61f6eca21d169bf506c3b592d4385c98.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 T = 40 ms Sink Desired Output level <
T = 40 ms Sink Desired Output level <
 Outline 2 Background and motivation Central Concepts of Component Technologies Save. CCT - A Component Technology for Vehicular Systems Target Domain Technology Overview Component Model Tools Example application – Adaptive Crusie Controller (ACC) Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
Outline 2 Background and motivation Central Concepts of Component Technologies Save. CCT - A Component Technology for Vehicular Systems Target Domain Technology Overview Component Model Tools Example application – Adaptive Crusie Controller (ACC) Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
 Background: Save/Save++ (and progress) Save (2003 -2006) Enabling systematic development of component-based software for safety critical embedded systems. Component technologies -> Save. CCT MDH, UU, KTH, Li. TH, (ABB, Bombardier, CC Systems, CR&T, Saab, Scania, Volvo Car and Volvo TD) Save++ (2006 -2007) integrates as a part of the progress project (2006 -2010) at MDH Improved theories, methods, technologies, and tools, based on Save and Save++, -> ( Save. CCT++ ) Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 3
Background: Save/Save++ (and progress) Save (2003 -2006) Enabling systematic development of component-based software for safety critical embedded systems. Component technologies -> Save. CCT MDH, UU, KTH, Li. TH, (ABB, Bombardier, CC Systems, CR&T, Saab, Scania, Volvo Car and Volvo TD) Save++ (2006 -2007) integrates as a part of the progress project (2006 -2010) at MDH Improved theories, methods, technologies, and tools, based on Save and Save++, -> ( Save. CCT++ ) Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 3
 Motivation More Electronics With Software 4 More Functionality Improve existing Functionality Lower price Software Crisis (1968): • Error-Prone • Late • Expensive Need Better Software Engineering Approaches! Component-Based Software Engineering Component Technology For Vehicular Applications! • Promising, successful in the PC domain • Component Technologies, target PC Applications • Vehicular Software Different from PC Software Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
Motivation More Electronics With Software 4 More Functionality Improve existing Functionality Lower price Software Crisis (1968): • Error-Prone • Late • Expensive Need Better Software Engineering Approaches! Component-Based Software Engineering Component Technology For Vehicular Applications! • Promising, successful in the PC domain • Component Technologies, target PC Applications • Vehicular Software Different from PC Software Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
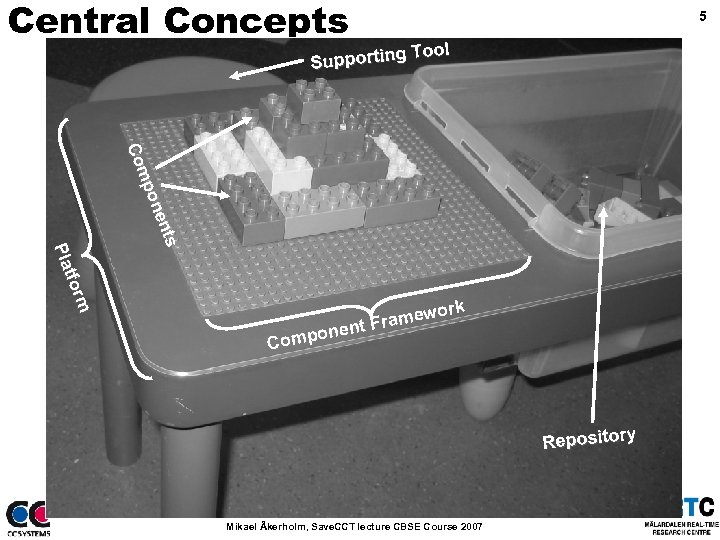 Central Concepts 5 Tool upporting S s s ent pon Com C m form tfor Pla Pl ork ramew t. F ponen Com Repository Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
Central Concepts 5 Tool upporting S s s ent pon Com C m form tfor Pla Pl ork ramew t. F ponen Com Repository Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
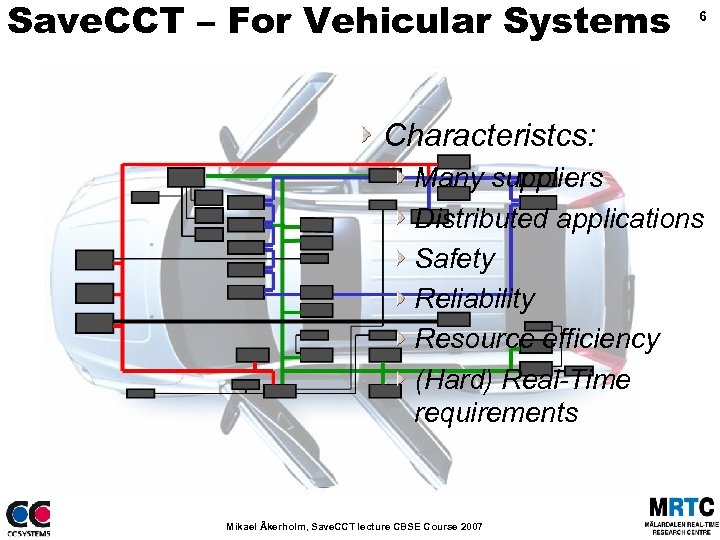 Save. CCT – For Vehicular Systems 6 Characteristcs: Many suppliers Distributed applications Safety Reliability Resource efficiency (Hard) Real-Time requirements Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
Save. CCT – For Vehicular Systems 6 Characteristcs: Many suppliers Distributed applications Safety Reliability Resource efficiency (Hard) Real-Time requirements Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
 Save. CCT Design Goals Efficient Development: Enable utilization of CBSE advantages, provide the necessary possibilities for the target domain Predictable Behavior: Need to be able to apply analysis of important runtime attributes during design-time, e. g. , Timing, Safety, Reliability, Memory needs, Processor demands Run-Time Efficiency: Ideally enable CBSE without run-time cost, compared to C programming with RTOS Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 7
Save. CCT Design Goals Efficient Development: Enable utilization of CBSE advantages, provide the necessary possibilities for the target domain Predictable Behavior: Need to be able to apply analysis of important runtime attributes during design-time, e. g. , Timing, Safety, Reliability, Memory needs, Processor demands Run-Time Efficiency: Ideally enable CBSE without run-time cost, compared to C programming with RTOS Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 7
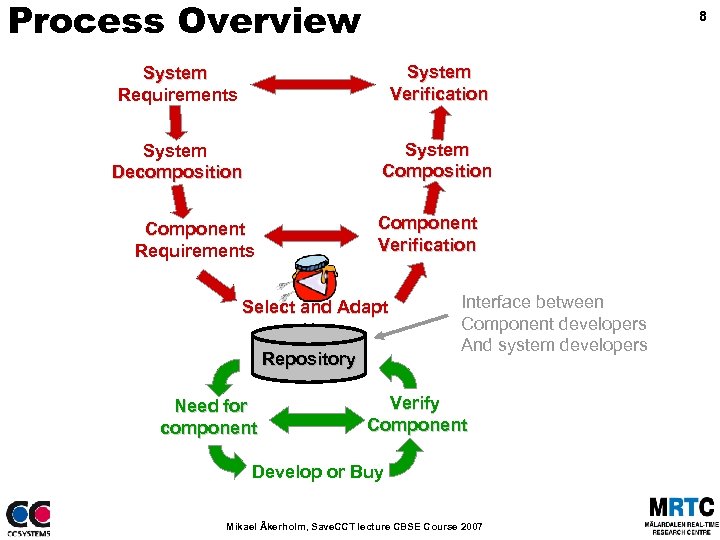 Process Overview 8 System Requirements System Verification System Decomposition System Composition Component Verification Component Requirements Select and Adapt Repository Need for component Interface between Component developers And system developers Verify Component Develop or Buy Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
Process Overview 8 System Requirements System Verification System Decomposition System Composition Component Verification Component Requirements Select and Adapt Repository Need for component Interface between Component developers And system developers Verify Component Develop or Buy Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
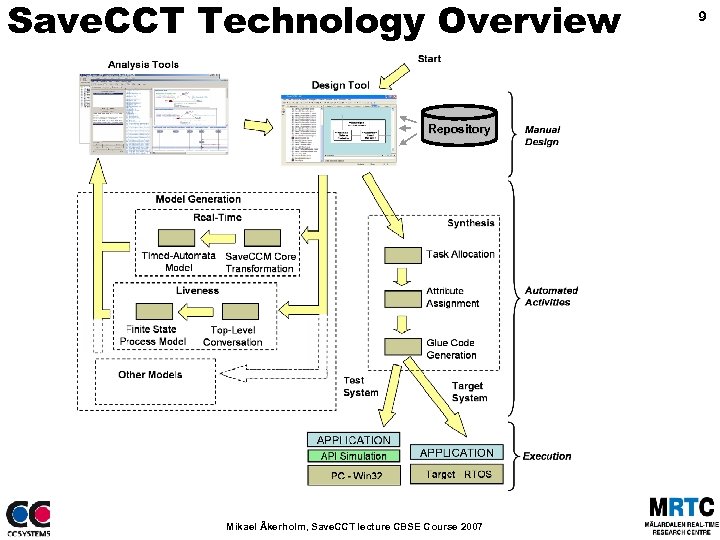 Save. CCT Technology Overview Repository Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 9
Save. CCT Technology Overview Repository Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 9
 The Save. CCM component model 10 Restictive in comparision to PC/Internet component models COM, . Net, EJB Enable analysis during design-time, and determinstic reproducable behaviour during runtime (test-time) Textual xml, and graphical UML influenced syntax Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
The Save. CCM component model 10 Restictive in comparision to PC/Internet component models COM, . Net, EJB Enable analysis during design-time, and determinstic reproducable behaviour during runtime (test-time) Textual xml, and graphical UML influenced syntax Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
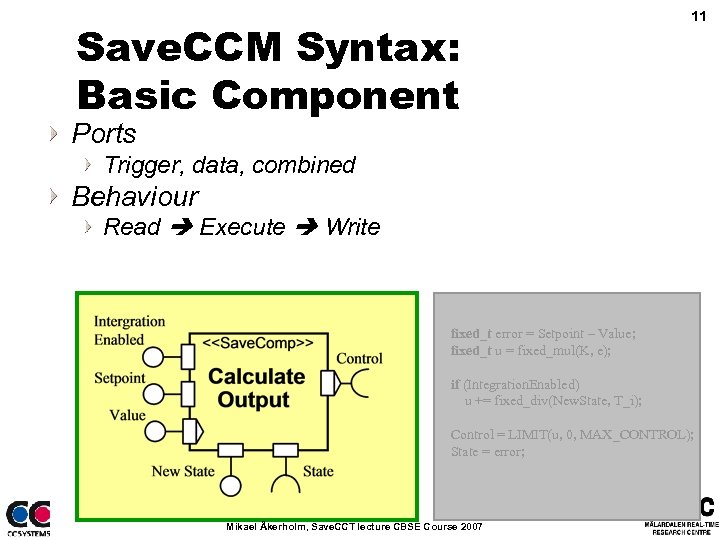 Save. CCM Syntax: Basic Component 11 Ports Trigger, data, combined Behaviour Read Execute Write fixed_t error = Setpoint – Value; fixed_t u = fixed_mul(K, e); if (Integration. Enabled) u += fixed_div(New. State, T_i); Control = LIMIT(u, 0, MAX_CONTROL); State = error; Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
Save. CCM Syntax: Basic Component 11 Ports Trigger, data, combined Behaviour Read Execute Write fixed_t error = Setpoint – Value; fixed_t u = fixed_mul(K, e); if (Integration. Enabled) u += fixed_div(New. State, T_i); Control = LIMIT(u, 0, MAX_CONTROL); State = error; Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
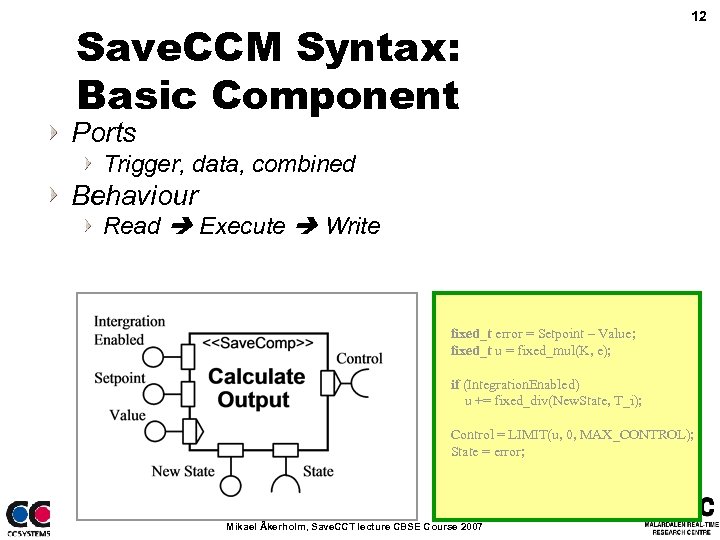 Save. CCM Syntax: Basic Component 12 Ports Trigger, data, combined Behaviour Read Execute Write fixed_t error = Setpoint – Value; fixed_t u = fixed_mul(K, e); if (Integration. Enabled) u += fixed_div(New. State, T_i); Control = LIMIT(u, 0, MAX_CONTROL); State = error; Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
Save. CCM Syntax: Basic Component 12 Ports Trigger, data, combined Behaviour Read Execute Write fixed_t error = Setpoint – Value; fixed_t u = fixed_mul(K, e); if (Integration. Enabled) u += fixed_div(New. State, T_i); Control = LIMIT(u, 0, MAX_CONTROL); State = error; Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
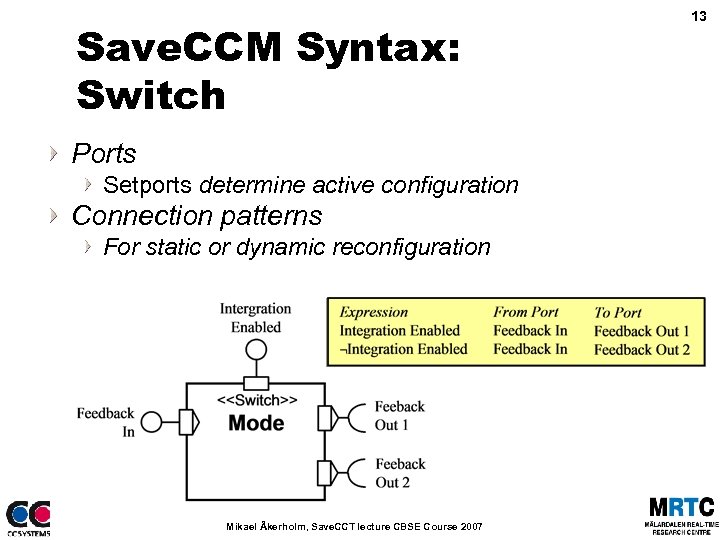 Save. CCM Syntax: Switch Ports Setports determine active configuration Connection patterns For static or dynamic reconfiguration Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 13
Save. CCM Syntax: Switch Ports Setports determine active configuration Connection patterns For static or dynamic reconfiguration Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 13
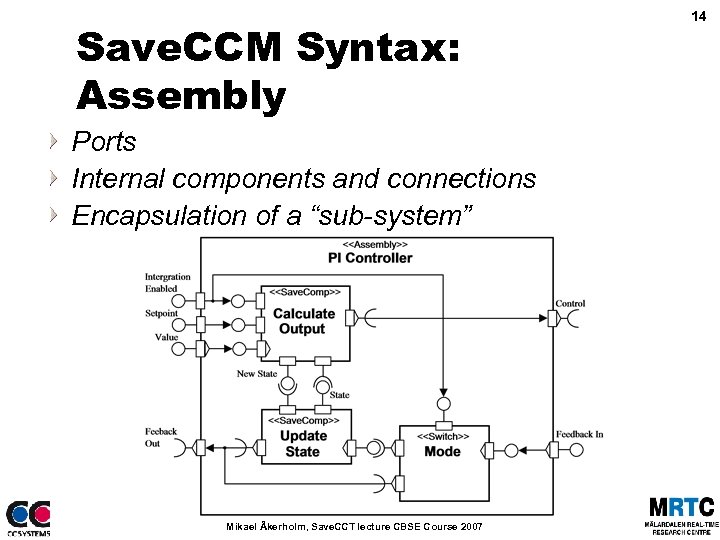 Save. CCM Syntax: Assembly Ports Internal components and connections Encapsulation of a “sub-system” Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 14
Save. CCM Syntax: Assembly Ports Internal components and connections Encapsulation of a “sub-system” Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 14
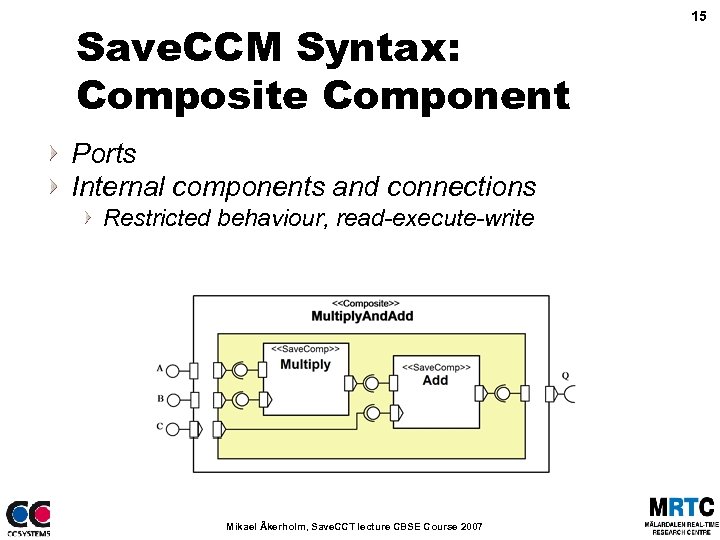 Save. CCM Syntax: Composite Component Ports Internal components and connections Restricted behaviour, read-execute-write Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 15
Save. CCM Syntax: Composite Component Ports Internal components and connections Restricted behaviour, read-execute-write Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 15
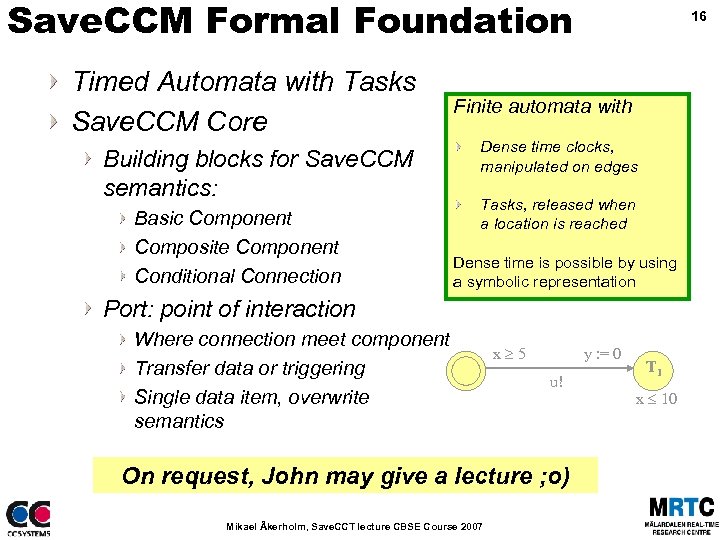 Save. CCM Formal Foundation Timed Automata with Tasks Save. CCM Core Building blocks for Save. CCM semantics: Basic Component Composite Component Conditional Connection 16 Finite automata with Dense time clocks, manipulated on edges Tasks, released when a location is reached Dense time is possible by using a symbolic representation Port: point of interaction Where connection meet component Transfer data or triggering Single data item, overwrite semantics x 5 y : = 0 u! On request, John may give a lecture ; o) Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 T 1 x 10
Save. CCM Formal Foundation Timed Automata with Tasks Save. CCM Core Building blocks for Save. CCM semantics: Basic Component Composite Component Conditional Connection 16 Finite automata with Dense time clocks, manipulated on edges Tasks, released when a location is reached Dense time is possible by using a symbolic representation Port: point of interaction Where connection meet component Transfer data or triggering Single data item, overwrite semantics x 5 y : = 0 u! On request, John may give a lecture ; o) Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 T 1 x 10
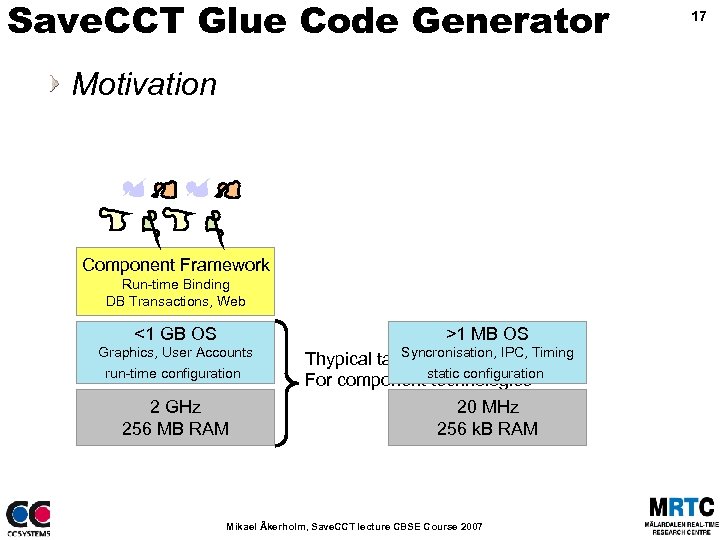 Save. CCT Glue Code Generator Motivation Component Framework Run-time Binding DB Transactions, Web <1 GB OS Graphics, User Accounts run-time configuration 2 GHz 256 MB RAM >1 MB OS Syncronisation, Thypical target platform IPC, Timing For component static configuration technologies 20 MHz 256 k. B RAM Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 17
Save. CCT Glue Code Generator Motivation Component Framework Run-time Binding DB Transactions, Web <1 GB OS Graphics, User Accounts run-time configuration 2 GHz 256 MB RAM >1 MB OS Syncronisation, Thypical target platform IPC, Timing For component static configuration technologies 20 MHz 256 k. B RAM Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 17
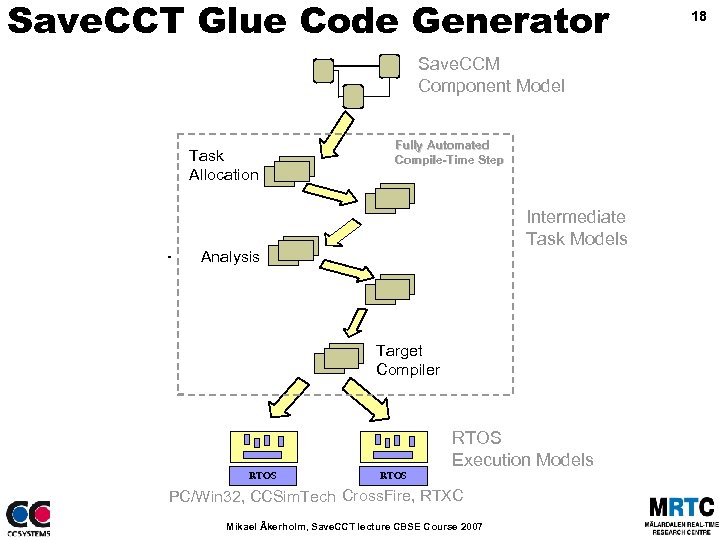 Save. CCT Glue Code Generator Save. CCM Component Model Task Allocation - Fully Automated Compile-Time Step Intermediate Task Models Analysis Target Compiler RTOS Execution Models RTOS PC/Win 32, CCSim. Tech Cross. Fire, RTXC Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 18
Save. CCT Glue Code Generator Save. CCM Component Model Task Allocation - Fully Automated Compile-Time Step Intermediate Task Models Analysis Target Compiler RTOS Execution Models RTOS PC/Win 32, CCSim. Tech Cross. Fire, RTXC Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 18
 Save. CCT Tools 19 (under continous improvement) Save IDE (under continous improvement) Component composition Several existing prototypes for graphical composition from masters thesis projects, currently under major revision Automated connectivity to analysis tools through translations of Save. CCM XML to timed automata with tasks ->Times (Timing and much more) Finite State Processes -> LTSA (Control loop liveness) Test Automated test tools, e, g. , test-complete and Lab. View, from CCSim. Tech Repository Under construction, will provide means for easy selection and specialisation of components through distingushing component versions, from component variants … Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
Save. CCT Tools 19 (under continous improvement) Save IDE (under continous improvement) Component composition Several existing prototypes for graphical composition from masters thesis projects, currently under major revision Automated connectivity to analysis tools through translations of Save. CCM XML to timed automata with tasks ->Times (Timing and much more) Finite State Processes -> LTSA (Control loop liveness) Test Automated test tools, e, g. , test-complete and Lab. View, from CCSim. Tech Repository Under construction, will provide means for easy selection and specialisation of components through distingushing component versions, from component variants … Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
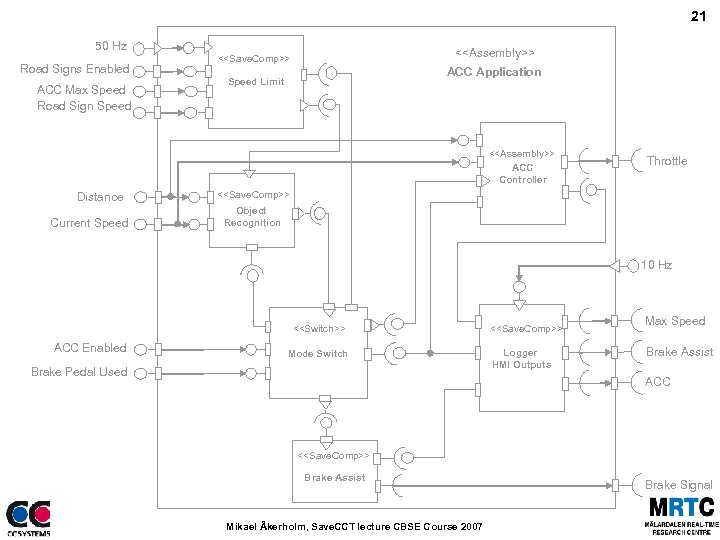
 Example Application 20 – Save. CCT in an industrial Environment Case Study at CC Systems Integrated our technology in a real industrial environment, i. e. , selected development tools and hardware from the company’s repertoire Cross. Fire ECU, CCSim. Tech simulation technique, target compiler Implemented a “fictive” vehicular control application with the technology, and used as basis for evaluation Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
Example Application 20 – Save. CCT in an industrial Environment Case Study at CC Systems Integrated our technology in a real industrial environment, i. e. , selected development tools and hardware from the company’s repertoire Cross. Fire ECU, CCSim. Tech simulation technique, target compiler Implemented a “fictive” vehicular control application with the technology, and used as basis for evaluation Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
 21 50 Hz Road Signs Enabled ACC Max Speed Road Sign Speed <
21 50 Hz Road Signs Enabled ACC Max Speed Road Sign Speed <
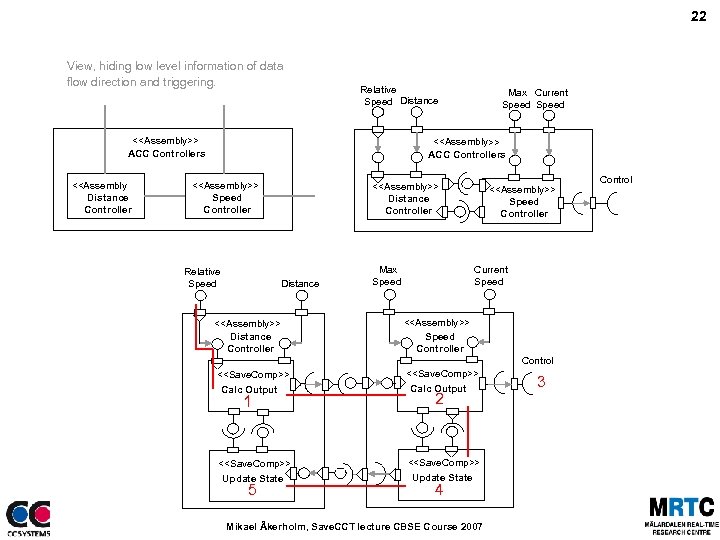 22 View, hiding low level information of data flow direction and triggering. Relative Speed Distance <
22 View, hiding low level information of data flow direction and triggering. Relative Speed Distance <
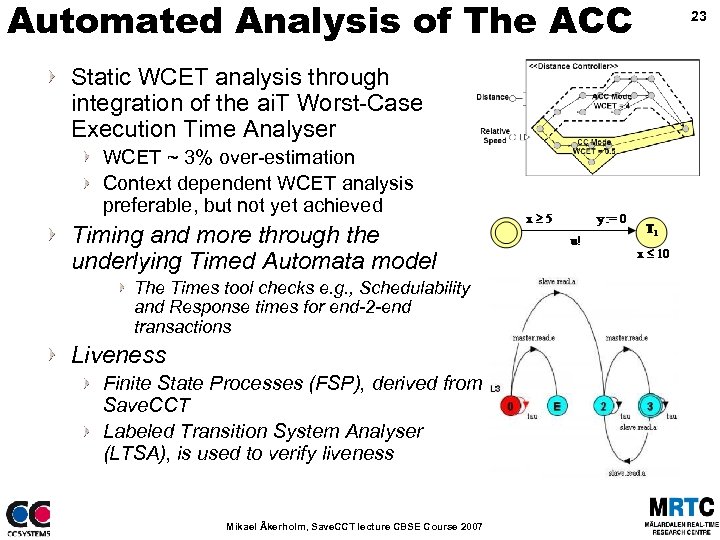 Automated Analysis of The ACC Static WCET analysis through integration of the ai. T Worst-Case Execution Time Analyser WCET ~ 3% over-estimation Context dependent WCET analysis preferable, but not yet achieved Timing and more through the underlying Timed Automata model The Times tool checks e. g. , Schedulability and Response times for end-2 -end transactions Liveness Finite State Processes (FSP), derived from Save. CCT Labeled Transition System Analyser (LTSA), is used to verify liveness Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 23
Automated Analysis of The ACC Static WCET analysis through integration of the ai. T Worst-Case Execution Time Analyser WCET ~ 3% over-estimation Context dependent WCET analysis preferable, but not yet achieved Timing and more through the underlying Timed Automata model The Times tool checks e. g. , Schedulability and Response times for end-2 -end transactions Liveness Finite State Processes (FSP), derived from Save. CCT Labeled Transition System Analyser (LTSA), is used to verify liveness Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007 23
 Questions 24 Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007
Questions 24 Mikael Åkerholm, Save. CCT lecture CBSE Course 2007


