72056cf0cc140057d01412abf677dbe1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 TCP/IP Servers • LPD (Printing) • SMTP (Mail) • FTP (File Transfer) • NTP (Network Time) • NNTP (News) • WEB
TCP/IP Servers • LPD (Printing) • SMTP (Mail) • FTP (File Transfer) • NTP (Network Time) • NNTP (News) • WEB
 Network Printing • Configure the printer hardware on the host system by using either the parallel or usb interfaces. • Add the Windows component “Other Network File and Printing Services” – uses port 515 (LPD) for BSD Unix printing • Or get HP Jet. Admin software for the system – uses port 9100 (Jet Direct) • Or get a network ready printer
Network Printing • Configure the printer hardware on the host system by using either the parallel or usb interfaces. • Add the Windows component “Other Network File and Printing Services” – uses port 515 (LPD) for BSD Unix printing • Or get HP Jet. Admin software for the system – uses port 9100 (Jet Direct) • Or get a network ready printer
 Printing cont. • Printer protocols: – Postscript (Adobe) • is a language executed by the printer • is very configurable – PCL (Hewlett Packard) • is a bit mapped graphics mode • is faster than postscript – ASCII (text) • Plain old printable characters
Printing cont. • Printer protocols: – Postscript (Adobe) • is a language executed by the printer • is very configurable – PCL (Hewlett Packard) • is a bit mapped graphics mode • is faster than postscript – ASCII (text) • Plain old printable characters
 Printer Setup (Network Ready) • Plug it in to the wall outlet (power) • Plug in the network cable • Power up the printer • Print the configuration sheet • Register the printer address (preferably non-routable)
Printer Setup (Network Ready) • Plug it in to the wall outlet (power) • Plug in the network cable • Power up the printer • Print the configuration sheet • Register the printer address (preferably non-routable)
 Printing • PDL (Print Description Languages), basically printer drivers. • Provide a standard interface from the application to the printer.
Printing • PDL (Print Description Languages), basically printer drivers. • Provide a standard interface from the application to the printer.
 Printer maintenance • Expendable supplies (paper and toner) • How to fix a paper jam • Monitor the printer output bin • Monitor the print quality • Clean the printer
Printer maintenance • Expendable supplies (paper and toner) • How to fix a paper jam • Monitor the printer output bin • Monitor the print quality • Clean the printer
 Simple Mail Trasnsfer Protocol • The protocol is very simple • Uses port 25 • All files are ascii text • Syntax: user@host. domain • Mail relay: user%host 1@host 2. domain • Mail Exchange (MX) – Allows mail server redirection
Simple Mail Trasnsfer Protocol • The protocol is very simple • Uses port 25 • All files are ascii text • Syntax: user@host. domain • Mail relay: user%host 1@host 2. domain • Mail Exchange (MX) – Allows mail server redirection
 SMTP Mail Servers • POP 2, POP 3 – – Uses port 109 or 110 Post Office Protocol, mail transfers to client, download all mail to the client (older protocol, replaced by): • IMAP – – Uses port 143 Internet Message Access Protocol, mail stays on server – Better for mobile (transient) clients • Webmail – uses a Web interface to access mail
SMTP Mail Servers • POP 2, POP 3 – – Uses port 109 or 110 Post Office Protocol, mail transfers to client, download all mail to the client (older protocol, replaced by): • IMAP – – Uses port 143 Internet Message Access Protocol, mail stays on server – Better for mobile (transient) clients • Webmail – uses a Web interface to access mail
 Mail Clients • Eudora – Commercial • Netscape Messenger – Comes with Netscape • Outlook – Comes with Windows 9 x, 2000 • Webmail, Groupwise – Uses any web browser
Mail Clients • Eudora – Commercial • Netscape Messenger – Comes with Netscape • Outlook – Comes with Windows 9 x, 2000 • Webmail, Groupwise – Uses any web browser
 Client Setup • Client can have separate mail server and smtp server. • Mail server is where our mail is received • SMTP server is where we send our messages • The Mail server can have virus and spam filters
Client Setup • Client can have separate mail server and smtp server. • Mail server is where our mail is received • SMTP server is where we send our messages • The Mail server can have virus and spam filters
 Spamming • Mail Relaying to an off site recipient • Testing SMTP mail – abuse. net • Configuration to prevent SPAM – allow only local domain relays to internet
Spamming • Mail Relaying to an off site recipient • Testing SMTP mail – abuse. net • Configuration to prevent SPAM – allow only local domain relays to internet
 Headers • From • Date: • Subject: • To: • Resent-date: • Resent-from:
Headers • From • Date: • Subject: • To: • Resent-date: • Resent-from:
 Attachments • Using mail to transfer files • Simple operation • Incompatible programs – Word for MAC vs. Word for PC –. pdf solves the compatibility problem • Dangers (viruses, trojan horses) – Executable programs that the client downloads and automatically executes
Attachments • Using mail to transfer files • Simple operation • Incompatible programs – Word for MAC vs. Word for PC –. pdf solves the compatibility problem • Dangers (viruses, trojan horses) – Executable programs that the client downloads and automatically executes
 Encoding Methods • Binary Files (programs, sound, video) • UUENCODE (UNIX) – one file per encode • MIME (WWW, POP, IMAP) – multiple files per encode • Bin. Hex (Apple) – one file per encode
Encoding Methods • Binary Files (programs, sound, video) • UUENCODE (UNIX) – one file per encode • MIME (WWW, POP, IMAP) – multiple files per encode • Bin. Hex (Apple) – one file per encode
 SMTP Example 1> telnet cc. usu. edu 25 2> 220 grumpy. usu. edu – ESMTP Server (PMDF V 5. 2 -32) 1> HELO pc 15. logan. tv 2> 250 grumpy. usu. edu Ok, “port 32443”@techsun. cs. usu. edu” [129. 123. 7. 33] 1> MAIL From:
SMTP Example 1> telnet cc. usu. edu 25 2> 220 grumpy. usu. edu – ESMTP Server (PMDF V 5. 2 -32) 1> HELO pc 15. logan. tv 2> 250 grumpy. usu. edu Ok, “port 32443”@techsun. cs. usu. edu” [129. 123. 7. 33] 1> MAIL From:
 SMTP Example cont. 1> The meeting is TOMORROW at 3: 00 PM! 1> 1>. 2> 250 2. 5. 0 Ok 1> QUIT 2> 221 2. 3. 0 Bye received. Goodbye.
SMTP Example cont. 1> The meeting is TOMORROW at 3: 00 PM! 1> 1>. 2> 250 2. 5. 0 Ok 1> QUIT 2> 221 2. 3. 0 Bye received. Goodbye.
 FTP • File Transfer Protocol – User – Anonymous • GET/PUT/DEL/CWD – GUI Interface • Binary/Ascii • Hash
FTP • File Transfer Protocol – User – Anonymous • GET/PUT/DEL/CWD – GUI Interface • Binary/Ascii • Hash
 FTP Example • requires 2 ports • telnet ftp. remotesite. com 21 – – – 220 ftp. remotesite. com FTP server ready user anonymous 331 password required for anonymous password user@cc. usu. edu 230 user anonymous logged in PORT 1200
FTP Example • requires 2 ports • telnet ftp. remotesite. com 21 – – – 220 ftp. remotesite. com FTP server ready user anonymous 331 password required for anonymous password user@cc. usu. edu 230 user anonymous logged in PORT 1200
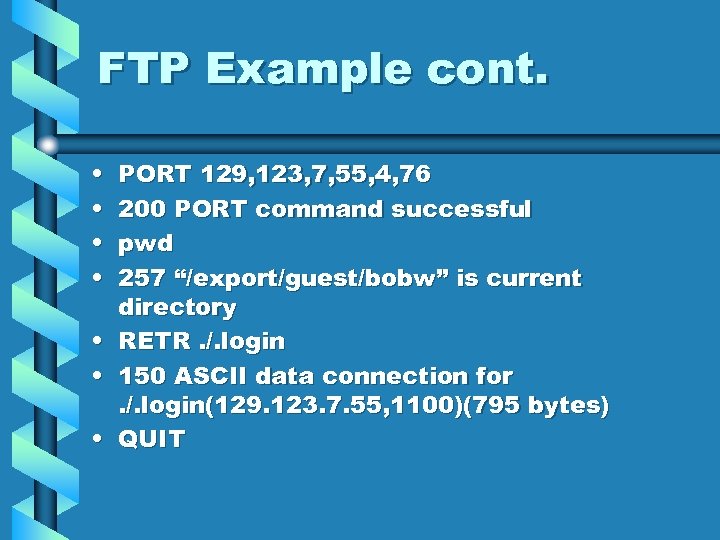 FTP Example cont. • • PORT 129, 123, 7, 55, 4, 76 200 PORT command successful pwd 257 “/export/guest/bobw” is current directory RETR. /. login 150 ASCII data connection for. /. login(129. 123. 7. 55, 1100)(795 bytes) QUIT
FTP Example cont. • • PORT 129, 123, 7, 55, 4, 76 200 PORT command successful pwd 257 “/export/guest/bobw” is current directory RETR. /. login 150 ASCII data connection for. /. login(129. 123. 7. 55, 1100)(795 bytes) QUIT
 NTP • Network Time Protocol • • – Uses port 123 UDP (User Datagram Protocol) Atomic Clock Synchronization Multiple Servers Used for – – – Distributed Databases Client/Server Security
NTP • Network Time Protocol • • – Uses port 123 UDP (User Datagram Protocol) Atomic Clock Synchronization Multiple Servers Used for – – – Distributed Databases Client/Server Security
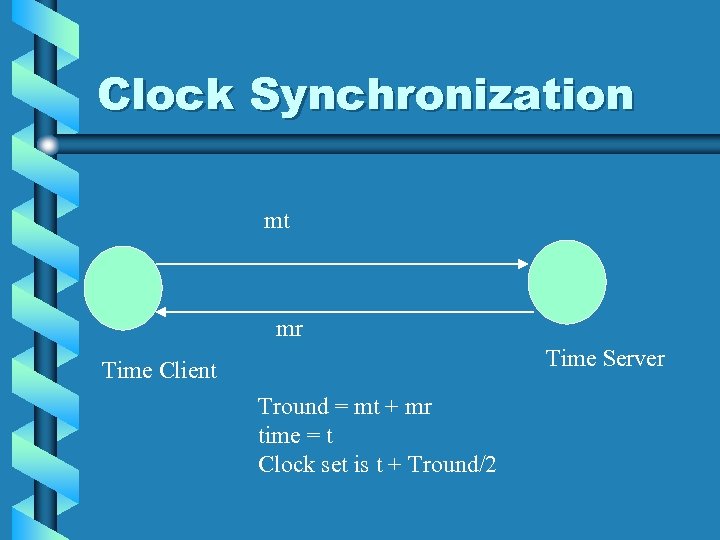 Clock Synchronization mt mr Time Server Time Client Tround = mt + mr time = t Clock set is t + Tround/2
Clock Synchronization mt mr Time Server Time Client Tround = mt + mr time = t Clock set is t + Tround/2
 NNTP • Network News Transfer Protocol – Uses port 119 • Distributed Bulletin Board – Uses a tree hierarchy • Minimizes Duplicate messages/disk space • Tree based distribution • Store and Forward
NNTP • Network News Transfer Protocol – Uses port 119 • Distributed Bulletin Board – Uses a tree hierarchy • Minimizes Duplicate messages/disk space • Tree based distribution • Store and Forward
 Web Browsers • Mosaic – More or less the first web browser • Netscape – Became extremely popular very quickly • Microsoft Internet Explorer – Plays catch up with Netscape • Hot. Java – Sun Microsystems Browser
Web Browsers • Mosaic – More or less the first web browser • Netscape – Became extremely popular very quickly • Microsoft Internet Explorer – Plays catch up with Netscape • Hot. Java – Sun Microsystems Browser
 Web Browsers Cont. • Web Browsers can cache pages and pictures locally to speed up access • Web Browsers can use a proxy server to remotely cache pages and pictures for many systems. • The proxy can act as a firewall and IP translator.
Web Browsers Cont. • Web Browsers can cache pages and pictures locally to speed up access • Web Browsers can use a proxy server to remotely cache pages and pictures for many systems. • The proxy can act as a firewall and IP translator.
 Web Servers • Apache • Roxen • Netscape • Microsoft – IIS
Web Servers • Apache • Roxen • Netscape • Microsoft – IIS
 Web Servers Cont. • Use http (hyper text transfer protocol) to create file and service access • Can have virtual servers to save IP addresses • Can have additional ports (services) • Most of the fancy stuff is done by the browser.
Web Servers Cont. • Use http (hyper text transfer protocol) to create file and service access • Can have virtual servers to save IP addresses • Can have additional ports (services) • Most of the fancy stuff is done by the browser.
 HTML • • • Hyper Text Markup Language Uses ascii text and commands Automatically formats text Sets up hyper links and displays pictures Connects to services such as ftp Start with
HTML • • • Hyper Text Markup Language Uses ascii text and commands Automatically formats text Sets up hyper links and displays pictures Connects to services such as ftp Start with
 XML • e. Xtensible Markup Language • Extends basic HTML to aid in creating documents and document systems. • Creates access to data bases
XML • e. Xtensible Markup Language • Extends basic HTML to aid in creating documents and document systems. • Creates access to data bases
 CGI’s Common Gateway Interface • Allow Web browsers to execute programs on the Web server. • Uses: Mail, finger, database, animation, sound • Found in /cgi directory in the Web page home • Are executable C, perl, java, or shell programs
CGI’s Common Gateway Interface • Allow Web browsers to execute programs on the Web server. • Uses: Mail, finger, database, animation, sound • Found in /cgi directory in the Web page home • Are executable C, perl, java, or shell programs
 ASP • Active Server Pages • Similar functions to CGI’s • Can do access counters, database access and online forms (fill in the blank)
ASP • Active Server Pages • Similar functions to CGI’s • Can do access counters, database access and online forms (fill in the blank)
 PHP • Personal Home Page Tools • Language for creating Web programs • Syntax is similar to Basic
PHP • Personal Home Page Tools • Language for creating Web programs • Syntax is similar to Basic
 Java • Developed by Sun • C++ context • Builds GUI’s (Graphical User Interfaces) • Handles animated objects on the web page
Java • Developed by Sun • C++ context • Builds GUI’s (Graphical User Interfaces) • Handles animated objects on the web page
 Security and the WEB • • • WEB files must be world readable. The WEB server may be run by root CGI’s can be dangerous security holes. • PHP, ASP, and VBscripts can have security holes (buffer overflows) • WEB servers are searched by many search engines that broadcast your data.
Security and the WEB • • • WEB files must be world readable. The WEB server may be run by root CGI’s can be dangerous security holes. • PHP, ASP, and VBscripts can have security holes (buffer overflows) • WEB servers are searched by many search engines that broadcast your data.



