381326ef4d258c481445b871e158be45.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 “Talent Management: Adding Value to the High Performing Organization” HPO CHANGE CONFERENCE March 3, 2004 Michael Friedman, F&L Group, Houston, Texas www. fandlgroup. com 713 -874 -1557 1
“Talent Management: Adding Value to the High Performing Organization” HPO CHANGE CONFERENCE March 3, 2004 Michael Friedman, F&L Group, Houston, Texas www. fandlgroup. com 713 -874 -1557 1
 Talent Management Answers These Questions! F & L Group WHO is the best candidate for a particular job? WHAT technical skills, experience & leadership competencies does each employee possess? WHERE can each employee best be deployed? WHEN is right time for new job? HOW will employees discover what skills are necessary to make a job or career move? 2
Talent Management Answers These Questions! F & L Group WHO is the best candidate for a particular job? WHAT technical skills, experience & leadership competencies does each employee possess? WHERE can each employee best be deployed? WHEN is right time for new job? HOW will employees discover what skills are necessary to make a job or career move? 2
 F & L Group We need to prove the economic value of Talent Management… and we can 3
F & L Group We need to prove the economic value of Talent Management… and we can 3
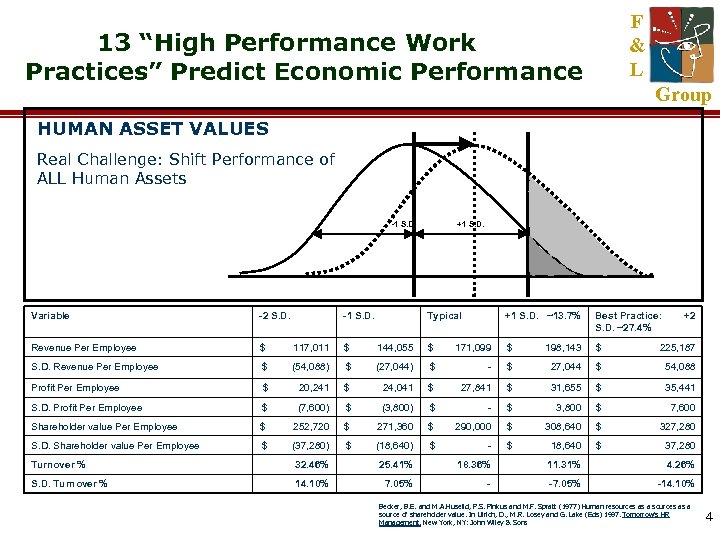 F & L 13 “High Performance Work Practices” Predict Economic Performance Group HUMAN ASSET VALUES Real Challenge: Shift Performance of ALL Human Assets -1 S. D. Variable -2 S. D. -1 S. D. Revenue Per Employee $ 117, 011 $ S. D. Revenue Per Employee $ (54, 088) Profit Per Employee $ S. D. Profit Per Employee +1 S. D. Typical +1 S. D. ~13. 7% Best Practice: S. D. ~27. 4% +2 144, 055 $ 171, 099 $ 198, 143 $ 225, 187 $ (27, 044) $ - $ 27, 044 $ 54, 088 20, 241 $ 24, 041 $ 27, 841 $ 31, 655 $ 35, 441 $ (7, 600) $ (3, 800) $ - $ 3, 800 $ 7, 600 Shareholder value Per Employee $ 252, 720 $ 271, 360 $ 290, 000 $ 308, 640 $ 327, 280 S. D. Shareholder value Per Employee $ (37, 280) $ (18, 640) $ - $ 18, 640 $ 37, 280 Turnover % 32. 46% 25. 41% 18. 36% 11. 31% 4. 26% S. D. Turnover % 14. 10% 7. 05% - -7. 05% -14. 10% Becker, B. E. and M. A. Huselid, P. S. Pinkus and M. F. Spratt (1977) Human resources as a source of shareholder value. In Ulrich, D. , M. R. Losey and G. Lake (Eds) 1997. Tomorrow’s HR Management. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons 4
F & L 13 “High Performance Work Practices” Predict Economic Performance Group HUMAN ASSET VALUES Real Challenge: Shift Performance of ALL Human Assets -1 S. D. Variable -2 S. D. -1 S. D. Revenue Per Employee $ 117, 011 $ S. D. Revenue Per Employee $ (54, 088) Profit Per Employee $ S. D. Profit Per Employee +1 S. D. Typical +1 S. D. ~13. 7% Best Practice: S. D. ~27. 4% +2 144, 055 $ 171, 099 $ 198, 143 $ 225, 187 $ (27, 044) $ - $ 27, 044 $ 54, 088 20, 241 $ 24, 041 $ 27, 841 $ 31, 655 $ 35, 441 $ (7, 600) $ (3, 800) $ - $ 3, 800 $ 7, 600 Shareholder value Per Employee $ 252, 720 $ 271, 360 $ 290, 000 $ 308, 640 $ 327, 280 S. D. Shareholder value Per Employee $ (37, 280) $ (18, 640) $ - $ 18, 640 $ 37, 280 Turnover % 32. 46% 25. 41% 18. 36% 11. 31% 4. 26% S. D. Turnover % 14. 10% 7. 05% - -7. 05% -14. 10% Becker, B. E. and M. A. Huselid, P. S. Pinkus and M. F. Spratt (1977) Human resources as a source of shareholder value. In Ulrich, D. , M. R. Losey and G. Lake (Eds) 1997. Tomorrow’s HR Management. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons 4
 RESEARCH SUMMARY F & L Group In an award-winning study by Mark Huselid, of about 1, 000 publicly held U. S. firms, a one standard deviation increase in Talent Management practices (i. e. employee recruitment and selection procedures, incentive compensation, performance management systems, extensive employee involvement and training). . . • Produced $27, 000 more in sales per employee • Almost $4, 000 in additional profit per employee • Decrease turnover significantly Source: The Leadership Machine by Michael M. Lombardo and Robert W. Eichinger, 2001, p. 162 5
RESEARCH SUMMARY F & L Group In an award-winning study by Mark Huselid, of about 1, 000 publicly held U. S. firms, a one standard deviation increase in Talent Management practices (i. e. employee recruitment and selection procedures, incentive compensation, performance management systems, extensive employee involvement and training). . . • Produced $27, 000 more in sales per employee • Almost $4, 000 in additional profit per employee • Decrease turnover significantly Source: The Leadership Machine by Michael M. Lombardo and Robert W. Eichinger, 2001, p. 162 5
 Let’s Talk About Competencies F & L Group You might already have developed a set of competencies-but are they just sitting on a bookshelf someplace? They should be more than just a checklist of behaviors or values If you’ve got the right set, competencies should translate into improved performance 6
Let’s Talk About Competencies F & L Group You might already have developed a set of competencies-but are they just sitting on a bookshelf someplace? They should be more than just a checklist of behaviors or values If you’ve got the right set, competencies should translate into improved performance 6
 Competencies F & L Group • We know what they areskills, behavior & attributes that “separate the best from the rest”. • Competencies are like muscles. You can see the difference. • Competencies explain Δ P 7
Competencies F & L Group • We know what they areskills, behavior & attributes that “separate the best from the rest”. • Competencies are like muscles. You can see the difference. • Competencies explain Δ P 7
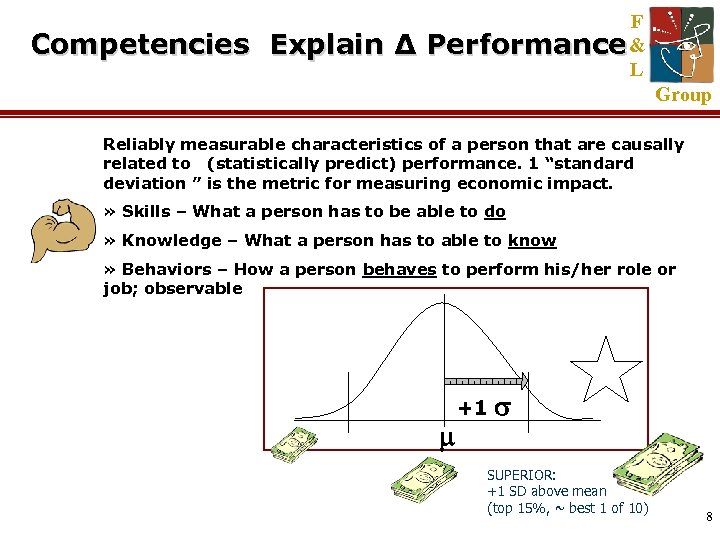 Competencies Explain Δ F Performance & L Group Reliably measurable characteristics of a person that are causally related to (statistically predict) performance. 1 “standard deviation ” is the metric for measuring economic impact. » Skills – What a person has to be able to do » Knowledge – What a person has to able to know » Behaviors – How a person behaves to perform his/her role or job; observable +1 SUPERIOR: +1 SD above mean (top 15%, ~ best 1 of 10) 8
Competencies Explain Δ F Performance & L Group Reliably measurable characteristics of a person that are causally related to (statistically predict) performance. 1 “standard deviation ” is the metric for measuring economic impact. » Skills – What a person has to be able to do » Knowledge – What a person has to able to know » Behaviors – How a person behaves to perform his/her role or job; observable +1 SUPERIOR: +1 SD above mean (top 15%, ~ best 1 of 10) 8
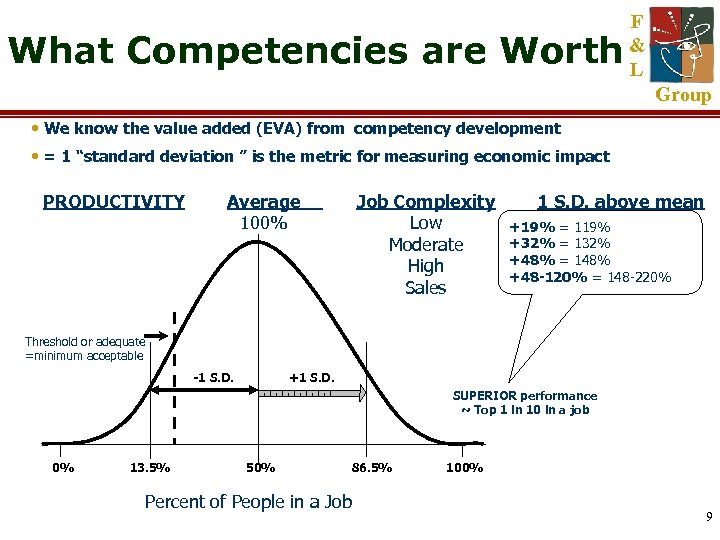 What Competencies are Worth F & L Group • We know the value added (EVA) from competency development • = 1 “standard deviation ” is the metric for measuring economic impact PRODUCTIVITY Average 100% Job Complexity Low Moderate High Sales 1 S. D. above mean +19% = 119% +32% = 132% +48% = 148% +48 -120% = 148 -220% Threshold or adequate =minimum acceptable -1 S. D. +1 S. D. SUPERIOR performance ~ Top 1 in 10 in a job 0% 13. 5% 50% 86. 5% Percent of People in a Job 100% 9
What Competencies are Worth F & L Group • We know the value added (EVA) from competency development • = 1 “standard deviation ” is the metric for measuring economic impact PRODUCTIVITY Average 100% Job Complexity Low Moderate High Sales 1 S. D. above mean +19% = 119% +32% = 132% +48% = 148% +48 -120% = 148 -220% Threshold or adequate =minimum acceptable -1 S. D. +1 S. D. SUPERIOR performance ~ Top 1 in 10 in a job 0% 13. 5% 50% 86. 5% Percent of People in a Job 100% 9
 A Model for Competency-based Talent Management F & L Group Vision & Business Strategy Organizational Capabilities ORGANIZATION ARCHITECT® Team Capabilities TEAM ARCHITECT® Succession Planning Recruiting & Selection CHOICES ARCHITECT® RECRUITING ARCHITECT® ® AMBIGUITY ARCHITECT Competencies Performance Management PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT ARCHITECT® Employee Appraiser™ Performance Manager™ Training and Development LEARNING ARCHITECT® CA – Development Planner Resource Architect Coaching and Feedback VOICES® LSA Coaching for Development™ Career Development FYI-For Your Improvement CA-Development Planner Book or Software CA-Development Planner Plus Online CAREER ARCHITECT® Expert System 10
A Model for Competency-based Talent Management F & L Group Vision & Business Strategy Organizational Capabilities ORGANIZATION ARCHITECT® Team Capabilities TEAM ARCHITECT® Succession Planning Recruiting & Selection CHOICES ARCHITECT® RECRUITING ARCHITECT® ® AMBIGUITY ARCHITECT Competencies Performance Management PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT ARCHITECT® Employee Appraiser™ Performance Manager™ Training and Development LEARNING ARCHITECT® CA – Development Planner Resource Architect Coaching and Feedback VOICES® LSA Coaching for Development™ Career Development FYI-For Your Improvement CA-Development Planner Book or Software CA-Development Planner Plus Online CAREER ARCHITECT® Expert System 10
 Competencies: Essential for Building Talent Maps F & L Group 11
Competencies: Essential for Building Talent Maps F & L Group 11
 Building Our Maps F & L Group Step 1 Research tells us what High Performers and High Learning Agility folks look like- they have specific competency patterns (‘Normative Studies’) Step 2 Research tell us what key technical skills, experiences and competencies are needed for a job Talent Mapping Brings These Together…. . 12
Building Our Maps F & L Group Step 1 Research tells us what High Performers and High Learning Agility folks look like- they have specific competency patterns (‘Normative Studies’) Step 2 Research tell us what key technical skills, experiences and competencies are needed for a job Talent Mapping Brings These Together…. . 12
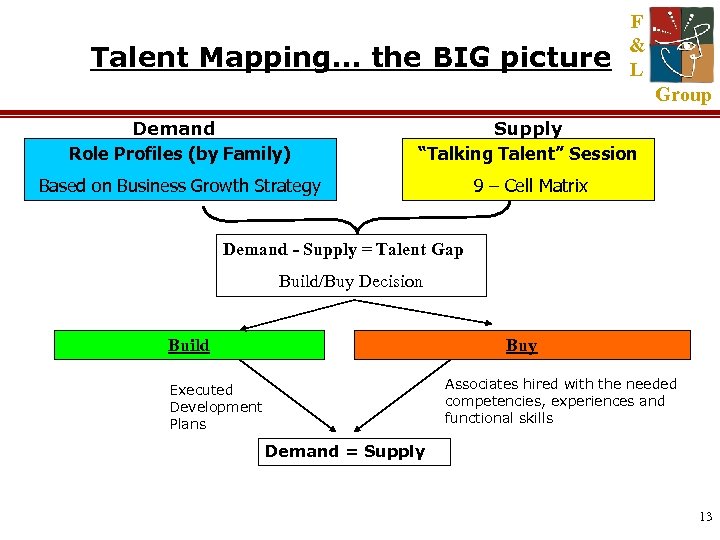 Talent Mapping… the BIG picture F & L Group Demand Role Profiles (by Family) Supply “Talking Talent” Session Based on Business Growth Strategy 9 – Cell Matrix Demand - Supply = Talent Gap Build/Buy Decision Build Buy Associates hired with the needed competencies, experiences and functional skills Executed Development Plans Demand = Supply 13
Talent Mapping… the BIG picture F & L Group Demand Role Profiles (by Family) Supply “Talking Talent” Session Based on Business Growth Strategy 9 – Cell Matrix Demand - Supply = Talent Gap Build/Buy Decision Build Buy Associates hired with the needed competencies, experiences and functional skills Executed Development Plans Demand = Supply 13
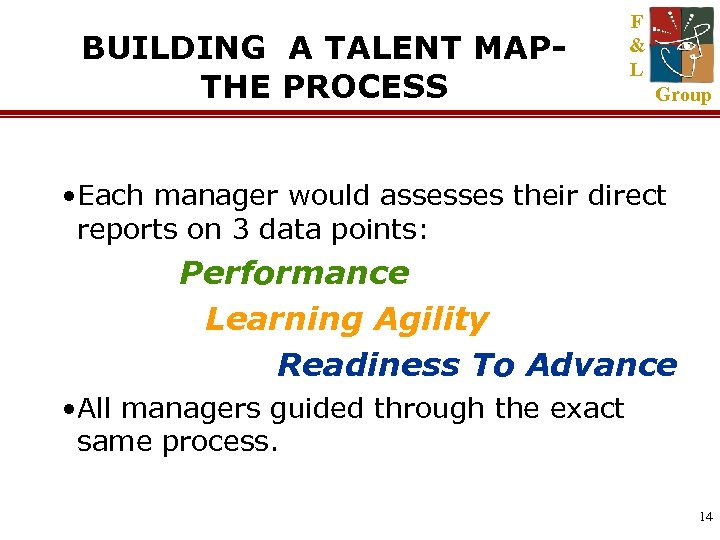 BUILDING A TALENT MAPTHE PROCESS F & L Group • Each manager would assesses their direct reports on 3 data points: Performance Learning Agility Readiness To Advance • All managers guided through the exact same process. 14
BUILDING A TALENT MAPTHE PROCESS F & L Group • Each manager would assesses their direct reports on 3 data points: Performance Learning Agility Readiness To Advance • All managers guided through the exact same process. 14
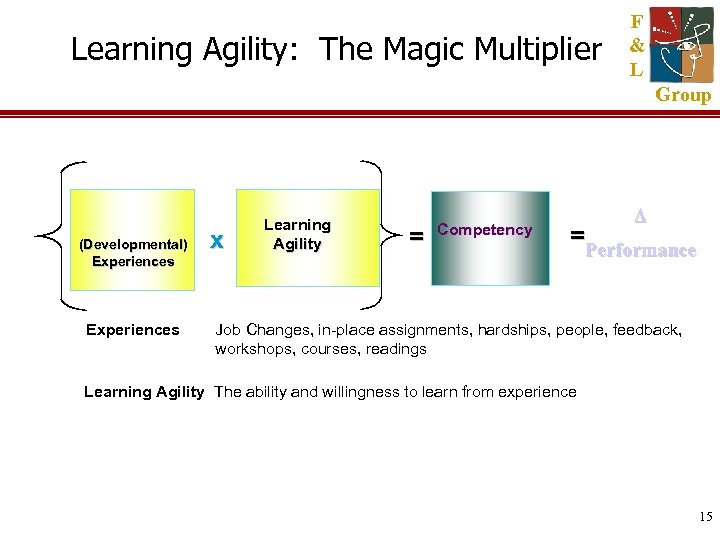 Learning Agility: The Magic Multiplier F & L Group (Developmental) Experiences x Learning Agility = Competency Δ = Performance Job Changes, in-place assignments, hardships, people, feedback, workshops, courses, readings Learning Agility The ability and willingness to learn from experience 15
Learning Agility: The Magic Multiplier F & L Group (Developmental) Experiences x Learning Agility = Competency Δ = Performance Job Changes, in-place assignments, hardships, people, feedback, workshops, courses, readings Learning Agility The ability and willingness to learn from experience 15
 HIGH PROFESSIONAL vs. HIGH POTENTIAL F & L Group • Recognized functional, technical, managerial expert • Can be counted on, especially in tough times • Consistent top performer • Is a good developer of subordinates • Usually performs well under all conditions • Would be difficult to replace in kind • Works independently with little or no supervision • Easily learns new technologies and/or functions • Clever problem-solver • Thinks strategically • Changes Behavior easily • Has wide interests • Low tolerance for marginal processes or people • Deals with ambiguity/complexity well 16
HIGH PROFESSIONAL vs. HIGH POTENTIAL F & L Group • Recognized functional, technical, managerial expert • Can be counted on, especially in tough times • Consistent top performer • Is a good developer of subordinates • Usually performs well under all conditions • Would be difficult to replace in kind • Works independently with little or no supervision • Easily learns new technologies and/or functions • Clever problem-solver • Thinks strategically • Changes Behavior easily • Has wide interests • Low tolerance for marginal processes or people • Deals with ambiguity/complexity well 16
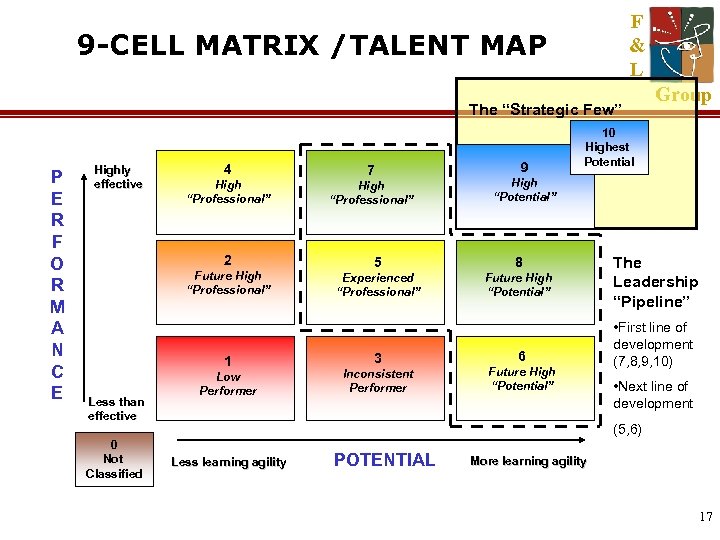 F & L 9 -CELL MATRIX /TALENT MAP The “Strategic Few” P E R F O R M A N C E Highly effective 4 High “Professional” 2 Future High “Professional” 1 Less than effective 0 Not Classified Low Performer 7 High “Professional” 9 10 Highest Potential High “Potential” 5 8 Experienced “Professional” Future High “Potential” 3 Inconsistent Performer Group 6 Future High “Potential” The Leadership “Pipeline” • First line of development (7, 8, 9, 10) • Next line of development (5, 6) Less learning agility POTENTIAL More learning agility 17
F & L 9 -CELL MATRIX /TALENT MAP The “Strategic Few” P E R F O R M A N C E Highly effective 4 High “Professional” 2 Future High “Professional” 1 Less than effective 0 Not Classified Low Performer 7 High “Professional” 9 10 Highest Potential High “Potential” 5 8 Experienced “Professional” Future High “Potential” 3 Inconsistent Performer Group 6 Future High “Potential” The Leadership “Pipeline” • First line of development (7, 8, 9, 10) • Next line of development (5, 6) Less learning agility POTENTIAL More learning agility 17
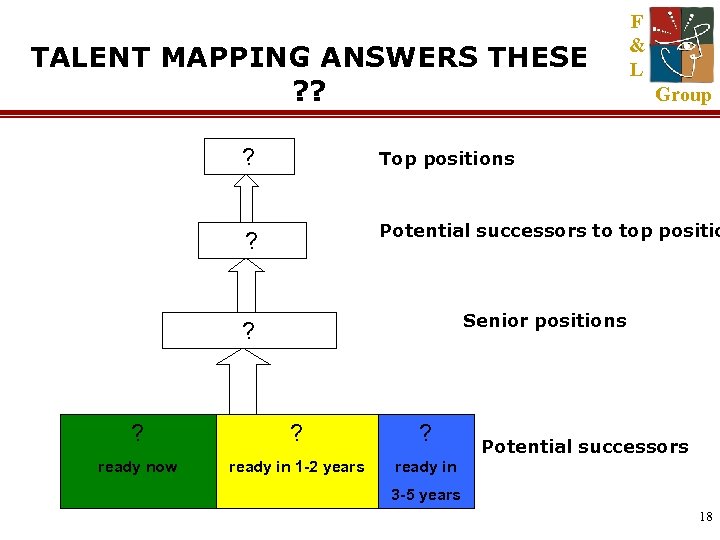 TALENT MAPPING ANSWERS THESE ? ? F & L Group ? Top positions ? Potential successors to top positio Senior positions ? ? ready now ready in 1 -2 years ready in Potential successors 3 -5 years 18
TALENT MAPPING ANSWERS THESE ? ? F & L Group ? Top positions ? Potential successors to top positio Senior positions ? ? ready now ready in 1 -2 years ready in Potential successors 3 -5 years 18
 Talent Mapping Means…. F & L Group Having an in-depth look at all associates, (beyond what may be offered from the HRIS)- including competency evaluation, experience, technical skills, interest, and mobility • • Providing a real time view of 'bench strength' of critical positions or functions • Identifying critical gaps in the workforce plan to improve the accuracy of 'build/buy/borrow' staffing decisions • Evaluating the skill level of different groups to pinpoint exact training needs (instead of 'shotgun approach') • Providing “People Intelligence” Reports to management, e. g. Human Capital Balance Sheet, Mobility Index, Potential Successor’s 19 Report
Talent Mapping Means…. F & L Group Having an in-depth look at all associates, (beyond what may be offered from the HRIS)- including competency evaluation, experience, technical skills, interest, and mobility • • Providing a real time view of 'bench strength' of critical positions or functions • Identifying critical gaps in the workforce plan to improve the accuracy of 'build/buy/borrow' staffing decisions • Evaluating the skill level of different groups to pinpoint exact training needs (instead of 'shotgun approach') • Providing “People Intelligence” Reports to management, e. g. Human Capital Balance Sheet, Mobility Index, Potential Successor’s 19 Report
 F&L Group 2365 Rice Boulevard, Suite 217 Houston, TX 7005 http: //www. fandlgroup. com fandlgroup@fandlgroup. com (713)874 -1557 20
F&L Group 2365 Rice Boulevard, Suite 217 Houston, TX 7005 http: //www. fandlgroup. com fandlgroup@fandlgroup. com (713)874 -1557 20


