
Taxation in South Korea DONE BY: ABDRAKHMAN AIDA ACC-332

The taxation system in South Korea is recognized as one of the most clear and transparent to the Asian region. Its feature is the strict separation of all taxes into two main groups: - Local; - National. In turn, both types of tax are divided into certain types of fees. For example, local presented regional (provincial) and urban.

National taxes are divided into: direct taxes, which include income tax, corporation tax, inheritance tax and gift indirect taxes, which include value-added tax, excise tax on alcoholic beverages, motor vehicle tax, a tax on phone users. Local taxes in turn are subdivided into: regional (provincial) taxes: license fee, a tax on road maintenance tax on the development of the region city taxes: excise tax on tobacco products, road tax, registration fee,
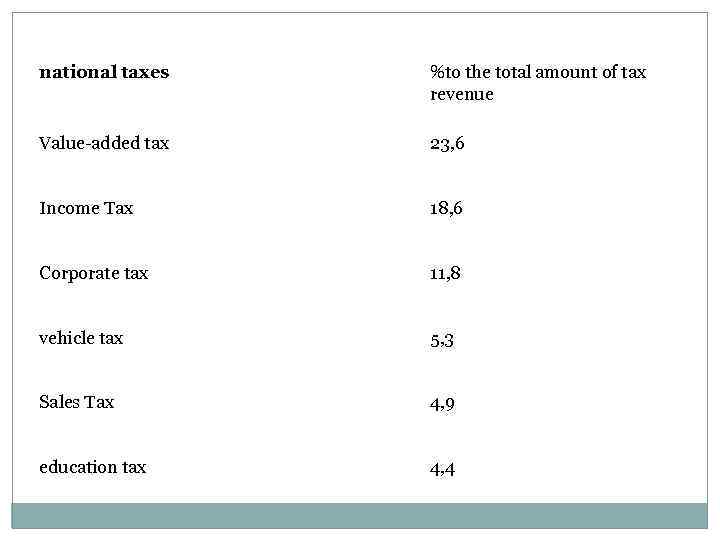
national taxes %to the total amount of tax revenue Value-added tax 23, 6 Income Tax 18, 6 Corporate tax 11, 8 vehicle tax 5, 3 Sales Tax 4, 9 education tax 4, 4
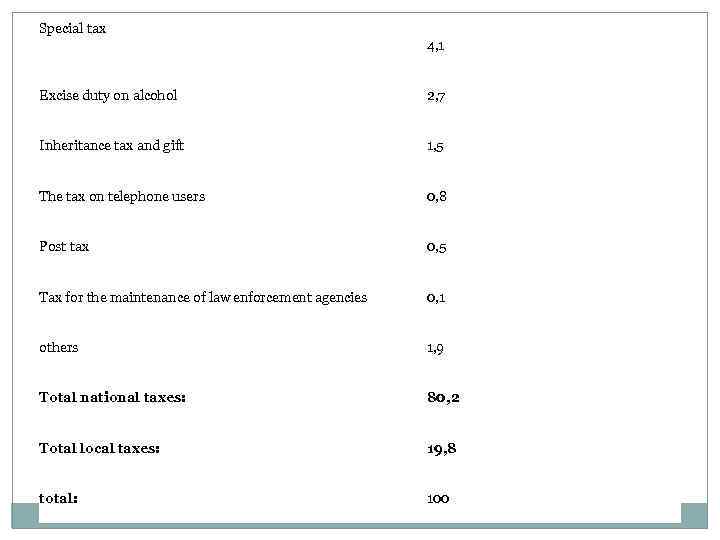
Special tax 4, 1 Excise duty on alcohol 2, 7 Inheritance tax and gift 1, 5 The tax on telephone users 0, 8 Post tax 0, 5 Tax for the maintenance of law enforcement agencies 0, 1 others 1, 9 Total national taxes: 80, 2 Total local taxes: 19, 8 total: 100
As can be seen from the table, the share of national taxes in total tax revenue was 80. 2%, while the share of local taxes - 19. 8% The largest share in the structure of national tax take: value-added tax - 23. 6%, income tax (income tax) - 18. 6%, 11. 8% corporate tax rate. National tax policy is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Finance and Economy, which also includes the National Tax Administration and the National Tax College. Administration of Taxation of the Ministry of Finance and Economy is responsible for planning the development of tax policy and tax laws National Tax College is responsible for training students who will later work by tax inspectors. The basis of the tax system of the country is a deliberate policy to stimulate exports abroad: - Exemption from taxes and duties, imports of intermediate goods and equipment - Sale of indirect taxation (eg commercial and corporate taxes) in the production of products intended for export - Save up to 50% tax on profits from export operations

Market and taxesthat's an interesting problem today. Interesting because taxes are an important tool for regulation of market relations.