18a6d4f59faee764547660976ebcf774.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Task Shifting “Clinical Mapping” Multi-country study WHO / OGAC In-country: Mo. H & WHO Academic Institutions: Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp, Belgium Partners in Health / Harvard Medical School 1
Task Shifting “Clinical Mapping” Multi-country study WHO / OGAC In-country: Mo. H & WHO Academic Institutions: Institute of Tropical Medicine, Antwerp, Belgium Partners in Health / Harvard Medical School 1
 Approach • Desk work: – Previous experiences with « delegation of clinical tasks to non-doctors » in Primary Health Care programs (mainly 1980 s) – Conceptualisation of task shifting – Tools for field visits • Field visits: to document experiences with innovative provider cadres in HIV care: Malawi, Uganda, Ethiopia, Haiti & Rwanda 2
Approach • Desk work: – Previous experiences with « delegation of clinical tasks to non-doctors » in Primary Health Care programs (mainly 1980 s) – Conceptualisation of task shifting – Tools for field visits • Field visits: to document experiences with innovative provider cadres in HIV care: Malawi, Uganda, Ethiopia, Haiti & Rwanda 2
 Results from desk work Ø Ø Framework Types of task shifting Evaluations done Conditions for successful task shifting 3
Results from desk work Ø Ø Framework Types of task shifting Evaluations done Conditions for successful task shifting 3
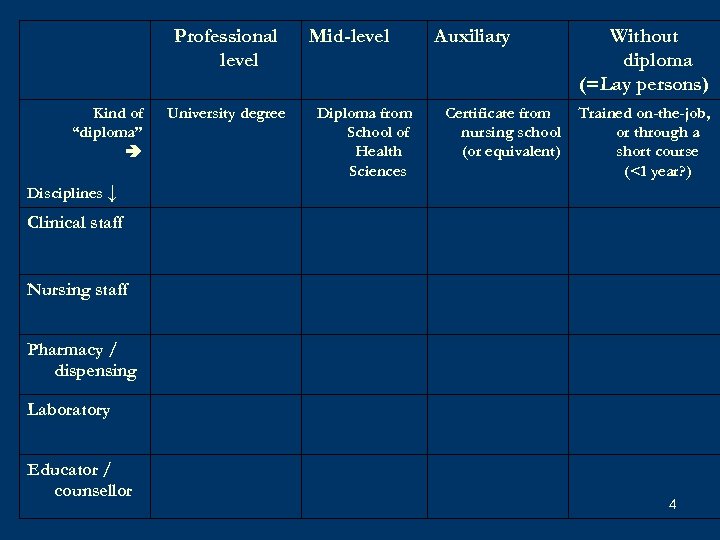 Professional level Kind of “diploma” University degree Mid-level Diploma from School of Health Sciences Auxiliary Certificate from nursing school (or equivalent) Without diploma (=Lay persons) Trained on-the-job, or through a short course (<1 year? ) Disciplines ↓ Clinical staff Nursing staff Pharmacy / dispensing Laboratory Educator / counsellor 4
Professional level Kind of “diploma” University degree Mid-level Diploma from School of Health Sciences Auxiliary Certificate from nursing school (or equivalent) Without diploma (=Lay persons) Trained on-the-job, or through a short course (<1 year? ) Disciplines ↓ Clinical staff Nursing staff Pharmacy / dispensing Laboratory Educator / counsellor 4
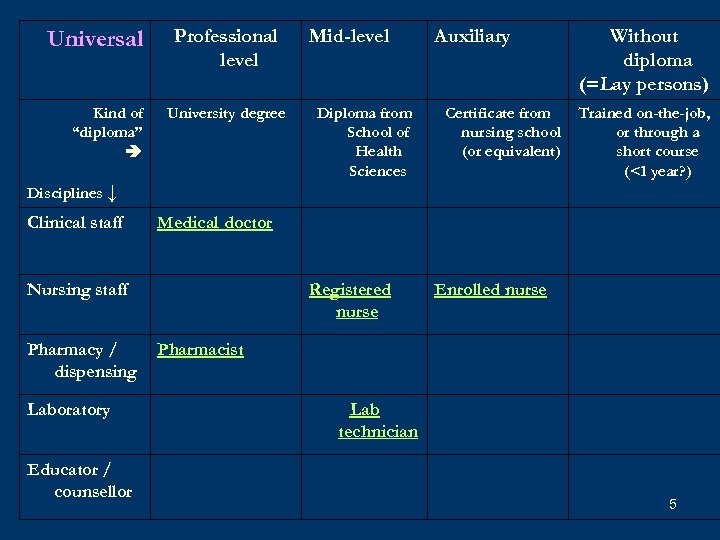 Universal Kind of “diploma” Professional level University degree Mid-level Diploma from School of Health Sciences Auxiliary Certificate from nursing school (or equivalent) Without diploma (=Lay persons) Trained on-the-job, or through a short course (<1 year? ) Disciplines ↓ Clinical staff Medical doctor Nursing staff Pharmacy / dispensing Laboratory Educator / counsellor Registered nurse Enrolled nurse Pharmacist Lab technician 5
Universal Kind of “diploma” Professional level University degree Mid-level Diploma from School of Health Sciences Auxiliary Certificate from nursing school (or equivalent) Without diploma (=Lay persons) Trained on-the-job, or through a short course (<1 year? ) Disciplines ↓ Clinical staff Medical doctor Nursing staff Pharmacy / dispensing Laboratory Educator / counsellor Registered nurse Enrolled nurse Pharmacist Lab technician 5
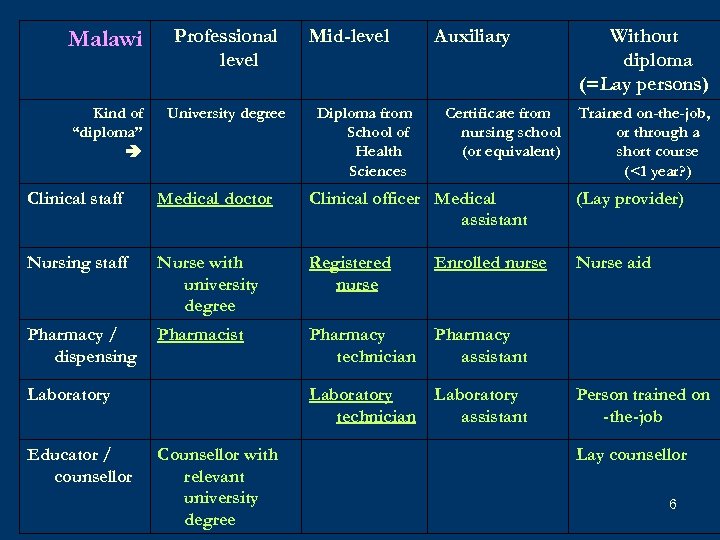 Malawi Professional level Kind of “diploma” University degree Mid-level Diploma from School of Health Sciences Auxiliary Certificate from nursing school (or equivalent) Without diploma (=Lay persons) Trained on-the-job, or through a short course (<1 year? ) Clinical staff Medical doctor Clinical officer Medical assistant (Lay provider) Nursing staff Nurse with university degree Registered nurse Enrolled nurse Nurse aid Pharmacy / dispensing Pharmacist Pharmacy technician Pharmacy assistant Laboratory technician Laboratory assistant Laboratory Educator / counsellor Counsellor with relevant university degree Person trained on -the-job Lay counsellor 6
Malawi Professional level Kind of “diploma” University degree Mid-level Diploma from School of Health Sciences Auxiliary Certificate from nursing school (or equivalent) Without diploma (=Lay persons) Trained on-the-job, or through a short course (<1 year? ) Clinical staff Medical doctor Clinical officer Medical assistant (Lay provider) Nursing staff Nurse with university degree Registered nurse Enrolled nurse Nurse aid Pharmacy / dispensing Pharmacist Pharmacy technician Pharmacy assistant Laboratory technician Laboratory assistant Laboratory Educator / counsellor Counsellor with relevant university degree Person trained on -the-job Lay counsellor 6
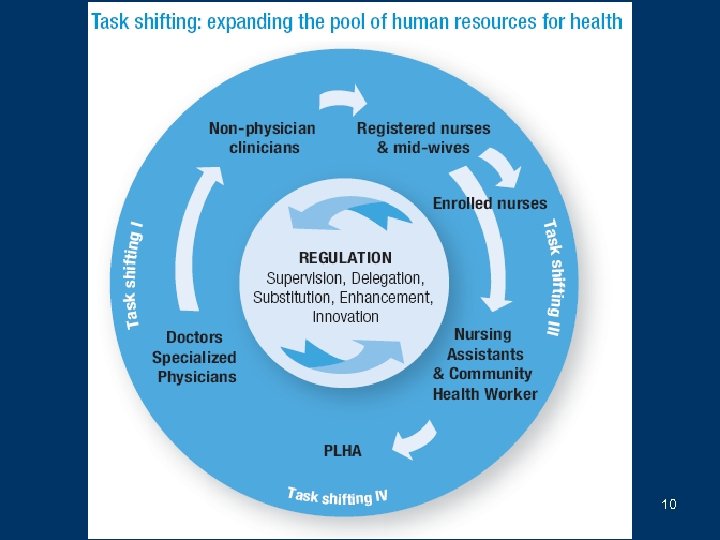
 4 main types of task shifting • Type I: from doctors to non-physician clinicians (clinical officers, medical assistants, physician-assistants, nurse-practitioners, …) • Type II: from clinicians to nurses • Type III: … to nursing aids, lay providers (including counsellors), community health workers • Type IV: self-management by PLHAs 7
4 main types of task shifting • Type I: from doctors to non-physician clinicians (clinical officers, medical assistants, physician-assistants, nurse-practitioners, …) • Type II: from clinicians to nurses • Type III: … to nursing aids, lay providers (including counsellors), community health workers • Type IV: self-management by PLHAs 7
 Type III Need to further separate Type III: – Depending on prior diploma: range: university graduates – primary school – Counsellors, becoming a new professional group – Nursing tasks – Clinical tasks = Lay providers, including « expert patients » 8
Type III Need to further separate Type III: – Depending on prior diploma: range: university graduates – primary school – Counsellors, becoming a new professional group – Nursing tasks – Clinical tasks = Lay providers, including « expert patients » 8
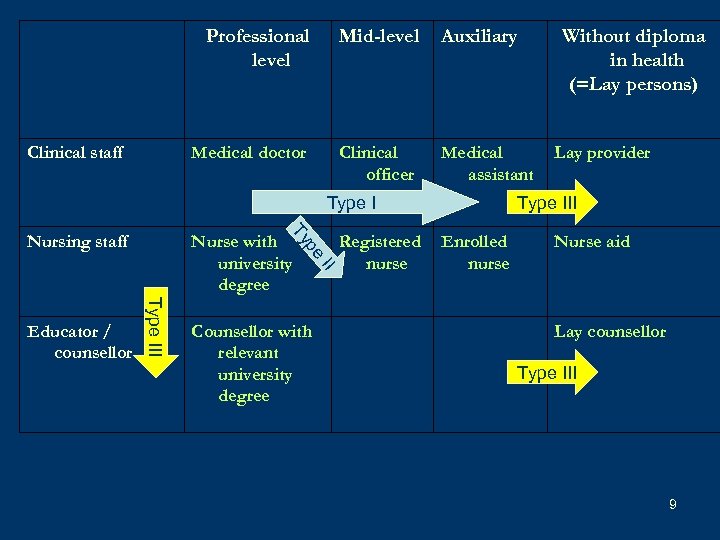 Professional level Auxiliary Medical doctor Clinical staff Mid-level Clinical officer Medical assistant Type I pe Ty Nursing staff Counsellor with relevant university degree Registered nurse II Type III Educator / counsellor Nurse with university degree Without diploma in health (=Lay persons) Lay provider Type III Enrolled nurse Nurse aid Lay counsellor Type III 9
Professional level Auxiliary Medical doctor Clinical staff Mid-level Clinical officer Medical assistant Type I pe Ty Nursing staff Counsellor with relevant university degree Registered nurse II Type III Educator / counsellor Nurse with university degree Without diploma in health (=Lay persons) Lay provider Type III Enrolled nurse Nurse aid Lay counsellor Type III 9
 10
10
 Prior experience? • Type I: non-physician clinicians in primary health care (PHC) • Type II: = happening in many (peripheral) places • Type III: – Community health workers = lay providers – Counsellors = quite new to HIV/AIDS – Expert patients = quite new… • Type IV: self-management (diabetes &c) 11
Prior experience? • Type I: non-physician clinicians in primary health care (PHC) • Type II: = happening in many (peripheral) places • Type III: – Community health workers = lay providers – Counsellors = quite new to HIV/AIDS – Expert patients = quite new… • Type IV: self-management (diabetes &c) 11
 Evaluations of task shifting • Non-physician clinicians = very positive • Community health workers (study UWC) can work « under certain conditions! » • Still less firm evidence for recent innovations e. g. – « Nurse-based ART delivery » – « Expert patients » 12
Evaluations of task shifting • Non-physician clinicians = very positive • Community health workers (study UWC) can work « under certain conditions! » • Still less firm evidence for recent innovations e. g. – « Nurse-based ART delivery » – « Expert patients » 12
 Task shifting: 4 basic conditions • Initial training – Basic diploma – Specific pre-service training • Guidelines / protocoles (simplification) • Continuing education – Supervision – Coaching – Refresher courses • Remuneration / career structure 13
Task shifting: 4 basic conditions • Initial training – Basic diploma – Specific pre-service training • Guidelines / protocoles (simplification) • Continuing education – Supervision – Coaching – Refresher courses • Remuneration / career structure 13
 Multi-country study • Main objective: documenting ‘best practices’ in task shifting for clinical HIV care • In each country: – Inventory of all types of health cadre + training – General information on HIV, health system, HRH, AIDS programme, … – Selection of ART delivery sites: ‘best practices’ (+ ‘routine practices’) 14
Multi-country study • Main objective: documenting ‘best practices’ in task shifting for clinical HIV care • In each country: – Inventory of all types of health cadre + training – General information on HIV, health system, HRH, AIDS programme, … – Selection of ART delivery sites: ‘best practices’ (+ ‘routine practices’) 14
 Field visits to ART sites Questionnaires: • For different cadre: detailed documentation of which cadre is actually performing which tasks (mainly interview, some observation) • For each facility: – info on patients, on outcomes, … – Inventory of staff + FTE for ART 15
Field visits to ART sites Questionnaires: • For different cadre: detailed documentation of which cadre is actually performing which tasks (mainly interview, some observation) • For each facility: – info on patients, on outcomes, … – Inventory of staff + FTE for ART 15
 Expected results? • Detailed insight in task shifting: – Which tasks? by whom? – Consistent? – Priorities? • Workload (FTE staff) for ART • Conditions for enabling task shifting • Outcomes? (with task shifting) 16
Expected results? • Detailed insight in task shifting: – Which tasks? by whom? – Consistent? – Priorities? • Workload (FTE staff) for ART • Conditions for enabling task shifting • Outcomes? (with task shifting) 16
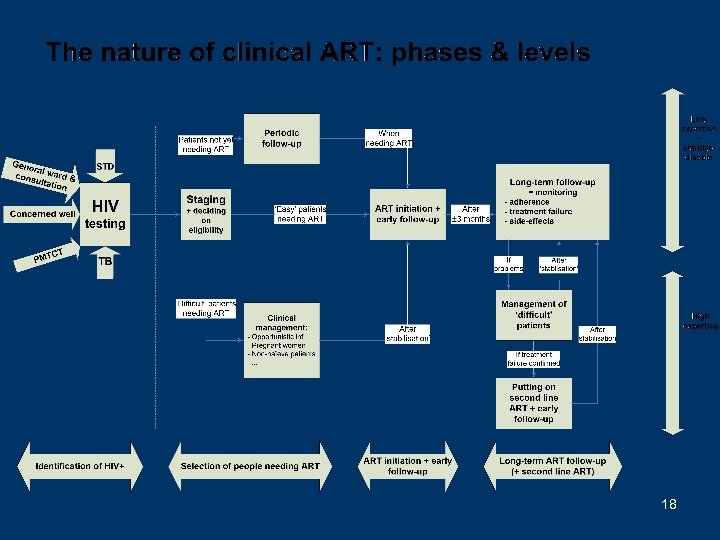
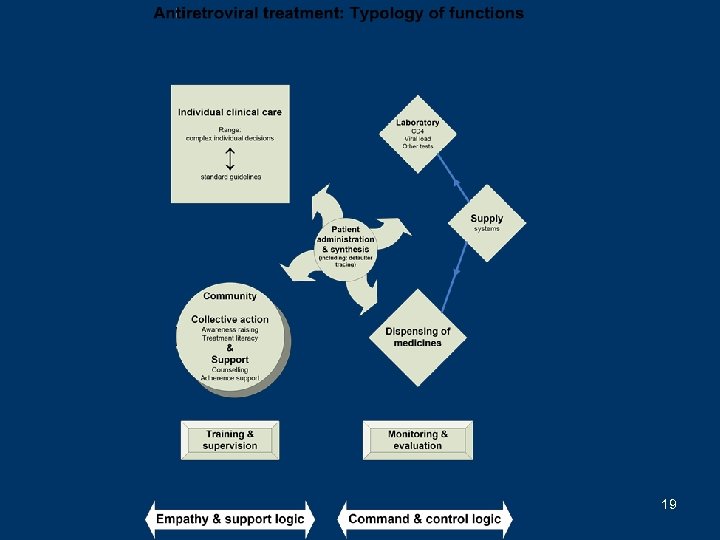
 « Bonus » material 17
« Bonus » material 17
 18
18
 19
19


