level 3 theme 5 Teaching and learnig models.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 26

TEACHING AND LEARNING MODELS © 2011 by The Johns Hopkins University. All rights reserved.

2 Outcomes Participants will be able to: v Apply models of thinking and questioning to relevant examples v Understand models for teaching that differentiate the curriculum v Discuss the features of each model and how to use them with their curriculum

Lev Vygotsky (Mind and Society, 1976) 3 v Elevated level of learning beyond current mastery v Interaction with others used as a pathway to enhance learning level v Learning capacity of the gifted is broader and deeper (zone of proximal development)
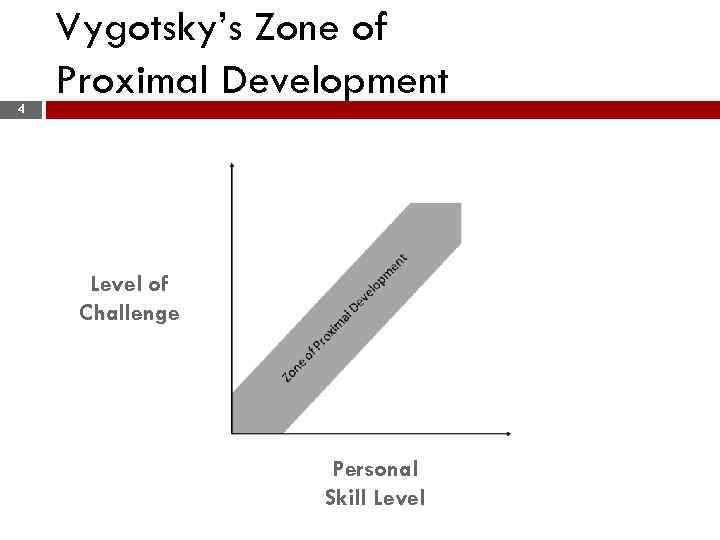
4 Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development Level of Challenge Personal Skill Level
What is Differentiation? 5 The process of differentiation is the deliberate adaptation and modification of the curriculum, instructional processes, and assessments in order to respond to the needs of gifted learners.

Building Rigor in Advanced Curriculum 6 v Start with an advanced curriculum base v Use diagnostic assessments to calibrate actual student learning levels v Employ task demands that require higher level thinking and problem-solving v Provide feedback on performance v Use assessment that is advanced

Building Rigor in Advanced Curriculum (cont. ) 7 v Track progress on advanced skills v Subgroup students by learning rate and progress on complex material v Adjust the curriculum level upward as evidence suggests readiness for targeted learners v Sustain growth in learning new content and skills
Teaching and Learning Models 8 v Reasoning Model v Problem-Based Learning Model v Questioning Model

How People Learn 9 v New knowledge is constructed based on existing conceptions and beliefs v Usable knowledge is connected and organized around important concepts that support transfer of learning v Deliberate learning strategies are used to scaffold instruction
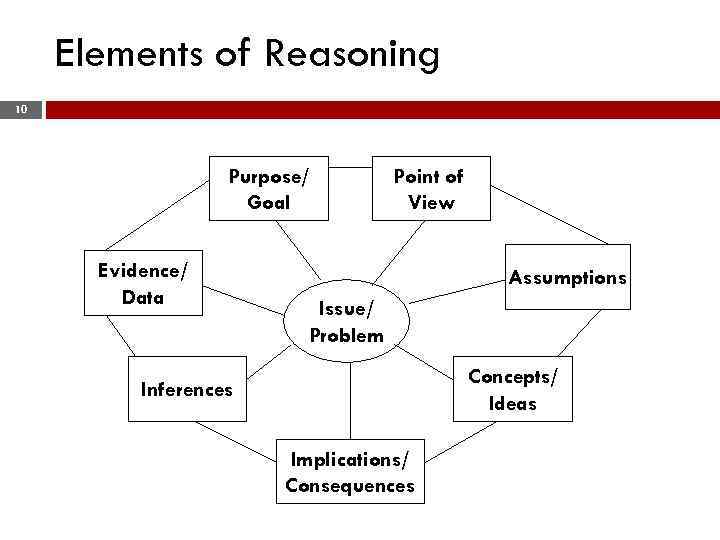
Elements of Reasoning 10 Purpose/ Goal Evidence/ Data Point of View Assumptions Issue/ Problem Concepts/ Ideas Inferences Implications/ Consequences

Reasoning Model 11 The Reasoning Model may be used in a variety of ways to: v Focus on one element, such as point of view v Use 3– 5 elements to explore an issue in discussion format v Write up an experiment v Analyze difficult text

Applying the Reasoning Model to Science 12 Read about a recent scientific discovery and answer these questions: v What is the issue? v What evidence is available to support the findings? v What are the consequences for society of the discovery?
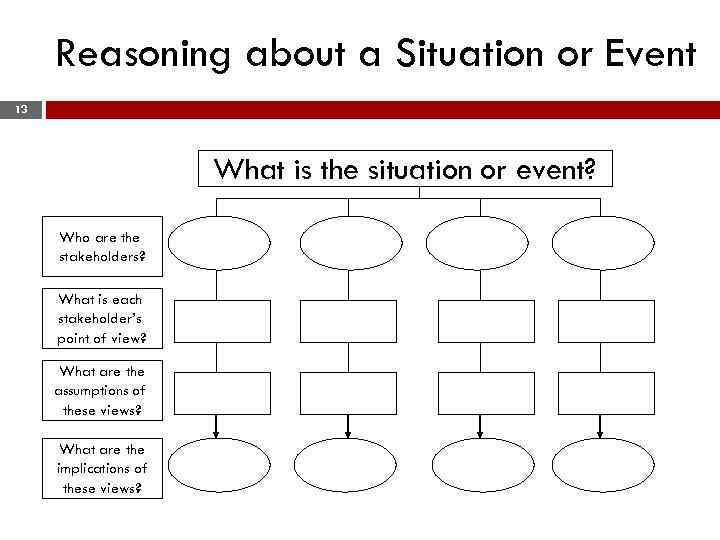
Reasoning about a Situation or Event 13 What is the situation or event? Who are the stakeholders? What is each stakeholder’s point of view? What are the assumptions of these views? What are the implications of these views?

Activity #1–Critical Thinking Using Event Analysis 14 Use the previous scaffold to create an analysis of one of these events: v World War II v Global warming v Terrorism

Problem Statement 15 You are the supervisor of the day shift of the Highway Patrol. It is 6: 00 a. m. on a steamy June morning. You are awakened by the ringing phone. When you answer you are told, “Come to the Queen’s Creek overpass on eastbound Interstate 64. There has been a major accident and you are needed. ” Quickly you dress and hurry to the overpass. As you approach the bridge, you see an overturned truck that is completely blocking both eastbound lanes of the freeway. You see “CORROSIVE” on small signs on the side and rear of the truck. The truck has lost at least one wheel and is resting on the freeway guard rail. There is a large gash in the side of the truck; from this gash, a clear liquid is running down the side of the truck, onto the road, and down the hill into Queen’s Creek. Steam is rising from the creek. All traffic has been halted and everyone has been told to remain in their cars. Many of the motorists in the traffic jam appear to be angry and frustrated. Police officers, firemen, and rescue squad workers are at the scene. They are all wearing coveralls and masks. The rescue squad is putting the unconscious truck driver onto a stretcher. Everyone seems hurried anxious.
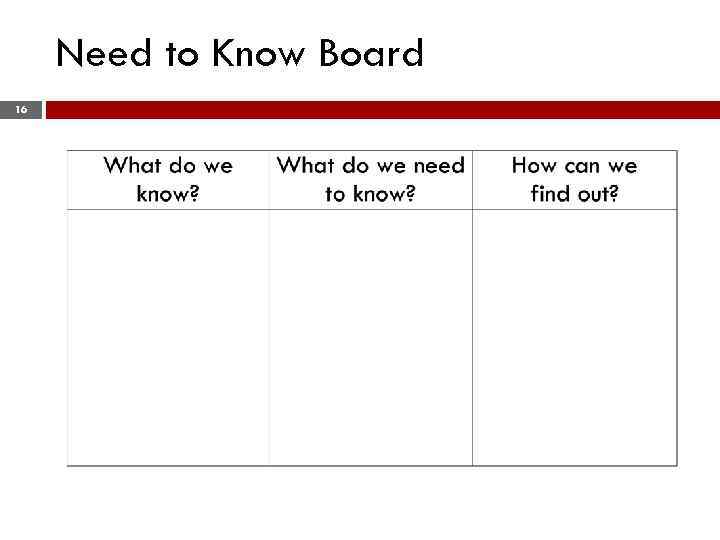
Need to Know Board 16

Activity #2–Need to Know Board 17 Complete the “Need to Know Board” based on the problem. v Identify all relevant data you know from the problem v Identify at least 12 things you need to know in order to address the problem v Cite sources you will use to address the questions you need to know

Creating Real-World Problems 18 v Define a stakeholder v Create a deadline or sense of tension v Withhold important information so students must figure it out v Describe a situation or problem that requires stakeholder action

Activity #3–Problem-Based Learning Scenario 19 Design a Problem-Based Learning scenario that you could use in teaching your subject and grade level.
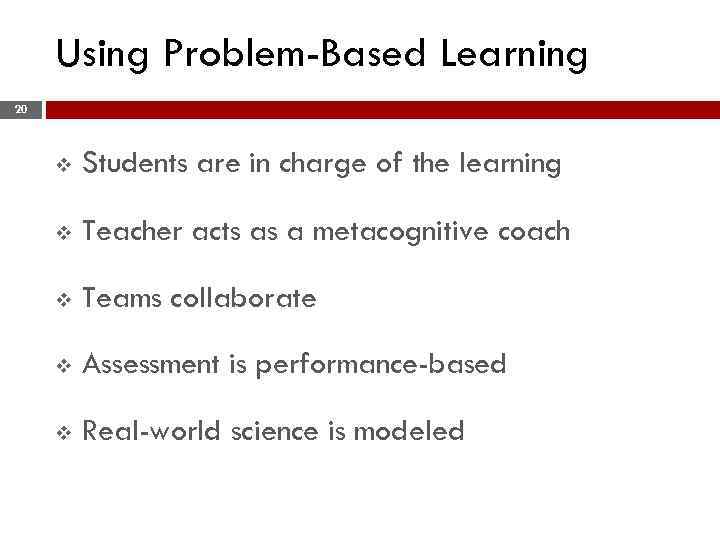
Using Problem-Based Learning 20 v Students are in charge of the learning v Teacher acts as a metacognitive coach v Teams collaborate v Assessment is performance-based v Real-world science is modeled
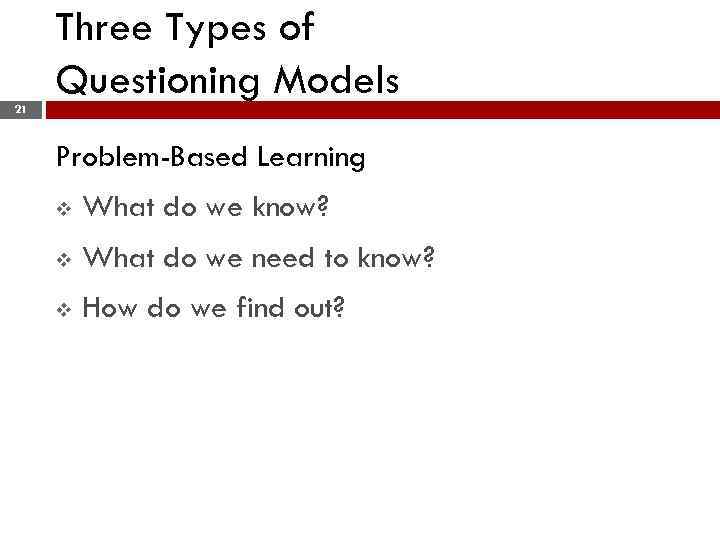
Three Types of Questioning Models 21 Problem-Based Learning v What do we know? v What do we need to know? v How do we find out?

Three Types of Questioning Models 22 Reasoning Model v What is the author’s purpose? v What data or evidence supports it? v What inferences do you draw from the evidence?

Three Types of Question Models (cont. ) 23 Taxonomy-Based v Who/What/When/Where? v Why? How? v What if…? v Pretend… v Which is better/best?
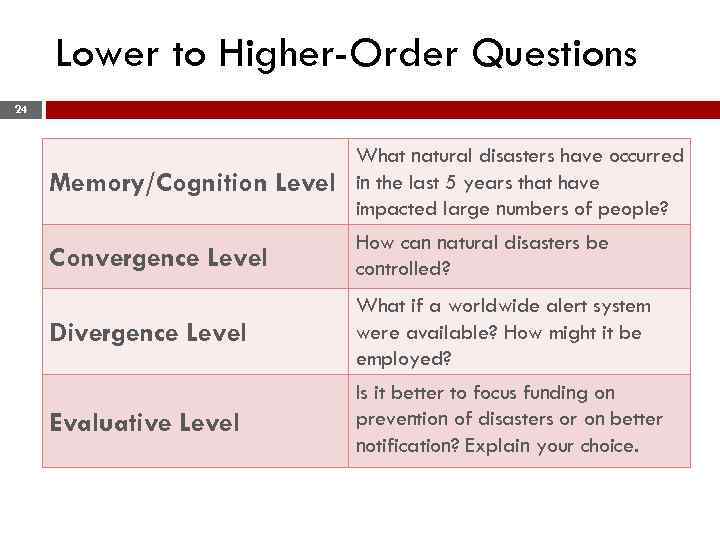
Lower to Higher-Order Questions 24 Memory/Cognition Level What natural disasters have occurred in the last 5 years that have impacted large numbers of people? Convergence Level How can natural disasters be controlled? Divergence Level What if a worldwide alert system were available? How might it be employed? Evaluative Level Is it better to focus funding on prevention of disasters or on better notification? Explain your choice.

Activity #4 25 Create a set of questions using the 4 -question strategy. Select one of these issues for your question set: v The use of nuclear power as an energy source v Global warming v Natural disasters

26 Discussion of the Models v What models can you use in the classroom with gifted learners? v What models will be easiest to implement? Why? v What models do you like the best? Why?
level 3 theme 5 Teaching and learnig models.pptx