cb805d72f2c774c984fc06b4ac97e85c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Teaching Romanian Language in Hungarian Language Schools: Experiences, Conclusions and Questions Dr. Tódor Erika Mária
Teaching Romanian Language in Hungarian Language Schools: Experiences, Conclusions and Questions Dr. Tódor Erika Mária
 Contents Minorites in the Romanian education system Data from Hungarian language schools Types of bilingualism Developments in teaching Romanian as a nonnative language Significant principles of non-native teaching philosophy The profile of the Hungarian-Romanian speaker – features of verbal behaviour
Contents Minorites in the Romanian education system Data from Hungarian language schools Types of bilingualism Developments in teaching Romanian as a nonnative language Significant principles of non-native teaching philosophy The profile of the Hungarian-Romanian speaker – features of verbal behaviour
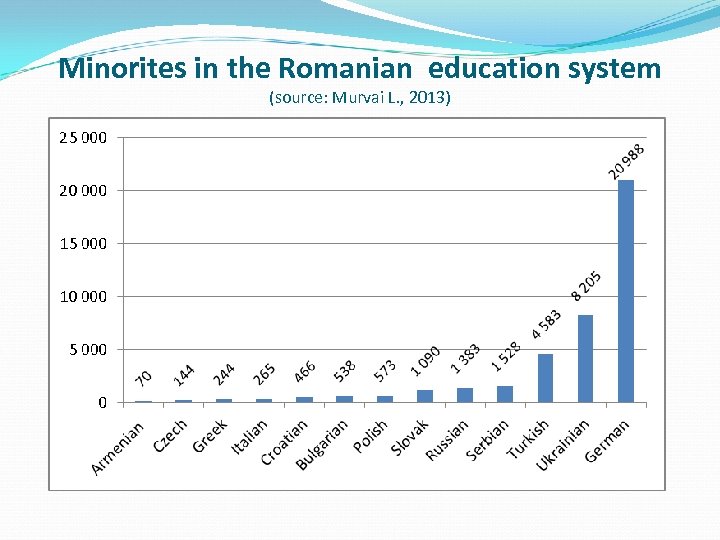 Minorites in the Romanian education system (source: Murvai L. , 2013)
Minorites in the Romanian education system (source: Murvai L. , 2013)
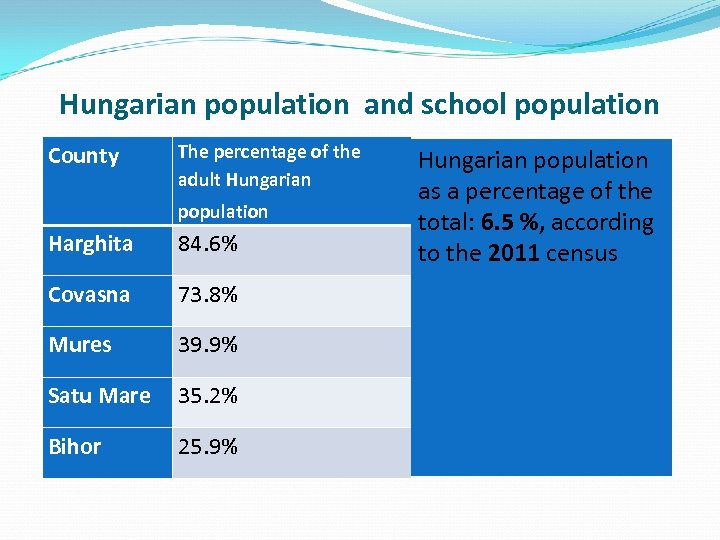 Hungarian population and school population County The percentage of the adult Hungarian population Harghita 84. 6% Covasna 73. 8% Mures 39. 9% Satu Mare 35. 2% Bihor 25. 9% Hungarian population as a percentage of the total: 6. 5 %, according to the 2011 census
Hungarian population and school population County The percentage of the adult Hungarian population Harghita 84. 6% Covasna 73. 8% Mures 39. 9% Satu Mare 35. 2% Bihor 25. 9% Hungarian population as a percentage of the total: 6. 5 %, according to the 2011 census
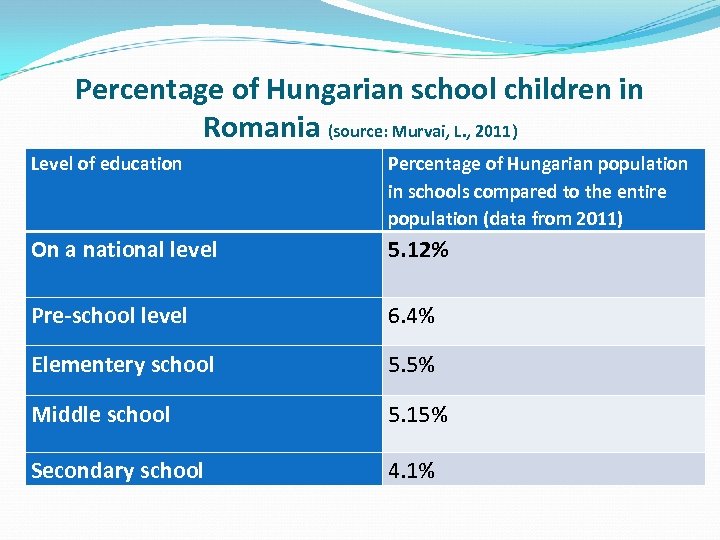 Percentage of Hungarian school children in Romania (source: Murvai, L. , 2011) Level of education Percentage of Hungarian population in schools compared to the entire population (data from 2011) On a national level Pre-school level 5. 12% Elementery school 5. 5% Middle school 5. 15% Secondary school 4. 1% 6. 4%
Percentage of Hungarian school children in Romania (source: Murvai, L. , 2011) Level of education Percentage of Hungarian population in schools compared to the entire population (data from 2011) On a national level Pre-school level 5. 12% Elementery school 5. 5% Middle school 5. 15% Secondary school 4. 1% 6. 4%
 Types of bilingualism (Horváth, I. , 2005 ) Nr. Types of bilingualism Percentage 1. Monolingualism 7. 6% 2. Asymmetric bilingualism 58. 8% 3. Balanced bilingualism 28. 8% 4. Subtractive bilingualism 1. 8% 5. Semilingualism 1. 4%
Types of bilingualism (Horváth, I. , 2005 ) Nr. Types of bilingualism Percentage 1. Monolingualism 7. 6% 2. Asymmetric bilingualism 58. 8% 3. Balanced bilingualism 28. 8% 4. Subtractive bilingualism 1. 8% 5. Semilingualism 1. 4%
 Educational failure, learning difficulty? “We were at the seaside, and we had to point to the things we wanted to buy…” (pupil, 5 th grade) “…if I travel by train, and Romanians ask me something, I do not speak, I tell them, I don’t know, I don’t speak Romanian… I would not speak. ” (pupil, 5 th grade) (focus group discussions with pupils in 2013 March-April)
Educational failure, learning difficulty? “We were at the seaside, and we had to point to the things we wanted to buy…” (pupil, 5 th grade) “…if I travel by train, and Romanians ask me something, I do not speak, I tell them, I don’t know, I don’t speak Romanian… I would not speak. ” (pupil, 5 th grade) (focus group discussions with pupils in 2013 March-April)
 School achievement 2014. Results of the mock test in Romanian language: (source: www. edu. ro) Exam passed: Harghita county: 36. 7% of the students Covasna county: 49. 1% of the students
School achievement 2014. Results of the mock test in Romanian language: (source: www. edu. ro) Exam passed: Harghita county: 36. 7% of the students Covasna county: 49. 1% of the students
 Obstacles to Romanian language learning ØNeither the educational policy, nor the content of the curriculum offers the opportunity for functional– pragmatic language acquisition. ØWhile designing the educational process, neither the linguistic, nor the cultural characteristics of students are taken into account. ØThe features of different language groups are not observed: compact/mass, diaspora, minority
Obstacles to Romanian language learning ØNeither the educational policy, nor the content of the curriculum offers the opportunity for functional– pragmatic language acquisition. ØWhile designing the educational process, neither the linguistic, nor the cultural characteristics of students are taken into account. ØThe features of different language groups are not observed: compact/mass, diaspora, minority
 Obstacles to Romanian language learning Ø Lack of interdisciplinary approach Ø Knowledge competences gained through education in their native language are not used (cultural and metacultural competences, language competences) Ø Lack of contrastive-comparative approach Ø Curriculum development is based on monolingual and monocultural logic.
Obstacles to Romanian language learning Ø Lack of interdisciplinary approach Ø Knowledge competences gained through education in their native language are not used (cultural and metacultural competences, language competences) Ø Lack of contrastive-comparative approach Ø Curriculum development is based on monolingual and monocultural logic.
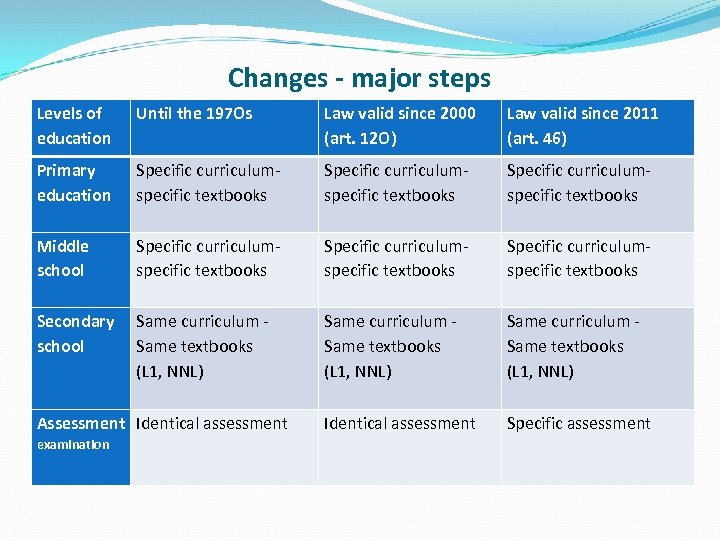 Changes - major steps Levels of education Until the 197 Os Law valid since 2000 (art. 12 O) Law valid since 2011 (art. 46) Primary education Specific curriculumspecific textbooks Middle school Specific curriculumspecific textbooks Secondary Same curriculum school Same textbooks (L 1, NNL) Same curriculum Same textbooks (L 1, NNL) Assessment Identical assessment Specific assessment examination
Changes - major steps Levels of education Until the 197 Os Law valid since 2000 (art. 12 O) Law valid since 2011 (art. 46) Primary education Specific curriculumspecific textbooks Middle school Specific curriculumspecific textbooks Secondary Same curriculum school Same textbooks (L 1, NNL) Same curriculum Same textbooks (L 1, NNL) Assessment Identical assessment Specific assessment examination
 Illuminating experiences ü The outlines of Romanian as non-native language (second language, environmental language): tailored methods for language teaching ü Introduction and making the concept behind the idea accepted: a specific teaching methodology ü Redefining scientific terminology in both languages
Illuminating experiences ü The outlines of Romanian as non-native language (second language, environmental language): tailored methods for language teaching ü Introduction and making the concept behind the idea accepted: a specific teaching methodology ü Redefining scientific terminology in both languages
 Illuminating experiences üResearch in the domain ü Conferences and publications ü Interdisciplinary networking ü Drafting curriculum based on the new approach (2006, 2012)
Illuminating experiences üResearch in the domain ü Conferences and publications ü Interdisciplinary networking ü Drafting curriculum based on the new approach (2006, 2012)
 Illuminating experiences ü Organizing teacher’s training ü Research in bilingual/multilingual behaviour, desciption of their specific situations
Illuminating experiences ü Organizing teacher’s training ü Research in bilingual/multilingual behaviour, desciption of their specific situations
 Profile of the Hungarian-Romanian speaker – features of verbal behaviour Linguistic interference Calques e. g. salt keeper for saltcellar, fishing stick for fishing rod (suport de sare –solniţă; băț de pescuit- undiță) Textbook
Profile of the Hungarian-Romanian speaker – features of verbal behaviour Linguistic interference Calques e. g. salt keeper for saltcellar, fishing stick for fishing rod (suport de sare –solniţă; băț de pescuit- undiță) Textbook
 Profile of the Hungarian-Romanian speaker – features of verbal behaviour Linguistic pseudo-creativity e. g. Through analogy: nouător for inovator (for innovator) Adoption/ adapting words from the native tongue e. g. Give me a canal, instead of ‘spoon’ (see Hun. kanál)
Profile of the Hungarian-Romanian speaker – features of verbal behaviour Linguistic pseudo-creativity e. g. Through analogy: nouător for inovator (for innovator) Adoption/ adapting words from the native tongue e. g. Give me a canal, instead of ‘spoon’ (see Hun. kanál)
 Socio-affective dimension of verbal behaviour Communicational anguish Fear of talking, fear of making mistakes Suppression of communicational intention Withdrawal into silence Displacement of communicational intention Code switching
Socio-affective dimension of verbal behaviour Communicational anguish Fear of talking, fear of making mistakes Suppression of communicational intention Withdrawal into silence Displacement of communicational intention Code switching
 Thank you for your attention! todor. erika@yahoo. com
Thank you for your attention! todor. erika@yahoo. com


