6eb08a4a8ca532573513b4428d19b931.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 T-Ray Reflection Computed Tomography Jeremy Pearce Electrical & Computer Engineering
T-Ray Reflection Computed Tomography Jeremy Pearce Electrical & Computer Engineering
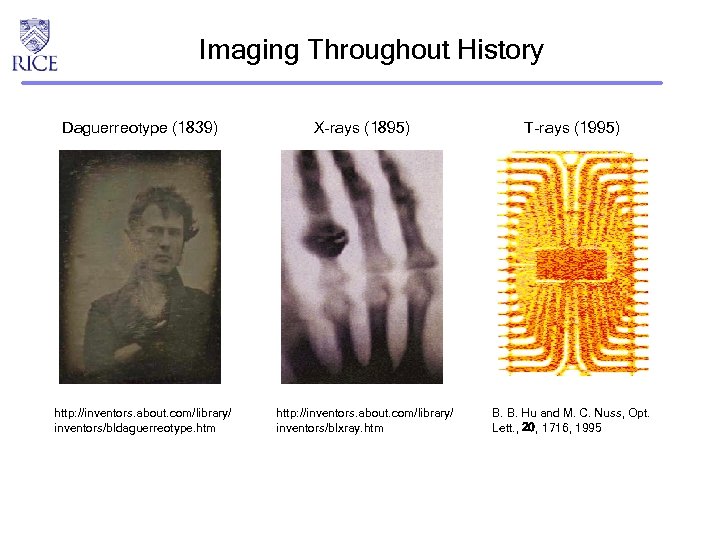 Imaging Throughout History Daguerreotype (1839) X-rays (1895) T-rays (1995) http: //inventors. about. com/library/ inventors/bldaguerreotype. htm http: //inventors. about. com/library/ inventors/blxray. htm B. B. Hu and M. C. Nuss, Opt. Lett. , 20, 1716, 1995
Imaging Throughout History Daguerreotype (1839) X-rays (1895) T-rays (1995) http: //inventors. about. com/library/ inventors/bldaguerreotype. htm http: //inventors. about. com/library/ inventors/blxray. htm B. B. Hu and M. C. Nuss, Opt. Lett. , 20, 1716, 1995
 Objectives Develop a T-ray imaging system that… • Is easy to align and use • Requires few measurements • Generates “high” resolution pictures
Objectives Develop a T-ray imaging system that… • Is easy to align and use • Requires few measurements • Generates “high” resolution pictures
 Outline • T-Rays • Principles of Tomography • T-Ray Reflection Computed Tomography • Discussion and Future Work
Outline • T-Rays • Principles of Tomography • T-Ray Reflection Computed Tomography • Discussion and Future Work
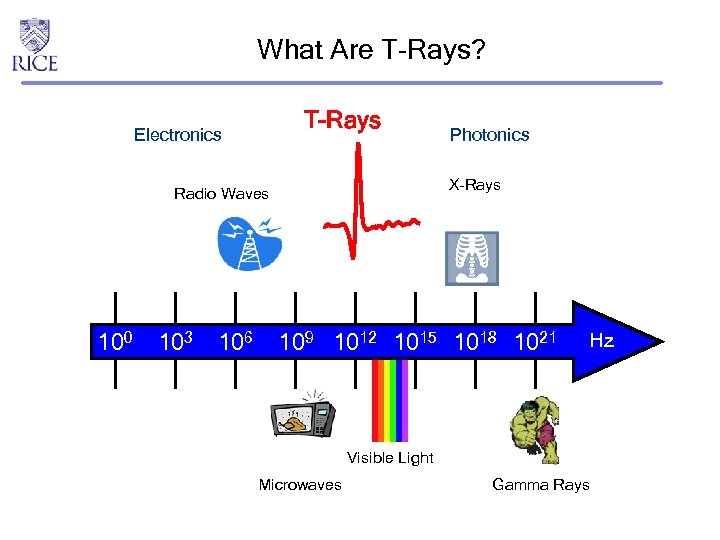 What Are T-Rays? T-Rays Electronics X-Rays Radio Waves 100 103 106 Photonics 109 1012 1015 1018 1021 Hz Visible Light Microwaves Gamma Rays
What Are T-Rays? T-Rays Electronics X-Rays Radio Waves 100 103 106 Photonics 109 1012 1015 1018 1021 Hz Visible Light Microwaves Gamma Rays
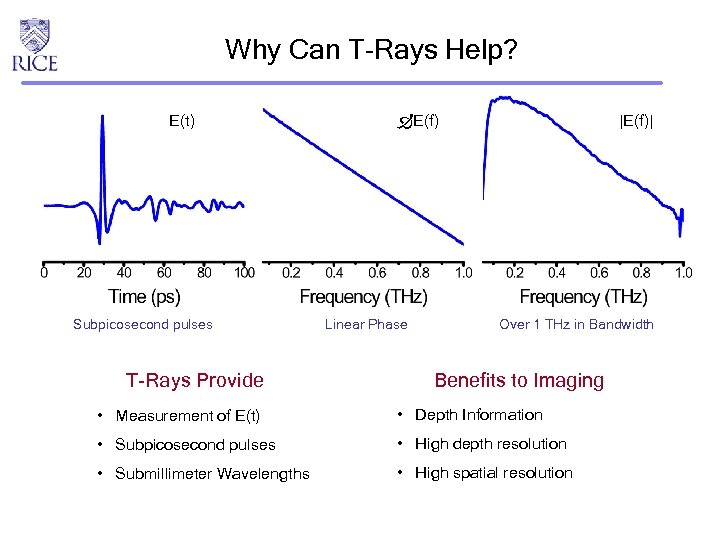 Why Can T-Rays Help? E(t) Subpicosecond pulses T-Rays Provide |E(f)| E(f) Linear Phase Over 1 THz in Bandwidth Benefits to Imaging • Measurement of E(t) • Depth Information • Subpicosecond pulses • High depth resolution • Submillimeter Wavelengths • High spatial resolution
Why Can T-Rays Help? E(t) Subpicosecond pulses T-Rays Provide |E(f)| E(f) Linear Phase Over 1 THz in Bandwidth Benefits to Imaging • Measurement of E(t) • Depth Information • Subpicosecond pulses • High depth resolution • Submillimeter Wavelengths • High spatial resolution
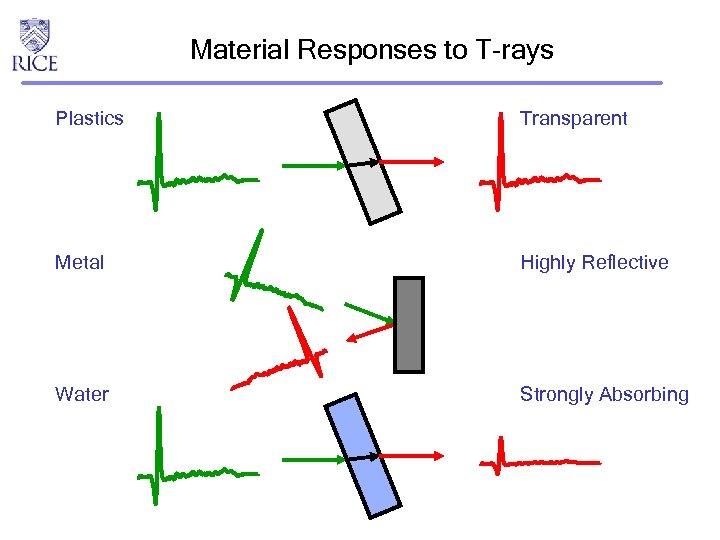 Material Responses to T-rays Plastics Transparent Metal Highly Reflective Water Strongly Absorbing
Material Responses to T-rays Plastics Transparent Metal Highly Reflective Water Strongly Absorbing
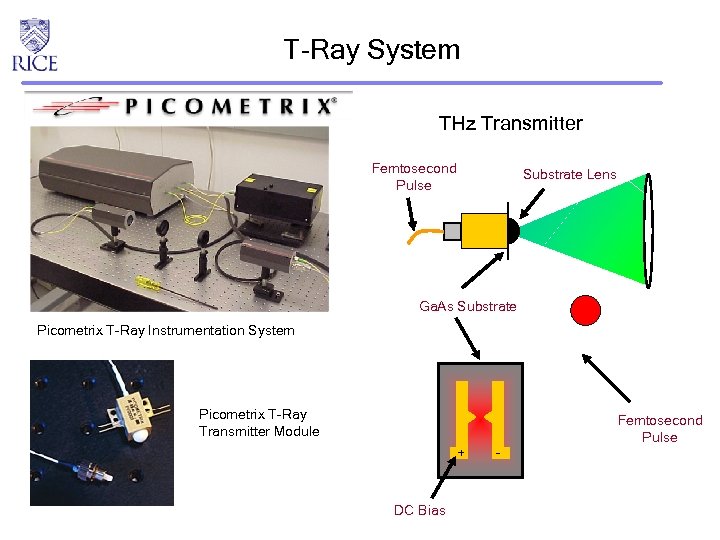 T-Ray System THz Transmitter Femtosecond Pulse Substrate Lens Ga. As Substrate Picometrix T-Ray Instrumentation System Picometrix T-Ray Transmitter Module + DC Bias - Femtosecond Pulse
T-Ray System THz Transmitter Femtosecond Pulse Substrate Lens Ga. As Substrate Picometrix T-Ray Instrumentation System Picometrix T-Ray Transmitter Module + DC Bias - Femtosecond Pulse
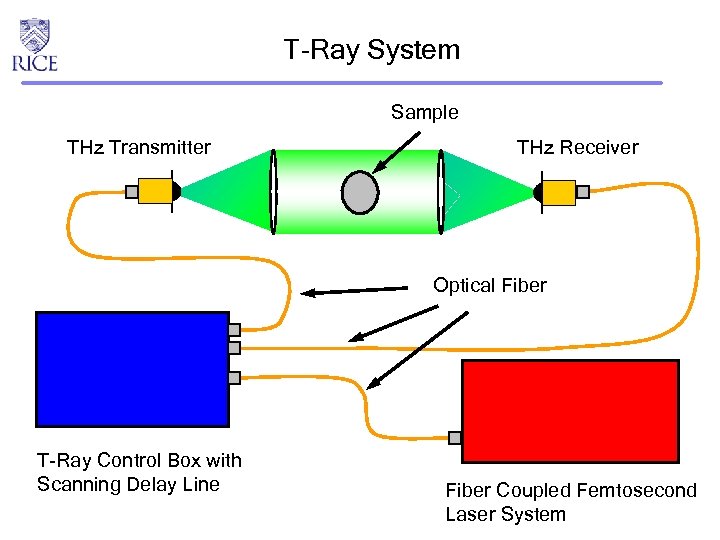 T-Ray System Sample THz Transmitter THz Receiver Optical Fiber T-Ray Control Box with Scanning Delay Line Fiber Coupled Femtosecond Laser System
T-Ray System Sample THz Transmitter THz Receiver Optical Fiber T-Ray Control Box with Scanning Delay Line Fiber Coupled Femtosecond Laser System
 Summary of T-Rays • Broad fractional bandwidth • Direct measurement of E(t) • Short wavelengths • Unique material responses
Summary of T-Rays • Broad fractional bandwidth • Direct measurement of E(t) • Short wavelengths • Unique material responses
 Outline • T-Rays • Principles of Tomography • T-Ray Reflection Computed Tomography • Discussion and Future Work
Outline • T-Rays • Principles of Tomography • T-Ray Reflection Computed Tomography • Discussion and Future Work
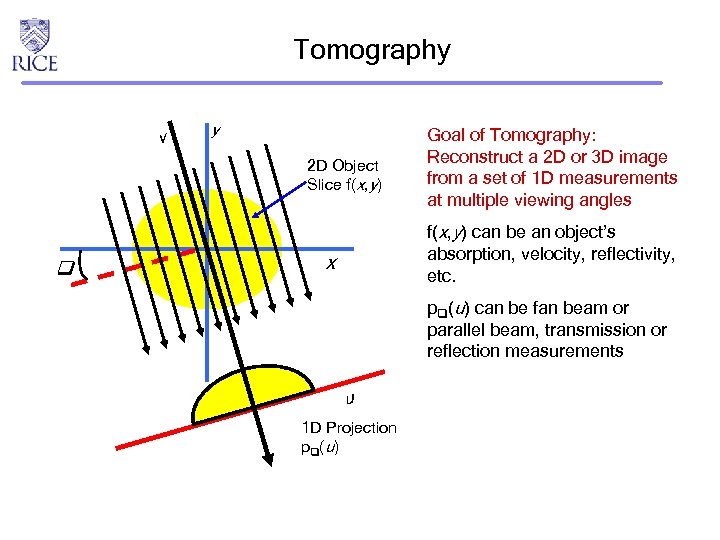 Tomography v y 2 D Object Slice f(x, y) Goal of Tomography: Reconstruct a 2 D or 3 D image from a set of 1 D measurements at multiple viewing angles f(x, y) can be an object’s absorption, velocity, reflectivity, etc. x p (u) can be fan beam or parallel beam, transmission or reflection measurements u 1 D Projection p (u)
Tomography v y 2 D Object Slice f(x, y) Goal of Tomography: Reconstruct a 2 D or 3 D image from a set of 1 D measurements at multiple viewing angles f(x, y) can be an object’s absorption, velocity, reflectivity, etc. x p (u) can be fan beam or parallel beam, transmission or reflection measurements u 1 D Projection p (u)
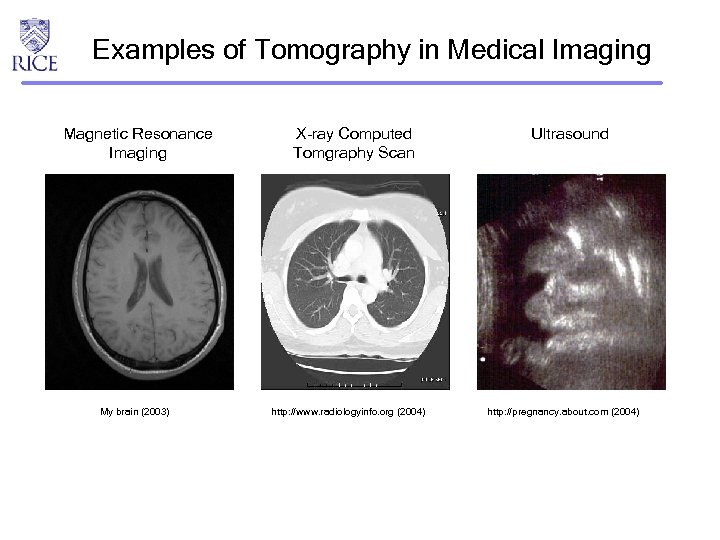 Examples of Tomography in Medical Imaging Magnetic Resonance Imaging My brain (2003) X-ray Computed Tomgraphy Scan http: //www. radiologyinfo. org (2004) Ultrasound http: //pregnancy. about. com (2004)
Examples of Tomography in Medical Imaging Magnetic Resonance Imaging My brain (2003) X-ray Computed Tomgraphy Scan http: //www. radiologyinfo. org (2004) Ultrasound http: //pregnancy. about. com (2004)
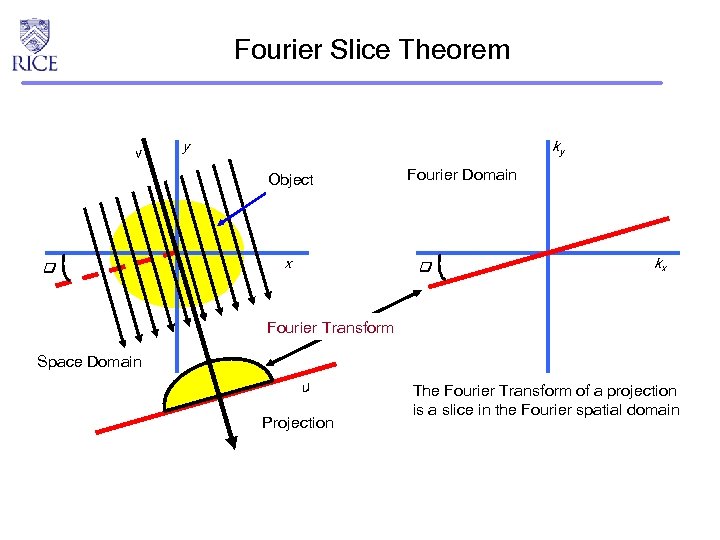 Fourier Slice Theorem v y ky Object x Fourier Domain kx Fourier Transform Space Domain u Projection The Fourier Transform of a projection is a slice in the Fourier spatial domain
Fourier Slice Theorem v y ky Object x Fourier Domain kx Fourier Transform Space Domain u Projection The Fourier Transform of a projection is a slice in the Fourier spatial domain
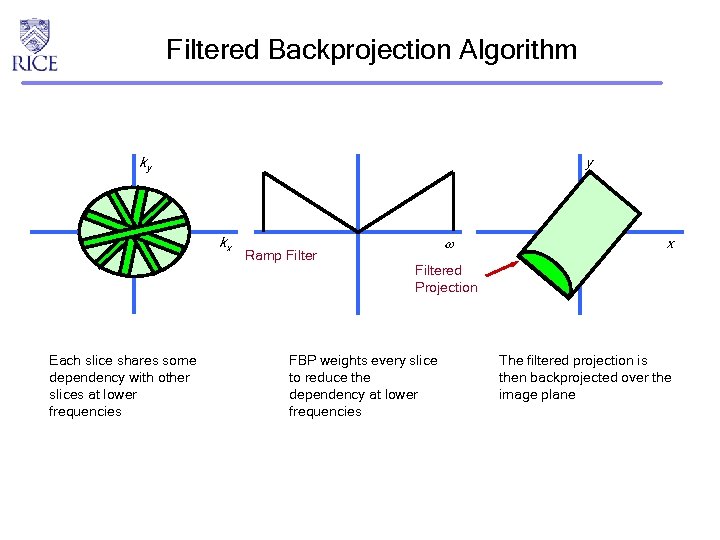 Filtered Backprojection Algorithm ky y kx Each slice shares some dependency with other slices at lower frequencies Ramp Filter x Filtered Projection FBP weights every slice to reduce the dependency at lower frequencies The filtered projection is then backprojected over the image plane
Filtered Backprojection Algorithm ky y kx Each slice shares some dependency with other slices at lower frequencies Ramp Filter x Filtered Projection FBP weights every slice to reduce the dependency at lower frequencies The filtered projection is then backprojected over the image plane
 Outline • T-Rays • Principles of Tomography • T-Ray Reflection Computed Tomography • Discussion and Future Work
Outline • T-Rays • Principles of Tomography • T-Ray Reflection Computed Tomography • Discussion and Future Work
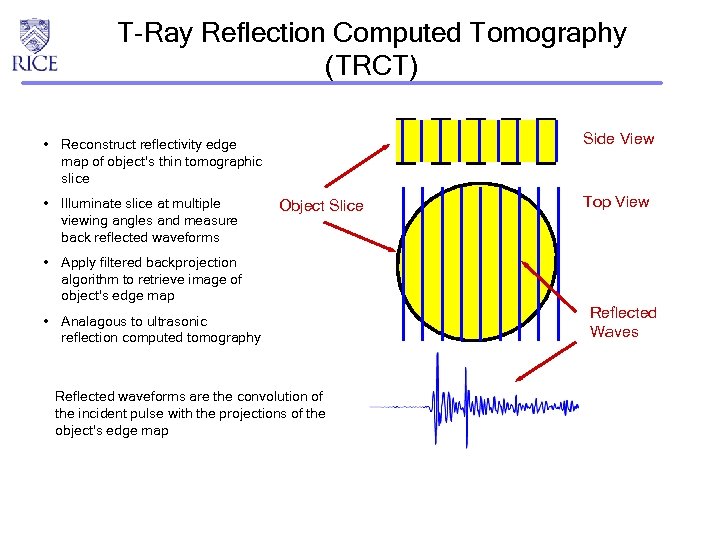 T-Ray Reflection Computed Tomography (TRCT) Side View • Reconstruct reflectivity edge map of object’s thin tomographic slice • Illuminate slice at multiple viewing angles and measure back reflected waveforms Object Slice • Apply filtered backprojection algorithm to retrieve image of object’s edge map • Analagous to ultrasonic reflection computed tomography Reflected waveforms are the convolution of the incident pulse with the projections of the object’s edge map Top View Reflected Waves
T-Ray Reflection Computed Tomography (TRCT) Side View • Reconstruct reflectivity edge map of object’s thin tomographic slice • Illuminate slice at multiple viewing angles and measure back reflected waveforms Object Slice • Apply filtered backprojection algorithm to retrieve image of object’s edge map • Analagous to ultrasonic reflection computed tomography Reflected waveforms are the convolution of the incident pulse with the projections of the object’s edge map Top View Reflected Waves
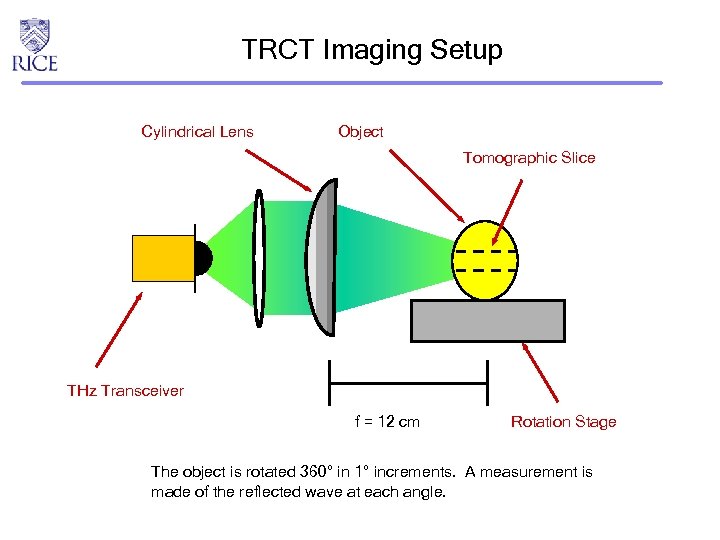 TRCT Imaging Setup Cylindrical Lens Object Tomographic Slice THz Transceiver f = 12 cm Rotation Stage The object is rotated 360° in 1° increments. A measurement is made of the reflected wave at each angle.
TRCT Imaging Setup Cylindrical Lens Object Tomographic Slice THz Transceiver f = 12 cm Rotation Stage The object is rotated 360° in 1° increments. A measurement is made of the reflected wave at each angle.
 Cross-Section of Test Object: Metal Square Post Dimensions: 1 in. x 1 in. Material: Aluminum
Cross-Section of Test Object: Metal Square Post Dimensions: 1 in. x 1 in. Material: Aluminum
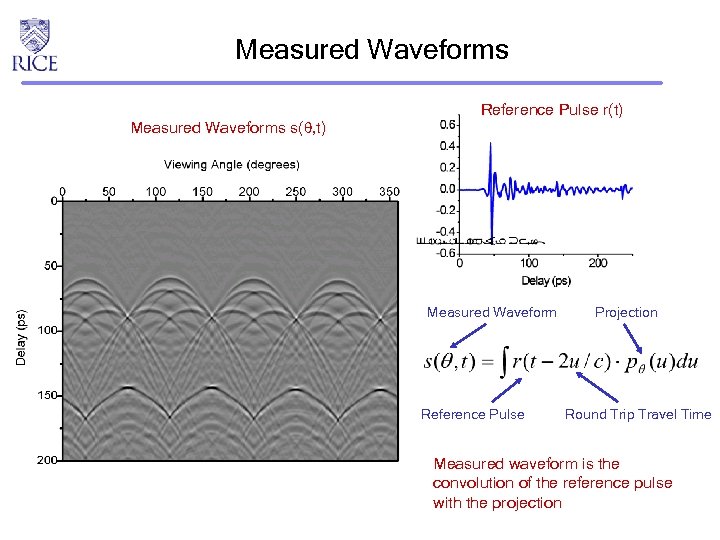 Measured Waveforms s( , t) Reference Pulse r(t) Measured Waveform Reference Pulse Projection Round Trip Travel Time Measured waveform is the convolution of the reference pulse with the projection
Measured Waveforms s( , t) Reference Pulse r(t) Measured Waveform Reference Pulse Projection Round Trip Travel Time Measured waveform is the convolution of the reference pulse with the projection
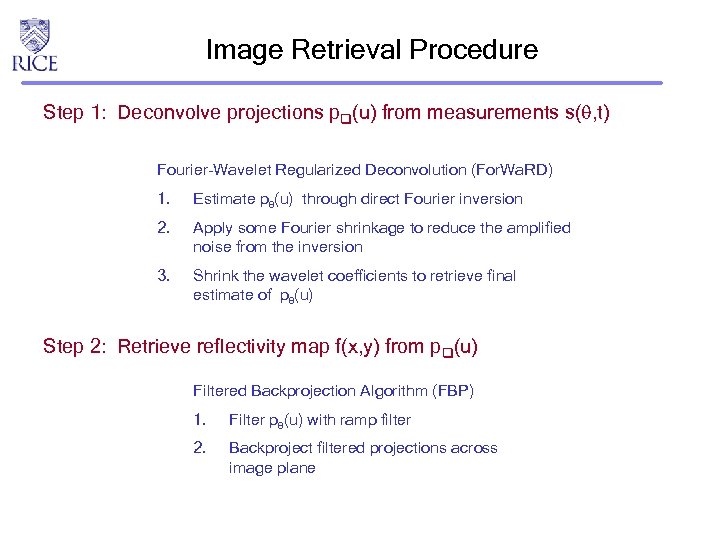 Image Retrieval Procedure Step 1: Deconvolve projections p (u) from measurements s( , t) Fourier-Wavelet Regularized Deconvolution (For. Wa. RD) 1. Estimate p (u) through direct Fourier inversion 2. Apply some Fourier shrinkage to reduce the amplified noise from the inversion 3. Shrink the wavelet coefficients to retrieve final estimate of p (u) Step 2: Retrieve reflectivity map f(x, y) from p (u) Filtered Backprojection Algorithm (FBP) 1. Filter p (u) with ramp filter 2. Backproject filtered projections across image plane
Image Retrieval Procedure Step 1: Deconvolve projections p (u) from measurements s( , t) Fourier-Wavelet Regularized Deconvolution (For. Wa. RD) 1. Estimate p (u) through direct Fourier inversion 2. Apply some Fourier shrinkage to reduce the amplified noise from the inversion 3. Shrink the wavelet coefficients to retrieve final estimate of p (u) Step 2: Retrieve reflectivity map f(x, y) from p (u) Filtered Backprojection Algorithm (FBP) 1. Filter p (u) with ramp filter 2. Backproject filtered projections across image plane
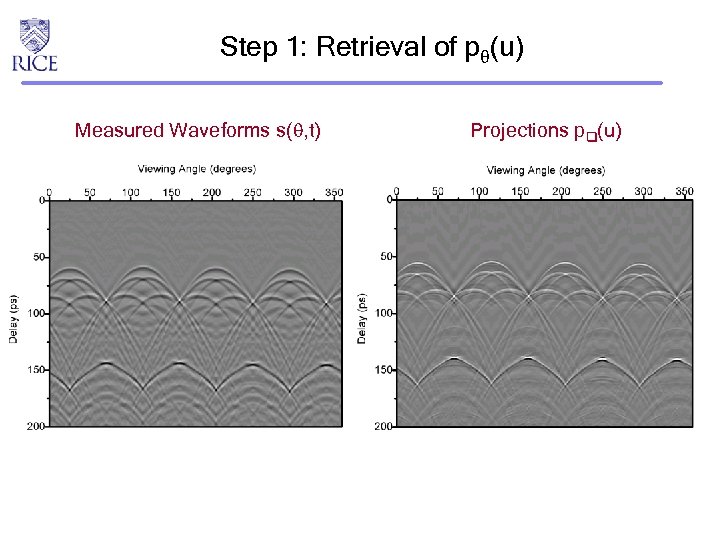 Step 1: Retrieval of p (u) Measured Waveforms s( , t) Projections p (u)
Step 1: Retrieval of p (u) Measured Waveforms s( , t) Projections p (u)
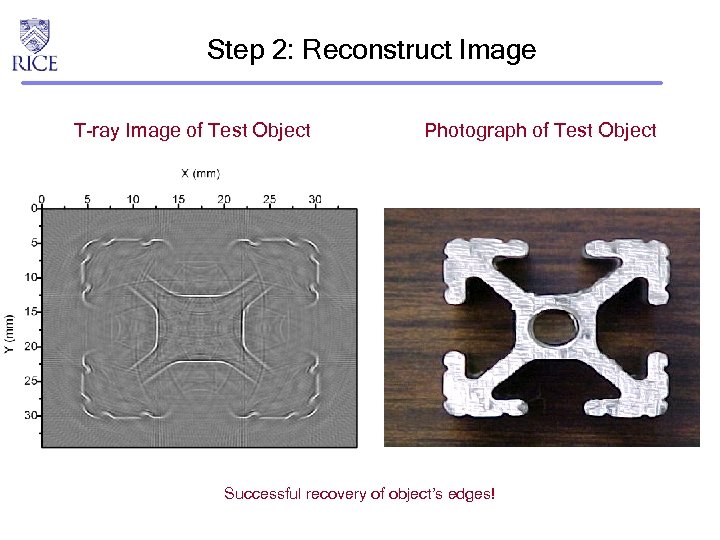 Step 2: Reconstruct Image T-ray Image of Test Object Photograph of Test Object Successful recovery of object’s edges!
Step 2: Reconstruct Image T-ray Image of Test Object Photograph of Test Object Successful recovery of object’s edges!
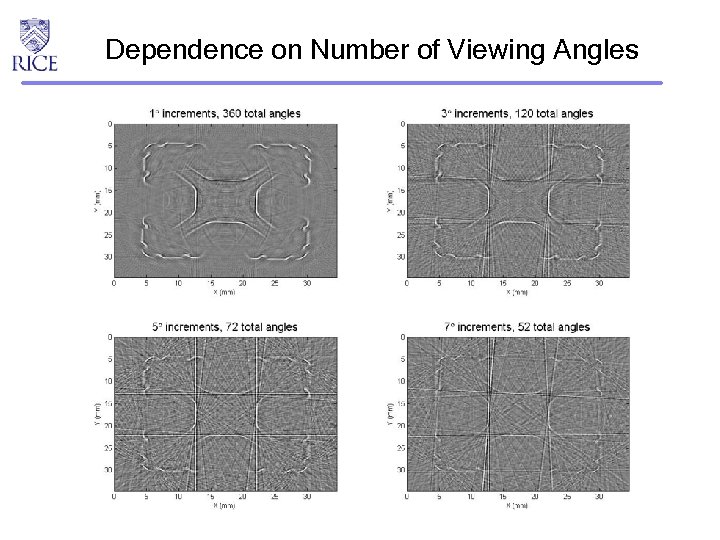 Dependence on Number of Viewing Angles
Dependence on Number of Viewing Angles
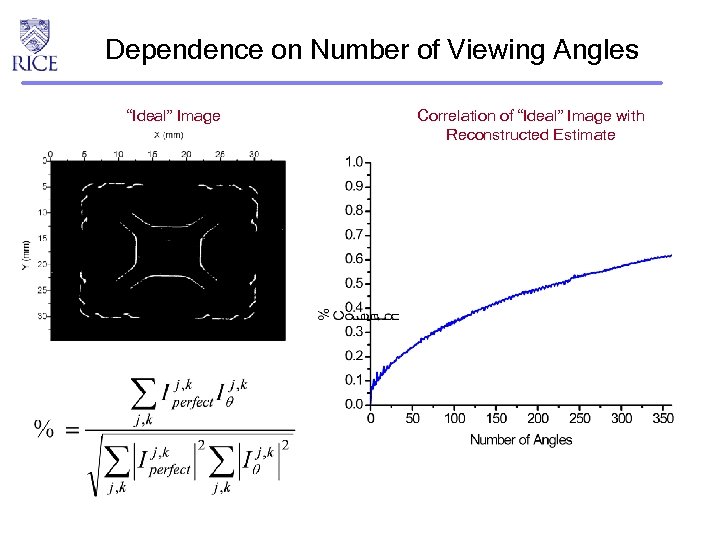 Dependence on Number of Viewing Angles “Ideal” Image Correlation of “Ideal” Image with Reconstructed Estimate
Dependence on Number of Viewing Angles “Ideal” Image Correlation of “Ideal” Image with Reconstructed Estimate
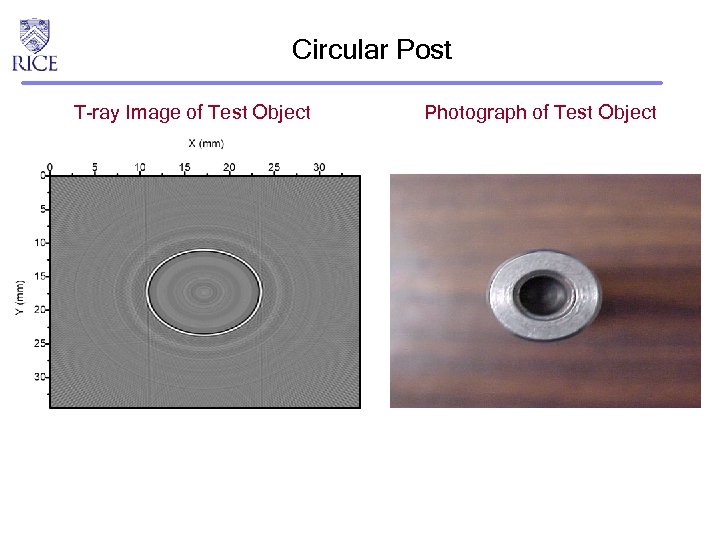 Circular Post T-ray Image of Test Object Photograph of Test Object
Circular Post T-ray Image of Test Object Photograph of Test Object
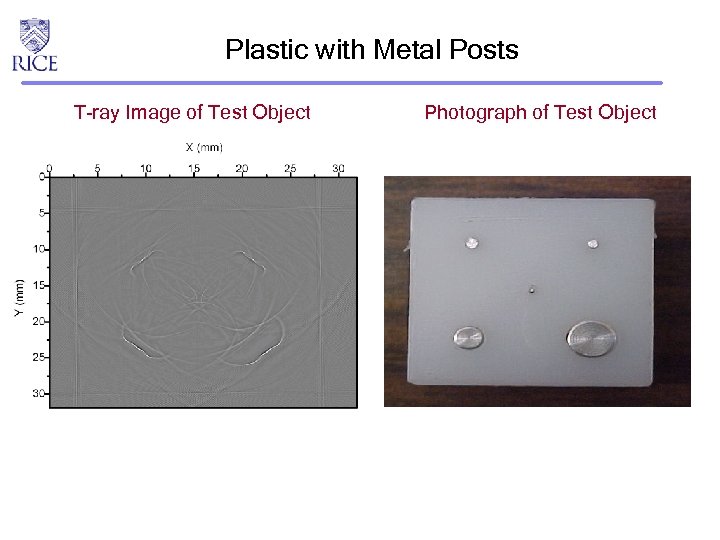 Plastic with Metal Posts T-ray Image of Test Object Photograph of Test Object
Plastic with Metal Posts T-ray Image of Test Object Photograph of Test Object
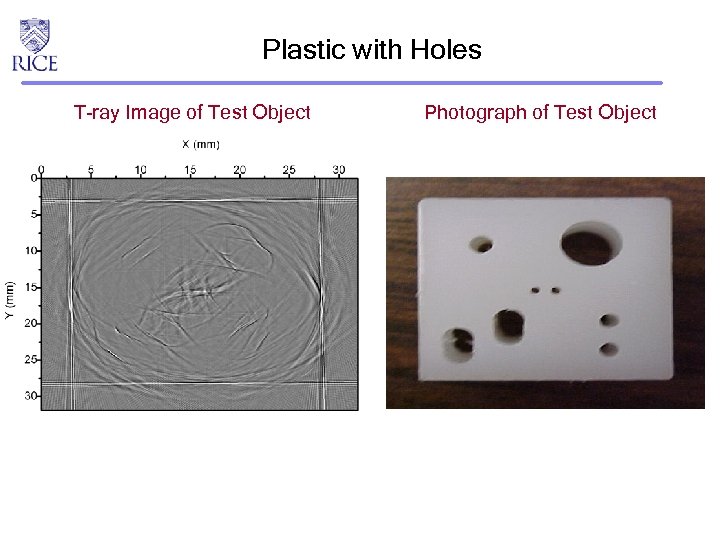 Plastic with Holes T-ray Image of Test Object Photograph of Test Object
Plastic with Holes T-ray Image of Test Object Photograph of Test Object
 Outline • T-Rays • Principles of Tomography • T-Ray Reflection Computed Tomography • Discussion and Future Work
Outline • T-Rays • Principles of Tomography • T-Ray Reflection Computed Tomography • Discussion and Future Work
 Does TRCT Meet Objectives Develop a T-ray imaging system that… • Is easy to align and use Uses single transceiver • Requires few measurements 360 waveforms or less • Generates “high” resolution pictures Resolution 100 m
Does TRCT Meet Objectives Develop a T-ray imaging system that… • Is easy to align and use Uses single transceiver • Requires few measurements 360 waveforms or less • Generates “high” resolution pictures Resolution 100 m
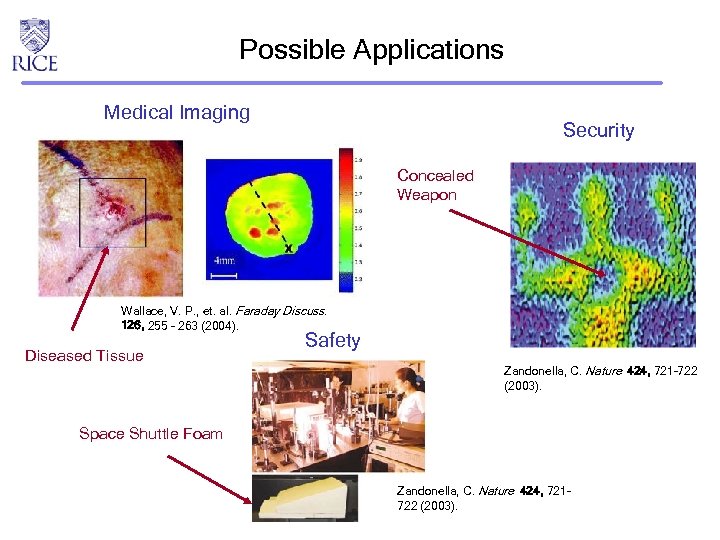 Possible Applications Medical Imaging Security Concealed Weapon Wallace, V. P. , et. al. Faraday Discuss. 126, 255 - 263 (2004). Diseased Tissue Safety Zandonella, C. Nature 424, 721– 722 (2003). Space Shuttle Foam Zandonella, C. Nature 424, 721– 722 (2003).
Possible Applications Medical Imaging Security Concealed Weapon Wallace, V. P. , et. al. Faraday Discuss. 126, 255 - 263 (2004). Diseased Tissue Safety Zandonella, C. Nature 424, 721– 722 (2003). Space Shuttle Foam Zandonella, C. Nature 424, 721– 722 (2003).
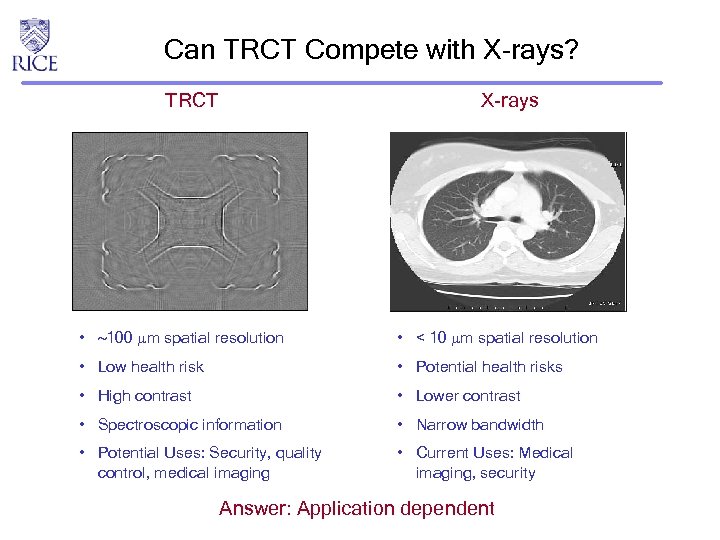 Can TRCT Compete with X-rays? TRCT X-rays • 100 m spatial resolution • < 10 m spatial resolution • Low health risk • Potential health risks • High contrast • Lower contrast • Spectroscopic information • Narrow bandwidth • Potential Uses: Security, quality control, medical imaging • Current Uses: Medical imaging, security Answer: Application dependent
Can TRCT Compete with X-rays? TRCT X-rays • 100 m spatial resolution • < 10 m spatial resolution • Low health risk • Potential health risks • High contrast • Lower contrast • Spectroscopic information • Narrow bandwidth • Potential Uses: Security, quality control, medical imaging • Current Uses: Medical imaging, security Answer: Application dependent
 Future System Improvements • Actual Transceiver Module • Increase Signal to Noise Ratio • Acquisition Speed: – 5 -6 sec. /meas. 100 msec. /meas. • 3 -D Imaging • Automated Software
Future System Improvements • Actual Transceiver Module • Increase Signal to Noise Ratio • Acquisition Speed: – 5 -6 sec. /meas. 100 msec. /meas. • 3 -D Imaging • Automated Software
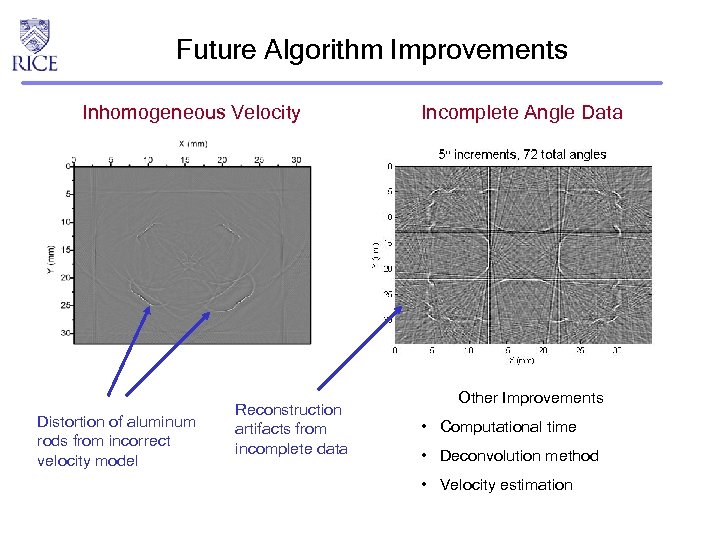 Future Algorithm Improvements Inhomogeneous Velocity Distortion of aluminum rods from incorrect velocity model Reconstruction artifacts from incomplete data Incomplete Angle Data Other Improvements • Computational time • Deconvolution method • Velocity estimation
Future Algorithm Improvements Inhomogeneous Velocity Distortion of aluminum rods from incorrect velocity model Reconstruction artifacts from incomplete data Incomplete Angle Data Other Improvements • Computational time • Deconvolution method • Velocity estimation
 Summary • Developed a new reflection mode T-ray imaging system • Tested system’s capabilities on a diverse set of objects • Compared TRCT to other commercially available imaging systems • Suggested improvements for imaging system and reconstruction algorithm
Summary • Developed a new reflection mode T-ray imaging system • Tested system’s capabilities on a diverse set of objects • Compared TRCT to other commercially available imaging systems • Suggested improvements for imaging system and reconstruction algorithm
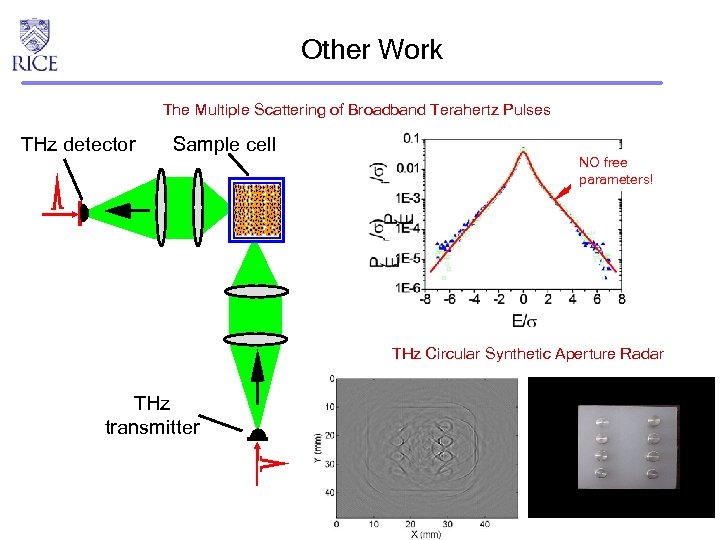 Other Work The Multiple Scattering of Broadband Terahertz Pulses THz detector Sample cell NO free parameters! THz Circular Synthetic Aperture Radar THz transmitter
Other Work The Multiple Scattering of Broadband Terahertz Pulses THz detector Sample cell NO free parameters! THz Circular Synthetic Aperture Radar THz transmitter
 Publications 1. J. Pearce, Z. Jian and D. M. Mittleman, “Spectral shifts as a signature of the onset of diffusion of broadband terahertz pulses, ” Optics Letters, accepted (2004). 2. J. Pearce, Z. Jian, and D. Mittleman, “Propagation of terahertz pulses in random media, ” Philosophical Transactions A, 362, 301 (2004). 3. J. Pearce, Z. Jian, and D. Mittleman, “Statistics of multiply scattered broadband terahertz pulses, ” Physical Review Letters, 91, 043903 (2003). 4. J. Pearce and D. Mittleman, “Scale model experimentation: Using terahertz pulses to study light scattering, ” Physics in Medicine and Biology, 47, 3823 (2002). 5. J. Pearce and D. Mittleman, “Definition of the Fresnel zone for broadband radiation, ” Physical Review E, 66, 056602 (2002). 6. J. Pearce and D. Mittleman, “The propagation of single-cycle THz pulses in random media, ” Optics Letters, 26, 2002 (2001).
Publications 1. J. Pearce, Z. Jian and D. M. Mittleman, “Spectral shifts as a signature of the onset of diffusion of broadband terahertz pulses, ” Optics Letters, accepted (2004). 2. J. Pearce, Z. Jian, and D. Mittleman, “Propagation of terahertz pulses in random media, ” Philosophical Transactions A, 362, 301 (2004). 3. J. Pearce, Z. Jian, and D. Mittleman, “Statistics of multiply scattered broadband terahertz pulses, ” Physical Review Letters, 91, 043903 (2003). 4. J. Pearce and D. Mittleman, “Scale model experimentation: Using terahertz pulses to study light scattering, ” Physics in Medicine and Biology, 47, 3823 (2002). 5. J. Pearce and D. Mittleman, “Definition of the Fresnel zone for broadband radiation, ” Physical Review E, 66, 056602 (2002). 6. J. Pearce and D. Mittleman, “The propagation of single-cycle THz pulses in random media, ” Optics Letters, 26, 2002 (2001).


