5f5c174c32b5a4d269a2485c5b585f91.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Taxonomies and Classification for Organizing Content Elizabeth Wong INF 385 E February 16, 2012

Presentation Outline What are classification and taxonomy? l How classification and taxonomy are relevant and useful to IA l Keep in mind l Questions l 2

Definitions by Distinction “Taxonomies? That’s classified information. ” -Jordan Cassel from The Accidental Taxonomist

Classification vs. Classification Scheme IA Glossary Definition of Classification: The sorting of things into pre-defined categories. l 4

Classification vs. Classification Scheme l Classification Scheme: “A tool for systematic organization of information resources. ” - GG Chowdury Organizing Information from the Shelf to the Web 5

Types of Classification Alphabetic l Numeric l Alphanumeric l Taxonomies l Facets l Etc. l 6

Many meanings of taxonomy l l Original Greek: taxis=arrangement and nomos=law or science (study of classification) Information- in general – 1990 s Two common usages 1) Narrow: A hierarchical classification or categorization system 2) Broad: Any means of organizing concepts of knowledge - Heather Hedden The Accidental Taxonomist l 7

Why organize? To make sense of information l To understand promote relationships l To understand the world better l 8

Taxonomies are. . . Any set of terms that share some organizing principle. – MSWeb team l Constructs that help people search, browse, and manage (intranet) content more effectively l 9

Seth Earley on Taxonomies l http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=6 BWo. L Ob. Dvc. Y 10

Taxonomies include Controlled vocabularies l Hierarchies l Information thesauri l Ontologies l 11

Controlled Vocabularies l “A restricted list of words or terms for some specialized purpose, usually for indexing, labeling, or categorizing. ” - Heather Hedden The Accidental Taxonomist 12
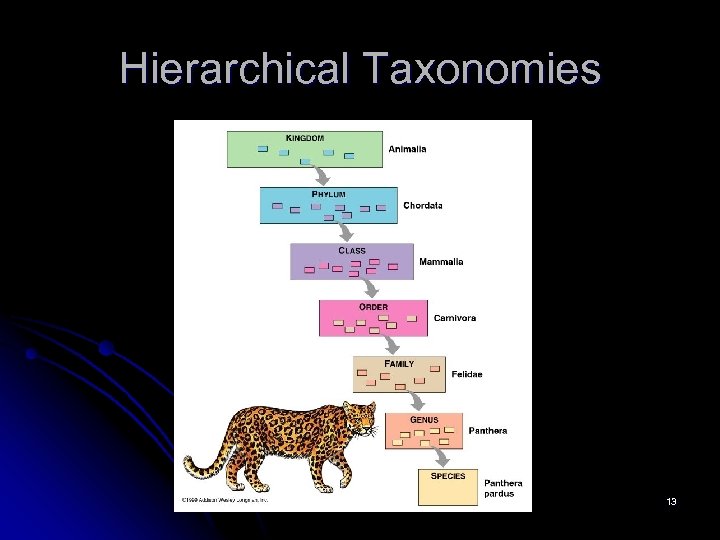
Hierarchical Taxonomies 13

Thesauri l Show three types of relationships: l l l Hierarchical (BT/NT) Associative (RT) Equivalence (Use/UF) 14
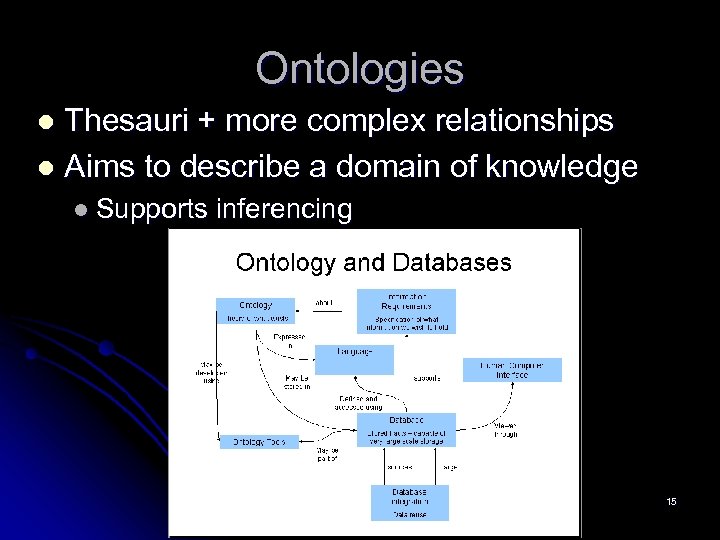
Ontologies Thesauri + more complex relationships l Aims to describe a domain of knowledge l l Supports inferencing 15

Applications and Purposes of Taxonomies Indexing support l Retrieval support l Organization and navigation support l l Ch. 20 in Information Architecture for the World Wide Web 16

Meeting your taxonomy needs Buy one l Adapt one l Build one l 17

Keep in mind Content l Users l Context l Be flexible and multidisciplinary! l 18

References l Chowdhury, GG, and Sudatta Chowdhury. Organizing Information from the Shelf to the Web. London: Facet, 2007. Print. l Doyle, Bob. "Glossary - Information Architecture Institute. " The Information Architecture Institute. Web. 13 Feb. 2012. <http: //www. iainstitute. org/en/learn/resources/glossary. php>. l Hedden, Heather. The Accidental Taxonomist. Medford, NJ: Information Today, 2010. Print. l Morville, Peter, and Louis Rosenfeld. Information Architecture and the World Wide Web. 3 rd ed. Sebastopol, CA: O'Reilly, 2007. Print. l Taylor, Arlene G. The Organization of Information. 2 nd ed. Westport, CT: Libraries Unlimited, 2004. Print. 19

Questions?
5f5c174c32b5a4d269a2485c5b585f91.ppt