 Tax and Society
Tax and Society
 What is tax? • (An amount of) money paid to the government, which is based on your income or the cost of goods or services you have bought (definition – Cambridge Dictionaries Online)
What is tax? • (An amount of) money paid to the government, which is based on your income or the cost of goods or services you have bought (definition – Cambridge Dictionaries Online)
 Who pays tax? • Anyone who has an income – wages, pensions etc – pays Income Tax. • Anyone who buys certain types of goods and services pays Value Added Tax (VAT). • Many companies and businesses pay Corporation Tax.
Who pays tax? • Anyone who has an income – wages, pensions etc – pays Income Tax. • Anyone who buys certain types of goods and services pays Value Added Tax (VAT). • Many companies and businesses pay Corporation Tax.
 How much income tax do people pay? • Income tax is payable on all income above a certain personal allowance. • In 2011 -12 the personal allowance = £ 7, 475 • The next £ 35, 000 is taxable at 20%. • Income between £ 42, 475 and £ 150, 000 is taxable at 40%. • Income above £ 150, 000 is taxable at 50%.
How much income tax do people pay? • Income tax is payable on all income above a certain personal allowance. • In 2011 -12 the personal allowance = £ 7, 475 • The next £ 35, 000 is taxable at 20%. • Income between £ 42, 475 and £ 150, 000 is taxable at 40%. • Income above £ 150, 000 is taxable at 50%.
 There are many types of tax that contribute to the UK’s budget. They include: • Income Tax — a tax on your personal income whether you are employed or self employed. This includes wages, pensions and interest on savings • Corporation Tax — paid by companies on their profits • Excise Duties — there are various excise duties, including Car Tax and tax on goods such as alcohol and tobacco • Value Added Tax (VAT) — you pay VAT, included in the price, when you buy goods and services. Some goods, including food and newspapers, don't attract VAT • Council Tax — a tax on the value or size of the home you live in, which helps pay for local services such as policing and rubbish collection.
There are many types of tax that contribute to the UK’s budget. They include: • Income Tax — a tax on your personal income whether you are employed or self employed. This includes wages, pensions and interest on savings • Corporation Tax — paid by companies on their profits • Excise Duties — there are various excise duties, including Car Tax and tax on goods such as alcohol and tobacco • Value Added Tax (VAT) — you pay VAT, included in the price, when you buy goods and services. Some goods, including food and newspapers, don't attract VAT • Council Tax — a tax on the value or size of the home you live in, which helps pay for local services such as policing and rubbish collection.
 UK public spending 2010– 11 • Total public spending was expected to be around £ 696 billion for the year 2010– 2011 • This equals around £ 11, 262 for every man, woman and child in the UK. • The biggest spending was on social protection (which includes cash benefits for sickness and disability, old age pensions, family benefits, tax credits).
UK public spending 2010– 11 • Total public spending was expected to be around £ 696 billion for the year 2010– 2011 • This equals around £ 11, 262 for every man, woman and child in the UK. • The biggest spending was on social protection (which includes cash benefits for sickness and disability, old age pensions, family benefits, tax credits).
 UK public spending 20091– 11 • Social protection £ 194 billion • Health £ 122 billion • Education £ 89 billion • Defence £ 40 billion • Public order and safety £ 35 billion
UK public spending 20091– 11 • Social protection £ 194 billion • Health £ 122 billion • Education £ 89 billion • Defence £ 40 billion • Public order and safety £ 35 billion
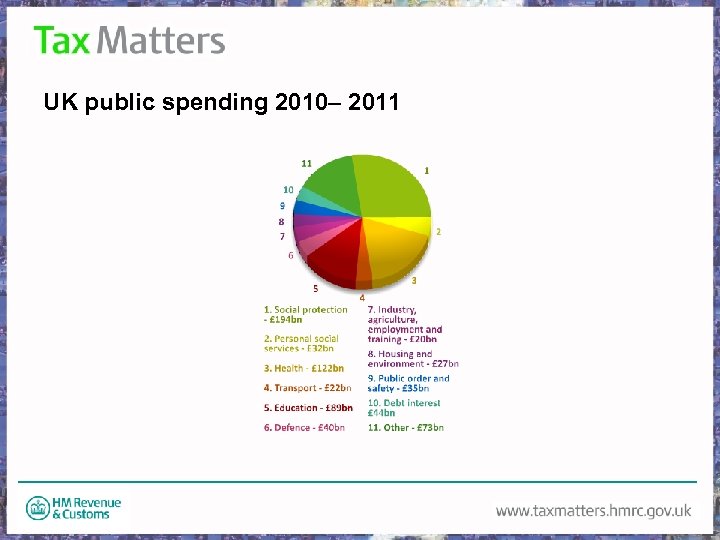 UK public spending 2010– 2011
UK public spending 2010– 2011
 When do you pay VAT and how much? Each EU country has its own rates of VAT. In the UK there are three: • Standard rate You pay VAT on most goods and services in the UK at the standard rate, which is 20 per cent. • Reduced rate In some cases, for example children's car seats and domestic fuel or power, you pay a reduced rate of 5 per cent. • Zero rate There are some goods on which you don't pay any VAT e. g. food (but NOT crisps, sweets and fizzy drinks), books and magazines.
When do you pay VAT and how much? Each EU country has its own rates of VAT. In the UK there are three: • Standard rate You pay VAT on most goods and services in the UK at the standard rate, which is 20 per cent. • Reduced rate In some cases, for example children's car seats and domestic fuel or power, you pay a reduced rate of 5 per cent. • Zero rate There are some goods on which you don't pay any VAT e. g. food (but NOT crisps, sweets and fizzy drinks), books and magazines.