e386a0ad93537eb552c5de3a19e45546.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Talking Freight Seminar Freight and Economic Development Glen Weisbrod Economic Development Research Group, Inc. 2 Oliver Street, 9 th Floor Boston, MA 02109 USA www. edrgroup. com
Talking Freight Seminar Freight and Economic Development Glen Weisbrod Economic Development Research Group, Inc. 2 Oliver Street, 9 th Floor Boston, MA 02109 USA www. edrgroup. com
 Three Themes 1. Freight Flows: changing due to National & Global Economic Markets. 2. Economic Development: depends on Market Access & Competitiveness. 3. Infrastructure Investment: directly affects Costs & Competitiveness. 2
Three Themes 1. Freight Flows: changing due to National & Global Economic Markets. 2. Economic Development: depends on Market Access & Competitiveness. 3. Infrastructure Investment: directly affects Costs & Competitiveness. 2
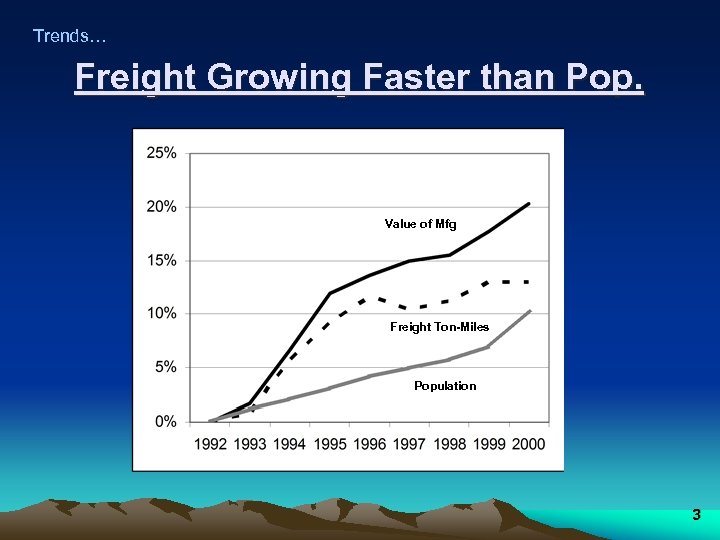 Trends… Freight Growing Faster than Pop. Value of Mfg Freight Ton-Miles Population 3
Trends… Freight Growing Faster than Pop. Value of Mfg Freight Ton-Miles Population 3
 Trends… Changing Freight Patterns • • • Higher value/weight Higher time sensitivity Overnight delivery Small package delivery trucks Air & Marine port dependence on rail & hwy Rail & truck companies focus on long-hauls 4
Trends… Changing Freight Patterns • • • Higher value/weight Higher time sensitivity Overnight delivery Small package delivery trucks Air & Marine port dependence on rail & hwy Rail & truck companies focus on long-hauls 4
 Economic Development… Congestion Costs of Delay Overnight Delivery Services –earlier pickup deadlines, fewer deliveries per driver Manufacturers –overtime for handling deliveries Concrete mixer trucks –shrink delivery area (spoilage) Shippers, Air/Water Ports, Rail – miss delivery deadlines or pad schedules 5
Economic Development… Congestion Costs of Delay Overnight Delivery Services –earlier pickup deadlines, fewer deliveries per driver Manufacturers –overtime for handling deliveries Concrete mixer trucks –shrink delivery area (spoilage) Shippers, Air/Water Ports, Rail – miss delivery deadlines or pad schedules 5
 Economic Development… Competitiveness & Productivity Effects on Business Location & Growth… • • Breadth of Suppliers & Labor Inputs Size of Customer Delivery Markets Economies of Scale in Serving Markets Transportation Choice: Reliability, Modes 6
Economic Development… Competitiveness & Productivity Effects on Business Location & Growth… • • Breadth of Suppliers & Labor Inputs Size of Customer Delivery Markets Economies of Scale in Serving Markets Transportation Choice: Reliability, Modes 6
 Economic Development… Urban Freight Limitation • Higher Cost to Serve Markets • Reduced Schedule Reliability • Reduced Access & Scale Economies Reduced Opportunity for Attracting and Growing Business … Smaller Market Area can be served within requirements for cost and service quality 7
Economic Development… Urban Freight Limitation • Higher Cost to Serve Markets • Reduced Schedule Reliability • Reduced Access & Scale Economies Reduced Opportunity for Attracting and Growing Business … Smaller Market Area can be served within requirements for cost and service quality 7
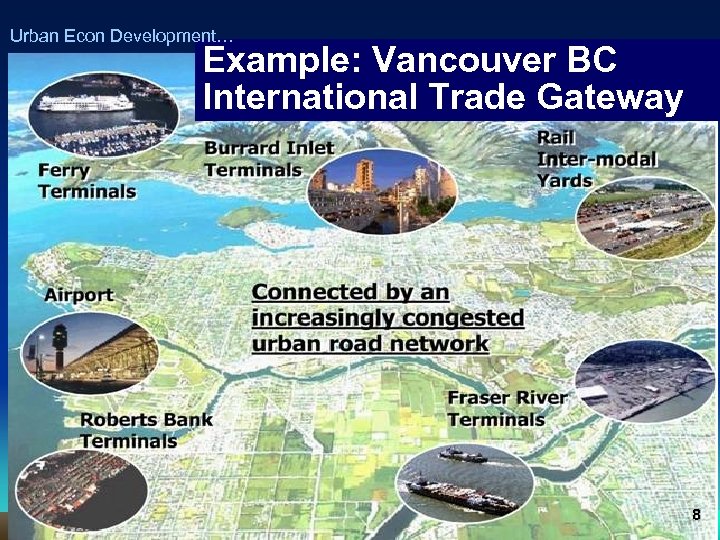 Urban Econ Development… Example: Vancouver BC International Trade Gateway 8
Urban Econ Development… Example: Vancouver BC International Trade Gateway 8
 Urban Econ Development… Vancouver No Build Scenario Ground Transport Diff: Build vs. Not • Cars – increase in travel expense ($134 million/yr) • Trucks – raise shipper costs; reduce business competitiveness & attraction ($280 million/yr) • Rail – capacity limitation: businesses seek alternative routes at higher cost (1100 railcars/day) Ports • Marine ports – higher cost, shift activity elsewhere • Airport – raise costs for airport use 9
Urban Econ Development… Vancouver No Build Scenario Ground Transport Diff: Build vs. Not • Cars – increase in travel expense ($134 million/yr) • Trucks – raise shipper costs; reduce business competitiveness & attraction ($280 million/yr) • Rail – capacity limitation: businesses seek alternative routes at higher cost (1100 railcars/day) Ports • Marine ports – higher cost, shift activity elsewhere • Airport – raise costs for airport use 9
 Urban Econ Development… Vancouver Economic Implications Economic Value of Gateway 30 Port Terminals, 22 Rail Yards, Airport, Border Crossings On Site: 75, 000 jobs, W. Canada: 145, 000 jobs Economic Impact of Constraint on Growth: • 7, 300 to 16, 300 jobs • $ 475 million to $ 1. 1 billion of GDP /year Economic Stakes for Cost Competitiveness: • Over 150, 000 jobs in production industries produce over $30 billion of exports /yr that depend on Vancouver Gateway competitiveness 10
Urban Econ Development… Vancouver Economic Implications Economic Value of Gateway 30 Port Terminals, 22 Rail Yards, Airport, Border Crossings On Site: 75, 000 jobs, W. Canada: 145, 000 jobs Economic Impact of Constraint on Growth: • 7, 300 to 16, 300 jobs • $ 475 million to $ 1. 1 billion of GDP /year Economic Stakes for Cost Competitiveness: • Over 150, 000 jobs in production industries produce over $30 billion of exports /yr that depend on Vancouver Gateway competitiveness 10
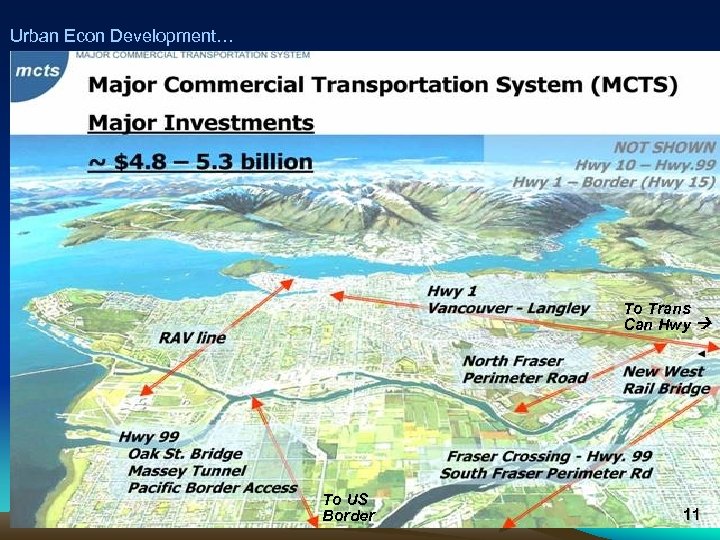 Urban Econ Development… Vancouver… To Trans Can Hwy To US Border 11
Urban Econ Development… Vancouver… To Trans Can Hwy To US Border 11
 Urban Economic Development… Strategies for Port/Gateway Areas • Access Corridor – Los Angeles (Alameda Corridor) • Satellite Ports – NY Port Inland Distribution Network • Feeder System – Rotterdam (Inland Ports) 12
Urban Economic Development… Strategies for Port/Gateway Areas • Access Corridor – Los Angeles (Alameda Corridor) • Satellite Ports – NY Port Inland Distribution Network • Feeder System – Rotterdam (Inland Ports) 12
 Urban Econ Development… Example: Chicago Rail Yards • 74 rail yards, 17 for intermodal (rail -truck) • delays at 600 grade crossings • congestion from 3200 daily truck trips transferring cargo from yard to yard • Abandoned & underutilized rail yards http: // hometown. aol. com/chirailfan/watchmap. html 13
Urban Econ Development… Example: Chicago Rail Yards • 74 rail yards, 17 for intermodal (rail -truck) • delays at 600 grade crossings • congestion from 3200 daily truck trips transferring cargo from yard to yard • Abandoned & underutilized rail yards http: // hometown. aol. com/chirailfan/watchmap. html 13
 Urban Econ Development… Chicago Scenario Impacts Scenarios (with & without reuse of abandoned rail yards) • Base Case: existing facilities, adjust over time • Shift Intermodal to Rim: periphery of region • Rationalization: Consolidate w/upgraded infrastructure • Minimal Rail Freight in City: Intermodal moves to periphery; loose-car business de-marketed • Bypass Chicago: Reroute trains to bypass routes 14
Urban Econ Development… Chicago Scenario Impacts Scenarios (with & without reuse of abandoned rail yards) • Base Case: existing facilities, adjust over time • Shift Intermodal to Rim: periphery of region • Rationalization: Consolidate w/upgraded infrastructure • Minimal Rail Freight in City: Intermodal moves to periphery; loose-car business de-marketed • Bypass Chicago: Reroute trains to bypass routes 14
 Economic Development… NCHRP Study 8 -42 How Can We Use Rail Freight Solutions to Address Roadway Congestion • Converging interests of private sector transport carriers and public planning agencies • Reducing Congestion and Road/Rail conflicts that adversely affect business profits, public safety and economic development opportunities • Developing Framework for Decision-making 15
Economic Development… NCHRP Study 8 -42 How Can We Use Rail Freight Solutions to Address Roadway Congestion • Converging interests of private sector transport carriers and public planning agencies • Reducing Congestion and Road/Rail conflicts that adversely affect business profits, public safety and economic development opportunities • Developing Framework for Decision-making 15
 Rural Economic Development… Rural Freight Limitations Higher Trucking Cost –due to “deadheading” Lower Availability When Needed –reliability reduced by vehicle shortages, delays Higher Rail Cost –full line cost for rail service to/from intermediate locations Reduced Opportunity for Attracting and Growing Business … Smaller Market Area can be served within requirements for cost and service quality Lower Value Added of existing products 16
Rural Economic Development… Rural Freight Limitations Higher Trucking Cost –due to “deadheading” Lower Availability When Needed –reliability reduced by vehicle shortages, delays Higher Rail Cost –full line cost for rail service to/from intermediate locations Reduced Opportunity for Attracting and Growing Business … Smaller Market Area can be served within requirements for cost and service quality Lower Value Added of existing products 16
 Rural Economic Development… Example: Appalachian Corridor T NY-17, Now I-86, Southern Tier Expressway Mountain Region of Southwest NY State, Near Pennsylvania Line Area had been economically distressed and losing jobs I-86 designation brought new freight distribution, manufacturing, and traffic-serving businesses. FHWA Study compared it to a similar area with no new highway connections 17
Rural Economic Development… Example: Appalachian Corridor T NY-17, Now I-86, Southern Tier Expressway Mountain Region of Southwest NY State, Near Pennsylvania Line Area had been economically distressed and losing jobs I-86 designation brought new freight distribution, manufacturing, and traffic-serving businesses. FHWA Study compared it to a similar area with no new highway connections 17
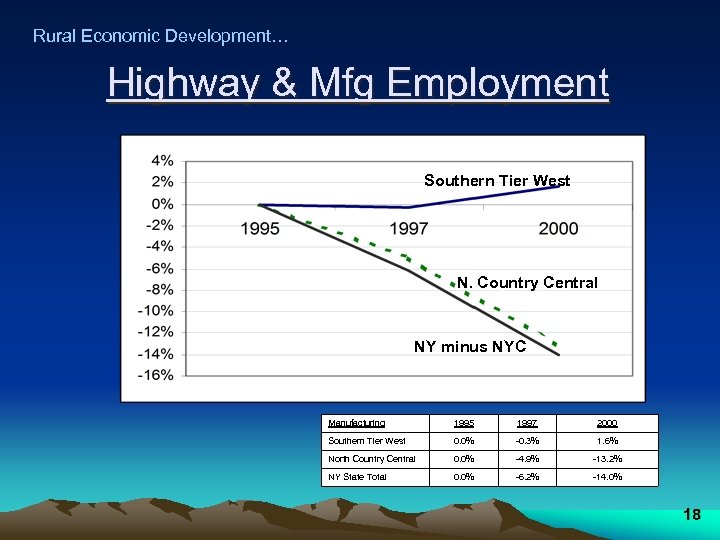 Rural Economic Development… Highway & Mfg Employment Southern Tier West N. Country Central NY minus NYC Manufacturing 1995 1997 2000 Southern Tier West 0. 0% -0. 3% 1. 6% North Country Central 0. 0% -4. 9% -13. 2% NY State Total 0. 0% -6. 2% -14. 0% 18
Rural Economic Development… Highway & Mfg Employment Southern Tier West N. Country Central NY minus NYC Manufacturing 1995 1997 2000 Southern Tier West 0. 0% -0. 3% 1. 6% North Country Central 0. 0% -4. 9% -13. 2% NY State Total 0. 0% -6. 2% -14. 0% 18
 Rural Economic Development… Example: Janesville, WI Regional automotive mfg cluster • Auto Mfg – GM, Chrysler • Parts Mfg –to S Carolina (BMW), Mexico & Mich. (Ford), Ontario & Missouri (Chrysler) • Reliance on just-in-time mfg, increasing needs for air and reliable truck movements • Current facilities cannot meet this need, reducing productivity and efficiency in mfg • Potential loss of jobs to Mexico or Canada 19
Rural Economic Development… Example: Janesville, WI Regional automotive mfg cluster • Auto Mfg – GM, Chrysler • Parts Mfg –to S Carolina (BMW), Mexico & Mich. (Ford), Ontario & Missouri (Chrysler) • Reliance on just-in-time mfg, increasing needs for air and reliable truck movements • Current facilities cannot meet this need, reducing productivity and efficiency in mfg • Potential loss of jobs to Mexico or Canada 19
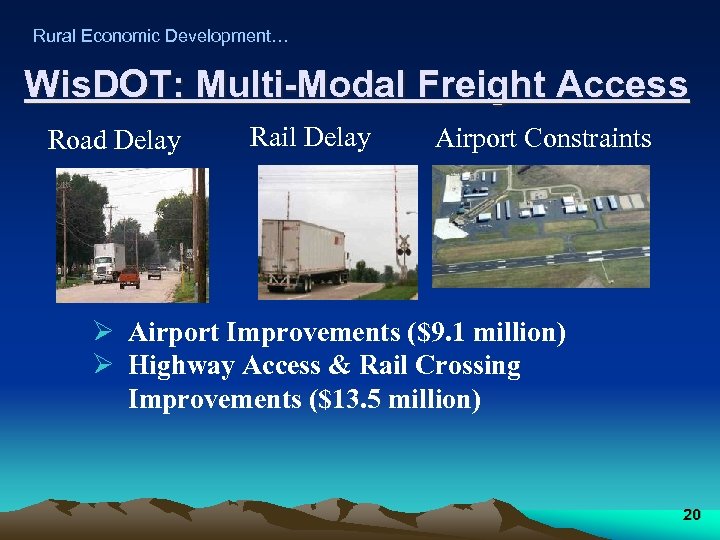 Rural Economic Development… Wis. DOT: Multi-Modal Freight Access Road Delay Rail Delay Airport Constraints Ø Airport Improvements ($9. 1 million) Ø Highway Access & Rail Crossing Improvements ($13. 5 million) 20
Rural Economic Development… Wis. DOT: Multi-Modal Freight Access Road Delay Rail Delay Airport Constraints Ø Airport Improvements ($9. 1 million) Ø Highway Access & Rail Crossing Improvements ($13. 5 million) 20
 Rural Economic Development… ARC Export Transportation Study Overseas Exports are Intermodal l. Truck to Air l Rail or Truck to Sea 21
Rural Economic Development… ARC Export Transportation Study Overseas Exports are Intermodal l. Truck to Air l Rail or Truck to Sea 21
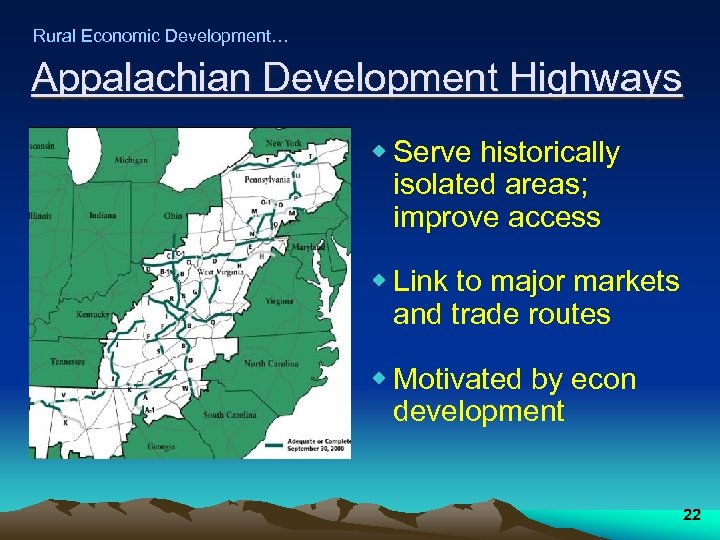 Rural Economic Development… Appalachian Development Highways w Serve historically isolated areas; improve access w Link to major markets and trade routes w Motivated by econ development 22
Rural Economic Development… Appalachian Development Highways w Serve historically isolated areas; improve access w Link to major markets and trade routes w Motivated by econ development 22
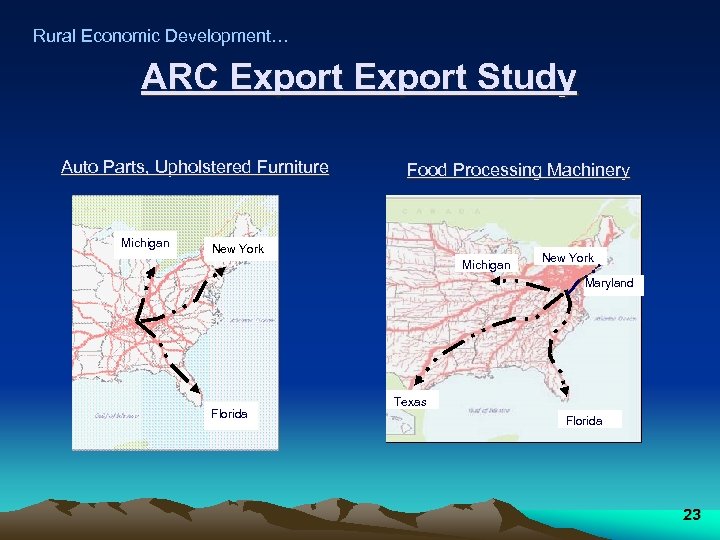 Rural Economic Development… ARC Export Study Auto Parts, Upholstered Furniture Michigan Food Processing Machinery New York Michigan New York Maryland Florida Texas Florida 23
Rural Economic Development… ARC Export Study Auto Parts, Upholstered Furniture Michigan Food Processing Machinery New York Michigan New York Maryland Florida Texas Florida 23
 Rural Economic Development… ARC Study Findings • There are limited E-W freeways, rail lines & intermodal connections across Appalachia, raising costs & constraining export opportunities. • States in eastern side export more to Europe because of easier access to east coast ports. • States in the western side export more within North America because of better access to industrial parts of Canada and Mexico. 24
Rural Economic Development… ARC Study Findings • There are limited E-W freeways, rail lines & intermodal connections across Appalachia, raising costs & constraining export opportunities. • States in eastern side export more to Europe because of easier access to east coast ports. • States in the western side export more within North America because of better access to industrial parts of Canada and Mexico. 24
 Conclusions… Freight Connections Alone Do Not Cause Economic Development …business growth & attraction depends on connections to markets, not just presence of a highway… ARC Guide: help planners identify opportunities related to new highways, and actions needed to pursue them. 25
Conclusions… Freight Connections Alone Do Not Cause Economic Development …business growth & attraction depends on connections to markets, not just presence of a highway… ARC Guide: help planners identify opportunities related to new highways, and actions needed to pursue them. 25
 Conclusions… But Failure to Provide Freight Access Constrains Economic Development • Lost opportunity for economic growth, good-paying jobs, new jobs for next generation. Potential Benefits of Infrastructure Investment… • Opportunity for success is not lost. 26
Conclusions… But Failure to Provide Freight Access Constrains Economic Development • Lost opportunity for economic growth, good-paying jobs, new jobs for next generation. Potential Benefits of Infrastructure Investment… • Opportunity for success is not lost. 26
 …On the Web FHWA Economic Development Studies (incl. I-86) www. fhwa. dot. gov/planning/econdev Vancouver Freight Gateway Study http: //www. edrgroup. com/pages/n 32. html North Country Transportation Studies www. danc. org/ncts Chicago Rail Freight Study www. edrgroup. com/pages/n 25. html ARC Guide to Economic Opportunities from Highways www. edrgroup. com/pages/n 11. html Library of Economic Impact Studies www. edrgroup. com 27
…On the Web FHWA Economic Development Studies (incl. I-86) www. fhwa. dot. gov/planning/econdev Vancouver Freight Gateway Study http: //www. edrgroup. com/pages/n 32. html North Country Transportation Studies www. danc. org/ncts Chicago Rail Freight Study www. edrgroup. com/pages/n 25. html ARC Guide to Economic Opportunities from Highways www. edrgroup. com/pages/n 11. html Library of Economic Impact Studies www. edrgroup. com 27


