0f63a36b8436774a878642cd1ef983c1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Teaching methodologies and the Practical English challenge Simon Smith ELC Teacher & President’s Office Special Assistant 1
Teaching methodologies and the Practical English challenge Simon Smith ELC Teacher & President’s Office Special Assistant 1
 Waving my axe at Ban’s door? l l Methodology is TESOL! Inspiration for this workshop – l Lovely and David W Today – Methodology curriculum 2
Waving my axe at Ban’s door? l l Methodology is TESOL! Inspiration for this workshop – l Lovely and David W Today – Methodology curriculum 2
 Lang acq 101 l Acquisition – – l Learning – l l Gradual development Communicative situations Conscious process of accumulating knowledge Babies acquire language Long-term residents of a country acquire language 3
Lang acq 101 l Acquisition – – l Learning – l l Gradual development Communicative situations Conscious process of accumulating knowledge Babies acquire language Long-term residents of a country acquire language 3
 Language proficiency l l Acquisition usually leads to greater proficiency Some parts of the language are more difficult to acquire than others – – l l Conrad effect Think about linguistic strata Lateralization Teenagers are quicker at learning language (and math) than young children – Cognitive skills are important too 4
Language proficiency l l Acquisition usually leads to greater proficiency Some parts of the language are more difficult to acquire than others – – l l Conrad effect Think about linguistic strata Lateralization Teenagers are quicker at learning language (and math) than young children – Cognitive skills are important too 4
 Affective ( emotional) filter l l l A term used by Stephen Krashen A barrier to acquisition/learning What activates the filter? – – – – Teenage self-consciousness Embarrassment about making funny sounds No empathy with the foreign culture or its speakers Boring textbooks No interesting activities Bad classroom environment Exhausting schedule 5
Affective ( emotional) filter l l l A term used by Stephen Krashen A barrier to acquisition/learning What activates the filter? – – – – Teenage self-consciousness Embarrassment about making funny sounds No empathy with the foreign culture or its speakers Boring textbooks No interesting activities Bad classroom environment Exhausting schedule 5
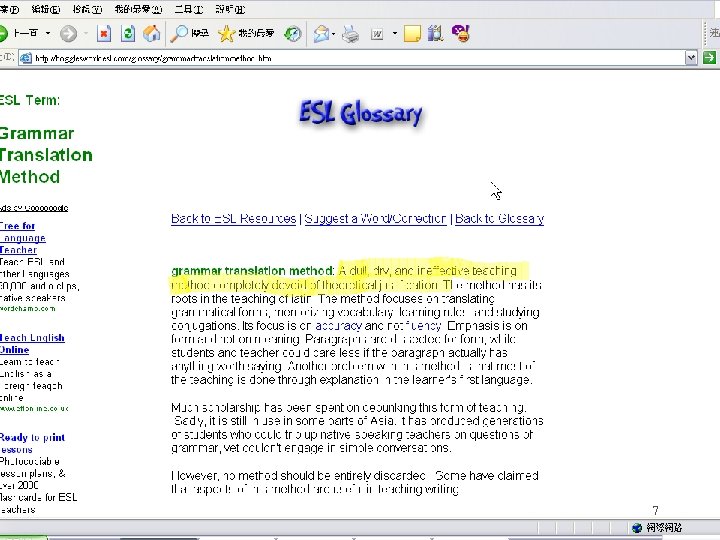
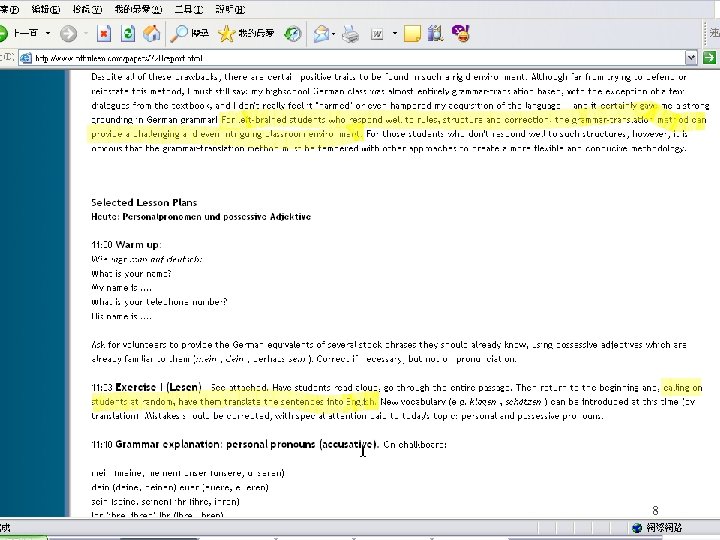
 Teaching methods: (1) Grammar translation l l l Like learning any other subject Students learn vocabulary and (prescriptive) grammar rules “Does not enable students to use language in the country” – – l This depends on the student! It is probably not true of the people in this room http: //www. nthuleen. com/papers/720 report. html 6
Teaching methods: (1) Grammar translation l l l Like learning any other subject Students learn vocabulary and (prescriptive) grammar rules “Does not enable students to use language in the country” – – l This depends on the student! It is probably not true of the people in this room http: //www. nthuleen. com/papers/720 report. html 6
 7
7
 8
8
 (2) Audiolingual method l l l Advocated by Robert Lado Essentially now discredited, because we now know that language acquisition is not a mechanical process Habit formation – – – l Based on drills (mechanical or meaningful) Keep doing it until students perform without errors (but of course they make errors in real life) Based on form, not function – This week: Present tense, not this week: Going shopping in the USA 9
(2) Audiolingual method l l l Advocated by Robert Lado Essentially now discredited, because we now know that language acquisition is not a mechanical process Habit formation – – – l Based on drills (mechanical or meaningful) Keep doing it until students perform without errors (but of course they make errors in real life) Based on form, not function – This week: Present tense, not this week: Going shopping in the USA 9
 Designer methods l The silent way – – l TPR – – l Teacher mostly remains silent. Students figure out language patterns using colored rods? ! Facilitates learning through discovery Mostly for kids Language input with body motions Acting out stories, giving commands Not really useful at advanced level Suggestopedia – – “LEARN ENGLISH IN THREE WEEKS!!!” Flashcards, soothing music Students are at a good state of “relaxed alertness” Both it and TPR are supposed to stimulate right brain motor activity 10
Designer methods l The silent way – – l TPR – – l Teacher mostly remains silent. Students figure out language patterns using colored rods? ! Facilitates learning through discovery Mostly for kids Language input with body motions Acting out stories, giving commands Not really useful at advanced level Suggestopedia – – “LEARN ENGLISH IN THREE WEEKS!!!” Flashcards, soothing music Students are at a good state of “relaxed alertness” Both it and TPR are supposed to stimulate right brain motor activity 10
 Communicative approach l l l Emphasis is on function, not form And on fluency and communicative quality, not grammatical and pronunciation errors Different attitude to errors – – l They are part of the learning process Just like broke – breaked – broke Interesting and meaningful input – Materials from the real world 11
Communicative approach l l l Emphasis is on function, not form And on fluency and communicative quality, not grammatical and pronunciation errors Different attitude to errors – – l They are part of the learning process Just like broke – breaked – broke Interesting and meaningful input – Materials from the real world 11
 Nunan’s five features of CLT l l l interaction in the target language authentic texts focus on learning process as well as target language include learner’s own personal experiences link to language activities outside the classroom 12
Nunan’s five features of CLT l l l interaction in the target language authentic texts focus on learning process as well as target language include learner’s own personal experiences link to language activities outside the classroom 12
 Is CLT the only valid approach? l Bax (2003) says NO – – l Most Czechs and Dutch (e. g. ) are taught by traditional means (GT) It is arrogant to assume that the Western CLT model is the best for all countries and all contexts Others might say – – Many authentic texts are way too difficult Personal experiences are too difficult for students to explain or discuss Or, students’ personal experiences are limited “Most of my language learning was NOT via CLT” 13
Is CLT the only valid approach? l Bax (2003) says NO – – l Most Czechs and Dutch (e. g. ) are taught by traditional means (GT) It is arrogant to assume that the Western CLT model is the best for all countries and all contexts Others might say – – Many authentic texts are way too difficult Personal experiences are too difficult for students to explain or discuss Or, students’ personal experiences are limited “Most of my language learning was NOT via CLT” 13
 Which methodology are we using now? l l (And I mean in PE-EMW…) A CLT approach – – l Some not especially authentic texts – l promotes interaction, sharing of personal experiences (not especially successfully) (some are very well written, but really hard) A rote memorization task (GT? ) – – Random items of vocabulary are learned for test Alarming washback effects 14
Which methodology are we using now? l l (And I mean in PE-EMW…) A CLT approach – – l Some not especially authentic texts – l promotes interaction, sharing of personal experiences (not especially successfully) (some are very well written, but really hard) A rote memorization task (GT? ) – – Random items of vocabulary are learned for test Alarming washback effects 14
 What approach should we adopt? l We need a framework – or a curriculum – which – – takes account of students’ actual English needs is not committed to any one methodology adapts to a range of tasks / activities which could be characterized as GT, CLT, LA, AL… generates positive washback (not memorization and non-participation) 15
What approach should we adopt? l We need a framework – or a curriculum – which – – takes account of students’ actual English needs is not committed to any one methodology adapts to a range of tasks / activities which could be characterized as GT, CLT, LA, AL… generates positive washback (not memorization and non-participation) 15
 Discussion 1 Is it important – or even possible – to teach PE-EMW in a communicative way? How did you learn your second language? What is the single biggest challenge (or constraint) of teaching PE-EMW? Which challenges 1. 2. 3. 4. a. b. can we control? can we not control? Talk about your own teaching methodology 5. a. b. c. d. e. f. How do you overcome the PE-EMW challenges? Do you use much group work? Pair work? Whole class work? Do you do any peer teaching? What’s your favorite activity for each level that you teach? Is it in the EMW book? How much time do you spend with the EMW book? 16 Do you or your students use any Chinese in class? Are you OK with the situation?
Discussion 1 Is it important – or even possible – to teach PE-EMW in a communicative way? How did you learn your second language? What is the single biggest challenge (or constraint) of teaching PE-EMW? Which challenges 1. 2. 3. 4. a. b. can we control? can we not control? Talk about your own teaching methodology 5. a. b. c. d. e. f. How do you overcome the PE-EMW challenges? Do you use much group work? Pair work? Whole class work? Do you do any peer teaching? What’s your favorite activity for each level that you teach? Is it in the EMW book? How much time do you spend with the EMW book? 16 Do you or your students use any Chinese in class? Are you OK with the situation?
 Communicative tasks l l l I like these, and they motivate students They have a non-linguistic outcome The learner is rewarded by something real, or kind of real – – résumés and interviews: get a “job” (applause) study abroad emails: get a personal email from a university 17
Communicative tasks l l l I like these, and they motivate students They have a non-linguistic outcome The learner is rewarded by something real, or kind of real – – résumés and interviews: get a “job” (applause) study abroad emails: get a personal email from a university 17
 Audiolingual activities l l Pronunciation drills Substitution drills – – l can be student led, in small groups can be whole class, in shuffling lines Choral repetition of discussion questions 18
Audiolingual activities l l Pronunciation drills Substitution drills – – l can be student led, in small groups can be whole class, in shuffling lines Choral repetition of discussion questions 18
 GT activities l Conversion – – l Group translation – – l keywords declarative sentences questions getting the gist of a paragraph getting nuances of key sentences Cloze tests (with function words missing) 19
GT activities l Conversion – – l Group translation – – l keywords declarative sentences questions getting the gist of a paragraph getting nuances of key sentences Cloze tests (with function words missing) 19
 Lexical approach: yet another methodology l Brain stores linguistic knowledge – – l Lewis (1993) and Schmitt (2000) say – – – l vocab (+features) and a bunch of grammar rules that’s basically what we have to learn the vocab is stored in chunks and collocations kith is stored with kin scotch is stored with rumour, and snake, and whisky Saying strong car or powerful tea or broken house gives away non-native speakers – a bit like the Conrad effect 20
Lexical approach: yet another methodology l Brain stores linguistic knowledge – – l Lewis (1993) and Schmitt (2000) say – – – l vocab (+features) and a bunch of grammar rules that’s basically what we have to learn the vocab is stored in chunks and collocations kith is stored with kin scotch is stored with rumour, and snake, and whisky Saying strong car or powerful tea or broken house gives away non-native speakers – a bit like the Conrad effect 20
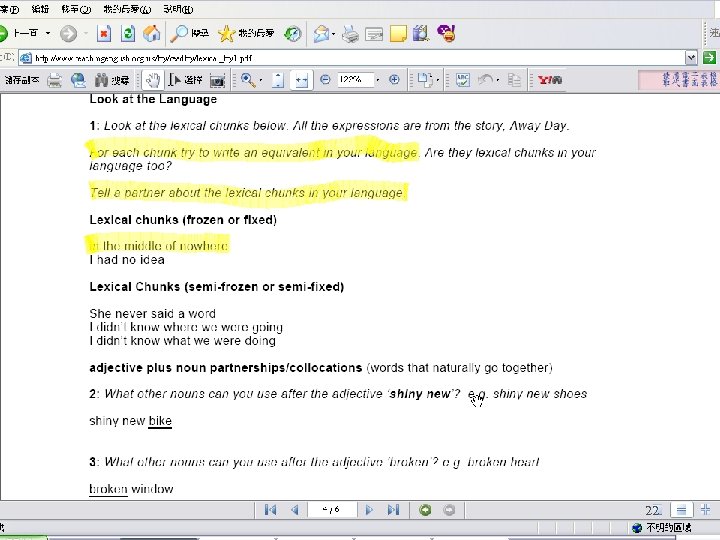
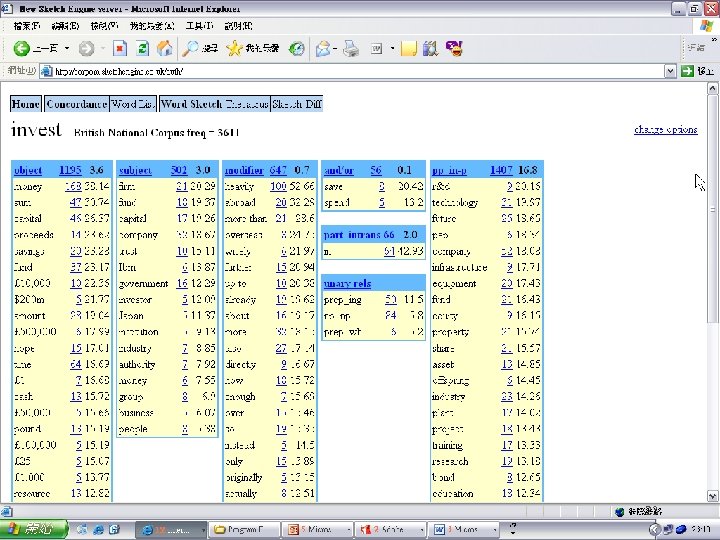
 Collocations and chunks l l An activity “In your own language? !? In Chinese? !? ” – – l “We have students who can barely string a sentence together, this is much too hard” – l note that this activity is intended for use in (eg) UK the teacher not knowing the language is irrelevant Well, take a look at a PE vocab list! www. sketchengine. co. uk egs 21
Collocations and chunks l l An activity “In your own language? !? In Chinese? !? ” – – l “We have students who can barely string a sentence together, this is much too hard” – l note that this activity is intended for use in (eg) UK the teacher not knowing the language is irrelevant Well, take a look at a PE vocab list! www. sketchengine. co. uk egs 21
 22
22
 23
23
 Council of Europe Framework (CEF) distinguishes l Declarative knowledge – – – l Existential competence – – – l knowing a word knowing a grammar pattern knowing a specific cultural taboo how to elicit help (like Randy’s list) paying attention awareness of the risk that a taboo might exist Skills & know-how – – Using a dictionary or thesaurus Using a CALL program, or the web, or Sketch Engine 24
Council of Europe Framework (CEF) distinguishes l Declarative knowledge – – – l Existential competence – – – l knowing a word knowing a grammar pattern knowing a specific cultural taboo how to elicit help (like Randy’s list) paying attention awareness of the risk that a taboo might exist Skills & know-how – – Using a dictionary or thesaurus Using a CALL program, or the web, or Sketch Engine 24
 CEFR linguistic activities l l l Reception Production Interaction – l R+P Mediation – “occupies an important place in the normal linguistic functioning of our societies” 25
CEFR linguistic activities l l l Reception Production Interaction – l R+P Mediation – “occupies an important place in the normal linguistic functioning of our societies” 25
 Discussion 2 Do you think, ideally, we should be teaching l – – – l grammar? vocabulary? English skills needed in the workplace? English skills needed for a student’s MCU studies? any non-linguistic skills? any translation or mediation skills? (Again, ideally) How would you use the Sketch Engine to teach, or prepare for class? 26
Discussion 2 Do you think, ideally, we should be teaching l – – – l grammar? vocabulary? English skills needed in the workplace? English skills needed for a student’s MCU studies? any non-linguistic skills? any translation or mediation skills? (Again, ideally) How would you use the Sketch Engine to teach, or prepare for class? 26
 Student needs l PE 7 and 8 kind of target “The Workplace”, and rightly so – – – l OK, very few MCU students – – l students write emails They should be able to handle a phone call but we do not train them in some common office English tasks work or study overseas work in foreign companies They work in Taiwan companies, but they do use English! 27
Student needs l PE 7 and 8 kind of target “The Workplace”, and rightly so – – – l OK, very few MCU students – – l students write emails They should be able to handle a phone call but we do not train them in some common office English tasks work or study overseas work in foreign companies They work in Taiwan companies, but they do use English! 27
 A huge chunk of the population uses English regularly l l l 7/11 clerks and Starbucks baristas need it Emails and faxes come in to companies Reports have to be read and summarized English instructions have to be written Translations have to be made – l Formal/informal; oral/written Email correspondence to/from Chinese and other Taiwanese colleagues is often in English! 28
A huge chunk of the population uses English regularly l l l 7/11 clerks and Starbucks baristas need it Emails and faxes come in to companies Reports have to be read and summarized English instructions have to be written Translations have to be made – l Formal/informal; oral/written Email correspondence to/from Chinese and other Taiwanese colleagues is often in English! 28
 Taiwan is bilingual anyway l People naturally code-switch all the time, using Taiwanese – – – l l Nowadays, to move in certain circles, you must be able to switch to English Translate this: – l for informality to give an impression of informality (eg with the boss) to exclude non-Taiwanese speakers Please fax me the candidate’s résumé, as I have an interview with her tomorrow Answer (overheard in my wife’s office) – 麻煩你把candidate的résumé fax給我, 我明天要跟她 interview 29
Taiwan is bilingual anyway l People naturally code-switch all the time, using Taiwanese – – – l l Nowadays, to move in certain circles, you must be able to switch to English Translate this: – l for informality to give an impression of informality (eg with the boss) to exclude non-Taiwanese speakers Please fax me the candidate’s résumé, as I have an interview with her tomorrow Answer (overheard in my wife’s office) – 麻煩你把candidate的résumé fax給我, 我明天要跟她 interview 29
 Study at MCU and English l For many students, in many disciplines, study involves English – – – l Big textbooks Big, incomprehensible textbooks taught by teachers without specialist skills We offer the departments no help with this? ? 30
Study at MCU and English l For many students, in many disciplines, study involves English – – – l Big textbooks Big, incomprehensible textbooks taught by teachers without specialist skills We offer the departments no help with this? ? 30
 All students at MCU study Chinese language and/or lit l l These programs are tailored to the different majors We should investigate ways of tailoring PE – – – upper program years not necessarily fully-blown content-based instruction (CBI) although that, if possible, would make a huge difference to language acquisition 31
All students at MCU study Chinese language and/or lit l l These programs are tailored to the different majors We should investigate ways of tailoring PE – – – upper program years not necessarily fully-blown content-based instruction (CBI) although that, if possible, would make a huge difference to language acquisition 31
 English for Academic Purposes? l l Academic reading skills Library/ internet research skills Essay writing skills Making inter-disciplinary connections – eg linguistics and sociology, physiology, psychology, information science 32
English for Academic Purposes? l l Academic reading skills Library/ internet research skills Essay writing skills Making inter-disciplinary connections – eg linguistics and sociology, physiology, psychology, information science 32
 English is a school subject? l This is all they get from high school – l l Just rules and vocab No, it’s a means of communication! Emphasize this by shock treatment – – – Early exposure to native speakers? Set the tone for 4 years of English study Not 1 year + 3 years 33
English is a school subject? l This is all they get from high school – l l Just rules and vocab No, it’s a means of communication! Emphasize this by shock treatment – – – Early exposure to native speakers? Set the tone for 4 years of English study Not 1 year + 3 years 33
 Materials platform l EMW style hardcopy publication? – – l Total reliance on e-classroom technology? – – l Students need something to clutch Equipment breaks So, somewhere between the two – l No, not dynamic Went wrong here before! Teachers have to get packs printed up at semester start, for example How about Moodle? 34
Materials platform l EMW style hardcopy publication? – – l Total reliance on e-classroom technology? – – l Students need something to clutch Equipment breaks So, somewhere between the two – l No, not dynamic Went wrong here before! Teachers have to get packs printed up at semester start, for example How about Moodle? 34
 Moodle Functions: • Setting up teaching materials, such as documents, audio/video files, powerpoint slides. • Creating teaching activities, such as handouts, discussions, self-assessments. • Engaging students’ involvement. • Assigning homework and online tests/quizzes. 35
Moodle Functions: • Setting up teaching materials, such as documents, audio/video files, powerpoint slides. • Creating teaching activities, such as handouts, discussions, self-assessments. • Engaging students’ involvement. • Assigning homework and online tests/quizzes. 35
 Next steps on curriculum l Needs analysis – l l Linking goals to a recognized reference framework (eg CEFR) Later… populating the framework – – – l l Establishing what our goals for the PE Challenge are creating tasks and activities validating existing ones uploading them Going live on PE 1 in the Fall (2007) And then year by year, in parallel with Testing 2010, thereafter 36
Next steps on curriculum l Needs analysis – l l Linking goals to a recognized reference framework (eg CEFR) Later… populating the framework – – – l l Establishing what our goals for the PE Challenge are creating tasks and activities validating existing ones uploading them Going live on PE 1 in the Fall (2007) And then year by year, in parallel with Testing 2010, thereafter 36
 We can’t change the world l l l We can’t change the Taiwan education system. We can’t really affect university policy. We can’t make optimal textbook choices We can’t change the class sizes. We can’t stop failing students taking 2, 3 or even 4 levels of PE concurrently We have no way to ensure MCU entrants know about the 4 year English program – l There will always be a motivation problem here We will work hard to implement English ability streaming, but not any time soon! – There will be many abilities in our PE classes 37
We can’t change the world l l l We can’t change the Taiwan education system. We can’t really affect university policy. We can’t make optimal textbook choices We can’t change the class sizes. We can’t stop failing students taking 2, 3 or even 4 levels of PE concurrently We have no way to ensure MCU entrants know about the 4 year English program – l There will always be a motivation problem here We will work hard to implement English ability streaming, but not any time soon! – There will be many abilities in our PE classes 37
 What we can do for students l Target students’ real MCU and workplace English needs – – l include academic skills if possible include appropriate mediation skills Show students that – – English is relevant to their lives English is a means of communication, not an academic subject 38
What we can do for students l Target students’ real MCU and workplace English needs – – l include academic skills if possible include appropriate mediation skills Show students that – – English is relevant to their lives English is a means of communication, not an academic subject 38
 What we can do for teachers l Free teachers to use the approaches and methodologies that work best for them – – – l Provide dynamic curriculum and materials – – l fewer constraints on writing goals for each level less reliance on vocab memorization reading tasks at appropriate level correct errors remove things that don’t work Gradual implementation – – – evaluation on the fly doesn’t seem such a mammoth task! curric and materials designers eat own lunch 39
What we can do for teachers l Free teachers to use the approaches and methodologies that work best for them – – – l Provide dynamic curriculum and materials – – l fewer constraints on writing goals for each level less reliance on vocab memorization reading tasks at appropriate level correct errors remove things that don’t work Gradual implementation – – – evaluation on the fly doesn’t seem such a mammoth task! curric and materials designers eat own lunch 39
 Implementation: emphasis on l participation – – l l l consultancy needs analysis careful reflection decisiveness transparency 40
Implementation: emphasis on l participation – – l l l consultancy needs analysis careful reflection decisiveness transparency 40
 A big vision for 2010: firsts for the Chinese-speaking world l MCU – l ELC – – l l the first US-accredited university the first professional university English test the first 4 -year English curriculum targeting the pre- and post-graduation needs of students Realizable? Yes! 41
A big vision for 2010: firsts for the Chinese-speaking world l MCU – l ELC – – l l the first US-accredited university the first professional university English test the first 4 -year English curriculum targeting the pre- and post-graduation needs of students Realizable? Yes! 41


