f041a60b195f4151a6f425c358a2be66.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
Technical Analysis Bar Charts Point and Figure Charts Moving Averages
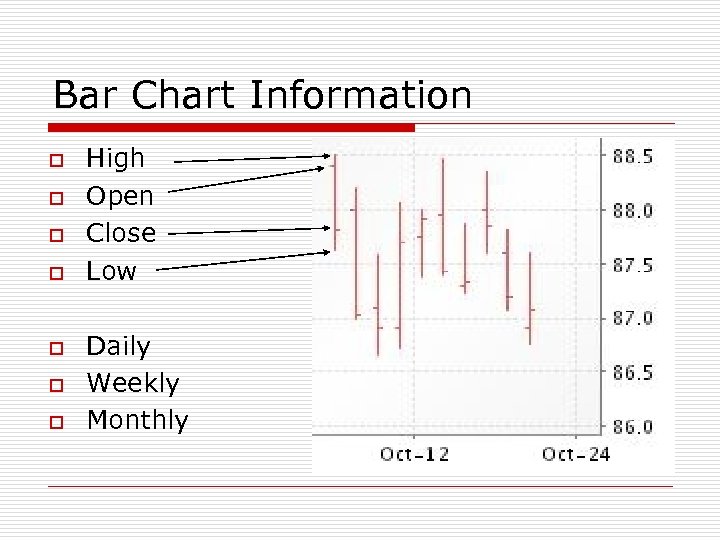
Bar Chart Information o o o o High Open Close Low Daily Weekly Monthly

Chart formations o o Trends Planes n n Other top and bottom formations Key Reversals Flags, Triangles and Pennants Gaps

Up Trend o Connect two or more daily price lows n o o Preferably 10 days apart When market closes below an uptrend line, a sell signal is generated Computer trading vs fundamental n n Computers may drive prices lower for a few days If fundamentals don’t support this, then prices will rally
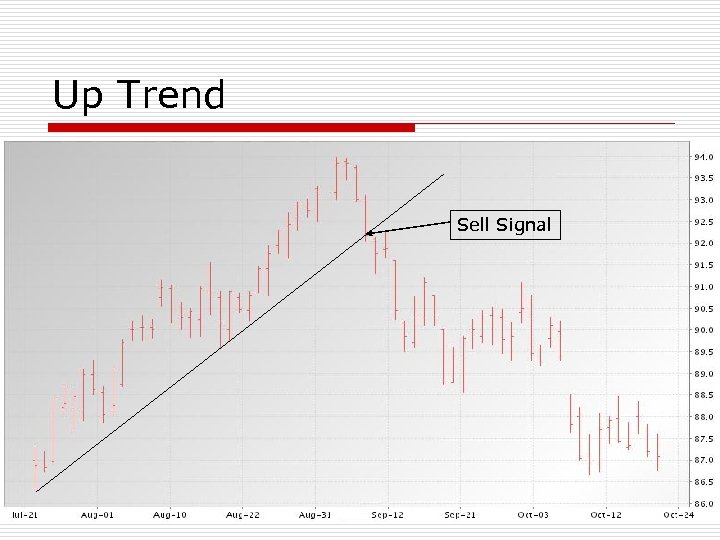
Up Trend Sell Signal

Down Trend o Connect two or more daily price highs n o o Preferably 10 days apart When market closes above a downtrend line, a buy signal is generated Computer trading vs fundamental n n Computers may drive prices higher for a few days If fundamentals don’t support this, then prices will decline
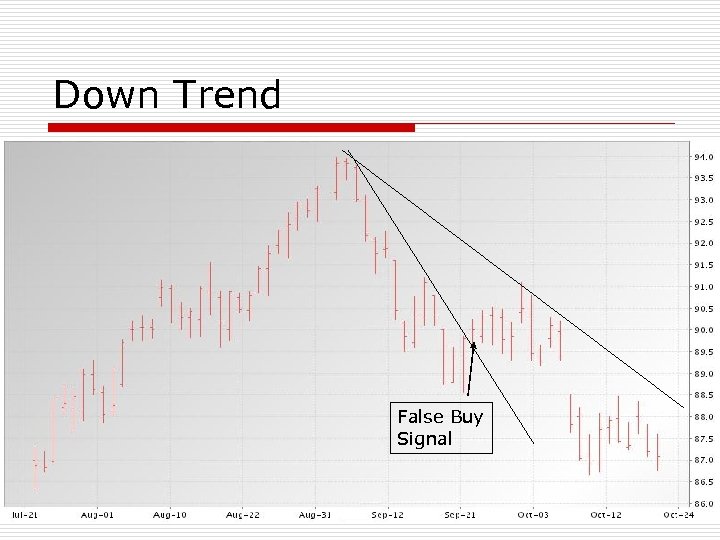
Down Trend False Buy Signal

Trend line market signals o Speculators n o Hedgers – Short n n o Buy and sell based on signals Place on sell signal May choose to offset on buy signal Hedgers – Long n n Place on buy signal May choose to offset on sell signal

Trend Line reliability o A close above a major down trend or below a major up trend will lead to a significant price move about 75% of the time

Resistant Planes o o Life-of-contract highs can be very difficult for market to penetrate Strong Fundamental conditions needed to move market above resistance Sell signal if market fails to take out resistance Buy signal if market closes above resistance (particularly 2 closes above)

Resistant Planes o o There also intermediate resistance planes These are not as hard to penetrate as life-of-contract highs are
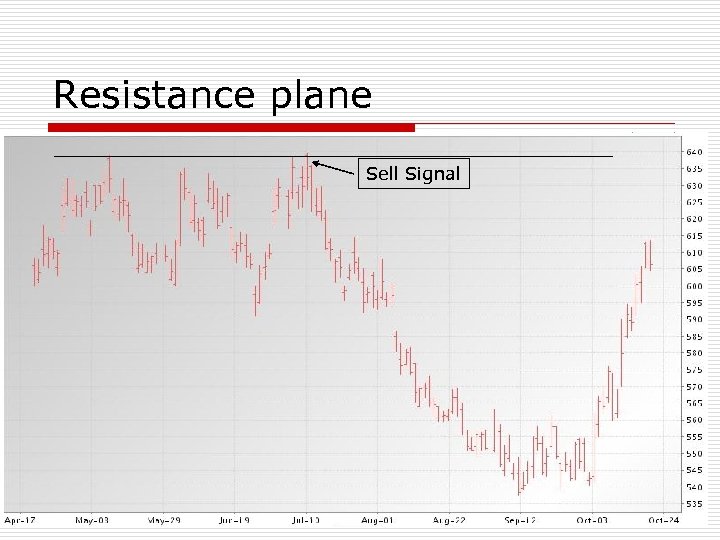
Resistance plane Sell Signal
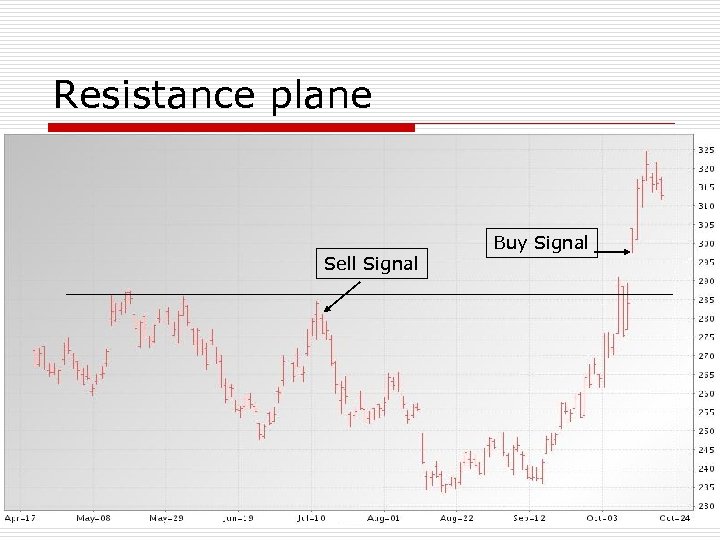
Resistance plane Sell Signal Buy Signal

Support Planes o o The mirror image of Resistance Planes Life-of-contract lows Buy signal if market fails to penetrate Sell signal if low is taken out
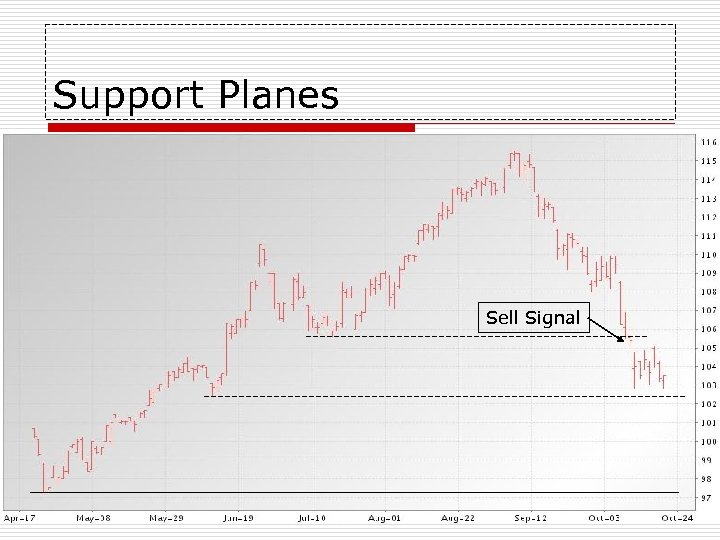
Support Planes Sell Signal

Hedgers and Technical Analysis o If understand trends and support and resistance planes: n n n Time placement of hedge Set realistic market targets Perhaps minimize margin calls

Other Bar Chart Formations o o o Double Top or Double Bottom Head and Shoulders Key Reversal Flags, Triangles and Pennants Gaps n Common, break away, measuring, exhaustion
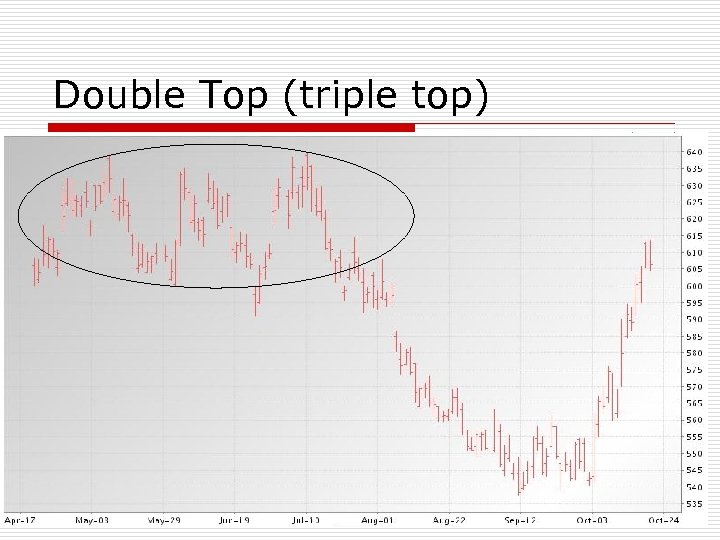
Double Top (triple top)
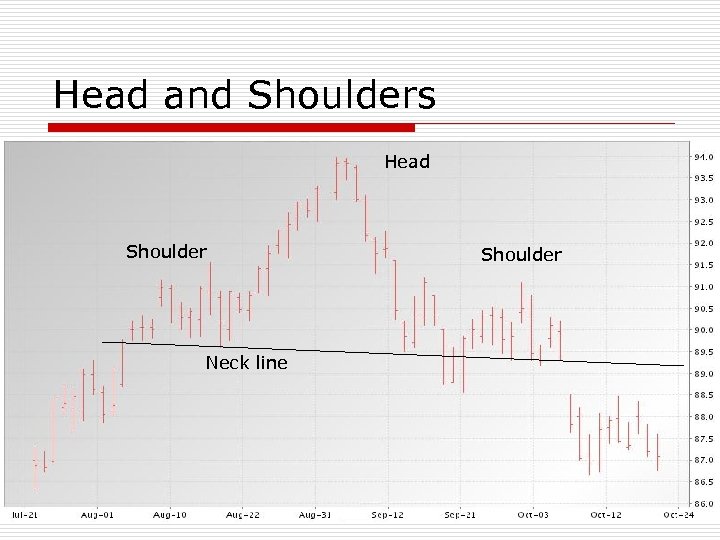
Head and Shoulders Head Shoulder Neck line Shoulder
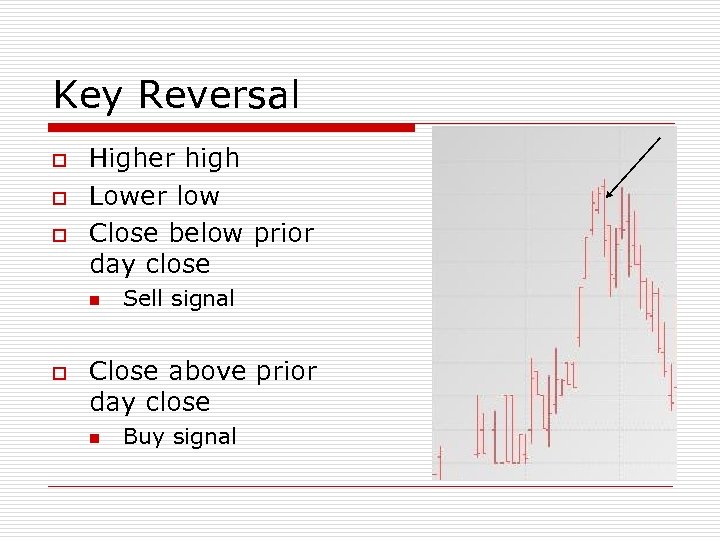
Key Reversal o o o Higher high Lower low Close below prior day close n o Sell signal Close above prior day close n Buy signal
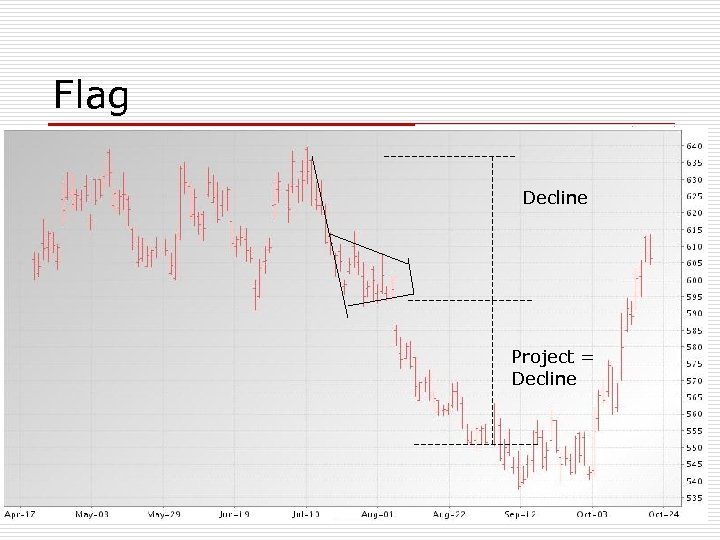
Flag Decline Project = Decline
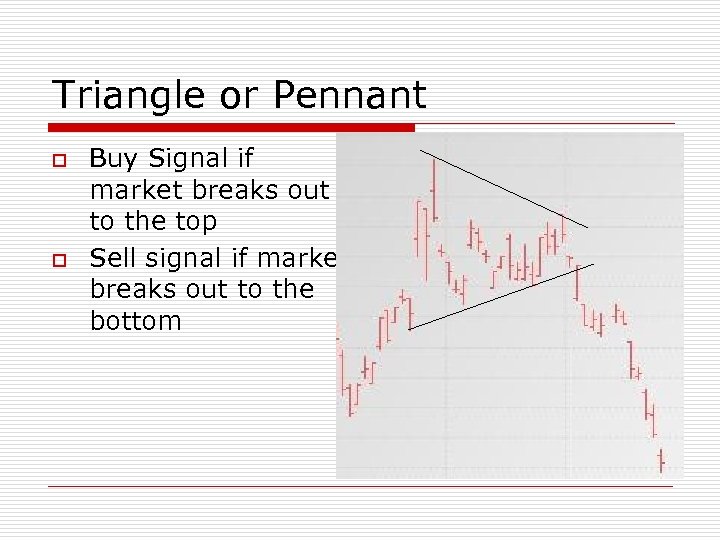
Triangle or Pennant o o Buy Signal if market breaks out to the top Sell signal if market breaks out to the bottom
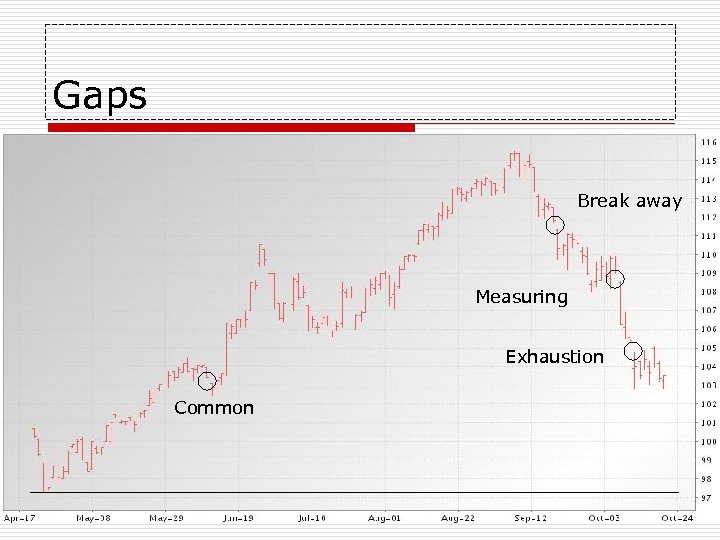
Gaps Break away Measuring Exhaustion Common
Complements to Chart Patterns o o o Trading Volume Open Interest Relative Strength Index (RSI)

Trading Volume o o o Barometer of level of intensity in the market If buy/sell signal occurs on a relatively high volume day, then it is more reliable High/low volume is relative to past trading and relative to specific contract

Guidelines for trading volume o o o Look at all months being traded for a particular commodity Interpret volume on limit up/down days very carefully Usually low prior to holiday, 3 day weekend, or major report

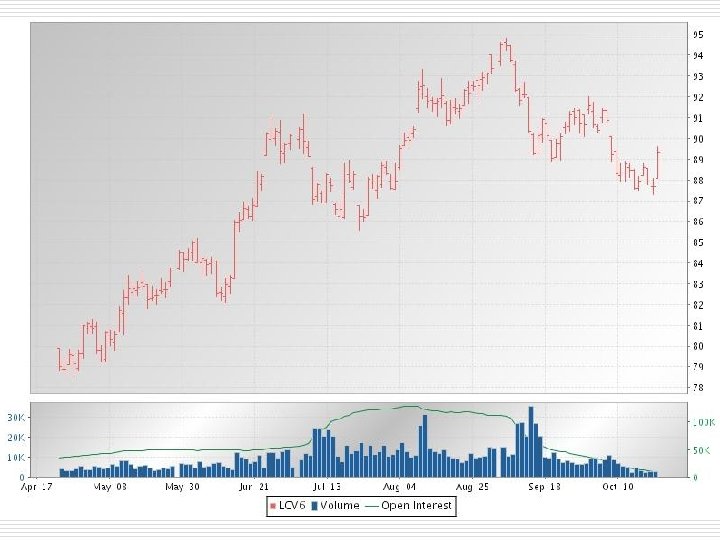
Open Interest o # of contracts that are outstanding n o No binding relationship between Open Interest and Trading Volume n o Have not been offset Day traders create volume, don’t change open interest Open Interest tends to peak and then decline prior to an uptrend reversal n Less reliable on downtrend reversal

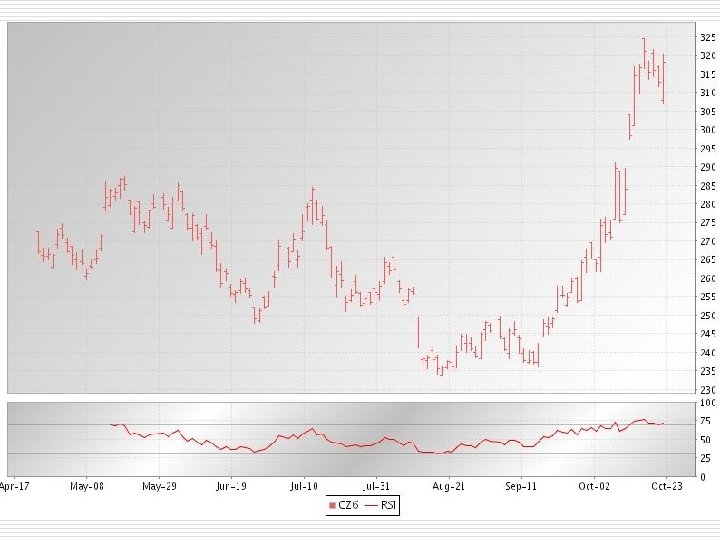
Relative Strength Index o o o Widely used measure of momentum in the market 14 day RSI is the most common To calculate n n n Record last 14 day price changes (closes) Sum the negative changes and positive changes and divide each by 14 to create (D) down average and (U) up average RSI=U/(U+D) * 100

RSI Market Indicator o RSI > 70 n o RSI < 30 n o o Market is thought to be over bought Market is thought to be over sold Numbers vary by commodity Major change in Supply or Demand may keep RSI above 70 or below 30 for an extended period of time

RSI example calculations o o Close 2. 40, 2. 38, 2. 36, 2. 40, 2. 44, 2. 42, 2. 44, 2. 48, 2. 56, 2. 48, 2. 52, 2. 50, 2. 46 Up. 02. 04. 08. 04 n o Down. 02. 02. 08. 02. 04 n o Up sum = 28/14 =2 Down sum = 22/14=1. 57 RSI = 2/(2+1. 57) * 100 = 56
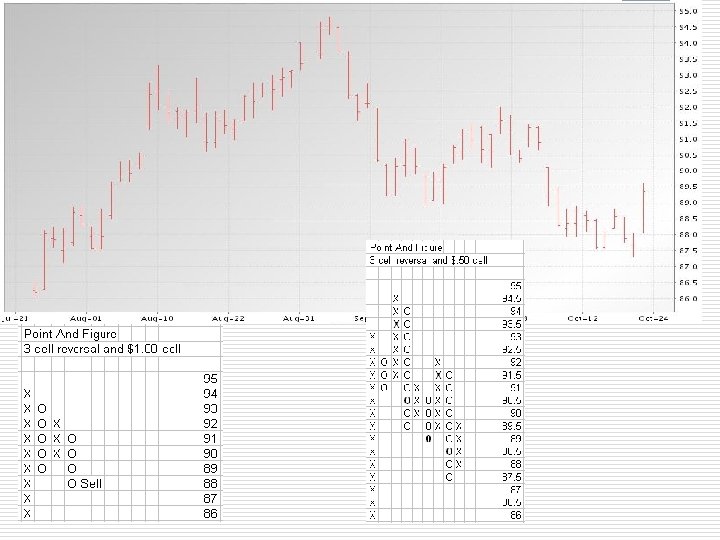
Point and Figure Charts o 2 CRITICAL parameters n n o o The cell size The reversal requirement Cell size – The value in terms of price increment for each cell Reversal requirement – Magnitude of price change required for a reversal
Point and Figure Charts o o o There is no time on chart X use to plot uptrending prices O use to plot downtrending prices Only use daily high or low, close doesn’t matter Buy/Sell signal generated when new Higher/Lower X/O is plotted

Moving Averages o May be a compliment to bar chart n n o Single Moving Average 40 -day Help signal turning points in market May be an alternative to bar chart n n n Two moving averages employed Example 3 -day and 10 -day Example 9 -day and 18 -day Sell signal when shorter cuts longer from top Buy signal when shorter cuts longer from bottom
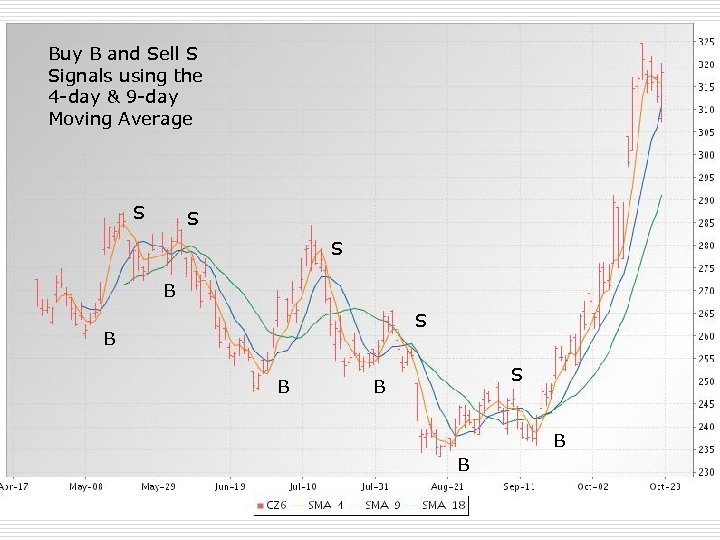
Buy B and Sell S Signals using the 4 -day & 9 -day Moving Average S S S B B B

Moving Averages o Advantages n n n o Provide clear market signals No guessing as to chart formation Good if there are trends in the data Disadvantage n n May generate multiple trades Don’t perform well in choppy (sideways) markets
Moving Average o Short Hedgers n n o Long Hedgers n n o Place on Sell signals Lift (offset) on Buy signals Place on Buy signals Lift (offset) on Sell signals Speculators n Buy and Sell and Offset on all signals

Technical Analysis Summary o o Technical Analysis does work It requires Work to make it work Need to study past technical analysis for several years worth of data on a particularly commodity before trading For hedgers n n Trends and Support/Resistance Planes Moving Averages
f041a60b195f4151a6f425c358a2be66.ppt