d0783013f649758674dad004fb7ebb4b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Technical and design issues in implementation Dr. Mohamed Ally Director and Professor Centre for Distance Education Athabasca University Canada New Zealand Presentation January 2010
Technical and design issues in implementation Dr. Mohamed Ally Director and Professor Centre for Distance Education Athabasca University Canada New Zealand Presentation January 2010
 Examples of Educational Activities using Mobile Technology Make a concept map summarizing a chapter Keep track of class schedules, assignments, and grades Ø Increase content accessibility for those with disabilities Ø Use a tutorial for self-study Ø Take part in a collaborative simulation Ø Do research on the web Ø Participate in a collaborative project Ø Track a community service learning project Ø Ø
Examples of Educational Activities using Mobile Technology Make a concept map summarizing a chapter Keep track of class schedules, assignments, and grades Ø Increase content accessibility for those with disabilities Ø Use a tutorial for self-study Ø Take part in a collaborative simulation Ø Do research on the web Ø Participate in a collaborative project Ø Track a community service learning project Ø Ø
 How mobile technology help in Education Ø Education is more than one way delivery of information l l l Interactive Support Practice Practical application Build learning communities
How mobile technology help in Education Ø Education is more than one way delivery of information l l l Interactive Support Practice Practical application Build learning communities
 Interactivity in Learning Object interactivity (proactive inquiry) - objects (buttons, people, things) are activated by using a keypad or other pointing device. Ø Linear interactivity (reactive pacing) - the user is able to move (forwards or backwards) through a predetermined linear sequence. Ø Support interactivity (reactive inquiry) generalized and context-sensitive support (help messages and tutorial supports). Ø
Interactivity in Learning Object interactivity (proactive inquiry) - objects (buttons, people, things) are activated by using a keypad or other pointing device. Ø Linear interactivity (reactive pacing) - the user is able to move (forwards or backwards) through a predetermined linear sequence. Ø Support interactivity (reactive inquiry) generalized and context-sensitive support (help messages and tutorial supports). Ø
 Interactivity (cont’d) Update Interactivity - individual application components or events in which a dialogue is initiated between the learner and mobilegenerated content (practice with feedback) Ø Construct Interactivity - the creation of an instructional environment in which the learner is required to manipulate component objects to achieve specific goals (assemble an apparatus). Ø Reflective Interactivity - text responses to prompts or questions where learners can reflect on their response and make their own judgment as to its accuracy or correctness. Ø
Interactivity (cont’d) Update Interactivity - individual application components or events in which a dialogue is initiated between the learner and mobilegenerated content (practice with feedback) Ø Construct Interactivity - the creation of an instructional environment in which the learner is required to manipulate component objects to achieve specific goals (assemble an apparatus). Ø Reflective Interactivity - text responses to prompts or questions where learners can reflect on their response and make their own judgment as to its accuracy or correctness. Ø
 Interactivity (cont’d) Ø Simulation Interactivity - extends the role of the learner to that of controller or operator, where individual selections determine the learning sequence. Ø Hyperlinked Interactivity (proactive navigation) - the learner has access to a wealth of information, and may "travel" at will through that knowledge base.
Interactivity (cont’d) Ø Simulation Interactivity - extends the role of the learner to that of controller or operator, where individual selections determine the learning sequence. Ø Hyperlinked Interactivity (proactive navigation) - the learner has access to a wealth of information, and may "travel" at will through that knowledge base.
 Interactivity (cont’d) Non-Immersive Contextual Interactivity extends the various interactive levels into a complete virtual learning environment (mutual elaboration) in which the learner is able to work in a meaningful, job-related context. Ø Immersive Virtual Interactivity - provides an interactive environment in which the learner is projected into a complete mobilegenerated world which responds to individual movement and actions. Ø
Interactivity (cont’d) Non-Immersive Contextual Interactivity extends the various interactive levels into a complete virtual learning environment (mutual elaboration) in which the learner is able to work in a meaningful, job-related context. Ø Immersive Virtual Interactivity - provides an interactive environment in which the learner is projected into a complete mobilegenerated world which responds to individual movement and actions. Ø
 Why Mobile Learning at Athabasca University Ø Course material accessible on mobile devices. Ø Need to find out if this was meeting student requirements. Ø The purpose of this study was to determine the devices being used by students, their experience with course materials access, and how useful they thought using mobile devices to access course materials was.
Why Mobile Learning at Athabasca University Ø Course material accessible on mobile devices. Ø Need to find out if this was meeting student requirements. Ø The purpose of this study was to determine the devices being used by students, their experience with course materials access, and how useful they thought using mobile devices to access course materials was.
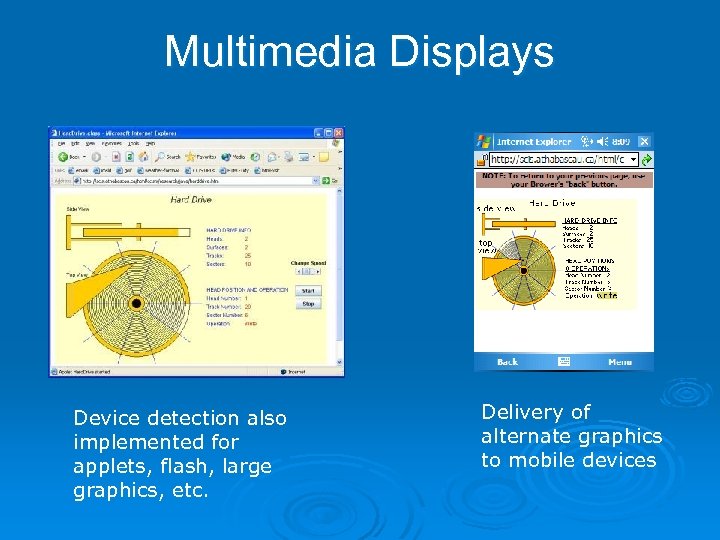
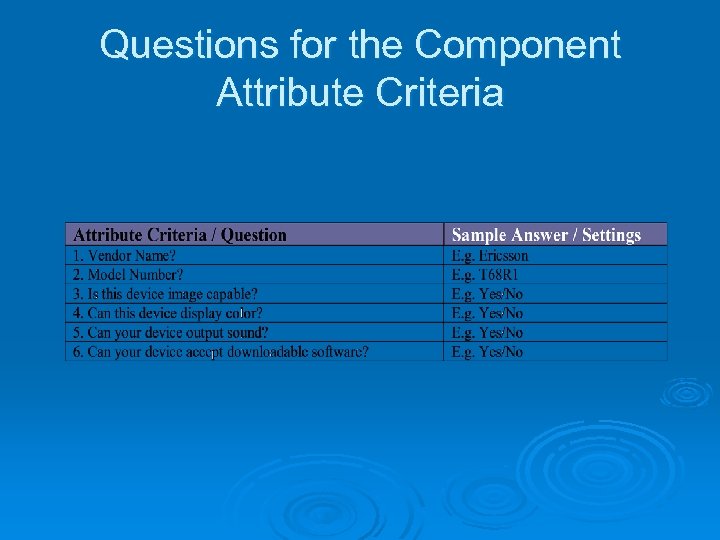
 Delivering to Specific Devices Device detection had been problematic because new devices and mobile OSs and browsers were constantly coming on stream. Ø Created problems for the device detection scheme used to determine the mobile device: Ø String user_agent = request. get. Header("user-agent"); Ø Changed to Java. Script to determine screen real estate: if (screen. width >= 800) { document. write('
Delivering to Specific Devices Device detection had been problematic because new devices and mobile OSs and browsers were constantly coming on stream. Ø Created problems for the device detection scheme used to determine the mobile device: Ø String user_agent = request. get. Header("user-agent"); Ø Changed to Java. Script to determine screen real estate: if (screen. width >= 800) { document. write('