e88f12fe700f56c4264b65925ac383aa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Taiwan’s Industrial Technology Innovation Department of Industrial Technology Ministry of Economic Affairs, R. O. C.
Taiwan’s Industrial Technology Innovation Department of Industrial Technology Ministry of Economic Affairs, R. O. C.
 Contents Overview- Evolution of Taiwan’s Economic Development Why Taiwan Matters Taiwan’s S&T Potentials Profile of Do. IT The Challenge and Vision 1
Contents Overview- Evolution of Taiwan’s Economic Development Why Taiwan Matters Taiwan’s S&T Potentials Profile of Do. IT The Challenge and Vision 1
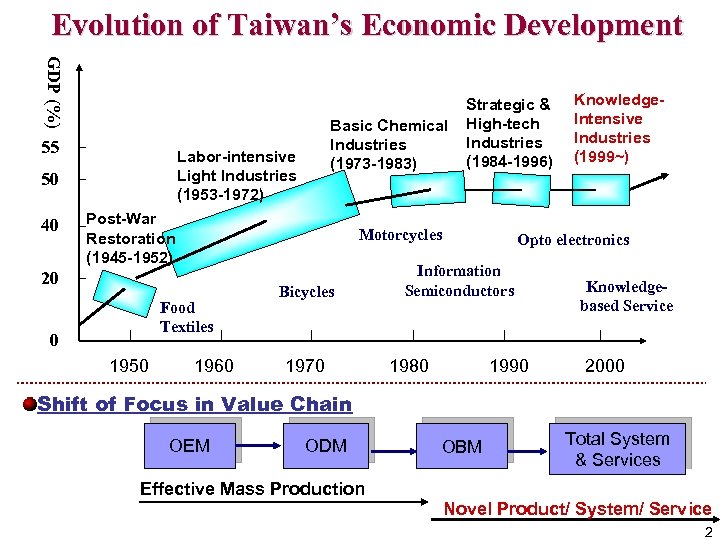 Evolution of Taiwan’s Economic Development GDP (%) 55 Labor-intensive Light Industries (1953 -1972) 50 40 Basic Chemical Industries (1973 -1983) Post-War Restoration (1945 -1952) Motorcycles 20 Food Textiles 0 1950 Strategic & High-tech Industries (1984 -1996) 1960 Bicycles 1970 Knowledge. Intensive Industries (1999~) Opto electronics Information Semiconductors 1980 1990 Knowledgebased Service 2000 Shift of Focus in Value Chain OEM ODM Effective Mass Production OBM Total System & Services Novel Product/ System/ Service 2
Evolution of Taiwan’s Economic Development GDP (%) 55 Labor-intensive Light Industries (1953 -1972) 50 40 Basic Chemical Industries (1973 -1983) Post-War Restoration (1945 -1952) Motorcycles 20 Food Textiles 0 1950 Strategic & High-tech Industries (1984 -1996) 1960 Bicycles 1970 Knowledge. Intensive Industries (1999~) Opto electronics Information Semiconductors 1980 1990 Knowledgebased Service 2000 Shift of Focus in Value Chain OEM ODM Effective Mass Production OBM Total System & Services Novel Product/ System/ Service 2
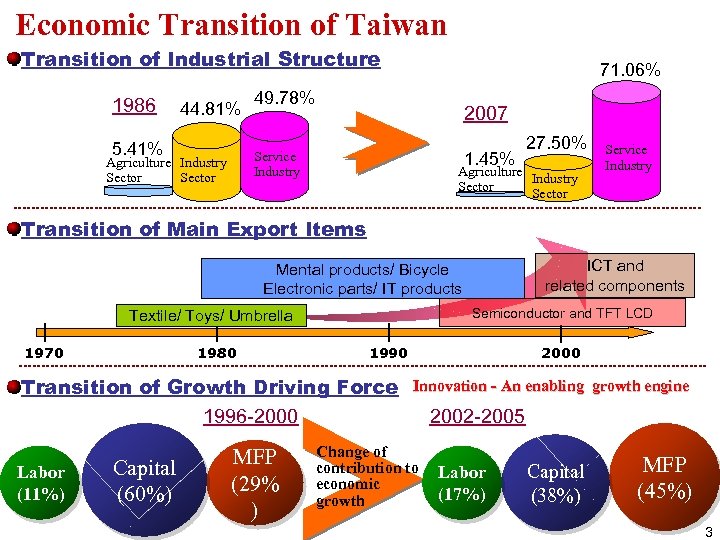 Economic Transition of Taiwan Transition of Industrial Structure 1986 44. 81% 5. 41% 71. 06% 49. 78% 2007 Service Industry Agriculture Industry Sector 1. 45% 27. 50% Agriculture Industry Sector Service Industry Transition of Main Export Items ICT and related components Mental products/ Bicycle Electronic parts/ IT products Semiconductor and TFT LCD Textile/ Toys/ Umbrella 1970 1980 1990 Transition of Growth Driving Force 1996 -2000 Labor (11%) Capital (60%) MFP (29% ) 2000 Innovation - An enabling growth engine Change of contribution to economic growth 2002 -2005 Labor (17%) Capital (38%) MFP (45%) 3
Economic Transition of Taiwan Transition of Industrial Structure 1986 44. 81% 5. 41% 71. 06% 49. 78% 2007 Service Industry Agriculture Industry Sector 1. 45% 27. 50% Agriculture Industry Sector Service Industry Transition of Main Export Items ICT and related components Mental products/ Bicycle Electronic parts/ IT products Semiconductor and TFT LCD Textile/ Toys/ Umbrella 1970 1980 1990 Transition of Growth Driving Force 1996 -2000 Labor (11%) Capital (60%) MFP (29% ) 2000 Innovation - An enabling growth engine Change of contribution to economic growth 2002 -2005 Labor (17%) Capital (38%) MFP (45%) 3
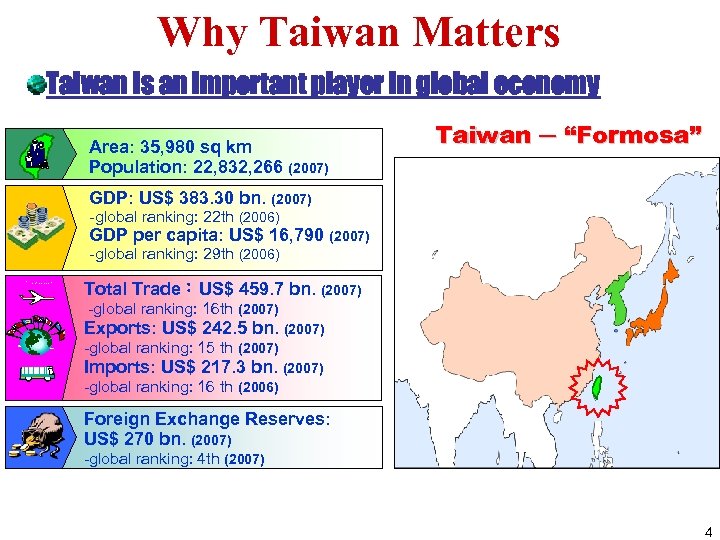 Why Taiwan Matters Taiwan is an important player in global economy Area: 35, 980 sq km Population: 22, 832, 266 (2007) Taiwan ─ “Formosa” GDP: US$ 383. 30 bn. (2007) -global ranking: 22 th (2006) GDP per capita: US$ 16, 790 (2007) -global ranking: 29 th (2006) Total Trade:US$ 459. 7 bn. (2007) -global ranking: 16 th (2007) Exports: US$ 242. 5 bn. (2007) -global ranking: 15 th (2007) Imports: US$ 217. 3 bn. (2007) -global ranking: 16 th (2006) Foreign Exchange Reserves: US$ 270 bn. (2007) -global ranking: 4 th (2007) 4
Why Taiwan Matters Taiwan is an important player in global economy Area: 35, 980 sq km Population: 22, 832, 266 (2007) Taiwan ─ “Formosa” GDP: US$ 383. 30 bn. (2007) -global ranking: 22 th (2006) GDP per capita: US$ 16, 790 (2007) -global ranking: 29 th (2006) Total Trade:US$ 459. 7 bn. (2007) -global ranking: 16 th (2007) Exports: US$ 242. 5 bn. (2007) -global ranking: 15 th (2007) Imports: US$ 217. 3 bn. (2007) -global ranking: 16 th (2006) Foreign Exchange Reserves: US$ 270 bn. (2007) -global ranking: 4 th (2007) 4
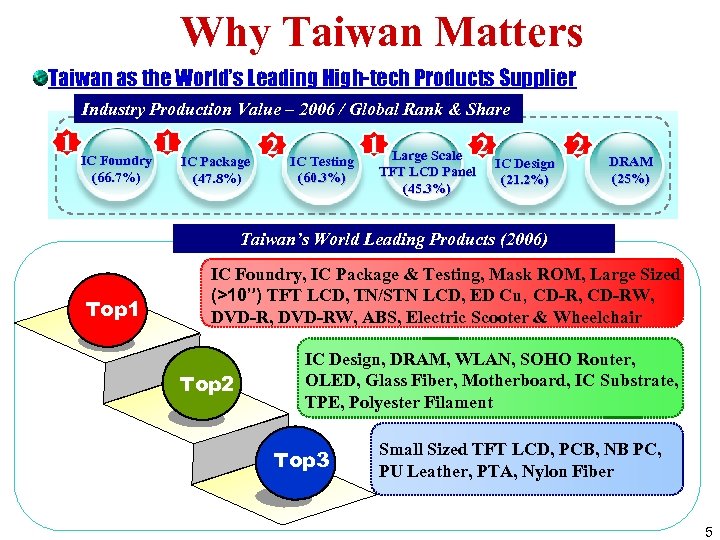 Why Taiwan Matters Taiwan as the World’s Leading High-tech Products Supplier Industry Production Value – 2006 / Global Rank & Share 1 1 IC Foundry (66. 7%) IC Package (47. 8%) 2 IC Testing (60. 3%) 1 2 2 IC Design Large Scale TFT LCD Panel (45. 3%) IC Design (21. 2%) DRAM (25%) Taiwan’s World Leading Products (2006) Top 1 IC Foundry, IC Package & Testing, Mask ROM, Large Sized (>10”) TFT LCD, TN/STN LCD, ED Cu, CD-RW, DVD-RW, ABS, Electric Scooter & Wheelchair Top 2 IC Design, DRAM, WLAN, SOHO Router, OLED, Glass Fiber, Motherboard, IC Substrate, TPE, Polyester Filament Top 3 Small Sized TFT LCD, PCB, NB PC, PU Leather, PTA, Nylon Fiber 5
Why Taiwan Matters Taiwan as the World’s Leading High-tech Products Supplier Industry Production Value – 2006 / Global Rank & Share 1 1 IC Foundry (66. 7%) IC Package (47. 8%) 2 IC Testing (60. 3%) 1 2 2 IC Design Large Scale TFT LCD Panel (45. 3%) IC Design (21. 2%) DRAM (25%) Taiwan’s World Leading Products (2006) Top 1 IC Foundry, IC Package & Testing, Mask ROM, Large Sized (>10”) TFT LCD, TN/STN LCD, ED Cu, CD-RW, DVD-RW, ABS, Electric Scooter & Wheelchair Top 2 IC Design, DRAM, WLAN, SOHO Router, OLED, Glass Fiber, Motherboard, IC Substrate, TPE, Polyester Filament Top 3 Small Sized TFT LCD, PCB, NB PC, PU Leather, PTA, Nylon Fiber 5
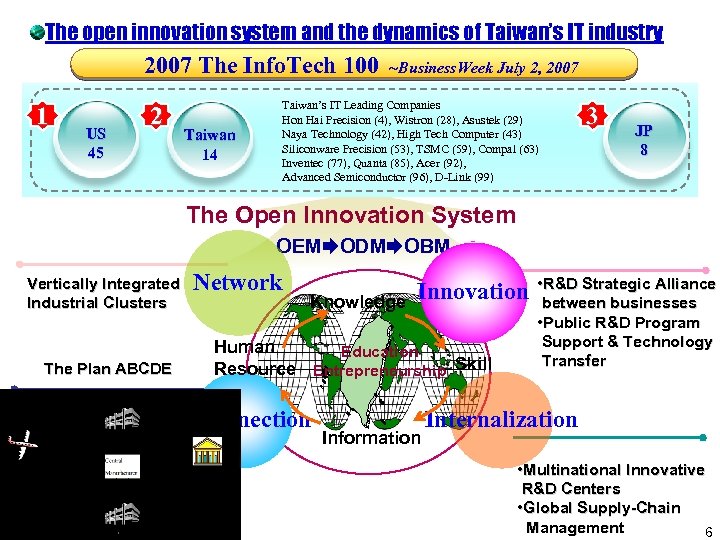 The open innovation system and the dynamics of Taiwan’s IT industry 2007 The Info. Tech 100 1 US 45 2 Taiwan 14 ~Business. Week July 2, 2007 Taiwan’s IT Leading Companies Hon Hai Precision (4), Wistron (28), Asustek (29) Naya Technology (42), High Tech Computer (43) Siliconware Precision (53), TSMC (59), Compal (63) Inventec (77), Quanta (85), Acer (92), Advanced Semiconductor (96), D-Link (99) 3 JP 8 The Open Innovation System OEM ODM OBM Vertically Integrated Industrial Clusters The Plan ABCDE Network Knowledge Innovation Human Education Resource Entrepreneurship Skill E-Connection Information • R&D Strategic Alliance between businesses • Public R&D Program Support & Technology Transfer Internalization • Multinational Innovative R&D Centers • Global Supply-Chain Management 6
The open innovation system and the dynamics of Taiwan’s IT industry 2007 The Info. Tech 100 1 US 45 2 Taiwan 14 ~Business. Week July 2, 2007 Taiwan’s IT Leading Companies Hon Hai Precision (4), Wistron (28), Asustek (29) Naya Technology (42), High Tech Computer (43) Siliconware Precision (53), TSMC (59), Compal (63) Inventec (77), Quanta (85), Acer (92), Advanced Semiconductor (96), D-Link (99) 3 JP 8 The Open Innovation System OEM ODM OBM Vertically Integrated Industrial Clusters The Plan ABCDE Network Knowledge Innovation Human Education Resource Entrepreneurship Skill E-Connection Information • R&D Strategic Alliance between businesses • Public R&D Program Support & Technology Transfer Internalization • Multinational Innovative R&D Centers • Global Supply-Chain Management 6
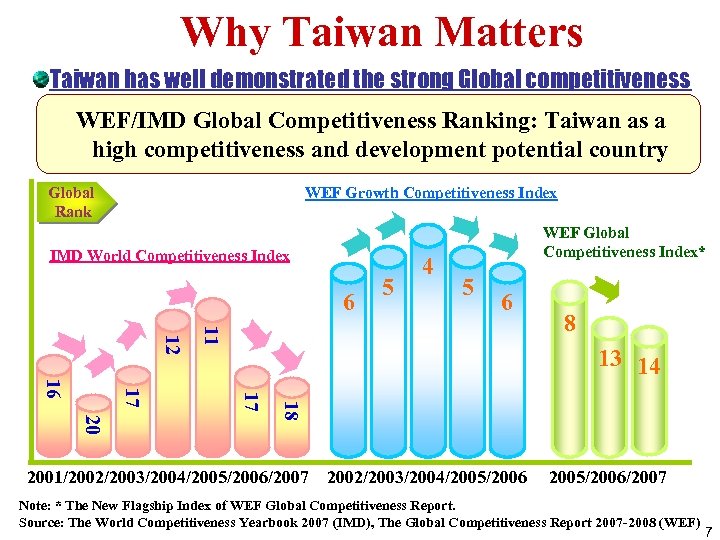 Why Taiwan Matters Taiwan has well demonstrated the strong Global competitiveness WEF/IMD Global Competitiveness Ranking: Taiwan as a high competitiveness and development potential country Global Rank WEF Growth Competitiveness Index IMD World Competitiveness Index 6 5 4 WEF Global Competitiveness Index* 5 6 11 12 8 13 14 20 18 17 17 16 2001/2002/2003/2004/2005/2006/2007 2002/2003/2004/2005/2006/2007 Note: * The New Flagship Index of WEF Global Competitiveness Report. Source: The World Competitiveness Yearbook 2007 (IMD), The Global Competitiveness Report 2007 -2008 (WEF) 7
Why Taiwan Matters Taiwan has well demonstrated the strong Global competitiveness WEF/IMD Global Competitiveness Ranking: Taiwan as a high competitiveness and development potential country Global Rank WEF Growth Competitiveness Index IMD World Competitiveness Index 6 5 4 WEF Global Competitiveness Index* 5 6 11 12 8 13 14 20 18 17 17 16 2001/2002/2003/2004/2005/2006/2007 2002/2003/2004/2005/2006/2007 Note: * The New Flagship Index of WEF Global Competitiveness Report. Source: The World Competitiveness Yearbook 2007 (IMD), The Global Competitiveness Report 2007 -2008 (WEF) 7
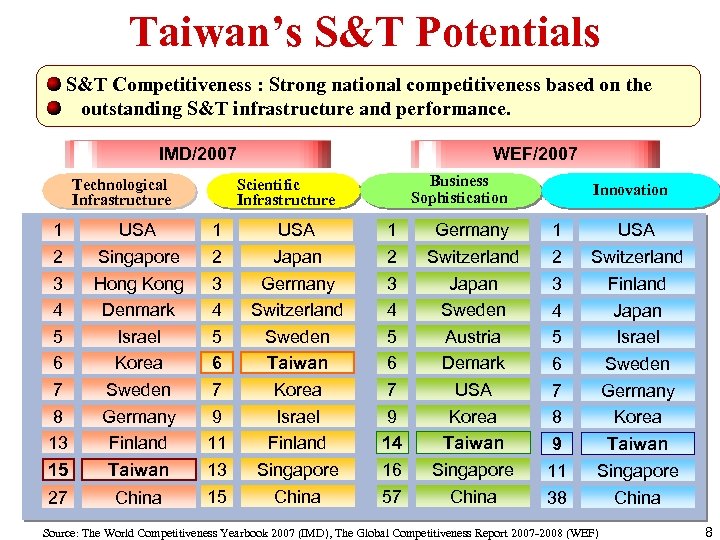 Taiwan’s S&T Potentials S&T Competitiveness : Strong national competitiveness based on the outstanding S&T infrastructure and performance. IMD/2007 Technological Infrastructure WEF/2007 Business Sophistication Scientific Infrastructure Innovation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 13 15 USA Singapore Hong Kong Denmark Israel Korea Sweden Germany Finland Taiwan 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 11 13 USA Japan Germany Switzerland Sweden Taiwan Korea Israel Finland Singapore 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 14 16 Germany Switzerland Japan Sweden Austria Demark USA Korea Taiwan Singapore 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 USA Switzerland Finland Japan Israel Sweden Germany Korea Taiwan Singapore 27 China 15 China 57 China 38 China Source: The World Competitiveness Yearbook 2007 (IMD), The Global Competitiveness Report 2007 -2008 (WEF) 8
Taiwan’s S&T Potentials S&T Competitiveness : Strong national competitiveness based on the outstanding S&T infrastructure and performance. IMD/2007 Technological Infrastructure WEF/2007 Business Sophistication Scientific Infrastructure Innovation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 13 15 USA Singapore Hong Kong Denmark Israel Korea Sweden Germany Finland Taiwan 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 11 13 USA Japan Germany Switzerland Sweden Taiwan Korea Israel Finland Singapore 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 14 16 Germany Switzerland Japan Sweden Austria Demark USA Korea Taiwan Singapore 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 USA Switzerland Finland Japan Israel Sweden Germany Korea Taiwan Singapore 27 China 15 China 57 China 38 China Source: The World Competitiveness Yearbook 2007 (IMD), The Global Competitiveness Report 2007 -2008 (WEF) 8
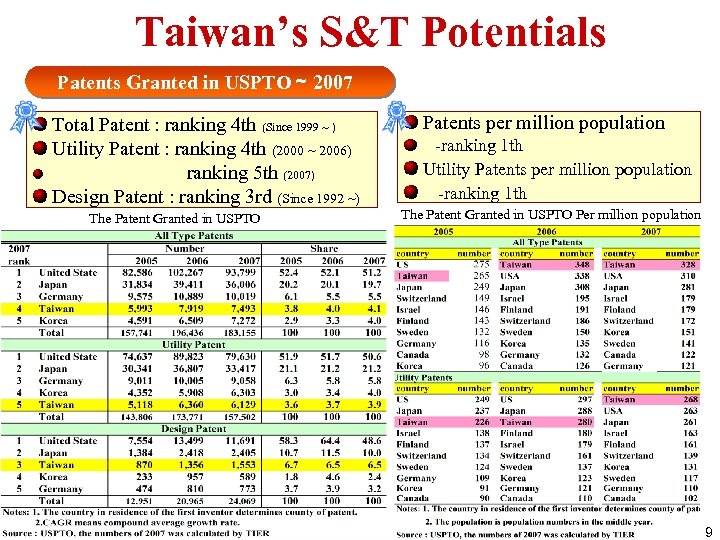 Taiwan’s S&T Potentials Patents Granted in USPTO~ 2007 Total Patent : ranking 4 th (Since 1999 ~ ) Utility Patent : ranking 4 th (2000 ~ 2006) ranking 5 th (2007) Design Patent : ranking 3 rd (Since 1992 ~) The Patent Granted in USPTO Patents per million population -ranking 1 th Utility Patents per million population -ranking 1 th The Patent Granted in USPTO Per million population 9
Taiwan’s S&T Potentials Patents Granted in USPTO~ 2007 Total Patent : ranking 4 th (Since 1999 ~ ) Utility Patent : ranking 4 th (2000 ~ 2006) ranking 5 th (2007) Design Patent : ranking 3 rd (Since 1992 ~) The Patent Granted in USPTO Patents per million population -ranking 1 th Utility Patents per million population -ranking 1 th The Patent Granted in USPTO Per million population 9
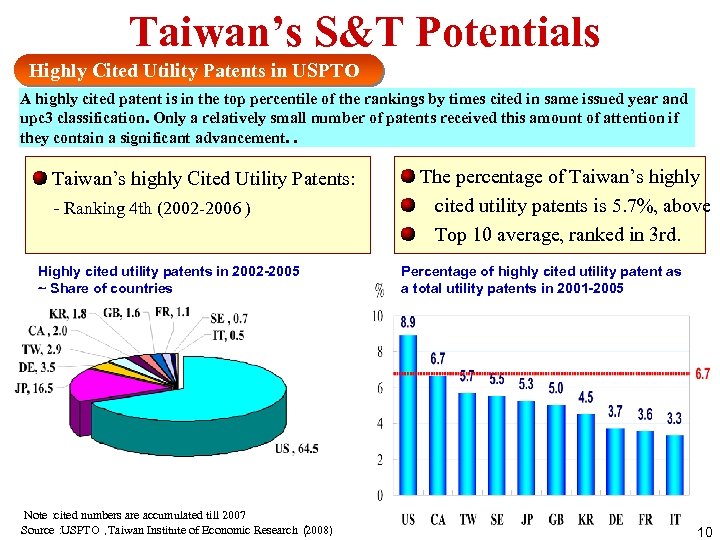 Taiwan’s S&T Potentials Highly Cited Utility Patents in USPTO A highly cited patent is in the top percentile of the rankings by times cited in same issued year and upc 3 classification. Only a relatively small number of patents received this amount of attention if they contain a significant advancement. . Taiwan’s highly Cited Utility Patents: - Ranking 4 th (2002 -2006 ) Highly cited utility patents in 2002 -2005 ~ Share of countries Note: cited numbers are accumulated till 2007 Source: USPTO, Taiwan Institute of Economic Research( 2008) The percentage of Taiwan’s highly cited utility patents is 5. 7%, above Top 10 average, ranked in 3 rd. Percentage of highly cited utility patent as a total utility patents in 2001 -2005 10
Taiwan’s S&T Potentials Highly Cited Utility Patents in USPTO A highly cited patent is in the top percentile of the rankings by times cited in same issued year and upc 3 classification. Only a relatively small number of patents received this amount of attention if they contain a significant advancement. . Taiwan’s highly Cited Utility Patents: - Ranking 4 th (2002 -2006 ) Highly cited utility patents in 2002 -2005 ~ Share of countries Note: cited numbers are accumulated till 2007 Source: USPTO, Taiwan Institute of Economic Research( 2008) The percentage of Taiwan’s highly cited utility patents is 5. 7%, above Top 10 average, ranked in 3 rd. Percentage of highly cited utility patent as a total utility patents in 2001 -2005 10
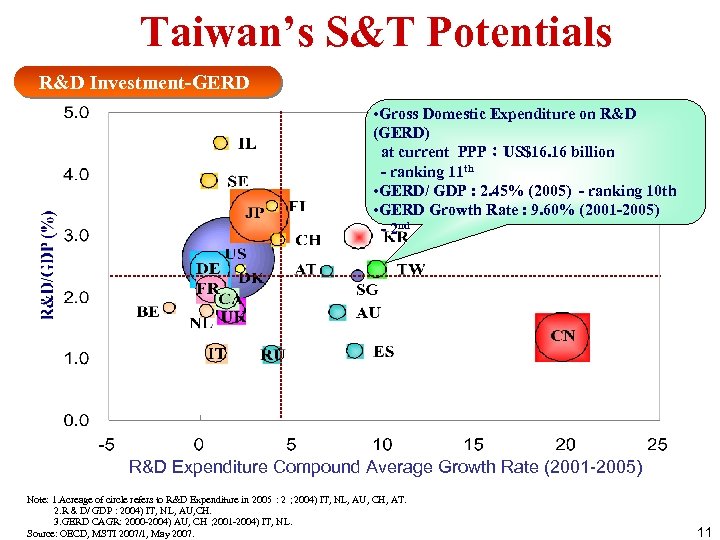 Taiwan’s S&T Potentials R&D Investment-GERD • Gross Domestic Expenditure on R&D (GERD) at current PPP:US$16. 16 billion - ranking 11 th • GERD/ GDP : 2. 45% (2005) - ranking 10 th • GERD Growth Rate : 9. 60% (2001 -2005) - 2 nd R&D Expenditure Compound Average Growth Rate (2001 -2005) Note: 1. Acreage of circle refers to R&D Expenditure in 2005 : 2; 2004) IT, NL, AU, CH, AT. 2. R&D/ GDP: 2004) IT, NL, AU, CH. 3. GERD CAGR: 2000 -2004) AU, CH; 2001 -2004) IT, NL. Source: OECD, MSTI 2007/1, May 2007. 11
Taiwan’s S&T Potentials R&D Investment-GERD • Gross Domestic Expenditure on R&D (GERD) at current PPP:US$16. 16 billion - ranking 11 th • GERD/ GDP : 2. 45% (2005) - ranking 10 th • GERD Growth Rate : 9. 60% (2001 -2005) - 2 nd R&D Expenditure Compound Average Growth Rate (2001 -2005) Note: 1. Acreage of circle refers to R&D Expenditure in 2005 : 2; 2004) IT, NL, AU, CH, AT. 2. R&D/ GDP: 2004) IT, NL, AU, CH. 3. GERD CAGR: 2000 -2004) AU, CH; 2001 -2004) IT, NL. Source: OECD, MSTI 2007/1, May 2007. 11
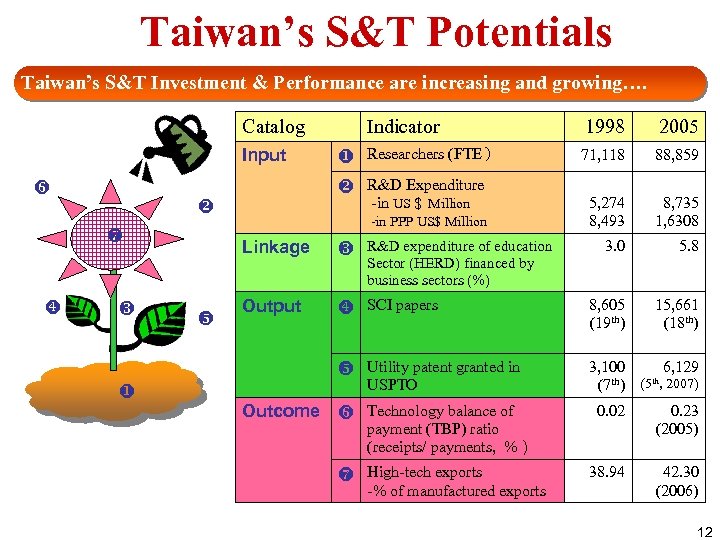 Taiwan’s S&T Potentials Taiwan’s S&T Investment & Performance are increasing and growing…. Catalog Input Indicator 1998 2005 Researchers (FTE) 71, 118 88, 859 5, 274 8, 493 8, 735 1, 6308 3. 0 5. 8 15, 661 (18 th) R&D Expenditure -in US$ Million -in PPP US$ Million R&D expenditure of education Sector (HERD) financed by business sectors (%) Output SCI papers 8, 605 (19 th) Linkage Utility patent granted in USPTO 3, 100 6, 129 (7 th) (5 th, 2007) Outcome Technology balance of 0. 02 0. 23 (2005) 38. 94 42. 30 (2006) payment (TBP) ratio (receipts/ payments, %) High-tech exports -% of manufactured exports 12
Taiwan’s S&T Potentials Taiwan’s S&T Investment & Performance are increasing and growing…. Catalog Input Indicator 1998 2005 Researchers (FTE) 71, 118 88, 859 5, 274 8, 493 8, 735 1, 6308 3. 0 5. 8 15, 661 (18 th) R&D Expenditure -in US$ Million -in PPP US$ Million R&D expenditure of education Sector (HERD) financed by business sectors (%) Output SCI papers 8, 605 (19 th) Linkage Utility patent granted in USPTO 3, 100 6, 129 (7 th) (5 th, 2007) Outcome Technology balance of 0. 02 0. 23 (2005) 38. 94 42. 30 (2006) payment (TBP) ratio (receipts/ payments, %) High-tech exports -% of manufactured exports 12
 Taiwan’s S&T Potentials Taiwan is getting online E-Government Ranking: top of the world E-Government Performance / Brown University – Taiwan ranked 1 st in 2002, 2004, 2005, 2 nd in 2006, 3 rd in 2007. Global Information Technology Report 2006 -2007 / WEF -- Taiwan ranked 8 th in Government Usage and, 6 th in Government Readiness World Information Society Report 2007 / ITU, Taiwan ranked 7 th worldwide in Digital Opportunity Index (DOI) amongst 181 countries surveyed. ICT subindex in Global Competitiveness Report 2006 -2007 / WEF, Taiwan ranked 10 th worldwide amongst 125 countries surveyed. Global Information Technology Report 2006 -2007 / WEF, Taiwan ranked 3 rd in Asia, 13 th worldwide in Networked Readiness Index (NRI) 13
Taiwan’s S&T Potentials Taiwan is getting online E-Government Ranking: top of the world E-Government Performance / Brown University – Taiwan ranked 1 st in 2002, 2004, 2005, 2 nd in 2006, 3 rd in 2007. Global Information Technology Report 2006 -2007 / WEF -- Taiwan ranked 8 th in Government Usage and, 6 th in Government Readiness World Information Society Report 2007 / ITU, Taiwan ranked 7 th worldwide in Digital Opportunity Index (DOI) amongst 181 countries surveyed. ICT subindex in Global Competitiveness Report 2006 -2007 / WEF, Taiwan ranked 10 th worldwide amongst 125 countries surveyed. Global Information Technology Report 2006 -2007 / WEF, Taiwan ranked 3 rd in Asia, 13 th worldwide in Networked Readiness Index (NRI) 13
 Taiwan’s S&T Potentials Well-established S&T Infrastructure Taiwan High Speed Rail Hsinchu Science Park Taipei Wireless City Hsinchu Ubiquitous Network Society Taichung Software Park Nankang Software Park U-Taiwan Taichung Central Taiwan Science Park Kaohsung Cyber city M-Taiwan Tainan Kaohsung e-Taiwan Southern Taiwan Science Park Southern Software Park 14
Taiwan’s S&T Potentials Well-established S&T Infrastructure Taiwan High Speed Rail Hsinchu Science Park Taipei Wireless City Hsinchu Ubiquitous Network Society Taichung Software Park Nankang Software Park U-Taiwan Taichung Central Taiwan Science Park Kaohsung Cyber city M-Taiwan Tainan Kaohsung e-Taiwan Southern Taiwan Science Park Southern Software Park 14
 Taiwan’s S&T Potentials An Excellent R&D Institute – ITRI ~ Where Taiwan’s high-tech began R&D Staff: 5, 744 Ph. D. : 917 Total Patents: 7, 245 Start-Ups : 140 15
Taiwan’s S&T Potentials An Excellent R&D Institute – ITRI ~ Where Taiwan’s high-tech began R&D Staff: 5, 744 Ph. D. : 917 Total Patents: 7, 245 Start-Ups : 140 15
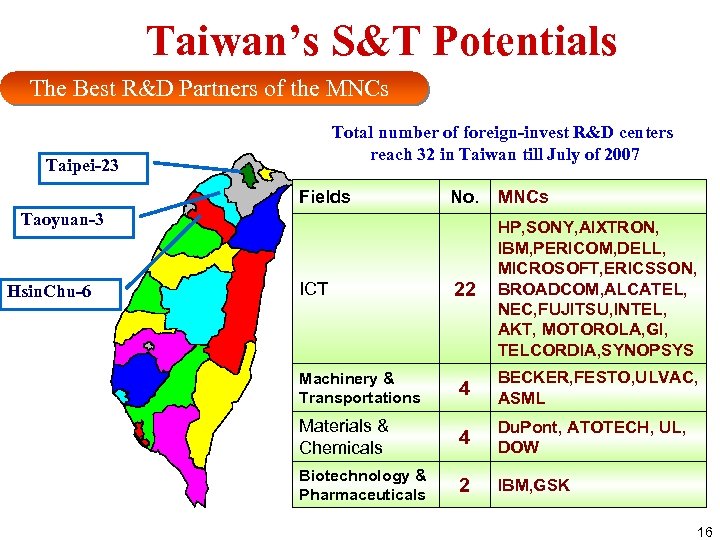 Taiwan’s S&T Potentials The Best R&D Partners of the MNCs Total number of foreign-invest R&D centers reach 32 in Taiwan till July of 2007 Taipei-23 Fields No. MNCs 22 HP, SONY, AIXTRON, IBM, PERICOM, DELL, MICROSOFT, ERICSSON, BROADCOM, ALCATEL, NEC, FUJITSU, INTEL, AKT, MOTOROLA, GI, TELCORDIA, SYNOPSYS Machinery & Transportations 4 BECKER, FESTO, ULVAC, ASML Materials & Chemicals 4 Du. Pont, ATOTECH, UL, DOW Biotechnology & Pharmaceuticals 2 IBM, GSK Taoyuan-3 Hsin. Chu-6 ICT 16
Taiwan’s S&T Potentials The Best R&D Partners of the MNCs Total number of foreign-invest R&D centers reach 32 in Taiwan till July of 2007 Taipei-23 Fields No. MNCs 22 HP, SONY, AIXTRON, IBM, PERICOM, DELL, MICROSOFT, ERICSSON, BROADCOM, ALCATEL, NEC, FUJITSU, INTEL, AKT, MOTOROLA, GI, TELCORDIA, SYNOPSYS Machinery & Transportations 4 BECKER, FESTO, ULVAC, ASML Materials & Chemicals 4 Du. Pont, ATOTECH, UL, DOW Biotechnology & Pharmaceuticals 2 IBM, GSK Taoyuan-3 Hsin. Chu-6 ICT 16
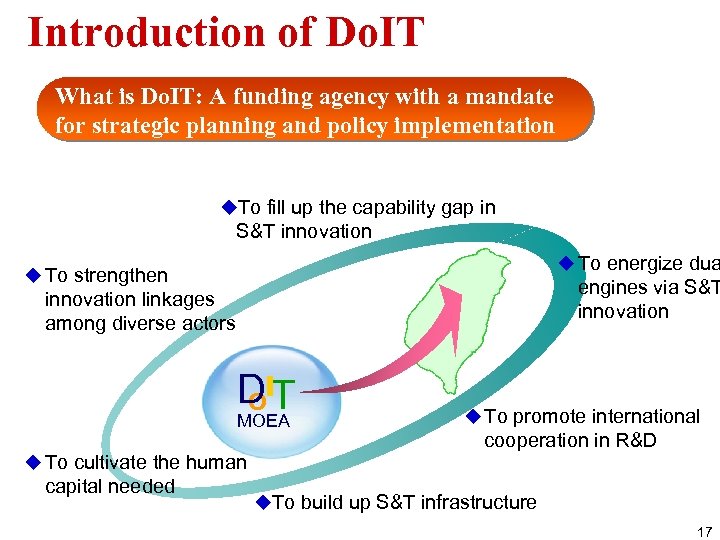 Introduction of Do. IT What is Do. IT: A funding agency with a mandate for strategic planning and policy implementation u. To fill up the capability gap in S&T innovation u To energize dua u To strengthen engines via S&T innovation linkages among diverse actors DIT O MOEA u To cultivate the human capital needed u To promote international cooperation in R&D u. To build up S&T infrastructure 17
Introduction of Do. IT What is Do. IT: A funding agency with a mandate for strategic planning and policy implementation u. To fill up the capability gap in S&T innovation u To energize dua u To strengthen engines via S&T innovation linkages among diverse actors DIT O MOEA u To cultivate the human capital needed u To promote international cooperation in R&D u. To build up S&T infrastructure 17
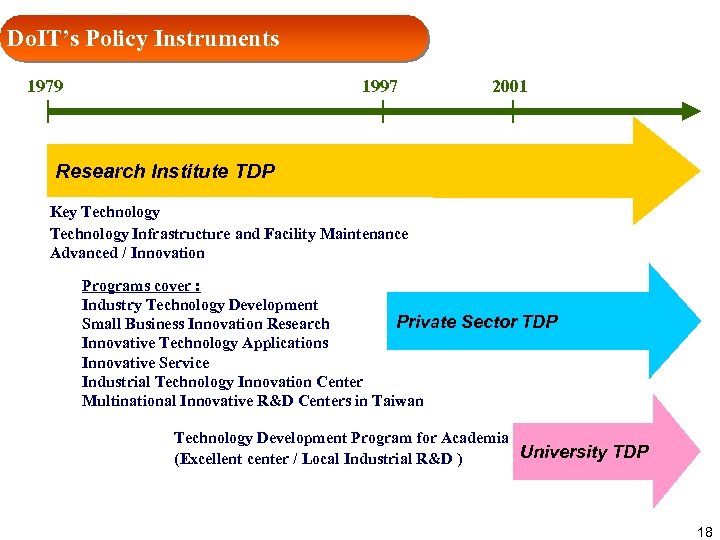 Do. IT’s Policy Instruments 1979 1997 2001 Research Institute TDP Key Technology Infrastructure and Facility Maintenance Advanced / Innovation Programs cover : Industry Technology Development Private Sector TDP Small Business Innovation Research Innovative Technology Applications Innovative Service Industrial Technology Innovation Center Multinational Innovative R&D Centers in Taiwan Technology Development Program for Academia University TDP (Excellent center / Local Industrial R&D ) 18
Do. IT’s Policy Instruments 1979 1997 2001 Research Institute TDP Key Technology Infrastructure and Facility Maintenance Advanced / Innovation Programs cover : Industry Technology Development Private Sector TDP Small Business Innovation Research Innovative Technology Applications Innovative Service Industrial Technology Innovation Center Multinational Innovative R&D Centers in Taiwan Technology Development Program for Academia University TDP (Excellent center / Local Industrial R&D ) 18
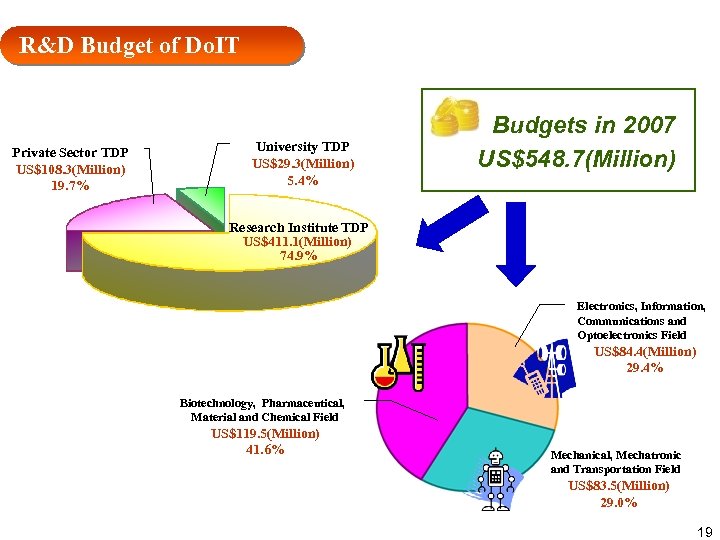 R&D Budget of Do. IT Private Sector TDP US$108. 3(Million) 19. 7% University TDP US$29. 3(Million) 5. 4% Budgets in 2007 US$548. 7(Million) Research Institute TDP US$411. 1(Million) 74. 9% Electronics, Information, Communications and Optoelectronics Field US$84. 4(Million) 29. 4% Biotechnology, Pharmaceutical, Material and Chemical Field US$119. 5(Million) 41. 6% Mechanical, Mechatronic and Transportation Field US$83. 5(Million) 29. 0% 19
R&D Budget of Do. IT Private Sector TDP US$108. 3(Million) 19. 7% University TDP US$29. 3(Million) 5. 4% Budgets in 2007 US$548. 7(Million) Research Institute TDP US$411. 1(Million) 74. 9% Electronics, Information, Communications and Optoelectronics Field US$84. 4(Million) 29. 4% Biotechnology, Pharmaceutical, Material and Chemical Field US$119. 5(Million) 41. 6% Mechanical, Mechatronic and Transportation Field US$83. 5(Million) 29. 0% 19
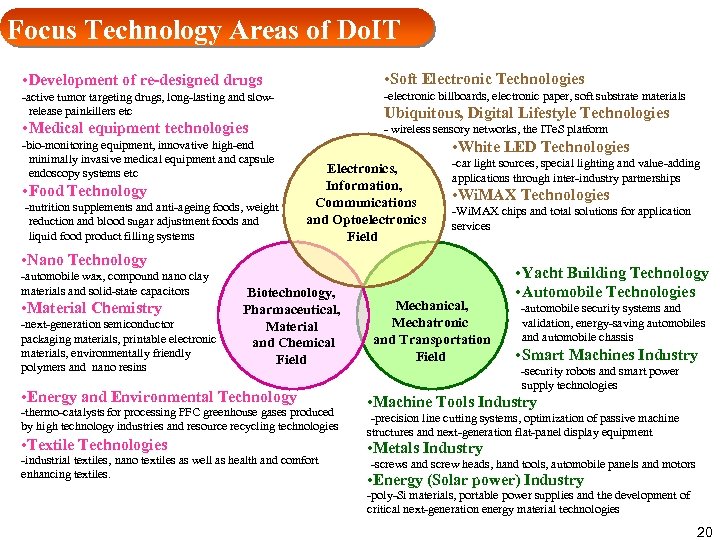 Focus Technology Areas of Do. IT • Development of re-designed drugs • Soft Electronic Technologies -active tumor targeting drugs, long-lasting and slowrelease painkillers etc -electronic billboards, electronic paper, soft substrate materials • Medical equipment technologies - wireless sensory networks, the ITe. S platform -bio-monitoring equipment, innovative high-end minimally invasive medical equipment and capsule endoscopy systems etc • Food Technology -nutrition supplements and anti-ageing foods, weight reduction and blood sugar adjustment foods and liquid food product filling systems Ubiquitous, Digital Lifestyle Technologies • White LED Technologies Electronics, Information, Communications and Optoelectronics Field -car light sources, special lighting and value-adding applications through inter-industry partnerships • Wi. MAX Technologies -Wi. MAX chips and total solutions for application services • Nano Technology -automobile wax, compound nano clay materials and solid-state capacitors • Material Chemistry -next-generation semiconductor packaging materials, printable electronic materials, environmentally friendly polymers and nano resins Biotechnology, Pharmaceutical, Material and Chemical Field • Energy and Environmental Technology -thermo-catalysts for processing PFC greenhouse gases produced by high technology industries and resource recycling technologies • Textile Technologies -industrial textiles, nano textiles as well as health and comfort enhancing textiles. Mechanical, Mechatronic and Transportation Field • Yacht Building Technology • Automobile Technologies -automobile security systems and validation, energy-saving automobiles and automobile chassis • Smart Machines Industry -security robots and smart power supply technologies • Machine Tools Industry -precision line cutting systems, optimization of passive machine structures and next-generation flat-panel display equipment • Metals Industry -screws and screw heads, hand tools, automobile panels and motors • Energy (Solar power) Industry -poly-Si materials, portable power supplies and the development of critical next-generation energy material technologies 20
Focus Technology Areas of Do. IT • Development of re-designed drugs • Soft Electronic Technologies -active tumor targeting drugs, long-lasting and slowrelease painkillers etc -electronic billboards, electronic paper, soft substrate materials • Medical equipment technologies - wireless sensory networks, the ITe. S platform -bio-monitoring equipment, innovative high-end minimally invasive medical equipment and capsule endoscopy systems etc • Food Technology -nutrition supplements and anti-ageing foods, weight reduction and blood sugar adjustment foods and liquid food product filling systems Ubiquitous, Digital Lifestyle Technologies • White LED Technologies Electronics, Information, Communications and Optoelectronics Field -car light sources, special lighting and value-adding applications through inter-industry partnerships • Wi. MAX Technologies -Wi. MAX chips and total solutions for application services • Nano Technology -automobile wax, compound nano clay materials and solid-state capacitors • Material Chemistry -next-generation semiconductor packaging materials, printable electronic materials, environmentally friendly polymers and nano resins Biotechnology, Pharmaceutical, Material and Chemical Field • Energy and Environmental Technology -thermo-catalysts for processing PFC greenhouse gases produced by high technology industries and resource recycling technologies • Textile Technologies -industrial textiles, nano textiles as well as health and comfort enhancing textiles. Mechanical, Mechatronic and Transportation Field • Yacht Building Technology • Automobile Technologies -automobile security systems and validation, energy-saving automobiles and automobile chassis • Smart Machines Industry -security robots and smart power supply technologies • Machine Tools Industry -precision line cutting systems, optimization of passive machine structures and next-generation flat-panel display equipment • Metals Industry -screws and screw heads, hand tools, automobile panels and motors • Energy (Solar power) Industry -poly-Si materials, portable power supplies and the development of critical next-generation energy material technologies 20
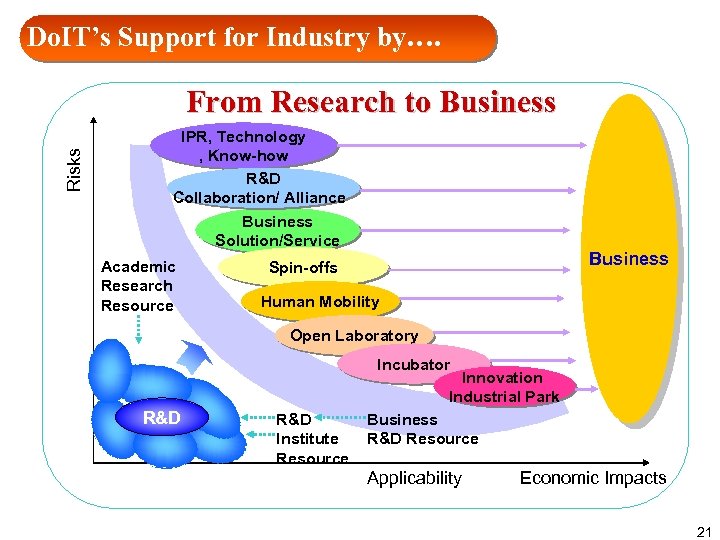 Do. IT’s Support for Industry by…. Risks From Research to Business IPR, Technology , Know-how R&D Collaboration/ Alliance Business Solution/Service Academic Research Resource Business Spin-offs Human Mobility Open Laboratory Incubator Innovation Industrial Park R&D Institute Resource Business R&D Resource Applicability Economic Impacts 21
Do. IT’s Support for Industry by…. Risks From Research to Business IPR, Technology , Know-how R&D Collaboration/ Alliance Business Solution/Service Academic Research Resource Business Spin-offs Human Mobility Open Laboratory Incubator Innovation Industrial Park R&D Institute Resource Business R&D Resource Applicability Economic Impacts 21
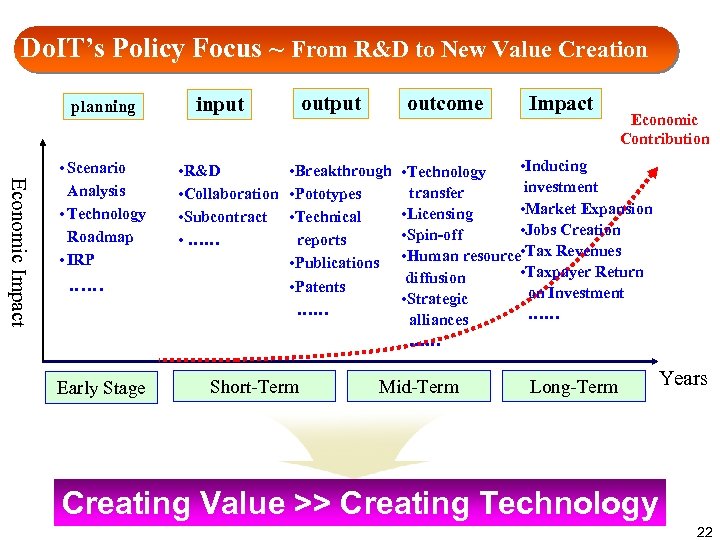 Do. IT’s Policy Focus ~ From R&D to New Value Creation planning Economic Impact • Scenario Analysis • Technology Roadmap • IRP …… Early Stage input outcome • R&D • Breakthrough • Collaboration • Pototypes • Subcontract • Technical • …… reports • Publications • Patents …… Short-Term Impact Economic Contribution • Inducing • Technology investment transfer • Market Expansion • Licensing • Jobs Creation • Spin-off • Human resource • Tax Revenues • Taxpayer Return diffusion on Investment • Strategic …… alliances …… Mid-Term Long-Term Years Creating Value >> Creating Technology 22
Do. IT’s Policy Focus ~ From R&D to New Value Creation planning Economic Impact • Scenario Analysis • Technology Roadmap • IRP …… Early Stage input outcome • R&D • Breakthrough • Collaboration • Pototypes • Subcontract • Technical • …… reports • Publications • Patents …… Short-Term Impact Economic Contribution • Inducing • Technology investment transfer • Market Expansion • Licensing • Jobs Creation • Spin-off • Human resource • Tax Revenues • Taxpayer Return diffusion on Investment • Strategic …… alliances …… Mid-Term Long-Term Years Creating Value >> Creating Technology 22
 The challenge and Vision The Challenge Ahead To come to terms with the trend towards globalization esp. in S&T To gather internal momentum for industrial innovation To lay sound foundation for diverse competitive advantages, moving beyond the OEM/ODM model To promote systematic innovation via inter-organizational integration To facilitate firms’ crossing the Valley of Death 23
The challenge and Vision The Challenge Ahead To come to terms with the trend towards globalization esp. in S&T To gather internal momentum for industrial innovation To lay sound foundation for diverse competitive advantages, moving beyond the OEM/ODM model To promote systematic innovation via inter-organizational integration To facilitate firms’ crossing the Valley of Death 23
 Vision for National Development up to 2015 ng nci va Ad Economy - innovalue • Innovation driven • Manpower development • Brand value • Integration for value-added • Fiscal & financial reform Prosperity Justice to ü 2007 -2015 average growth: 4~5% ü Per capita GDP in 2015: US$30, 000 ü Unemployment kept below 4% Environment - green, sustainable • Win-win for environment, energy, and industry • Sustainable use of resources • Friendly ecology Global - tolerant, open, multiplicity Society - fair, just, caring • Social security • Narrowing wealth gap • Manpower policy Sustainability • Invest Taiwan first • Global positioning • Cross-strait economic links Government -able, honorable, slim, professional • Able and anti-corrupt • Fiscal strength • Legal reengineering 24
Vision for National Development up to 2015 ng nci va Ad Economy - innovalue • Innovation driven • Manpower development • Brand value • Integration for value-added • Fiscal & financial reform Prosperity Justice to ü 2007 -2015 average growth: 4~5% ü Per capita GDP in 2015: US$30, 000 ü Unemployment kept below 4% Environment - green, sustainable • Win-win for environment, energy, and industry • Sustainable use of resources • Friendly ecology Global - tolerant, open, multiplicity Society - fair, just, caring • Social security • Narrowing wealth gap • Manpower policy Sustainability • Invest Taiwan first • Global positioning • Cross-strait economic links Government -able, honorable, slim, professional • Able and anti-corrupt • Fiscal strength • Legal reengineering 24
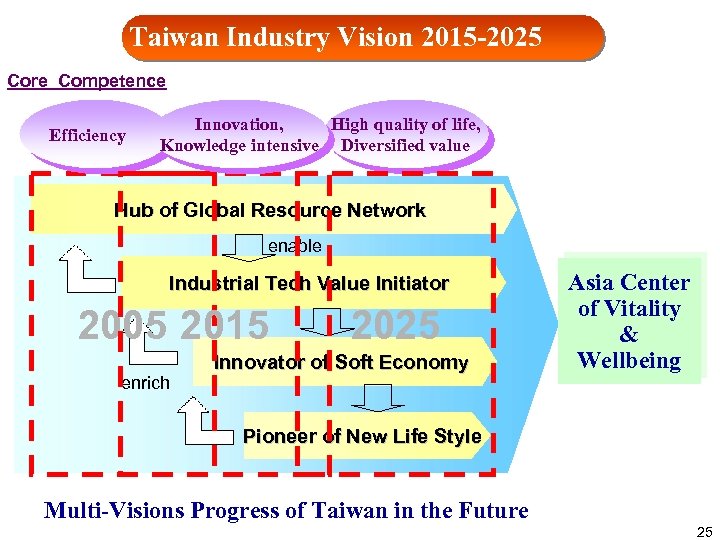 Taiwan Industry Vision 2015 -2025 Core Competence Efficiency Innovation, High quality of life, Knowledge intensive Diversified value Hub of Global Resource Network enable Industrial Tech Value Initiator 2005 2015 enrich 2025 Innovator of Soft Economy Asia Center of Vitality & Wellbeing Pioneer of New Life Style Multi-Visions Progress of Taiwan in the Future 25
Taiwan Industry Vision 2015 -2025 Core Competence Efficiency Innovation, High quality of life, Knowledge intensive Diversified value Hub of Global Resource Network enable Industrial Tech Value Initiator 2005 2015 enrich 2025 Innovator of Soft Economy Asia Center of Vitality & Wellbeing Pioneer of New Life Style Multi-Visions Progress of Taiwan in the Future 25
 Do. IT makes a better future, always with you. Innovation, just do it. 26
Do. IT makes a better future, always with you. Innovation, just do it. 26


