ac720673eab730e9c51c6cbe2c14e652.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 1
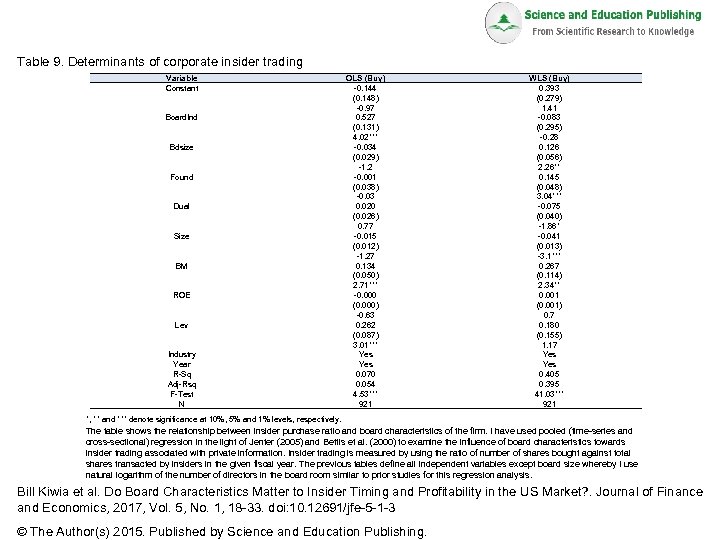
Table 9. Determinants of corporate insider trading Variable Constant Board. Ind Bdsize Found Dual Size BM ROE Lev Industry Year R-Sq Adj-Rsq F-Test N OLS (Buy) -0. 144 (0. 148) -0. 97 0. 527 (0. 131) 4. 02*** -0. 034 (0. 029) -1. 2 -0. 001 (0. 038) -0. 03 0. 020 (0. 026) 0. 77 -0. 015 (0. 012) -1. 27 0. 134 (0. 050) 2. 71*** -0. 000 (0. 000) -0. 63 0. 262 (0. 087) 3. 01*** Yes 0. 070 0. 054 4. 53*** 921 WLS (Buy) 0. 393 (0. 279) 1. 41 -0. 083 (0. 295) -0. 28 0. 126 (0. 056) 2. 26** 0. 145 (0. 048) 3. 04*** -0. 075 (0. 040) -1. 86* -0. 041 (0. 013) -3. 1*** 0. 267 (0. 114) 2. 34** 0. 001 (0. 001) 0. 7 0. 180 (0. 155) 1. 17 Yes 0. 405 0. 395 41. 03*** 921 *, ** and *** denote significance at 10%, 5% and 1% levels, respectively. The table shows the relationship between insider purchase ratio and board characteristics of the firm. I have used pooled (time-series and cross-sectional) regression in the light of Jenter (2005) and Bettis et al. (2000) to examine the influence of board characteristics towards insider trading associated with private information. Insider trading is measured by using the ratio of number of shares bought against total shares transacted by insiders in the given fiscal year. The previous tables define all independent variables except board size whereby I use natural logarithm of the number of directors in the board room similar to prior studies for this regression analysis. Bill Kiwia et al. Do Board Characteristics Matter to Insider Timing and Profitability in the US Market? . Journal of Finance and Economics, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 1, 18 -33. doi: 10. 12691/jfe-5 -1 -3 © The Author(s) 2015. Published by Science and Education Publishing.
ac720673eab730e9c51c6cbe2c14e652.ppt