071d60f79620777604b988d286206194.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Task Learning by Instruction: Benefits and Challenges for Intelligent Interactive Systems Jim Blythe, Prateek Tandon and Mandar Tillu USC Information Sciences Institute USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 1

Overview Complex tasks in intelligent assistants Overview of task learning by instruction in Tailor Integration with other task-related capabilities Challenges and new approaches in specifying tasks USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 2
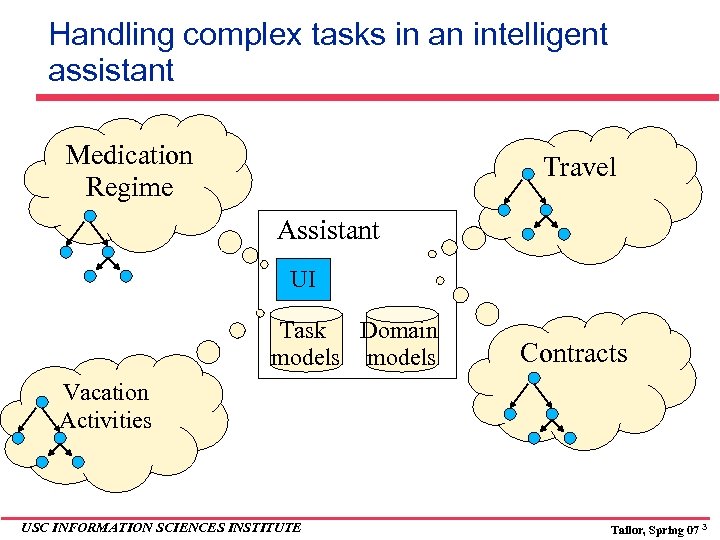
Handling complex tasks in an intelligent assistant Medication Regime Travel Assistant UI Task Domain models Contracts Vacation Activities USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 3
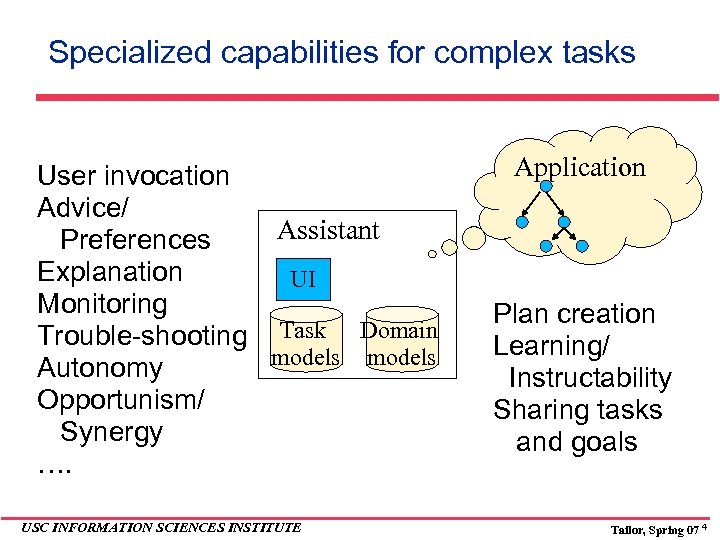
Specialized capabilities for complex tasks User invocation Advice/ Assistant Preferences Explanation UI Monitoring Trouble-shooting Task Domain models Autonomy Opportunism/ Synergy …. USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Application Plan creation Learning/ Instructability Sharing tasks and goals Tailor, Spring 07 4
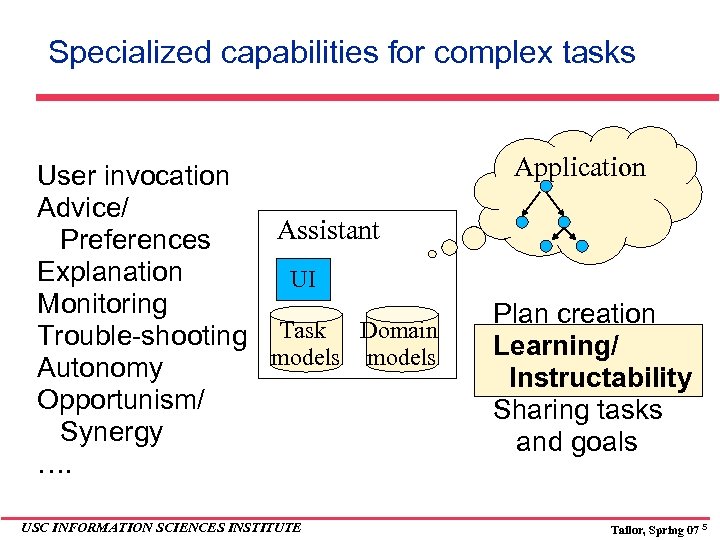
Specialized capabilities for complex tasks User invocation Advice/ Assistant Preferences Explanation UI Monitoring Trouble-shooting Task Domain models Autonomy Opportunism/ Synergy …. USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Application Plan creation Learning/ Instructability Sharing tasks and goals Tailor, Spring 07 5

Modifying a procedure with Tailor: “Task Learning by Instruction” User enters text instruction, e. g. “You don’t need authorization when the cost is below $2000. ” Tailor interprets by (1) recognizing type of modification, (2) mapping terms to its task and world ontology, To purchase equipment: (3) analyzing the proposed modification. {def. Procedure Purchase. Equip two one bids 1. find To purchase equipment: cue: [do: (purchase $obj_id)] form 10 C 2. fill out precond: (and (user $user) (p. Sel. Id $obj_id)) 1. find two bids 3. if it costs > $500 body: 2. fill out form 10 C request authorization [seq: 3. request authorization [do: (find_bids $obj $bid)] two managers from two managers 3½. record purchase [context: (use_form $obj) 4. if authorization granted do: (complete_form $obj)] on web site place order with [select: (and (total_priceauthorization granted 4. if $bid $price) (< $priceplace order with 2000)) purchasing $obj $user)]]]} USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE [do: (get_authorizationpurchasing Tailor, Spring 07 6
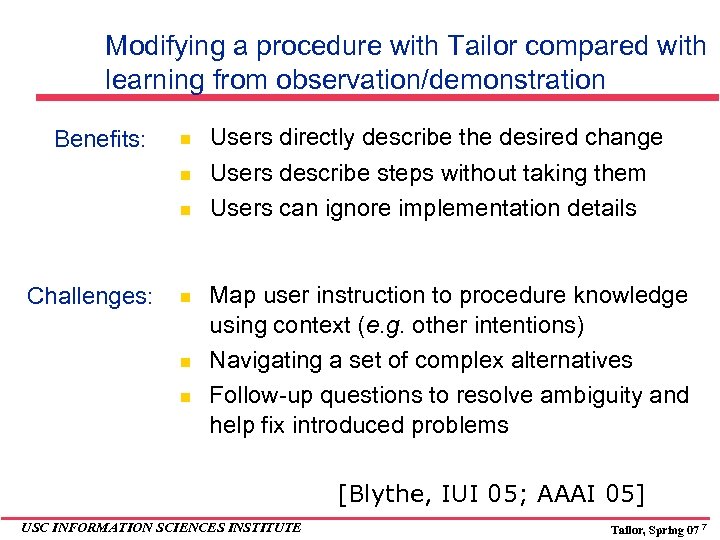
Modifying a procedure with Tailor compared with learning from observation/demonstration Benefits: Challenges: Users directly describe the desired change Users describe steps without taking them Users can ignore implementation details Map user instruction to procedure knowledge using context (e. g. other intentions) Navigating a set of complex alternatives Follow-up questions to resolve ambiguity and help fix introduced problems [Blythe, IUI 05; AAAI 05] USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 7

User describes a new task e. g. “list hotels within +miles of +meeting” USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 8
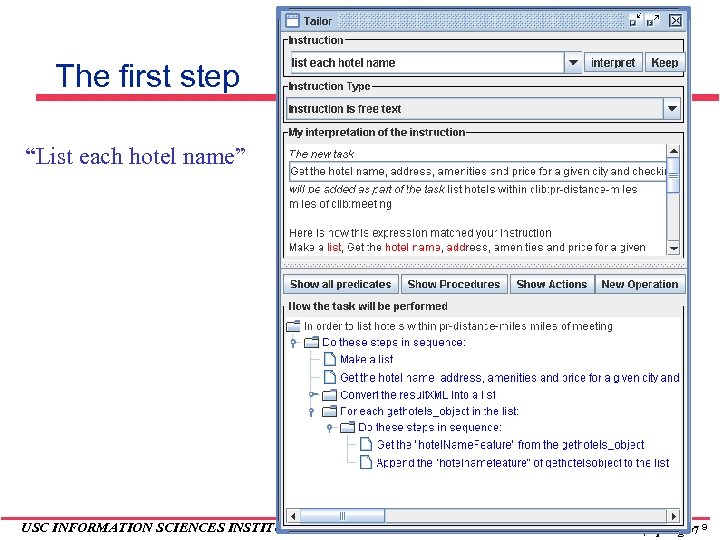
The first step “List each hotel name” USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 9
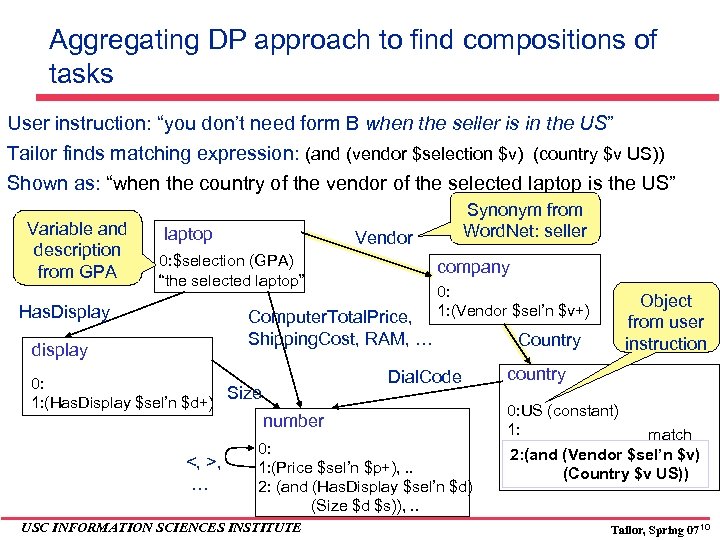
Aggregating DP approach to find compositions of tasks User instruction: “you don’t need form B when the seller is in the US” Tailor finds matching expression: (and (vendor $selection $v) (country $v US)) Shown as: “when the country of the vendor of the selected laptop is the US” Variable and description from GPA laptop Vendor 0: $selection (GPA) “the selected laptop” Has. Display company Computer. Total. Price, Shipping. Cost, RAM, … display 0: Size 1: (Has. Display $sel’n $d+) <, >, … Synonym from Word. Net: seller 0: 1: (Vendor $sel’n $v+) Dial. Code number 0: 1: (Price $sel’n $p+), . . 2: (and (Has. Display $sel’n $d) (Size $d $s)), . . USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Object from user instruction Country country 0: US (constant) 1: match 2: (and (Vendor $sel’n $v) (Country $v US)) Tailor, Spring 07 10
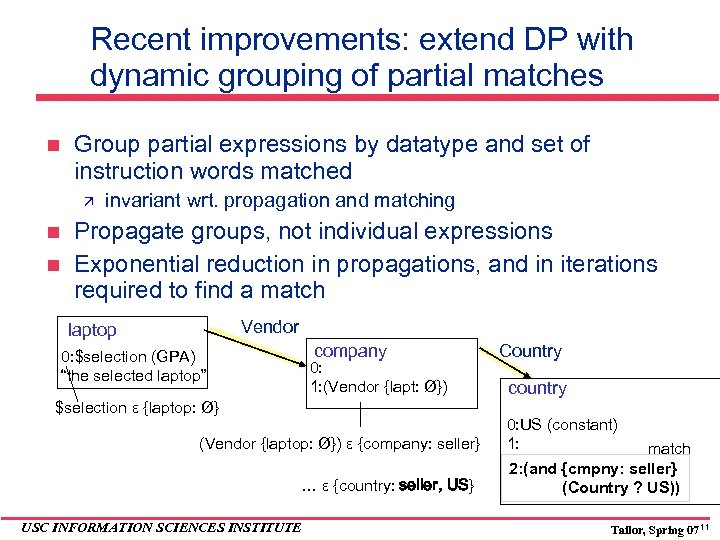
Recent improvements: extend DP with dynamic grouping of partial matches Group partial expressions by datatype and set of instruction words matched invariant wrt. propagation and matching Propagate groups, not individual expressions Exponential reduction in propagations, and in iterations required to find a match Vendor laptop company 0: $selection (GPA) “the selected laptop” 0: 1: (Vendor {lapt: Ø}) $selection ε {laptop: Ø} (Vendor {laptop: Ø}) ε {company: seller} … ε {country: seller, US} USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Country country 0: US (constant) 1: match 2: (and {cmpny: seller} (Country ? US)) Tailor, Spring 07 11
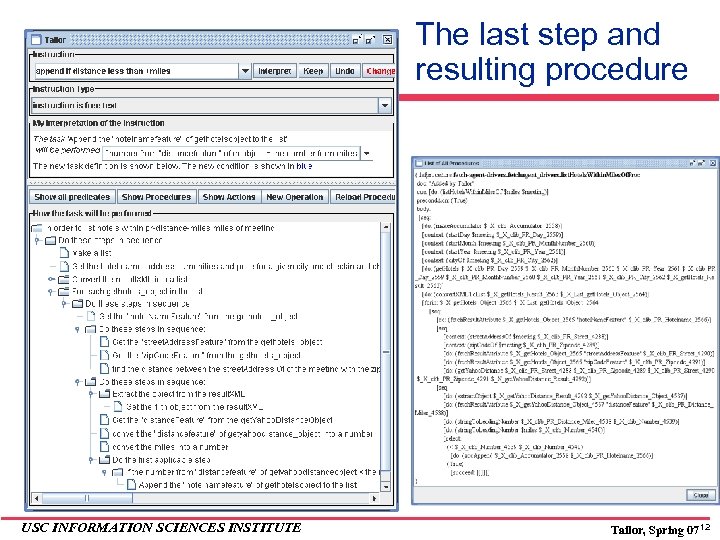
The last step and resulting procedure USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 12

Overview Task learning in desktop systems Overview of task learning by instruction Integration with other task-related capabilities Challenges and new approaches in specifying tasks USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 13

Challenges highlighted by Tailor prototype Users unsure of the “next step” Many alternative input sets for primitive procedures More context-dependent menus and wizards Fewer options, although there are several valid alternatives Full list is overwhelming: be selective and summarize Constraints on inputs of primitive procedures Procedure hard to understand Combining tasks built by users – inappropriate information Hide substeps Hide parameters Allow drill-down USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 14
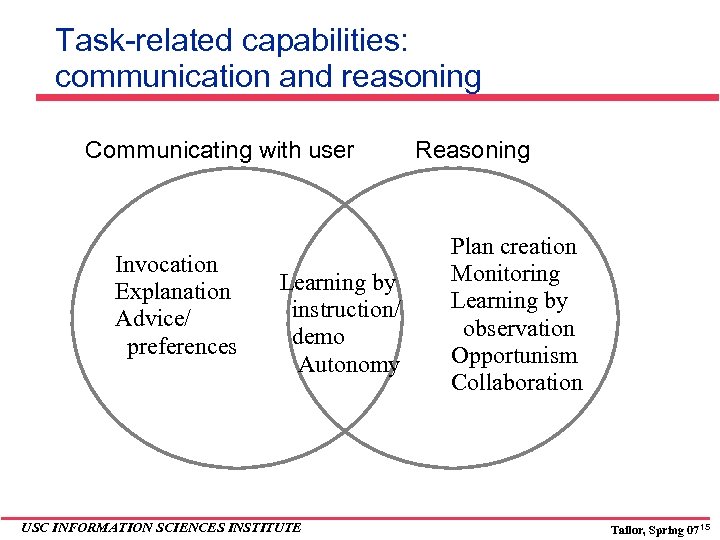
Task-related capabilities: communication and reasoning Communicating with user Invocation Explanation Advice/ preferences Learning by instruction/ demo Autonomy USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Reasoning Plan creation Monitoring Learning by observation Opportunism Collaboration Tailor, Spring 07 15
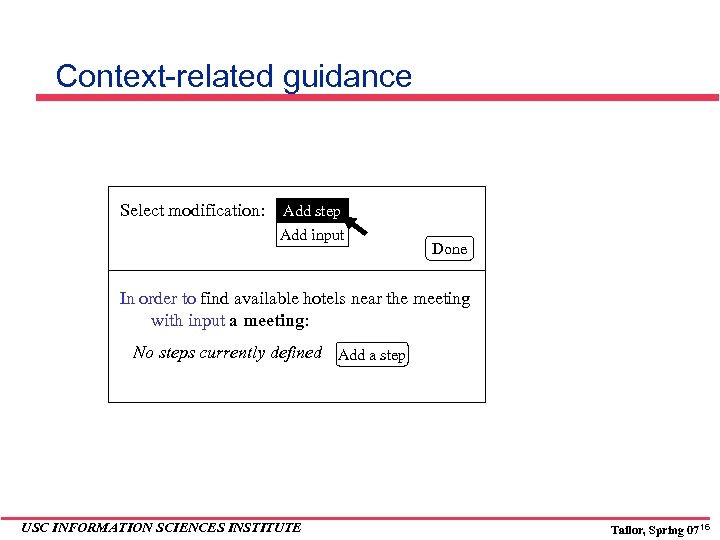
Context-related guidance Select modification: Add step Add input Done In order to find available hotels near the meeting with input a meeting: No steps currently defined Add a step USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 16
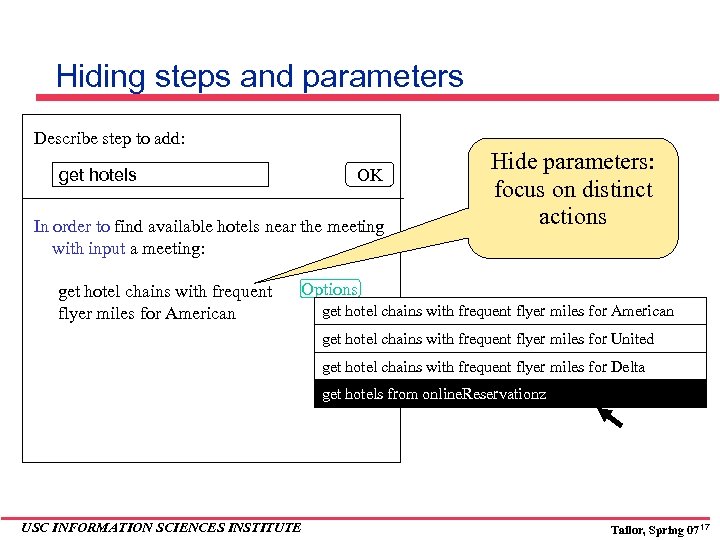
Hiding steps and parameters Describe step to add: get hotels OK In order to find available hotels near the meeting with input a meeting: get hotel chains with frequent flyer miles for American Hide parameters: focus on distinct actions Options get hotel chains with frequent flyer miles for American get hotel chains with frequent flyer miles for United get hotel chains with frequent flyer miles for Delta get hotels from online. Reservationz USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 17
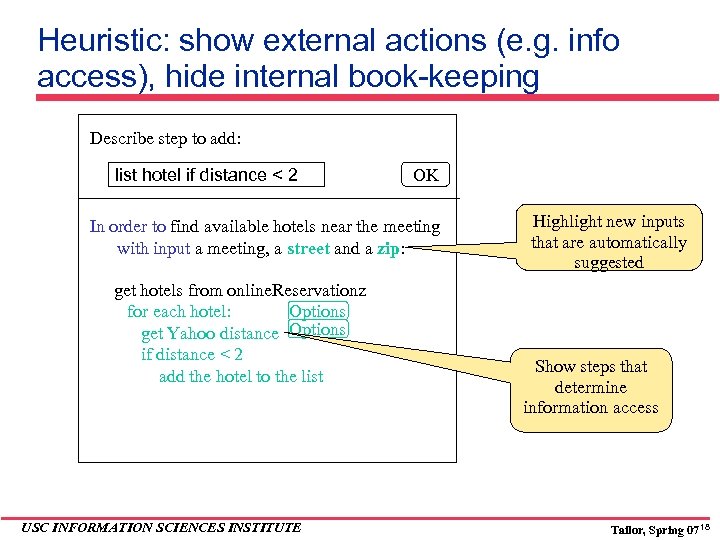
Heuristic: show external actions (e. g. info access), hide internal book-keeping Describe step to add: list hotel if distance < 2 OK In order to find available hotels near the meeting with input a meeting, a street and a zip: get hotels from online. Reservationz for each hotel: Options get Yahoo distance Options if distance < 2 add the hotel to the list USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Highlight new inputs that are automatically suggested Show steps that determine information access Tailor, Spring 07 18
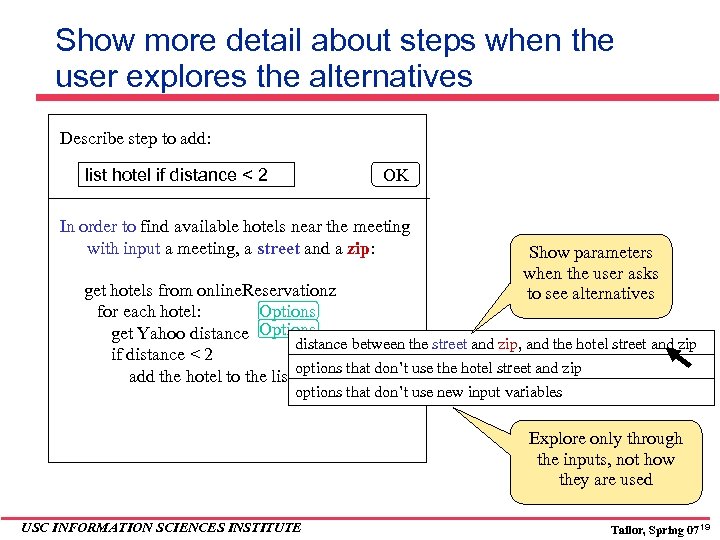
Show more detail about steps when the user explores the alternatives Describe step to add: list hotel if distance < 2 OK In order to find available hotels near the meeting with input a meeting, a street and a zip: Show parameters when the user asks to see alternatives get hotels from online. Reservationz for each hotel: Options get Yahoo distance Options distance between the street and zip, and the hotel street and zip if distance < 2 add the hotel to the list options that don’t use the hotel street and zip options that don’t use new input variables Explore only through the inputs, not how they are used USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 19
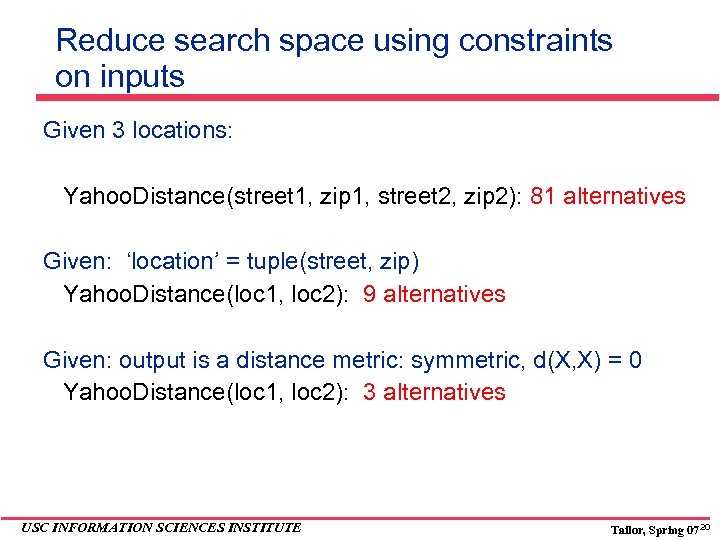
Reduce search space using constraints on inputs Given 3 locations: Yahoo. Distance(street 1, zip 1, street 2, zip 2): 81 alternatives Given: ‘location’ = tuple(street, zip) Yahoo. Distance(loc 1, loc 2): 9 alternatives Given: output is a distance metric: symmetric, d(X, X) = 0 Yahoo. Distance(loc 1, loc 2): 3 alternatives USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 20
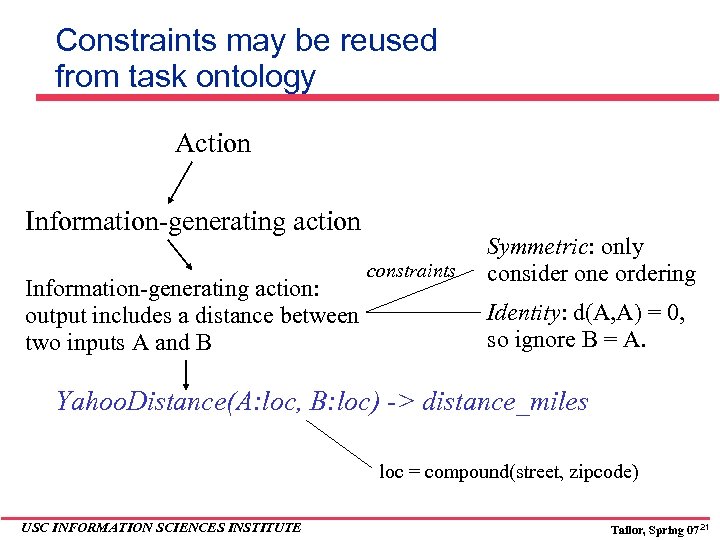
Constraints may be reused from task ontology Action Information-generating action: output includes a distance between two inputs A and B constraints Symmetric: only consider one ordering Identity: d(A, A) = 0, so ignore B = A. Yahoo. Distance(A: loc, B: loc) -> distance_miles loc = compound(street, zipcode) USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 21
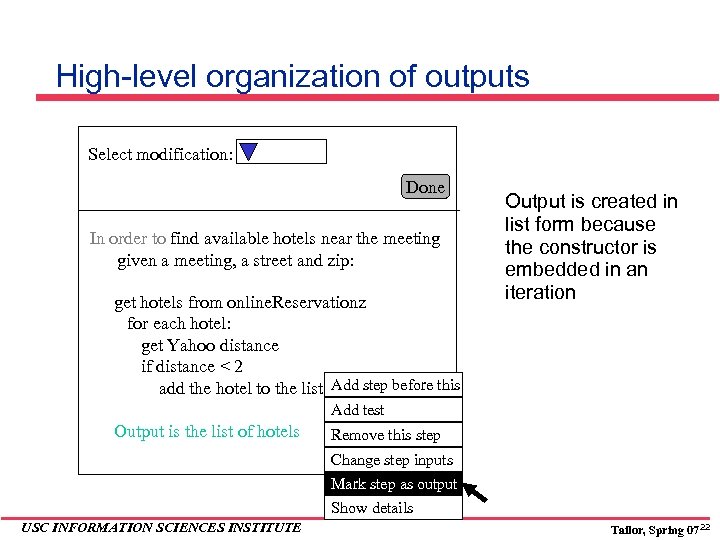
High-level organization of outputs Select modification: Done In order to find available hotels near the meeting given a meeting, a street and zip: get hotels from online. Reservationz for each hotel: get Yahoo distance if distance < 2 add the hotel to the list Add step before this Output is created in list form because the constructor is embedded in an iteration Add test Output is the list of hotels Remove this step Change step inputs Mark step as output Show details USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 22
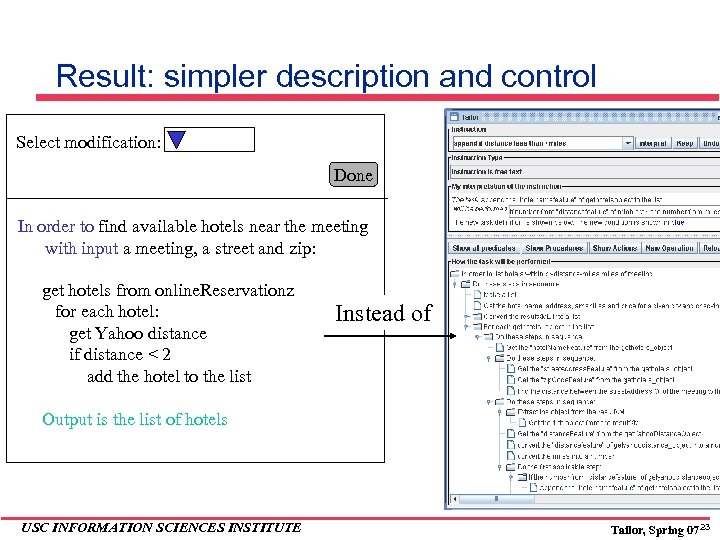
Result: simpler description and control Select modification: Done In order to find available hotels near the meeting with input a meeting, a street and zip: get hotels from online. Reservationz for each hotel: get Yahoo distance if distance < 2 add the hotel to the list Instead of Output is the list of hotels USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 23
Current work Creating primitive procedures while creating top-level procedure, not before. Using examples from previously-build procedures to select steps, bindings and follow-ups Constraints: representation, input and use USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 24

Summary Learning complex activities from instruction. Similar issues in modules that communicate about tasks Many potential matches for an instruction Describing learned tasks: find the ‘right’ level of initial detail and allow drill-down Utilize constraints on possible procedure inputs USC INFORMATION SCIENCES INSTITUTE Tailor, Spring 07 25
071d60f79620777604b988d286206194.ppt