6189a06c514dd97a0c400776a832e78f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Task 10. 5 -High Precision SC Cavity Alignment/Diagnostics/BPM with HOM Measurements Nicoleta Baboi, Ursula van Rienen Roger M. Jones DESY, Univ. of Rostock, Univ. of Manchester/ Cockcroft Inst. R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 1

Task 10. 5 -Overview Ø Participating institutes/staffing Ø HOM diagnostic measurement method and results achieved to date Ø Breakdown of each sub-task Ø Milestones/goals Ø Finances/budget profile Ø Summary R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 2

R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 3

Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics in SC Accelerator Cavities -Staff ØSub-task leaders: Nicoleta Baboi (DESY), Ursula van Rienen (Univ. Rostock), Roger M. Jones (CI/Univ. Manchester). ØPDRAs: Hans-Walter Glock (Univ. Rostock), Ian Shinton (CI/Univ. of Manchester), TBA (DESY) ØPh. Ds: Nawin Juntong (CI/Univ. Manchester), Chris Glasman (CI/Univ. Manchester) C. Glasman, CI/Univ. of Manchester Ph. d student (PT on FP 7) N. Juntong, CI/Univ. of I. Shinton, CI/Univ. of Manchester Ph. d student Manchester PDRA (PT on FP 7) H-W Glock, Univ. of U. Van Rienen, Rostock, PDRA Univ. of Rostock R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 N. Baboi, DESY 4

Task 10. 5 HOMs in SC Accelerator Cavities Ø HOM based monitors can radically contribute to the improvement of the beam quality in existing accelerator facilities FLASH at DESY and ERLP at Daresbury Laboratory, as well as the stretched wire test HOM characterisation facility at the Cockcroft Institute, CMTF at DESY, and further facilities using superconducting cavities such as the future XFEL, ILC and 4 GLS. Ø The existing international work with SLAC and FNAL, USA, and KEK, Japan is expected to continue as it has important implications on maintaining beam quality in the development of the 16, 000 or more main linac accelerating cavities for the ILC. Ø Participating institutes: - DESY, Germany - Cockcroft Institute, UK - Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester, UK - Institute of General Electrical Engineering, University of Rostock, Germany - ASTe. C, Daresbury Laboratory, UK R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 5
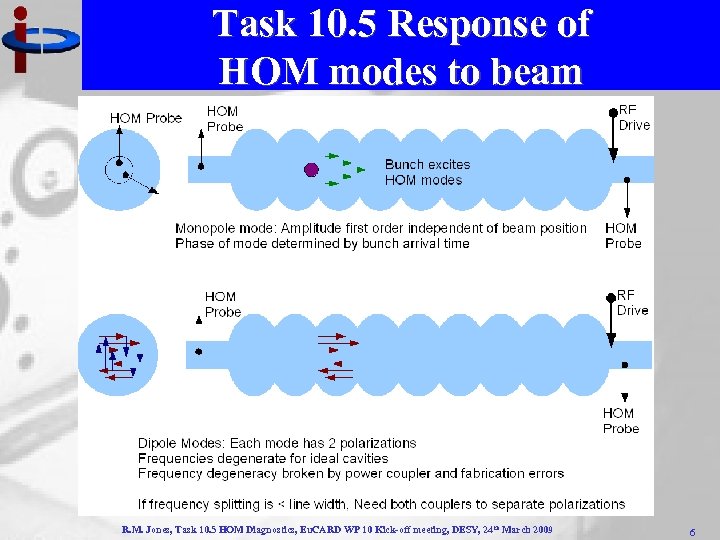
Task 10. 5 Response of HOM modes to beam R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 6
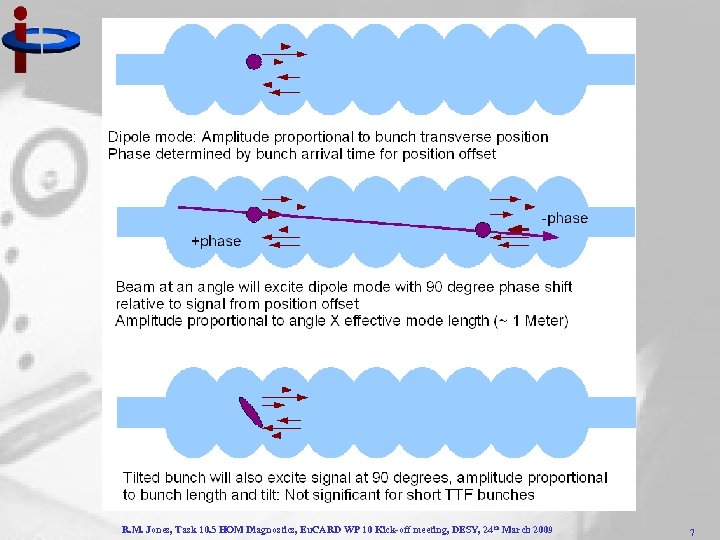
R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 7
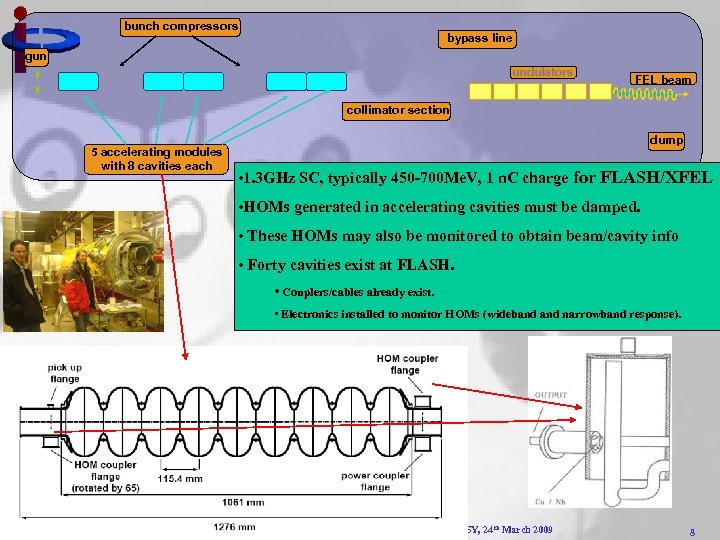
bunch compressors bypass line gun undulators FEL beam collimator section 5 accelerating modules with 8 cavities each dump • 1. 3 GHz SC, typically 450 -700 Me. V, 1 n. C charge for FLASH/XFEL • HOMs generated in accelerating cavities must be damped. • These HOMs may also be monitored to obtain beam/cavity info • Forty cavities exist at FLASH. • Couplers/cables already exist. • Electronics installed to monitor HOMs (wideband narrowband response). R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 8
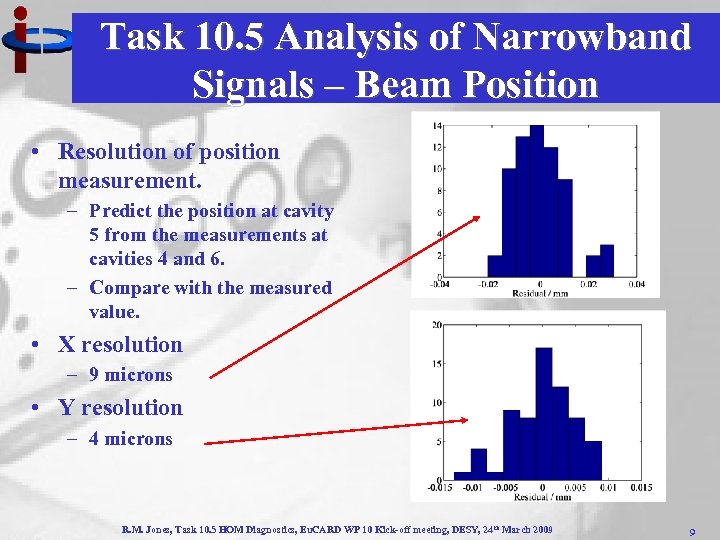
Task 10. 5 Analysis of Narrowband Signals – Beam Position • Resolution of position measurement. – Predict the position at cavity 5 from the measurements at cavities 4 and 6. – Compare with the measured value. • X resolution – 9 microns • Y resolution – 4 microns R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 9
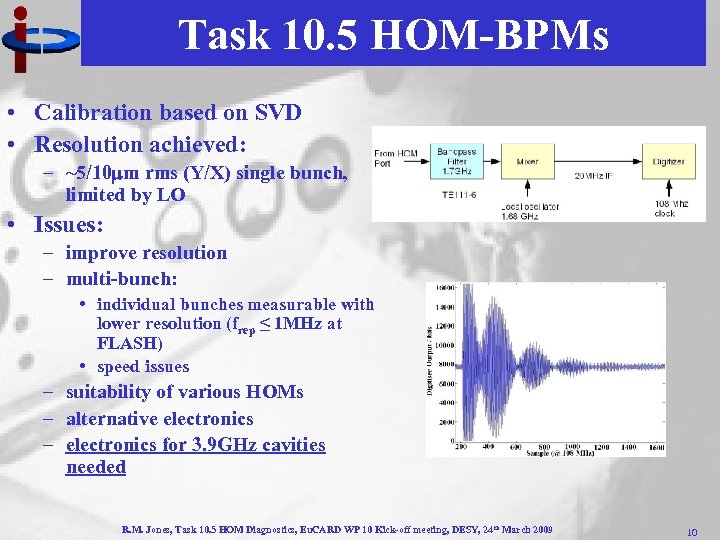
Task 10. 5 HOM-BPMs • Calibration based on SVD • Resolution achieved: – ~5/10 m rms (Y/X) single bunch, limited by LO • Issues: – improve resolution – multi-bunch: • individual bunches measurable with lower resolution (frep ≤ 1 MHz at FLASH) • speed issues – suitability of various HOMs – alternative electronics – electronics for 3. 9 GHz cavities needed R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 10

Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics in SC Accelerator Cavities –Task Breakdown Task Name Coordinating Institute/Univ. 10. 5. 1 HOMBPM DESY 10. 5. 2 HOMCD 10. 5. 3 HOMDG Cockcroft/Univ. Manchester Univ. Rostock R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 11

Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics Task Breakdown 10. 5. 1 HOM based Beam Position Monitors (HOMBPM) ØInitial electronics have been developed for single bunch and installed at FLASH allowing the beam to be centered precisely. ØMethod needs to be verified with additional modes ØMulti-bunch issues need to be understood. ØThe 3. 9 GHz bunch shaping cavities being installed in FLASH and XFEL can readily dilute the beam emittance –important to instrument with electronics modules to diagnose the beam position and improve emittance. ØCharacterisation of HOMBPMs after DESY installation in summer 2009. 10. 5. 2 HOM Cavity Diagnostics and ALICE/ERLP (HOMCD) ØHOM spectrum allows one to ascertain the cavity alignment and cell geometry. Will investigate: ØMechanical deviations of individual cells from the ideal geometry, ØCell-to-cell misalignment, ØDeformation of fields by couplers. R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 I. Shinton, CI/Univ. Manchester PDRA at FLASH (DESY) HOM shift C. Glasman, CI/Univ. Manchester Ph. D. student at FLASH (DESY) HOM Shift 12

10. 5. 2 HOM Cavity Diagnostics and ALICE/ERLP (HOMCD) contin. This part of the project requires beam-based measurements at FLASH, DESY and ALICE and RF-based measurements using the wire test facility at CI. 10. 5. 3 HOM Distributions and Geometrical Dependences (HOMDG) ØCombining finite element and S-matrix cascading techniques allows the eigenmodes in multiple accelerating cells and cavities to efficiently modeled. The University of Rostock and the University of Manchester have developed a suite of codes. ØWill apply these powerful computing methods in order to specify allowable tolerances on fabrication and alignment of the TESLA cells and cavities Ian Shinton’s Beam Time Shifts at FLASH (DESY) January 2007 (R. M. Jones, CI/Univ. of Manchester Faculty also participated) 7/1/07 -13/1/07: Participated in HOM shifts September 2007 25/9/07 -29/9/07: Attended as part of HOM shift groups of SLAC, FERMI and KEK – calibration data taken, HOM phase measurements taken across module 4, multibunch data taken January 2008 (Hans-Walter Glock, Univ. Rostock, also participated) 15/1/08 -23/1/08: 5 shifts in total: remote access control of the machine achieved, 5 collaborative shifts in which calibration data was taken, Multibunch data taken, Phase measurements taken across module 5 for various offsets (beam moved in a circle) – broadband data. September 2008 (C. Glasman, CI/Univ. of Manchester Ph. D. student also participated) 21/9/08 – 29/9/08: 1: Collaborative shift, 3 HOM phase/position assigned shifts th March 2009 R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 13

10. 5. 1 HOMBPM Highlights Ø Purpose: on-line measuring device for 1. beam alignment on the axes of the 3. 9 GHz cavities (& 1. 3 GHz cavities) in FLASH (&XFEL&ILC) 2. measurement of beam position at the cavity locations Ø Task: -develop, build, test electronics for 3. 9 GHz cavities -interpret signals and integrate in control system -measure cavity alignment HOM-couplers (pick-ups) Ø HOM-couplers -one at each cavity end -enable monitoring the HOMs excited by beam R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 14
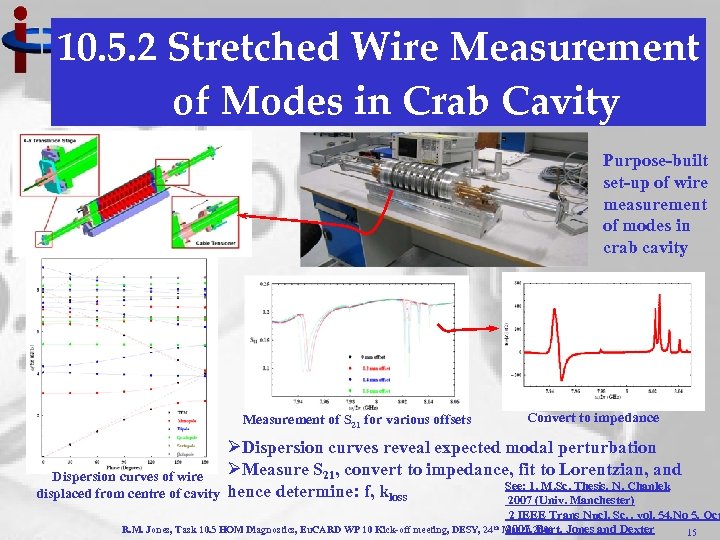
10. 5. 2 Stretched Wire Measurement of Modes in Crab Cavity Purpose-built set-up of wire measurement of modes in crab cavity Measurement of S 21 for various offsets Dispersion curves of wire displaced from centre of cavity Convert to impedance ØDispersion curves reveal expected modal perturbation ØMeasure S 21, convert to impedance, fit to Lorentzian, and See: 1. M. Sc. Thesis, N. Chanlek hence determine: f, kloss 2007 (Univ. Manchester) 2 IEEE Trans Nucl. Sc. , vol. 54, No 5, Oct 2007, Burt, Jones and Dexter 15 R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009

Task 10. 5. 2 HOMCD –Future Development for ALICE/ERLP ØExperience gained on FLASH measurements is invaluable. ØHOMs in ALICE TESLA cavities will provide information on: Ø 1. Beam position (effectively a built-in BPM) Ø 2. Alignment of cells (and groups thereof). Schematic illustrating ALICE CI/Univ. of Manchester PDRA I. Shinton (left) and Ph. D. student N. Juntong (right; supported by the Thai Government) will participate in ALICE commissioning in Nov/Dec 2008 ØProposal for similar HOM diagnostic measurement on ALICE R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 16
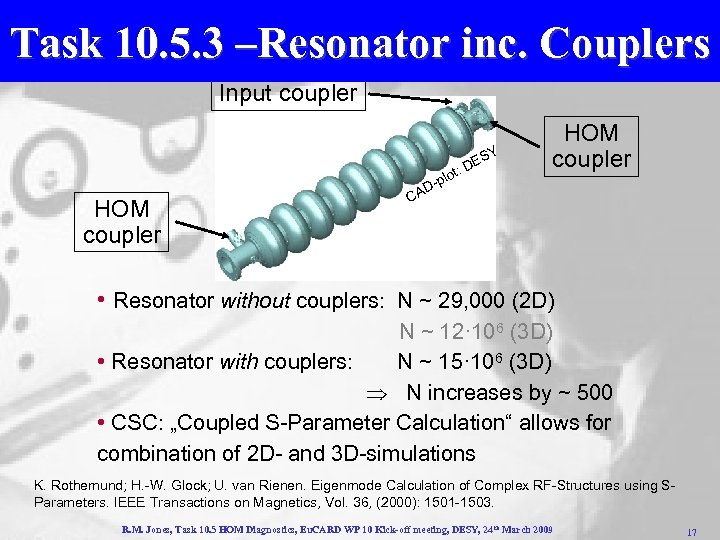
Task 10. 5. 3 –Resonator inc. Couplers Input coupler SY HOM coupler E t: D plo HOM coupler D- CA • Resonator without couplers: N ~ 29, 000 (2 D) N ~ 12· 106 (3 D) • Resonator with couplers: N ~ 15· 106 (3 D) N increases by ~ 500 • CSC: „Coupled S-Parameter Calculation“ allows for combination of 2 D- and 3 D-simulations K. Rothemund; H. -W. Glock; U. van Rienen. Eigenmode Calculation of Complex RF-Structures using SParameters. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, Vol. 36, (2000): 1501 -1503. R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 17
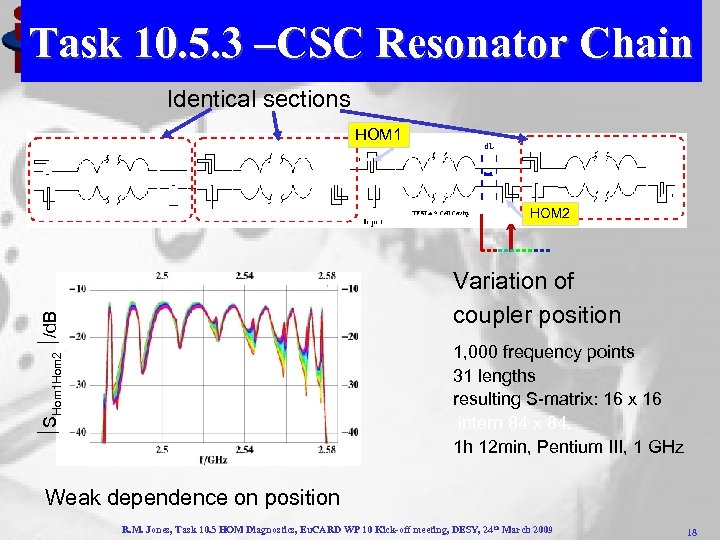
Task 10. 5. 3 –CSC Resonator Chain Identical sections HOM 1 HOM 2 SHom 1 Hom 2 /d. B Variation of coupler position 1, 000 frequency points 31 lengths resulting S-matrix: 16 x 16 intern 84 x 84, 1 h 12 min, Pentium III, 1 GHz Weak dependence on position R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 18
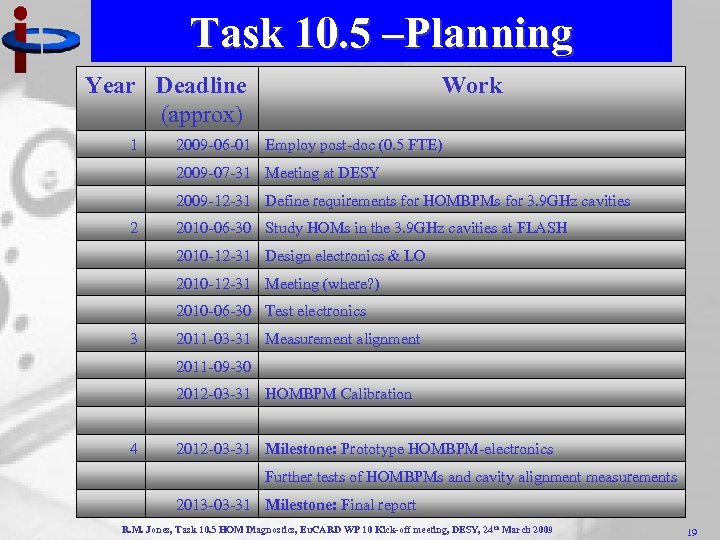
Task 10. 5 –Planning Year Deadline (approx) 1 Work 2009 -06 -01 Employ post-doc (0. 5 FTE) 2009 -07 -31 Meeting at DESY 2009 -12 -31 Define requirements for HOMBPMs for 3. 9 GHz cavities 2 2010 -06 -30 Study HOMs in the 3. 9 GHz cavities at FLASH 2010 -12 -31 Design electronics & LO 2010 -12 -31 Meeting (where? ) 2010 -06 -30 Test electronics 3 2011 -03 -31 Measurement alignment 2011 -09 -30 2012 -03 -31 HOMBPM Calibration 4 2012 -03 -31 Milestone: Prototype HOMBPM-electronics Further tests of HOMBPMs and cavity alignment measurements 2013 -03 -31 Milestone: Final report R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 19

Task 10. 5 –Milestones/Deliverables Description/title 10. 5. 1. 1 Prototype of HOMBPM electronics and code to probe beam centering on 3. 9 GHz cavities P 40 10. 5. 1. 2 Report on experimental method and code R 48 Description/title Nature 1 Delivery month 2 Milestones 10. 5. 1. 1 Nature 1 Delivery month 2 Deliverables HOM alignment for 3. 9 GHz cavity electronics D verification 40 Sub-structure and cavity alignment from HOM R signal –algorithm and implementation 48 Final report 48 10. 5. 2. 1 R 10. 5. 3. 1 1=prototype; R=report R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 20
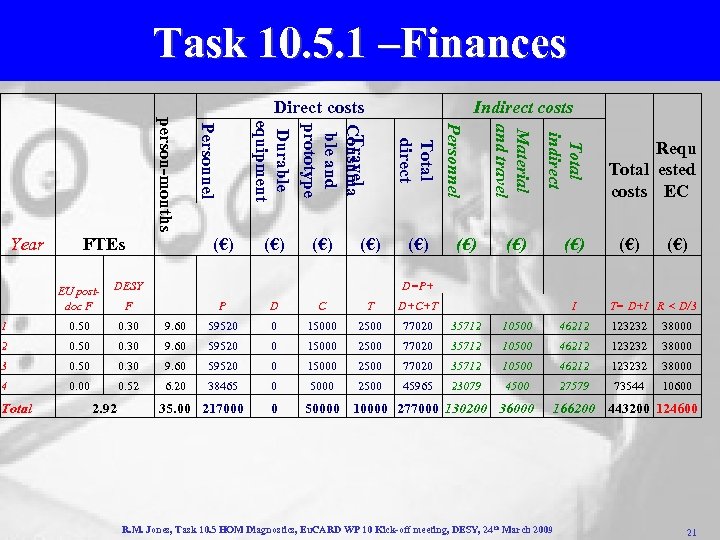
Task 10. 5. 1 –Finances (€) Total indirect (€) Material and travel (€) Personnel Total direct (€) FTEs Indirect costs Travel Consuma ble and prototype Durable equipment Personnel person-months Year Direct costs (€) (€) Requ Total ested costs EC (€) EU postdoc F DESY F P D C T D+C+T I 1 0. 50 0. 30 9. 60 59520 0 15000 2500 77020 35712 10500 46212 123232 38000 2 0. 50 0. 30 9. 60 59520 0 15000 2500 77020 35712 10500 46212 123232 38000 3 0. 50 0. 30 9. 60 59520 0 15000 2500 77020 35712 10500 46212 123232 38000 4 0. 00 0. 52 6. 20 38465 0 5000 2500 45965 23079 4500 27579 73544 10600 Total 2. 92 D=P+ 35. 00 217000 0 50000 10000 277000 130200 36000 T= D+I R < D/3 166200 443200 124600 R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 21

Task 10. 5. 2 –Finances R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 22

Task 10. 5. 3 –Finances R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 23
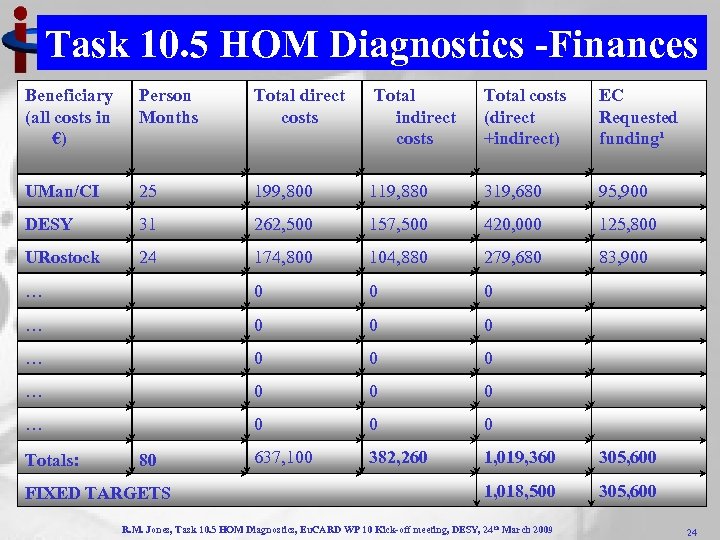
Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics -Finances Beneficiary (all costs in €) Person Months Total direct costs Total indirect costs Total costs (direct +indirect) EC Requested funding¹ UMan/CI 25 199, 800 119, 880 319, 680 95, 900 DESY 31 262, 500 157, 500 420, 000 125, 800 URostock 24 174, 800 104, 880 279, 680 83, 900 … 0 0 0 … 0 0 0 Totals: 80 637, 100 382, 260 1, 019, 360 305, 600 1, 018, 500 305, 600 FIXED TARGETS R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 24

Summary of Task 10. 5 ØHOM characterisation of cavity wake-fields and beam dynamics for ILC/XFEL. Globalised scattering technique provides a unique method to enable trapped modes in modules to be probed. Ø HOMs as BPM diagnostic for ILC/XFEL: FP 7 proposal as part of DESY/Cockcroft/Univs Manchester & Rostock collaboration. Experimental and simulation/analytical aspects at FLASH/DESY. Ø 3. 9 GHz bunch-shaping cavities due to be installed at FLASH will have a significantly larger wakefields (~ a 3). Major part of program will be entail characterising these cavities –beam and cavity alignment R. M. Jones, Task 10. 5 HOM Diagnostics, Eu. CARD WP 10 Kick-off meeting, DESY, 24 th March 2009 25
6189a06c514dd97a0c400776a832e78f.ppt