanent Deputy Chairman: Minister of Education and Training Ø Members: – Deputy Ministers of Science and Technology; Industry and Trade; Agriculture and Rural Development; Health; Finance; Planning and Investment; Internal Affairs – CEO of EVN Ø Direction Board of the National Planning (established: 8/2011) – Head: Deputy Minister of Education and Training 12
 Allocation for Education and Training 1. Education and training for 3 purposes: – Certificate education: by MOET – Education training for R&D institutions, management and regulatory body: by MOST – Education and training for utility: by EVN (Training at VAEI, VARANS, EVN). 2. Overseas Education and Training • Through IAEA’s assistance: via TC projects • Through bilateral cooperation with Russia, Japan, Korea, France and other countries. • By EPC (Engineering, Procurement and Construction) contract with vendors. 13
Allocation for Education and Training 1. Education and training for 3 purposes: – Certificate education: by MOET – Education training for R&D institutions, management and regulatory body: by MOST – Education and training for utility: by EVN (Training at VAEI, VARANS, EVN). 2. Overseas Education and Training • Through IAEA’s assistance: via TC projects • Through bilateral cooperation with Russia, Japan, Korea, France and other countries. • By EPC (Engineering, Procurement and Construction) contract with vendors. 13
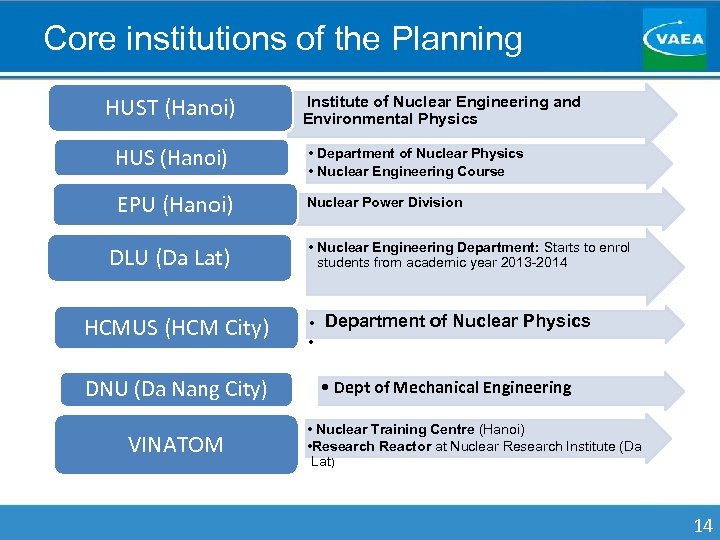 Core institutions of the Planning HUST (Hanoi) HUS (Hanoi) EPU (Hanoi) DLU (Da Lat) HCMUS (HCM City) DNU (Da Nang City) VINATOM • Institute of Nuclear Engineering and Environmental Physics • Department of Nuclear Physics • Nuclear Engineering Course • Nuclear Power Division • Nuclear Engineering Department: Starts to enrol students from academic year 2013 -2014 • • Department of Nuclear Physics • Dept of Mechanical Engineering • Nuclear Training Centre (Hanoi) • Research Reactor at Nuclear Research Institute (Da Lat) 14
Core institutions of the Planning HUST (Hanoi) HUS (Hanoi) EPU (Hanoi) DLU (Da Lat) HCMUS (HCM City) DNU (Da Nang City) VINATOM • Institute of Nuclear Engineering and Environmental Physics • Department of Nuclear Physics • Nuclear Engineering Course • Nuclear Power Division • Nuclear Engineering Department: Starts to enrol students from academic year 2013 -2014 • • Department of Nuclear Physics • Dept of Mechanical Engineering • Nuclear Training Centre (Hanoi) • Research Reactor at Nuclear Research Institute (Da Lat) 14
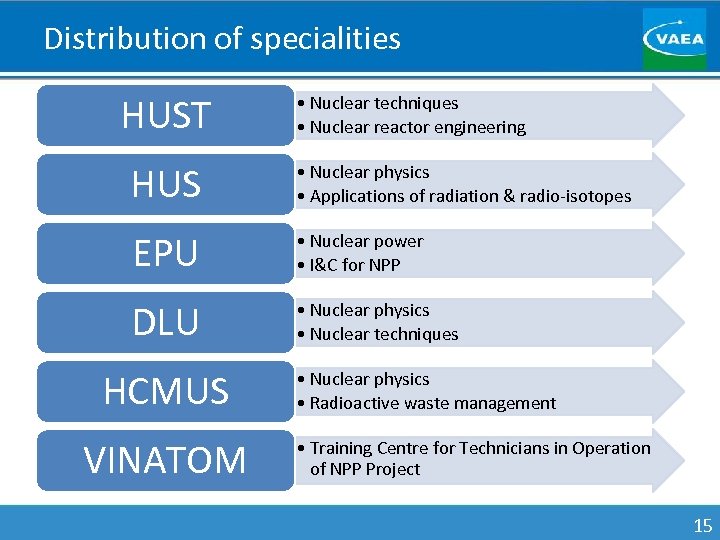 Distribution of specialities HUST • Nuclear techniques • Nuclear reactor engineering HUS • Nuclear physics • Applications of radiation & radio-isotopes EPU • Nuclear power • I&C for NPP DLU • Nuclear physics • Nuclear techniques HCMUS VINATOM • Nuclear physics • Radioactive waste management • Training Centre for Technicians in Operation of NPP Project 15
Distribution of specialities HUST • Nuclear techniques • Nuclear reactor engineering HUS • Nuclear physics • Applications of radiation & radio-isotopes EPU • Nuclear power • I&C for NPP DLU • Nuclear physics • Nuclear techniques HCMUS VINATOM • Nuclear physics • Radioactive waste management • Training Centre for Technicians in Operation of NPP Project 15
 Hanoi University of Science and Technology • School of Nuclear Engineering & Environmental Physics (SNEEP) – Enrolment: ~ 40 undergraduate students/year – Teaching staff: 18 (1 Ass. Prof. , 2 Ph. Ds) – Engineer programme (5 years): • Nuclear Power Engineering • Nuclear Applied Engineering • Other schools, faculties: Chemical Engineering SCE; Electrical Engineering SEE; Material Science and Technology FMST; Engineering Physics SEP; Heat Engineering and Refrigeration 16
Hanoi University of Science and Technology • School of Nuclear Engineering & Environmental Physics (SNEEP) – Enrolment: ~ 40 undergraduate students/year – Teaching staff: 18 (1 Ass. Prof. , 2 Ph. Ds) – Engineer programme (5 years): • Nuclear Power Engineering • Nuclear Applied Engineering • Other schools, faculties: Chemical Engineering SCE; Electrical Engineering SEE; Material Science and Technology FMST; Engineering Physics SEP; Heat Engineering and Refrigeration 16
 Hanoi University of Science (HUS) • Department of Nuclear Physics: – Teaching staff: 4 Assoc. Profs, 2 Ph. D, 8 Masters – Laboratories: Electrostatic Accelerator (Pelletron 5 SDH-2), gamma spectrometry, experimental & advanced nuclear physics, nuclear electronics, data processing, elementary particle physics, sample preparation • BSc Programmes: – Nuclear Physics: ~ 20 students/year (from 2012: 50 students/year) – Nuclear Engineering/Technology~ 40 students/year – Material Science: – Radiochemistry: ~ 10 students/year • Field of research: Particle Physics; Nuclear Structure; Environment Analysis and Radiation Safety; Nuclear Fuel; Nuclear Reactor Safety Analysis; Nuclear Reaction 17
Hanoi University of Science (HUS) • Department of Nuclear Physics: – Teaching staff: 4 Assoc. Profs, 2 Ph. D, 8 Masters – Laboratories: Electrostatic Accelerator (Pelletron 5 SDH-2), gamma spectrometry, experimental & advanced nuclear physics, nuclear electronics, data processing, elementary particle physics, sample preparation • BSc Programmes: – Nuclear Physics: ~ 20 students/year (from 2012: 50 students/year) – Nuclear Engineering/Technology~ 40 students/year – Material Science: – Radiochemistry: ~ 10 students/year • Field of research: Particle Physics; Nuclear Structure; Environment Analysis and Radiation Safety; Nuclear Fuel; Nuclear Reactor Safety Analysis; Nuclear Reaction 17
 Electric Power University (EPU) • Nuclear Power Division: – 58 students in nuclear engineering in 2010 -2011 (after 1 st year: top 3 have been sent to Russia) – Second group of in 2011 -2012 • Education scheme: – Domestic: 4. 5 years + 1 year of internship – Foreign cooperation (Russia, Czech, Japan): First 2 years in EPU (basic training, foreign language), last 2 years abroad, diploma will be issued by both EPU and its foreign partners. • Planned laboratories: – Nuclear physics and radiation safety: being deployed and will be lectured in the coming academic year – Advanced nuclear physics – Simulation system of NPPs – Critical assembly. 18
Electric Power University (EPU) • Nuclear Power Division: – 58 students in nuclear engineering in 2010 -2011 (after 1 st year: top 3 have been sent to Russia) – Second group of in 2011 -2012 • Education scheme: – Domestic: 4. 5 years + 1 year of internship – Foreign cooperation (Russia, Czech, Japan): First 2 years in EPU (basic training, foreign language), last 2 years abroad, diploma will be issued by both EPU and its foreign partners. • Planned laboratories: – Nuclear physics and radiation safety: being deployed and will be lectured in the coming academic year – Advanced nuclear physics – Simulation system of NPPs – Critical assembly. 18
 Da Lat University (DLU) • Faculties: Mathematics, Physics (nuclear physics: 5 -10 students/year), Chemistry (radiochemistry), Biology (radiobiology), Environmental Science, . . . • Nuclear Engineering Department: – Established in 2011 – First enrolment: 2012 -2013 – Curriculum (Bachelor of engineering): 4. 5 year, 150 credits (1 credit = 15 lecture hours/30 lab hours with 3 selective professional module: • Nuclear reactor engineering and Nuclear energy • Radio-environmental monitoring and control • Applied nuclear engineering – Teaching staff: 01 Assoc. Prof. (radiochemistry), 4 Ph. Ds (3 in nuclear physics, 1 in radiobiology) 19
Da Lat University (DLU) • Faculties: Mathematics, Physics (nuclear physics: 5 -10 students/year), Chemistry (radiochemistry), Biology (radiobiology), Environmental Science, . . . • Nuclear Engineering Department: – Established in 2011 – First enrolment: 2012 -2013 – Curriculum (Bachelor of engineering): 4. 5 year, 150 credits (1 credit = 15 lecture hours/30 lab hours with 3 selective professional module: • Nuclear reactor engineering and Nuclear energy • Radio-environmental monitoring and control • Applied nuclear engineering – Teaching staff: 01 Assoc. Prof. (radiochemistry), 4 Ph. Ds (3 in nuclear physics, 1 in radiobiology) 19
 Ho Chi Minh University of Science (HCMUS) • Department of Nuclear Physics: 40 students/year since 2010 (BSc prog. of 4 years), 25 -30 Master students/year, 1 -2 Ph. D students/year • Teaching staff: 25 (1 Professors, 9 Ph. Ds, 9 Masters) • Nuclear Engineering Programme: – Start from 2012 – Specialities: • Nuclear energy and power • Medical physics • Nuclear engineering • Laboratories (4): Basic radiation, advanced lab, nuclear electronic 20
Ho Chi Minh University of Science (HCMUS) • Department of Nuclear Physics: 40 students/year since 2010 (BSc prog. of 4 years), 25 -30 Master students/year, 1 -2 Ph. D students/year • Teaching staff: 25 (1 Professors, 9 Ph. Ds, 9 Masters) • Nuclear Engineering Programme: – Start from 2012 – Specialities: • Nuclear energy and power • Medical physics • Nuclear engineering • Laboratories (4): Basic radiation, advanced lab, nuclear electronic 20
 Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute - VINATOM • Nuclear Training Centre (Hanoi): – Started its operation in April 2011 – Activities done: organizing training courses (Complementary courses for MOST’s staff; Intensive courses in nuclear power, nuclear science and technology; Training course to grant certificate of practice for technical support activities) – Other activities: • Russian language course for students to be sent to Russia • Preparation for installation of training simulator • Preparation of textbook (translation from Russia, English, . . . ) • Nuclear Research Institute (Da Lat): – Research Reactor: • First criticality: 1963 • Thermal power: 500 k. W – Training centre for technicians 21
Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute - VINATOM • Nuclear Training Centre (Hanoi): – Started its operation in April 2011 – Activities done: organizing training courses (Complementary courses for MOST’s staff; Intensive courses in nuclear power, nuclear science and technology; Training course to grant certificate of practice for technical support activities) – Other activities: • Russian language course for students to be sent to Russia • Preparation for installation of training simulator • Preparation of textbook (translation from Russia, English, . . . ) • Nuclear Research Institute (Da Lat): – Research Reactor: • First criticality: 1963 • Thermal power: 500 k. W – Training centre for technicians 21
 On-going activities under MOST Ø Preparing a National Master Plan for HRD: - Conducting a survey on the status of manpower in nuclear-related organizations of different ministries (MOST, MOIT, MONRE, ENV, VARANS, VINATOM, VAEA etc. ) and assessing the need for nuclear workforce up to 2015, 2020 to report to National Steering Committees; - Making recommendations/suggestions and proposal for HRD strategy for Vietnam, aiming at fulfilment of the manpower need for the 1 st Nuclear Power Program (NPP); - Drafting a Master Plan for HRD and submit to the Government for approval ; - Coordinating the implementation of such Master Plan. 22
On-going activities under MOST Ø Preparing a National Master Plan for HRD: - Conducting a survey on the status of manpower in nuclear-related organizations of different ministries (MOST, MOIT, MONRE, ENV, VARANS, VINATOM, VAEA etc. ) and assessing the need for nuclear workforce up to 2015, 2020 to report to National Steering Committees; - Making recommendations/suggestions and proposal for HRD strategy for Vietnam, aiming at fulfilment of the manpower need for the 1 st Nuclear Power Program (NPP); - Drafting a Master Plan for HRD and submit to the Government for approval ; - Coordinating the implementation of such Master Plan. 22
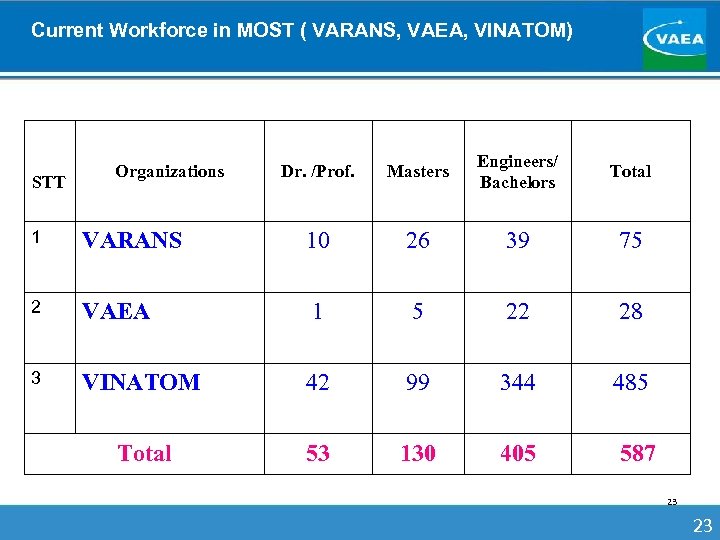 Current Workforce in MOST ( VARANS, VAEA, VINATOM) STT Organizations Dr. /Prof. Masters Engineers/ Bachelors Total 1 VARANS 10 26 39 75 2 VAEA 1 5 22 28 3 VINATOM 42 99 344 485 Total 53 130 405 587 23 23
Current Workforce in MOST ( VARANS, VAEA, VINATOM) STT Organizations Dr. /Prof. Masters Engineers/ Bachelors Total 1 VARANS 10 26 39 75 2 VAEA 1 5 22 28 3 VINATOM 42 99 344 485 Total 53 130 405 587 23 23
 HRD Plan for MOST Ø MOST: Establishing a plan to send staffs of VARANS, VINATOM, VAEA to study in Russia, Japan. Ø 2011 -2012: 26 persons studied basic nuclear safety in Japan (JNES) Ø 2011 -2012: 20 persons studied NPP technology (VVER 1000), legal documents, PI, etc. in Rusia Ø VARANS: Manpower Planning for Regulatory body Ø VINATOM: Manpower Planning for R&D and TSO, focusing on the HRD for Nuclear Science and Technology Center to be established in VINATOM; Ø VAEA: Preparing a National Master Plan for HRD in the field of atomic energy, incl. NPP; coordinating the activities of the MOST’s Working Group on HRD since 2012. 24
HRD Plan for MOST Ø MOST: Establishing a plan to send staffs of VARANS, VINATOM, VAEA to study in Russia, Japan. Ø 2011 -2012: 26 persons studied basic nuclear safety in Japan (JNES) Ø 2011 -2012: 20 persons studied NPP technology (VVER 1000), legal documents, PI, etc. in Rusia Ø VARANS: Manpower Planning for Regulatory body Ø VINATOM: Manpower Planning for R&D and TSO, focusing on the HRD for Nuclear Science and Technology Center to be established in VINATOM; Ø VAEA: Preparing a National Master Plan for HRD in the field of atomic energy, incl. NPP; coordinating the activities of the MOST’s Working Group on HRD since 2012. 24
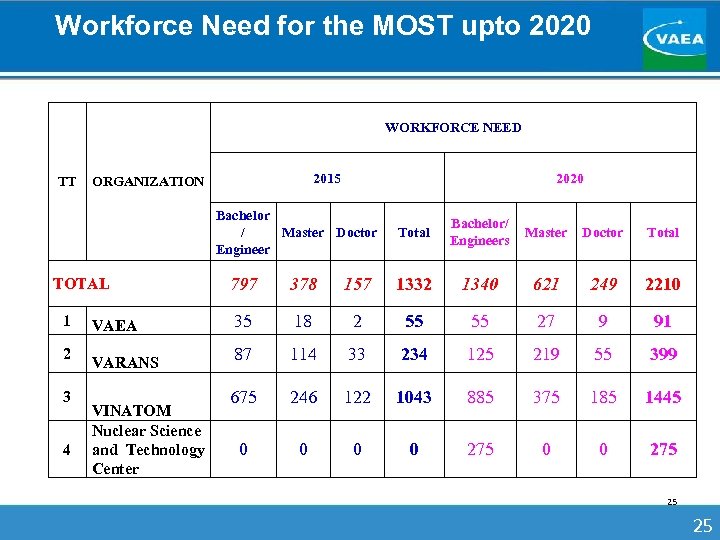 Workforce Need for the MOST upto 2020 WORKFORCE NEED TT 2015 ORGANIZATION 2020 Bachelor / Master Doctor Engineer 2 3 4 Bachelor/ Engineers Master Doctor Total 797 378 157 1332 1340 621 249 2210 VAEA 35 18 2 55 55 27 9 91 VARANS 87 114 33 234 125 219 55 399 675 246 122 1043 885 375 185 1445 0 0 275 TOTAL 1 Total VINATOM Nuclear Science and Technology Center 25 25
Workforce Need for the MOST upto 2020 WORKFORCE NEED TT 2015 ORGANIZATION 2020 Bachelor / Master Doctor Engineer 2 3 4 Bachelor/ Engineers Master Doctor Total 797 378 157 1332 1340 621 249 2210 VAEA 35 18 2 55 55 27 9 91 VARANS 87 114 33 234 125 219 55 399 675 246 122 1043 885 375 185 1445 0 0 275 TOTAL 1 Total VINATOM Nuclear Science and Technology Center 25 25
 On-going HRD activities under MOST Ø Collaborating with relevant ministries to issue policies on HRD in order to ensure qualified workforce for NPP. Ø Coordinating the establishment of Sub-Committee on Education and Public Communication for NPP. Ø Implementing annual training plans for R&D, TSO, Management and regulatory organisations belonging to MOST; Ø Strengthening the cooperation with IAEA and other countries on HRD; 26
On-going HRD activities under MOST Ø Collaborating with relevant ministries to issue policies on HRD in order to ensure qualified workforce for NPP. Ø Coordinating the establishment of Sub-Committee on Education and Public Communication for NPP. Ø Implementing annual training plans for R&D, TSO, Management and regulatory organisations belonging to MOST; Ø Strengthening the cooperation with IAEA and other countries on HRD; 26
 On-going HRD activities under other ministries Ø MOET: Overall coordinating the National HRD Scheme in the Field of Atomic Energy up to 2020 Ø EVN : has developed a more detailed Plan for “Human resource training for NPP projects in Ninh. Thuan”. Ø Other Ministries are in collaboration with MOST to set up their own plan for HRD under National HRD Plan in service of NPP Program. Ø EPU: curriculum on nuclear power technology is under completion. 27
On-going HRD activities under other ministries Ø MOET: Overall coordinating the National HRD Scheme in the Field of Atomic Energy up to 2020 Ø EVN : has developed a more detailed Plan for “Human resource training for NPP projects in Ninh. Thuan”. Ø Other Ministries are in collaboration with MOST to set up their own plan for HRD under National HRD Plan in service of NPP Program. Ø EPU: curriculum on nuclear power technology is under completion. 27
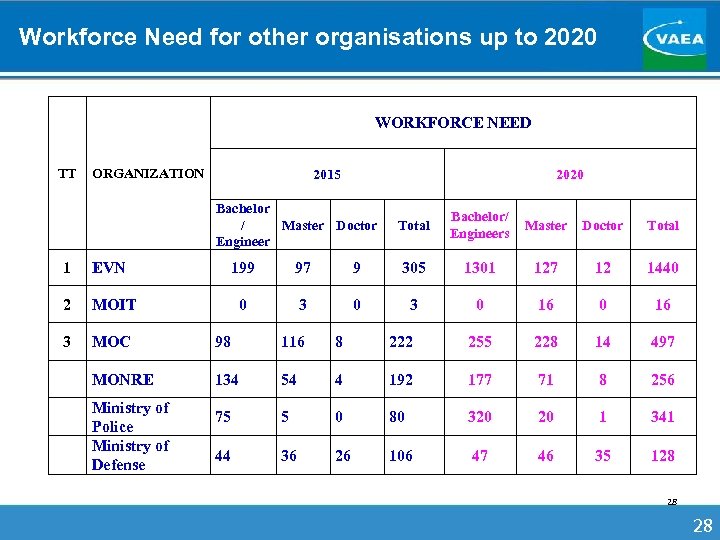 Workforce Need for other organisations up to 2020 WORKFORCE NEED TT ORGANIZATION 2015 2020 Bachelor / Master Doctor Engineer 1 EVN 2 MOIT 3 MOC 98 116 8 MONRE 134 54 75 44 Ministry of Police Ministry of Defense Total Bachelor/ Engineers Master Doctor Total 199 97 9 305 1301 127 12 1440 0 3 0 16 222 255 228 14 497 4 192 177 71 8 256 5 0 80 320 20 1 341 36 26 106 47 46 35 128 28 28
Workforce Need for other organisations up to 2020 WORKFORCE NEED TT ORGANIZATION 2015 2020 Bachelor / Master Doctor Engineer 1 EVN 2 MOIT 3 MOC 98 116 8 MONRE 134 54 75 44 Ministry of Police Ministry of Defense Total Bachelor/ Engineers Master Doctor Total 199 97 9 305 1301 127 12 1440 0 3 0 16 222 255 228 14 497 4 192 177 71 8 256 5 0 80 320 20 1 341 36 26 106 47 46 35 128 28 28
 International Cooperation (1) Ø 03/2010: MOET-ROSATOM MOU on the plan of professional training in atomic energy industry Ø 04/2011: MOET-EVN Cooperation Agreement on HRD for nuclear power Ø 10/2011: Mo. U on the cooperation to establish the Atomic Energy Information Center supported by ROSATOM (located in HUST & started operation from April 2012. Ø Students trained abroad: Ø 2010: 29 students were sent to Russia to study, specialized in NPP related issues (nuclear safety, development of legal documents, licensing, inspection, etc. . ) Ø 2011: 70 students were enrolled and sent to Russia for university education; Ø 2012: MOST’s staff were sent for short-training courses in ROSATOM Ø 2013: Specific courses are being negotiated. 29
International Cooperation (1) Ø 03/2010: MOET-ROSATOM MOU on the plan of professional training in atomic energy industry Ø 04/2011: MOET-EVN Cooperation Agreement on HRD for nuclear power Ø 10/2011: Mo. U on the cooperation to establish the Atomic Energy Information Center supported by ROSATOM (located in HUST & started operation from April 2012. Ø Students trained abroad: Ø 2010: 29 students were sent to Russia to study, specialized in NPP related issues (nuclear safety, development of legal documents, licensing, inspection, etc. . ) Ø 2011: 70 students were enrolled and sent to Russia for university education; Ø 2012: MOST’s staff were sent for short-training courses in ROSATOM Ø 2013: Specific courses are being negotiated. 29
 International Cooperation (2) • Cooperation with Russia – Specialist education in MPEI (financed by EVN); MEPh. I Obninsk (from 2010, co-financed by Vietnam & ROSATOM) – Other bilateral cooperation: VARANS-Rostechnadzor, VAST & VINATOM-JINR (Dubna), . . . Vietnamese students sent to MEPh. I Obninsk for nuc. eng. edu. • Cooperation with Japan – Long & successful history of cooperation in HRD in the field of atomic energy (with MEXT, METI, NISA, JNES, JAIF, JAEA, JAERI, RADA, nuclear companies) • Others: Korea, France, India, USA, FNCA, ANENT, . . . 16 staffs of VARANS trained at Japan Nuclear Safety Training Center (2011) 30
International Cooperation (2) • Cooperation with Russia – Specialist education in MPEI (financed by EVN); MEPh. I Obninsk (from 2010, co-financed by Vietnam & ROSATOM) – Other bilateral cooperation: VARANS-Rostechnadzor, VAST & VINATOM-JINR (Dubna), . . . Vietnamese students sent to MEPh. I Obninsk for nuc. eng. edu. • Cooperation with Japan – Long & successful history of cooperation in HRD in the field of atomic energy (with MEXT, METI, NISA, JNES, JAIF, JAEA, JAERI, RADA, nuclear companies) • Others: Korea, France, India, USA, FNCA, ANENT, . . . 16 staffs of VARANS trained at Japan Nuclear Safety Training Center (2011) 30
 Đạo đức công vụ của cán bộ trong ngành năng lượng nguyên tử 4 month- training course on nuclear safety at CICET (ROSATOM) 31
Đạo đức công vụ của cán bộ trong ngành năng lượng nguyên tử 4 month- training course on nuclear safety at CICET (ROSATOM) 31
 Đạo đức công vụ của cán bộ trong ngành năng lượng nguyên tử MOST’s staff at a JNES two-month training course on basic nuclear safety (2012) 32
Đạo đức công vụ của cán bộ trong ngành năng lượng nguyên tử MOST’s staff at a JNES two-month training course on basic nuclear safety (2012) 32
 International Cooperation (3) • Assistance from IAEA: TC Projects, RCA, other funding • 2012 -2013: 8 national TC Projects (VIE) & 42 regional/interregional TC projects (RAS&INT): 5 VIE &13 RAS projects are related to Nuc. Power • Types of assistance: Workshop, review meetings, training courses, expert missions, scientific visits, fellowship, equipment. 33
International Cooperation (3) • Assistance from IAEA: TC Projects, RCA, other funding • 2012 -2013: 8 national TC Projects (VIE) & 42 regional/interregional TC projects (RAS&INT): 5 VIE &13 RAS projects are related to Nuc. Power • Types of assistance: Workshop, review meetings, training courses, expert missions, scientific visits, fellowship, equipment. 33
 NKM activities in 2012 -2013 • • Collecting the reports from NRI on the manpower, scientific articles, documents related to Dalat Research reactor during the past years. Organizing a seminar on NKM in Dalat (12/2012) : 30 participants (VINATOM, NRI, CANTI, Dalat Univ. , VAEA) Circulating to get the comments and feedbacks from scientists/experts; Facilitating NRI to have plan for transfering NK to young staff (Seminars, OJT, . etc) as an example; Disseminating 3 IAEA’s documents on NKM to MOST, VAEA, VINATOM experts (drafted Vietnamese version) Preparing for the next Seminar in Hanoi in the 3 rd Quarter of 2013; Putting IAEA’s documents on NKM, E&T onto VAEA’s Website 34
NKM activities in 2012 -2013 • • Collecting the reports from NRI on the manpower, scientific articles, documents related to Dalat Research reactor during the past years. Organizing a seminar on NKM in Dalat (12/2012) : 30 participants (VINATOM, NRI, CANTI, Dalat Univ. , VAEA) Circulating to get the comments and feedbacks from scientists/experts; Facilitating NRI to have plan for transfering NK to young staff (Seminars, OJT, . etc) as an example; Disseminating 3 IAEA’s documents on NKM to MOST, VAEA, VINATOM experts (drafted Vietnamese version) Preparing for the next Seminar in Hanoi in the 3 rd Quarter of 2013; Putting IAEA’s documents on NKM, E&T onto VAEA’s Website 34
 NKM photos NKM SEMINARIN DALAT NRI 2012 35
NKM photos NKM SEMINARIN DALAT NRI 2012 35
 Recent VAEA activities in 2012 MEETING, WORKSHOPS, SEMINARS 2012 INIR Mission (4 -14 Dec. 2012) National WS on PI, (5/2012) NEPIO Seminar (8/2012) 36
Recent VAEA activities in 2012 MEETING, WORKSHOPS, SEMINARS 2012 INIR Mission (4 -14 Dec. 2012) National WS on PI, (5/2012) NEPIO Seminar (8/2012) 36
 CHALLENGES • The long-term availability of qualified human resources in view of the continued exploitation of nuclear energy; • The need for and the importance of training and teaching of skills through involvement in R&D in all subject areas (design and construction, nuclear safety, radiation protection, radioactive waste and spent fuel management, operation of installations and decommissioning); 37
CHALLENGES • The long-term availability of qualified human resources in view of the continued exploitation of nuclear energy; • The need for and the importance of training and teaching of skills through involvement in R&D in all subject areas (design and construction, nuclear safety, radiation protection, radioactive waste and spent fuel management, operation of installations and decommissioning); 37
 CHALLENGES • The aging problem within the workforce, and as a result, leading to a real risk of the loss of nuclear knowledge if no measures are taken; • Preservation of skills in the nuclear field requires a general effort involving public and private players including the nuclear industry itself; • Financing: high-cost investment needed for HRD program. 38
CHALLENGES • The aging problem within the workforce, and as a result, leading to a real risk of the loss of nuclear knowledge if no measures are taken; • Preservation of skills in the nuclear field requires a general effort involving public and private players including the nuclear industry itself; • Financing: high-cost investment needed for HRD program. 38
 4. CONCLUSIONS 39
4. CONCLUSIONS 39
 Conclusions (1) Ø Human Resource Development is a key factor to ensure the success of the implementation of the Strategy for Peaceful Utilization of atomic energy in Vietnam Ø Human resources needed for the development of atomic energy: to ensure competent workforce to meet the requirements of en-users: regulatory body, utilities and R&D institutions. Ø Policies for human resources of the nuclear power programme: • Measures/Incentives for students to study in Vietnam and overseas; • Policies for trainers and working staff in nuclear energy organizations; • Incentive/Attractive measures foreign /Vietnamese nuclear experts; 40
Conclusions (1) Ø Human Resource Development is a key factor to ensure the success of the implementation of the Strategy for Peaceful Utilization of atomic energy in Vietnam Ø Human resources needed for the development of atomic energy: to ensure competent workforce to meet the requirements of en-users: regulatory body, utilities and R&D institutions. Ø Policies for human resources of the nuclear power programme: • Measures/Incentives for students to study in Vietnam and overseas; • Policies for trainers and working staff in nuclear energy organizations; • Incentive/Attractive measures foreign /Vietnamese nuclear experts; 40
 IAEA’s recommendations Ø More work needs to be done to finalise the detailed training requirements for staff in the different organisations/functions and to determine how this training will be provided. Ø More coordination is needed between the ‘suppliers’ of human resources (MOET, Universities, Training Centres) and their ‘customers’ (EVN, VAEA, VARANS, VINATOM, etc. ) to ensure that supply matches demand in a timely manner. Ø The integrated strategy and plan for HRD needs to identify: all organisational human resource requirements; timing; qualifications; design and implementation of the education, training and experience programmes; coordination of the placement of students after graduation / training; and educational and employment incentives to aid long term retention. 41
IAEA’s recommendations Ø More work needs to be done to finalise the detailed training requirements for staff in the different organisations/functions and to determine how this training will be provided. Ø More coordination is needed between the ‘suppliers’ of human resources (MOET, Universities, Training Centres) and their ‘customers’ (EVN, VAEA, VARANS, VINATOM, etc. ) to ensure that supply matches demand in a timely manner. Ø The integrated strategy and plan for HRD needs to identify: all organisational human resource requirements; timing; qualifications; design and implementation of the education, training and experience programmes; coordination of the placement of students after graduation / training; and educational and employment incentives to aid long term retention. 41
 Thank you for your attention! 42
Thank you for your attention! 42


