b4cafa1e12654300bf5ebc1d8f4e5e7e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Stakeholders' Needs Definition Process Hervé Panetto, Professor University of Lorraine, TELECOM Nancy Research Centre for Automatic Control (CRAN UMR 7039 CNRS) Chair of IFAC CC 5 « Manufacturing and Logistics Systems » Herve. Panetto@univ-Lorraine. fr Based on slides from Alain Faisandier (MAP Systems)
SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Stakeholders' Needs Definition Process Hervé Panetto, Professor University of Lorraine, TELECOM Nancy Research Centre for Automatic Control (CRAN UMR 7039 CNRS) Chair of IFAC CC 5 « Manufacturing and Logistics Systems » Herve. Panetto@univ-Lorraine. fr Based on slides from Alain Faisandier (MAP Systems)
 Copyright This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution. Non. Commercial-Share. Alike 3. 0 available online at http: //creativecommons. org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3. 0/
Copyright This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution. Non. Commercial-Share. Alike 3. 0 available online at http: //creativecommons. org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3. 0/
 CONTENT 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS AND REQUIREMENTS 2 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 - CONCEPT OF NEED 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
CONTENT 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS AND REQUIREMENTS 2 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 - CONCEPT OF NEED 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
 STAKEHOLDERS' NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 2 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 - CONCEPT OF NEED 1 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 - APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
STAKEHOLDERS' NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 2 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 - CONCEPT OF NEED 1 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 - APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
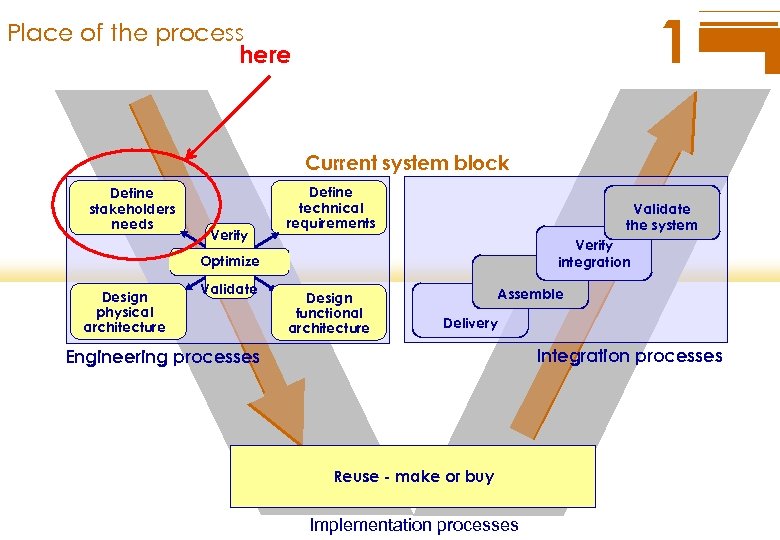 1 Place of the process here Current system block Define stakeholders needs Verify Define technical requirements Validate the system Verify integration Optimize Design physical architecture Validate Design functional architecture Assemble Delivery Integration processes Engineering processes Reuse - make or buy Implementation processes
1 Place of the process here Current system block Define stakeholders needs Verify Define technical requirements Validate the system Verify integration Optimize Design physical architecture Validate Design functional architecture Assemble Delivery Integration processes Engineering processes Reuse - make or buy Implementation processes
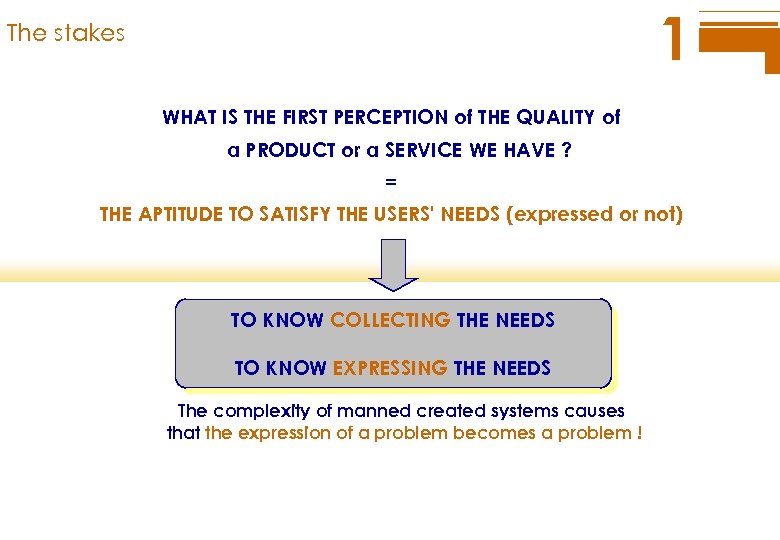 1 The stakes WHAT IS THE FIRST PERCEPTION of THE QUALITY of a PRODUCT or a SERVICE WE HAVE ? = THE APTITUDE TO SATISFY THE USERS' NEEDS (expressed or not) TO KNOW COLLECTING THE NEEDS TO KNOW EXPRESSING THE NEEDS The complexity of manned created systems causes that the expression of a problem becomes a problem !
1 The stakes WHAT IS THE FIRST PERCEPTION of THE QUALITY of a PRODUCT or a SERVICE WE HAVE ? = THE APTITUDE TO SATISFY THE USERS' NEEDS (expressed or not) TO KNOW COLLECTING THE NEEDS TO KNOW EXPRESSING THE NEEDS The complexity of manned created systems causes that the expression of a problem becomes a problem !
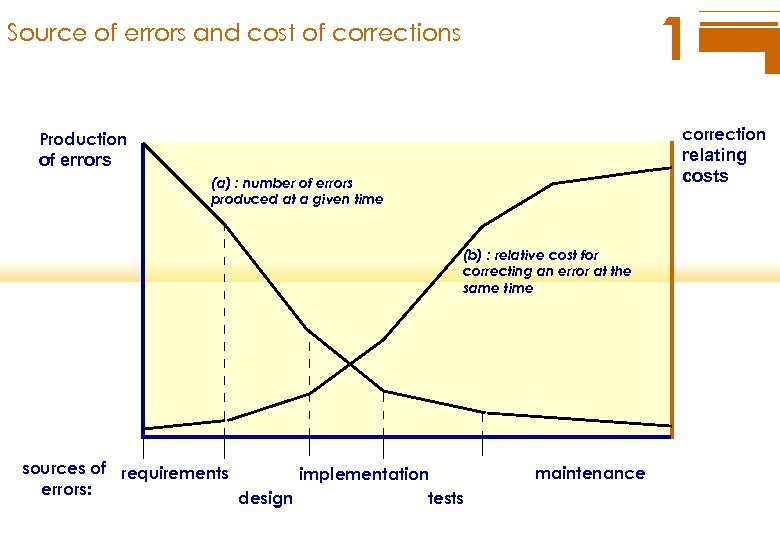 1 Source of errors and cost of corrections correction Production relating costs of errors (a) : number of errors produced at a given time (b) : relative cost for correcting an error at the same time sources of requirements errors: implementation design tests maintenance
1 Source of errors and cost of corrections correction Production relating costs of errors (a) : number of errors produced at a given time (b) : relative cost for correcting an error at the same time sources of requirements errors: implementation design tests maintenance
 Main difficulties encountered 1 How to correctly express the needs ? How to make them understood ? Most of the time, the needs are not satisfied because Ø needs are not clearly identified, limited and expressed Ø "WRONG" comprehension of the relation between customer and supplier Ø no clear separation between the problem and the solution (what ? / how ? ) Ø communication difficulties (tool for dialogue) between the stakeholders Ø the negative perception of a problem to be solved I have an answer, is there anybody with a question ? Woody ALLEN
Main difficulties encountered 1 How to correctly express the needs ? How to make them understood ? Most of the time, the needs are not satisfied because Ø needs are not clearly identified, limited and expressed Ø "WRONG" comprehension of the relation between customer and supplier Ø no clear separation between the problem and the solution (what ? / how ? ) Ø communication difficulties (tool for dialogue) between the stakeholders Ø the negative perception of a problem to be solved I have an answer, is there anybody with a question ? Woody ALLEN
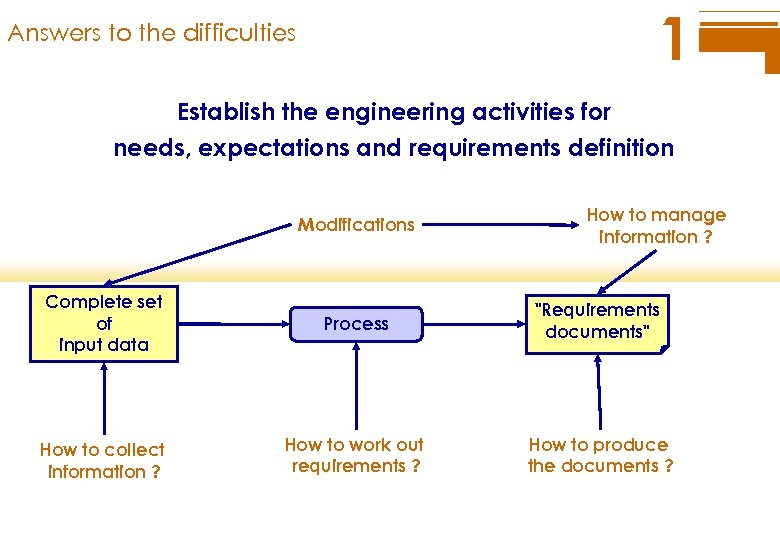 1 Answers to the difficulties Establish the engineering activities for needs, expectations and requirements definition Modifications How to manage information ? Complete set of input data Process "Requirements documents" How to collect information ? How to work out requirements ? How to produce the documents ?
1 Answers to the difficulties Establish the engineering activities for needs, expectations and requirements definition Modifications How to manage information ? Complete set of input data Process "Requirements documents" How to collect information ? How to work out requirements ? How to produce the documents ?
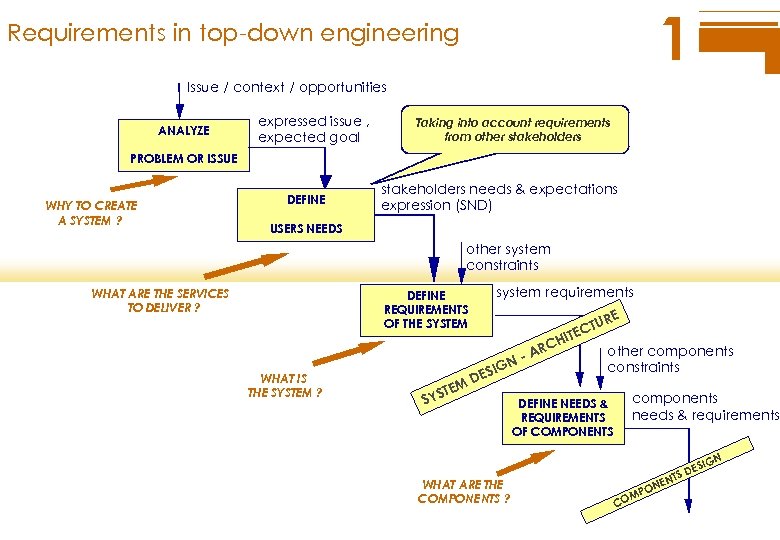 1 Requirements in top-down engineering Issue / context / opportunities ANALYZE expressed issue , expected goal Taking into account requirements from other stakeholders PROBLEM OR ISSUE WHY TO CREATE A SYSTEM ? DEFINE stakeholders needs & expectations expression (SND) USERS NEEDS other system constraints WHAT ARE THE SERVICES TO DELIVER ? system requirements DEFINE REQUIREMENTS OF THE SYSTEM RE CH TU ITEC WHAT IS THE SYSTEM ? IGN ES SYS D EM T R -A other components constraints components needs & requirements DEFINE NEEDS & REQUIREMENTS OF COMPONENTS IGN WHAT ARE THE COMPONENTS ? N NE CO O MP ES TS D
1 Requirements in top-down engineering Issue / context / opportunities ANALYZE expressed issue , expected goal Taking into account requirements from other stakeholders PROBLEM OR ISSUE WHY TO CREATE A SYSTEM ? DEFINE stakeholders needs & expectations expression (SND) USERS NEEDS other system constraints WHAT ARE THE SERVICES TO DELIVER ? system requirements DEFINE REQUIREMENTS OF THE SYSTEM RE CH TU ITEC WHAT IS THE SYSTEM ? IGN ES SYS D EM T R -A other components constraints components needs & requirements DEFINE NEEDS & REQUIREMENTS OF COMPONENTS IGN WHAT ARE THE COMPONENTS ? N NE CO O MP ES TS D
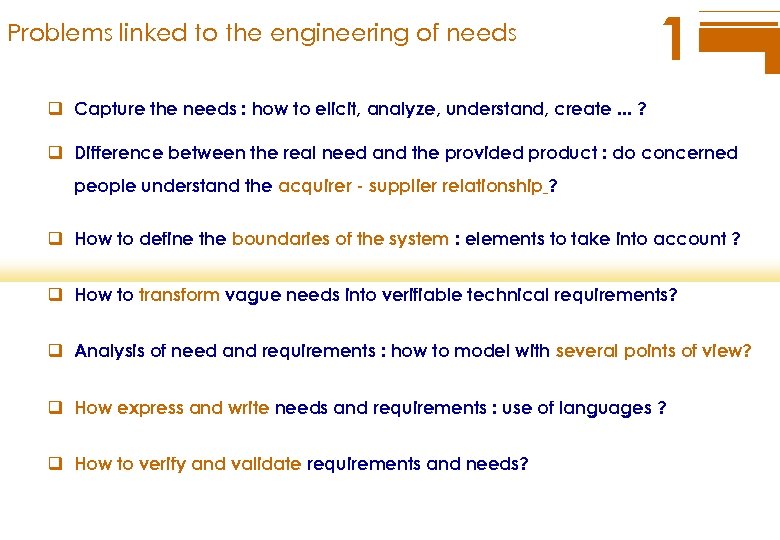 Problems linked to the engineering of needs 1 q Capture the needs : how to elicit, analyze, understand, create. . . ? q Difference between the real need and the provided product : do concerned people understand the acquirer - supplier relationship ? q How to define the boundaries of the system : elements to take into account ? q How to transform vague needs into verifiable technical requirements? q Analysis of need and requirements : how to model with several points of view? q How express and write needs and requirements : use of languages ? q How to verify and validate requirements and needs?
Problems linked to the engineering of needs 1 q Capture the needs : how to elicit, analyze, understand, create. . . ? q Difference between the real need and the provided product : do concerned people understand the acquirer - supplier relationship ? q How to define the boundaries of the system : elements to take into account ? q How to transform vague needs into verifiable technical requirements? q Analysis of need and requirements : how to model with several points of view? q How express and write needs and requirements : use of languages ? q How to verify and validate requirements and needs?
 STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 3 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 – CONCEPT OF NEED 2 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLEV MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 3 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 – CONCEPT OF NEED 2 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLEV MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
 Definitions (1) 2 Need (expectation – stakeholder requirement – user requirement Necessity or desire expected by a "end user". ¦ Expressed in terms of a client, and end user ¦ Service, objective, capability expected from the future system by the end users Requirement (technical requirement – system requirement) Clarified expression of a need presented in a formal language (computable, graphic, mathematic, …) or natural. A requirement must be implementable and verifiable. ¦ Translation of needs in terms that can be understood by a designer to develop a solution Product What is or will be provided to an "end user" to meet his needs / expectations. A product is the result of the execution of a process. (ISO 9000 : 2000)
Definitions (1) 2 Need (expectation – stakeholder requirement – user requirement Necessity or desire expected by a "end user". ¦ Expressed in terms of a client, and end user ¦ Service, objective, capability expected from the future system by the end users Requirement (technical requirement – system requirement) Clarified expression of a need presented in a formal language (computable, graphic, mathematic, …) or natural. A requirement must be implementable and verifiable. ¦ Translation of needs in terms that can be understood by a designer to develop a solution Product What is or will be provided to an "end user" to meet his needs / expectations. A product is the result of the execution of a process. (ISO 9000 : 2000)
 Definitions (1 bis) Diapo 2 Stakeholders Needs Document – SND (User Requirements Document URD) Document by which the acquirer expresses the needs / expectations (or the person in charge to express) in terms of services and constraints (interfaces with the environment & constraints on the solution). This work implies that studies determine with precision the needs of the end users. Technical Requirements Document - TRD Contractual document between acquirer and supplier, written by the acquirer or the supplier of a product and by whom applicable technical requirements are expressed. Expression of : - expectations of the product in term of functions, performances, interfaces, - constraints of use, environment and support (logistics, maintenance), - constraints for the design, manufacturing and validation of the product …
Definitions (1 bis) Diapo 2 Stakeholders Needs Document – SND (User Requirements Document URD) Document by which the acquirer expresses the needs / expectations (or the person in charge to express) in terms of services and constraints (interfaces with the environment & constraints on the solution). This work implies that studies determine with precision the needs of the end users. Technical Requirements Document - TRD Contractual document between acquirer and supplier, written by the acquirer or the supplier of a product and by whom applicable technical requirements are expressed. Expression of : - expectations of the product in term of functions, performances, interfaces, - constraints of use, environment and support (logistics, maintenance), - constraints for the design, manufacturing and validation of the product …
 Definitions (2) Stakeholder 2 Party having a right, share or claim in a system or in its possession of characteristics that meets that party's needs and expectations (ISO 15288 : 2008) Acquirer the stakeholder that acquires or procures a product or a service from a supplier (ISO 15288 : 2008) Supplier an organization or an individual that enters into an agreement with the acquirer for the supply of a product or a service (ISO 15288 : 2008) User Individual who or group that benefits from a system during its utilization 15288 : 2008) (ISO
Definitions (2) Stakeholder 2 Party having a right, share or claim in a system or in its possession of characteristics that meets that party's needs and expectations (ISO 15288 : 2008) Acquirer the stakeholder that acquires or procures a product or a service from a supplier (ISO 15288 : 2008) Supplier an organization or an individual that enters into an agreement with the acquirer for the supply of a product or a service (ISO 15288 : 2008) User Individual who or group that benefits from a system during its utilization 15288 : 2008) (ISO
 STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 2 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 - CONCEPT OF NEED 3 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 2 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 - CONCEPT OF NEED 3 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
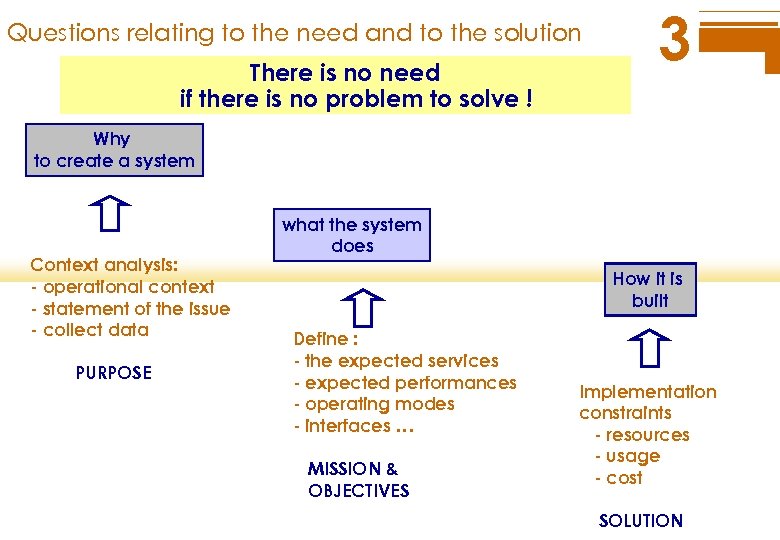 Questions relating to the need and to the solution There is no need if there is no problem to solve ! 3 Why to create a system Context analysis: - operational context - statement of the issue - collect data PURPOSE what the system does How it is built Define : - the expected services - expected performances - operating modes - interfaces … MISSION & OBJECTIVES Implementation constraints - resources - usage - cost SOLUTION
Questions relating to the need and to the solution There is no need if there is no problem to solve ! 3 Why to create a system Context analysis: - operational context - statement of the issue - collect data PURPOSE what the system does How it is built Define : - the expected services - expected performances - operating modes - interfaces … MISSION & OBJECTIVES Implementation constraints - resources - usage - cost SOLUTION
 What is a need ? 3 q A need comes from a lack, a dissatisfaction, a new expectation : it appears, there is emergence. q The response to a need is an action (service) or a set of actions provided by a system, a product. ¦ This system provides services to somebody or something while acting on somebody or something. q The need is valid when we can answer the questions : ¦ Why this need appears ? ¦ What are the possible causes and the risks of its disappearance ?
What is a need ? 3 q A need comes from a lack, a dissatisfaction, a new expectation : it appears, there is emergence. q The response to a need is an action (service) or a set of actions provided by a system, a product. ¦ This system provides services to somebody or something while acting on somebody or something. q The need is valid when we can answer the questions : ¦ Why this need appears ? ¦ What are the possible causes and the risks of its disappearance ?
 What are the needs for ? Get a common understanding of a problem to solve q. For the acquirer: ¦ Clearly define its needs and expectations ¦ To be understood by the supplier q. For the supplier : ¦ Understand clearly what he has to do and why ¦ To be understood by the acquirer q. For the enterprises and organizations partners : ¦ Align projects onto the strategies ¦ Accumulate on skills and projects ¦ Decrease the risk of total or partial setback 3
What are the needs for ? Get a common understanding of a problem to solve q. For the acquirer: ¦ Clearly define its needs and expectations ¦ To be understood by the supplier q. For the supplier : ¦ Understand clearly what he has to do and why ¦ To be understood by the acquirer q. For the enterprises and organizations partners : ¦ Align projects onto the strategies ¦ Accumulate on skills and projects ¦ Decrease the risk of total or partial setback 3
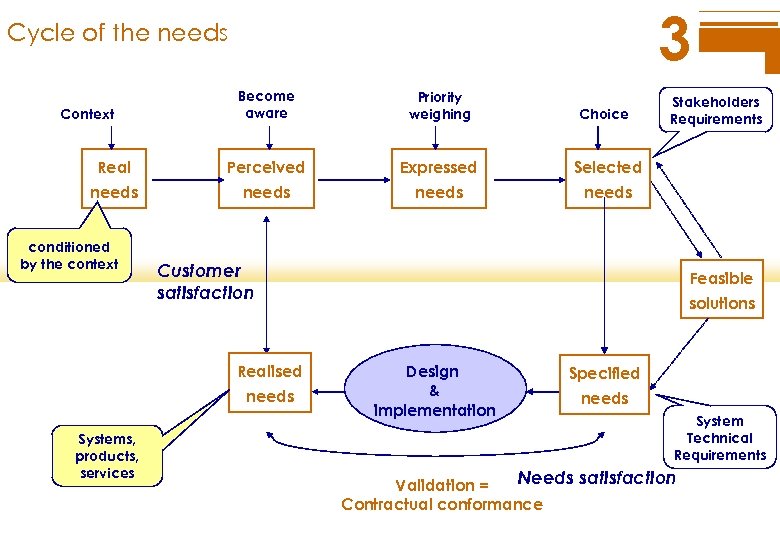 3 Cycle of the needs Become aware Priority weighing Choice Real Perceived Expressed Selected needs Context conditioned by the context Customer satisfaction Realised needs Systems, products, services Stakeholders Requirements Feasible solutions Design & implementation Specified needs System Technical Requirements Needs satisfaction Validation = Contractual conformance
3 Cycle of the needs Become aware Priority weighing Choice Real Perceived Expressed Selected needs Context conditioned by the context Customer satisfaction Realised needs Systems, products, services Stakeholders Requirements Feasible solutions Design & implementation Specified needs System Technical Requirements Needs satisfaction Validation = Contractual conformance
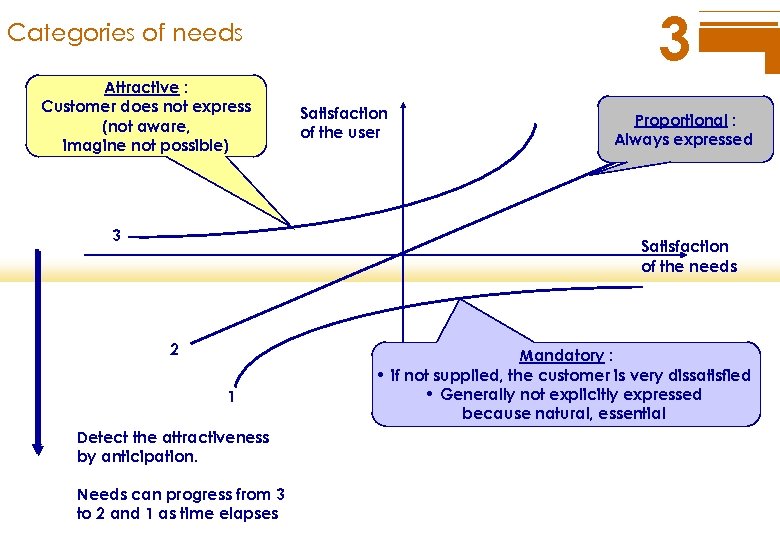 3 Categories of needs Attractive : Customer does not express (not aware, imagine not possible) 3 Satisfaction of the user Proportional : Always expressed Satisfaction of the needs 2 1 Detect the attractiveness by anticipation. Needs can progress from 3 to 2 and 1 as time elapses Mandatory : • if not supplied, the customer is very dissatisfied • Generally not explicitly expressed because natural, essential
3 Categories of needs Attractive : Customer does not express (not aware, imagine not possible) 3 Satisfaction of the user Proportional : Always expressed Satisfaction of the needs 2 1 Detect the attractiveness by anticipation. Needs can progress from 3 to 2 and 1 as time elapses Mandatory : • if not supplied, the customer is very dissatisfied • Generally not explicitly expressed because natural, essential
 Principles of needs elicitation 3 In order to provide a better "satisfaction of the end users", apply the following principles during the identification of needs : q Structure the listening of users : organize interviews, q Collect "facts" other than any opinion or interpretation from the collector, q Formulate potential solutions starting from the facts ; validate systematically those potential solutions with the users, q Focus on essential (details are not lost but deduced), q Work in group (search for consensus and creativity of group), q Determine the right level of abstraction (20 to 30 global needs).
Principles of needs elicitation 3 In order to provide a better "satisfaction of the end users", apply the following principles during the identification of needs : q Structure the listening of users : organize interviews, q Collect "facts" other than any opinion or interpretation from the collector, q Formulate potential solutions starting from the facts ; validate systematically those potential solutions with the users, q Focus on essential (details are not lost but deduced), q Work in group (search for consensus and creativity of group), q Determine the right level of abstraction (20 to 30 global needs).
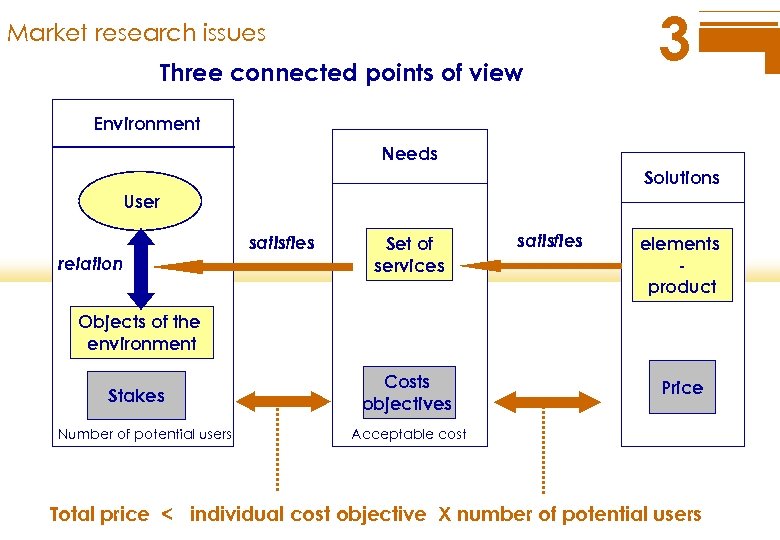 Market research issues Three connected points of view 3 Environment Needs Solutions User relation satisfies Set of services satisfies elements product Objects of the environment Stakes Number of potential users Costs objectives Price Acceptable cost Total price < individual cost objective X number of potential users
Market research issues Three connected points of view 3 Environment Needs Solutions User relation satisfies Set of services satisfies elements product Objects of the environment Stakes Number of potential users Costs objectives Price Acceptable cost Total price < individual cost objective X number of potential users
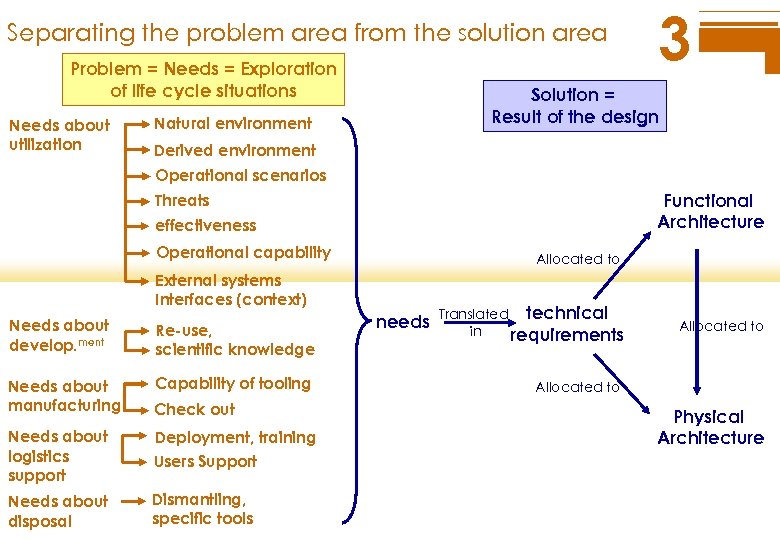 Separating the problem area from the solution area Problem = Needs = Exploration of life cycle situations Needs about utilization 3 Solution = Result of the design Natural environment Derived environment Operational scenarios Functional Architecture Threats effectiveness Operational capability Allocated to External systems Interfaces (context) Needs about develop. ment Re-use, scientific knowledge Needs about manufacturing Capability of tooling Check out Needs about logistics support Users Support Needs about disposal Dismantling, specific tools Deployment, training needs Translated technical in requirements Allocated to Physical Architecture
Separating the problem area from the solution area Problem = Needs = Exploration of life cycle situations Needs about utilization 3 Solution = Result of the design Natural environment Derived environment Operational scenarios Functional Architecture Threats effectiveness Operational capability Allocated to External systems Interfaces (context) Needs about develop. ment Re-use, scientific knowledge Needs about manufacturing Capability of tooling Check out Needs about logistics support Users Support Needs about disposal Dismantling, specific tools Deployment, training needs Translated technical in requirements Allocated to Physical Architecture
 Practicing the needs definition Exercise : Mission – Purpose – Objectives Stages 3
Practicing the needs definition Exercise : Mission – Purpose – Objectives Stages 3
 STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 2 - DEFINITIONS 3 – CONCEPT OF NEED 4 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 2 - DEFINITIONS 3 – CONCEPT OF NEED 4 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
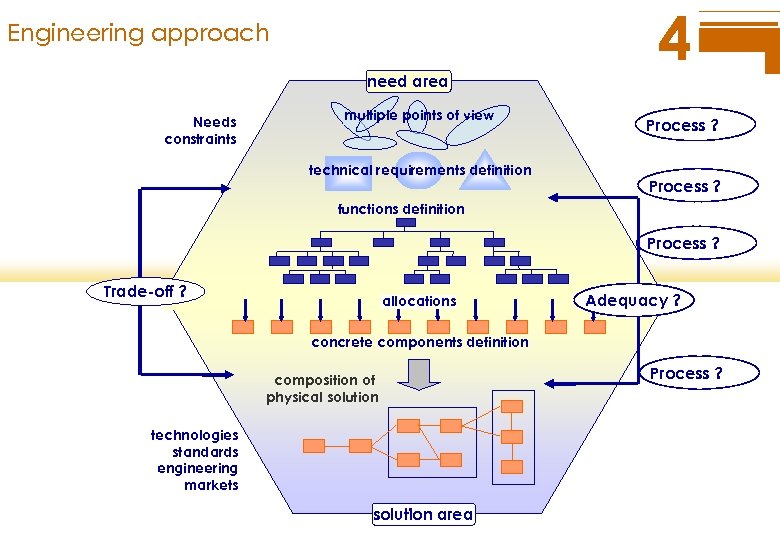 Engineering approach need area Needs constraints multiple points of view technical requirements definition 4 Process ? functions definition Process ? Trade-off ? allocations Adequacy ? concrete components definition composition of physical solution technologies standards engineering markets solution area Process ?
Engineering approach need area Needs constraints multiple points of view technical requirements definition 4 Process ? functions definition Process ? Trade-off ? allocations Adequacy ? concrete components definition composition of physical solution technologies standards engineering markets solution area Process ?
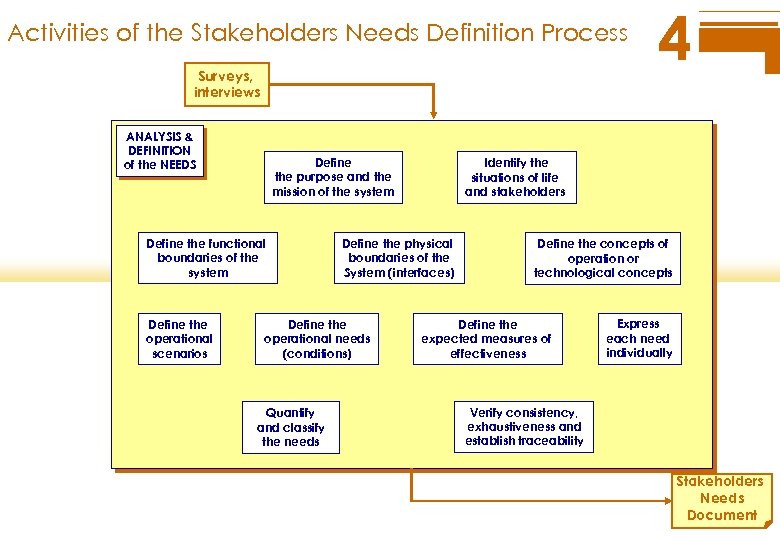 Activities of the Stakeholders Needs Definition Process Surveys, interviews ANALYSIS & DEFINITION of the NEEDS Define the purpose and the mission of the system Define the functional boundaries of the system Define the operational scenarios Quantify and classify the needs Identify the situations of life and stakeholders Define the physical boundaries of the System (interfaces) Define the operational needs (conditions) 4 Define the concepts of operation or technological concepts Define the expected measures of effectiveness Express each need individually Verify consistency, exhaustiveness and establish traceability Stakeholders Needs Document
Activities of the Stakeholders Needs Definition Process Surveys, interviews ANALYSIS & DEFINITION of the NEEDS Define the purpose and the mission of the system Define the functional boundaries of the system Define the operational scenarios Quantify and classify the needs Identify the situations of life and stakeholders Define the physical boundaries of the System (interfaces) Define the operational needs (conditions) 4 Define the concepts of operation or technological concepts Define the expected measures of effectiveness Express each need individually Verify consistency, exhaustiveness and establish traceability Stakeholders Needs Document
 The process activities in detail (1) 4 Expected results of the process ¦ set of expectations, desires, requirements representing the needs of the customers, users, ¦ contexts of use of the users (capacities, environment of work) ¦ a basis to establish the technical requirements of the system, ¦ a basis to establish the operational acceptance of the supplied products and services. Activities 1) Identify the stakeholders, in every situation of the system life 2) Identify and clarify the object and the context of use of the system 3) Establish the concepts of operation of the system, or technological concepts supported by the system 4) Identify the operational needs. . .
The process activities in detail (1) 4 Expected results of the process ¦ set of expectations, desires, requirements representing the needs of the customers, users, ¦ contexts of use of the users (capacities, environment of work) ¦ a basis to establish the technical requirements of the system, ¦ a basis to establish the operational acceptance of the supplied products and services. Activities 1) Identify the stakeholders, in every situation of the system life 2) Identify and clarify the object and the context of use of the system 3) Establish the concepts of operation of the system, or technological concepts supported by the system 4) Identify the operational needs. . .
 The process activities in detail (2) 4 5) Identify the constraints imposed on the system by the various stakeholders 6) Quantify the needs (and the constraints) 7) Classify the needs (and the constraints) 8) Identify and solve the conflicts between the needs 9) Establish the traceability, upstream and downstream, make sure that the whole of identified needs meet the real need (Validation process), 10) Write the Stakeholders Needs Document.
The process activities in detail (2) 4 5) Identify the constraints imposed on the system by the various stakeholders 6) Quantify the needs (and the constraints) 7) Classify the needs (and the constraints) 8) Identify and solve the conflicts between the needs 9) Establish the traceability, upstream and downstream, make sure that the whole of identified needs meet the real need (Validation process), 10) Write the Stakeholders Needs Document.
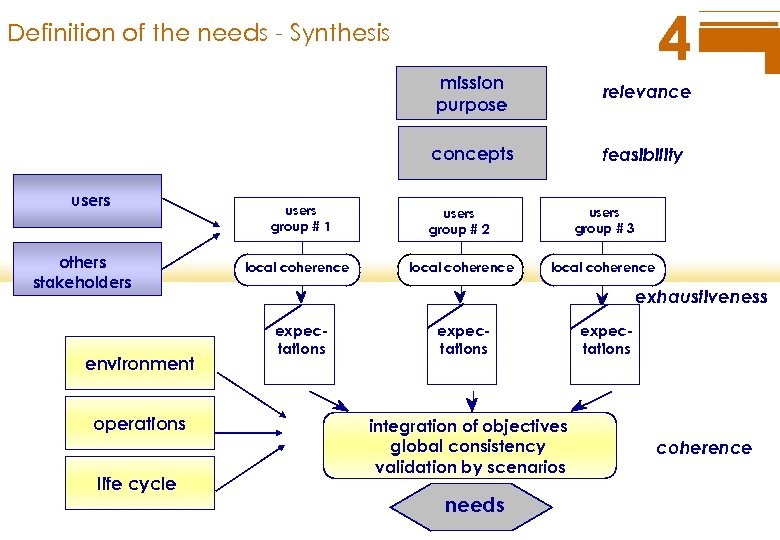 4 Definition of the needs - Synthesis mission purpose concepts users others stakeholders environment operations life cycle users group # 1 local coherence relevance feasibility users group # 2 users group # 3 local coherence exhaustiveness expectations integration of objectives global consistency validation by scenarios needs expectations coherence
4 Definition of the needs - Synthesis mission purpose concepts users others stakeholders environment operations life cycle users group # 1 local coherence relevance feasibility users group # 2 users group # 3 local coherence exhaustiveness expectations integration of objectives global consistency validation by scenarios needs expectations coherence
 STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 2 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 - CONCEPTS OF NEED 5 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 2 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 - CONCEPTS OF NEED 5 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
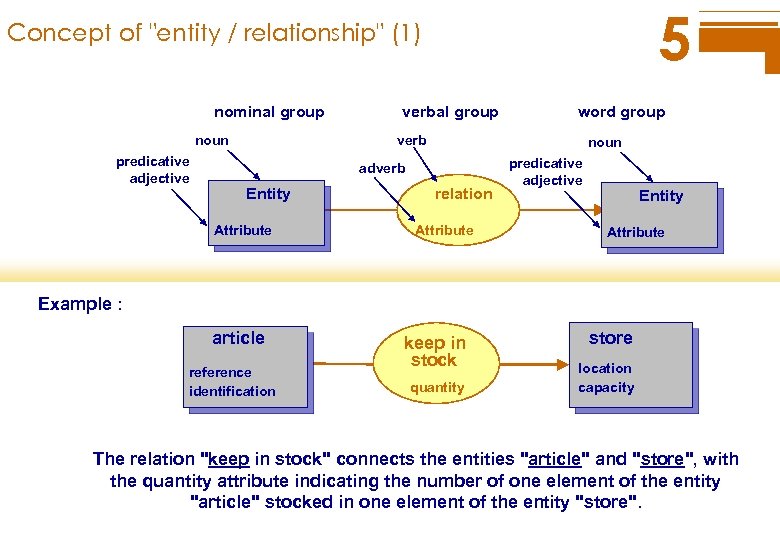 5 Concept of "entity / relationship" (1) nominal group noun predicative adjective verbal group word group verb noun adverb Entity Attribute relation Attribute predicative adjective Entity Attribute Example : article reference identification keep in stock quantity store location capacity The relation "keep in stock" connects the entities "article" and "store", with the quantity attribute indicating the number of one element of the entity "article" stocked in one element of the entity "store".
5 Concept of "entity / relationship" (1) nominal group noun predicative adjective verbal group word group verb noun adverb Entity Attribute relation Attribute predicative adjective Entity Attribute Example : article reference identification keep in stock quantity store location capacity The relation "keep in stock" connects the entities "article" and "store", with the quantity attribute indicating the number of one element of the entity "article" stocked in one element of the entity "store".
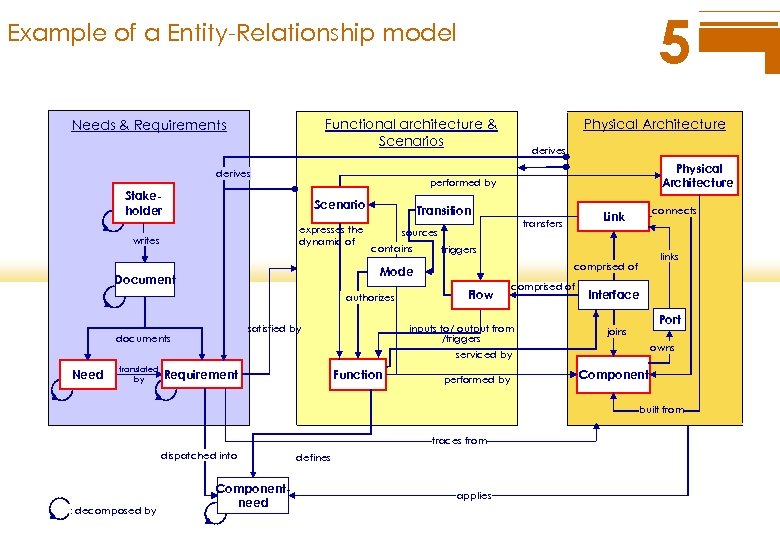 5 Example of a Entity-Relationship model Physical Architecture Functional architecture & Scenarios Needs & Requirements derives Physical Architecture performed by Stakeholder Scenario writes expresses the dynamic of Transition sources contains triggers authorizes documents Flow comprised of inputs to/ output from /triggers satisfied by links comprised of Mode Document connects Link transfers Interface Port joins owns serviced by Need translated by Requirement Function performed by Component built from traces from dispatched into : decomposed by Componentneed defines applies
5 Example of a Entity-Relationship model Physical Architecture Functional architecture & Scenarios Needs & Requirements derives Physical Architecture performed by Stakeholder Scenario writes expresses the dynamic of Transition sources contains triggers authorizes documents Flow comprised of inputs to/ output from /triggers satisfied by links comprised of Mode Document connects Link transfers Interface Port joins owns serviced by Need translated by Requirement Function performed by Component built from traces from dispatched into : decomposed by Componentneed defines applies
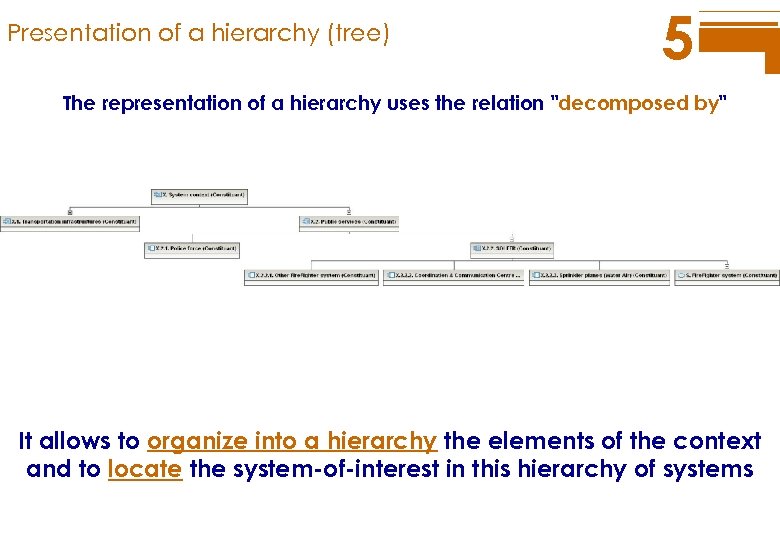 Presentation of a hierarchy (tree) 5 The representation of a hierarchy uses the relation "decomposed by" It allows to organize into a hierarchy the elements of the context and to locate the system-of-interest in this hierarchy of systems
Presentation of a hierarchy (tree) 5 The representation of a hierarchy uses the relation "decomposed by" It allows to organize into a hierarchy the elements of the context and to locate the system-of-interest in this hierarchy of systems
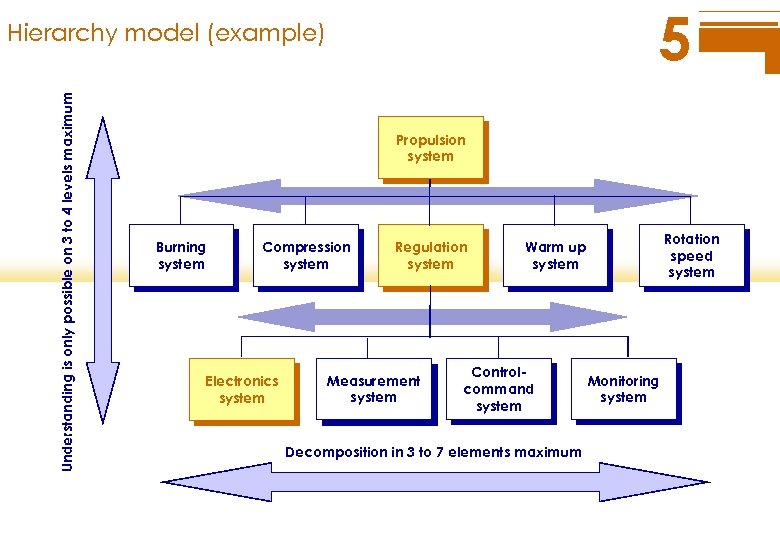 5 Understanding is only possible on 3 to 4 levels maximum Hierarchy model (example) Propulsion system Burning system Compression system Electronics system Regulation system Measurement system Rotation speed system Warm up system Controlcommand system Decomposition in 3 to 7 elements maximum Monitoring system
5 Understanding is only possible on 3 to 4 levels maximum Hierarchy model (example) Propulsion system Burning system Compression system Electronics system Regulation system Measurement system Rotation speed system Warm up system Controlcommand system Decomposition in 3 to 7 elements maximum Monitoring system
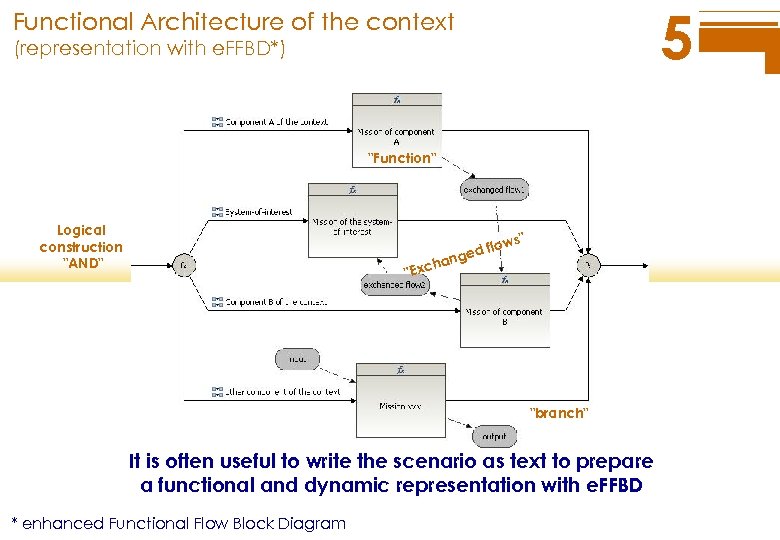 5 Functional Architecture of the context (representation with e. FFBD*) "Function" Logical construction "AND" s" low ed f ang h "Exc "branch" It is often useful to write the scenario as text to prepare a functional and dynamic representation with e. FFBD * enhanced Functional Flow Block Diagram
5 Functional Architecture of the context (representation with e. FFBD*) "Function" Logical construction "AND" s" low ed f ang h "Exc "branch" It is often useful to write the scenario as text to prepare a functional and dynamic representation with e. FFBD * enhanced Functional Flow Block Diagram
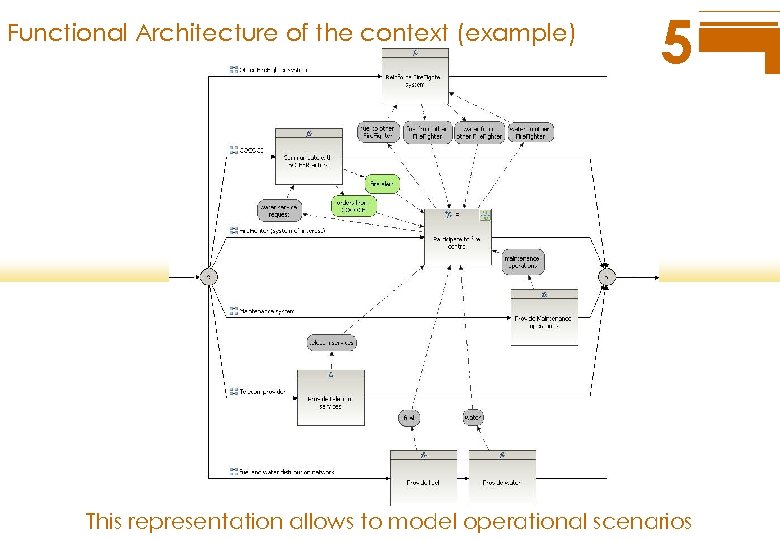 Functional Architecture of the context (example) 5 This representation allows to model operational scenarios
Functional Architecture of the context (example) 5 This representation allows to model operational scenarios
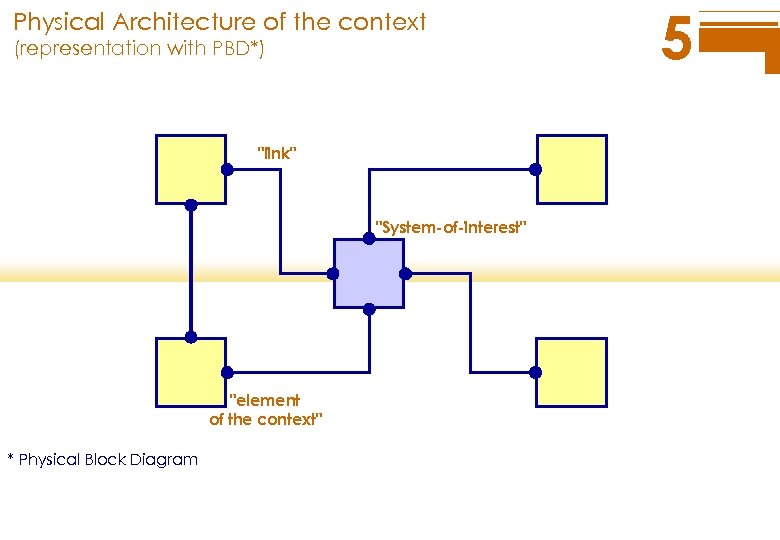 Physical Architecture of the context (representation with PBD*) "link" "System-of-interest" "element of the context" * Physical Block Diagram 5
Physical Architecture of the context (representation with PBD*) "link" "System-of-interest" "element of the context" * Physical Block Diagram 5
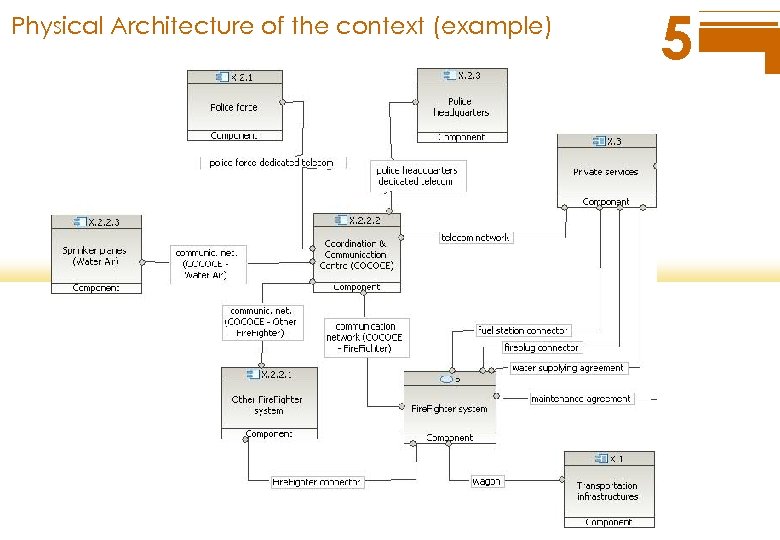 Physical Architecture of the context (example) 5
Physical Architecture of the context (example) 5
 Practicing the needs definition Exercise : Characterisation of the context (environment of the system) 5
Practicing the needs definition Exercise : Characterisation of the context (environment of the system) 5
 STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 2 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 – CONCEPT OF NEED 6 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 2 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 – CONCEPT OF NEED 6 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
 Classification of needs 6 Summarize : q Expected services : sets of actions to perform the mission of the system q Expected effectiveness : effectiveness attached to the expected services q Operational modes : the various states of the system during its utilization q Operational scenarios : make explicit the dynamic interactions with the components of the context, the sequence of the actions to provide the expected services q Interfaces or interactions : flows (inputs, outputs of matter, energy, information) exchanged with the components of the context q Physical connections : from the system toward the components of the context q Human factors : human characteristics to take into account in systems including operator roles q Dependability : essentially availability, safety, survivability, and reliability, maintenability only if relevant at this level q Security (of information) : availability, integrity and confidentiality of information q Operational environment : external conditions submitted by the system when in operation q Means : quantified elements needed by the system to perform its services (consumed inputs, energy and external means) ; elements produced by the system (produced outputs) q Transport, storage : characteristics of transportation means, of storage means for the components q Constraints : limitations generated by the enabling systems (production, deployment, support/maintenance, etc. ), physical dimensions, extensions, policies, etc.
Classification of needs 6 Summarize : q Expected services : sets of actions to perform the mission of the system q Expected effectiveness : effectiveness attached to the expected services q Operational modes : the various states of the system during its utilization q Operational scenarios : make explicit the dynamic interactions with the components of the context, the sequence of the actions to provide the expected services q Interfaces or interactions : flows (inputs, outputs of matter, energy, information) exchanged with the components of the context q Physical connections : from the system toward the components of the context q Human factors : human characteristics to take into account in systems including operator roles q Dependability : essentially availability, safety, survivability, and reliability, maintenability only if relevant at this level q Security (of information) : availability, integrity and confidentiality of information q Operational environment : external conditions submitted by the system when in operation q Means : quantified elements needed by the system to perform its services (consumed inputs, energy and external means) ; elements produced by the system (produced outputs) q Transport, storage : characteristics of transportation means, of storage means for the components q Constraints : limitations generated by the enabling systems (production, deployment, support/maintenance, etc. ), physical dimensions, extensions, policies, etc.
 6 Stakeholders Needs Document template (1) 1. Introduction (Object, Reference and applicable documents, terminology) 2. Presentation of the system q Purpose, Mission and Objectives of the system q Context of the system (physical and functional structure) q List of the Stakeholders 3. Stakeholders needs q Operational modes (nominal, degraded) and operational scenarios q Operational needs: o Expected services o Expected measures of effectiveness, autonomy, duration of life o Interactions / interfaces ans physical connections with the elements of the context o Human factors and ergonomics o Dependability (availability, safety, survivability) o Information security (availability, integrity, confidentiality) o Operational environment o Means (inputs consumed and used, outputs produced) o Transportation, storage 1/2
6 Stakeholders Needs Document template (1) 1. Introduction (Object, Reference and applicable documents, terminology) 2. Presentation of the system q Purpose, Mission and Objectives of the system q Context of the system (physical and functional structure) q List of the Stakeholders 3. Stakeholders needs q Operational modes (nominal, degraded) and operational scenarios q Operational needs: o Expected services o Expected measures of effectiveness, autonomy, duration of life o Interactions / interfaces ans physical connections with the elements of the context o Human factors and ergonomics o Dependability (availability, safety, survivability) o Information security (availability, integrity, confidentiality) o Operational environment o Means (inputs consumed and used, outputs produced) o Transportation, storage 1/2
 Stakeholders Needs Document template (2) 6 q Constraints of enabling systems or services o Implementation (and design) constraints o Transfer for use constraints o Disposal constraints o Logistics support and maintenance constraints o Production and Manufacturing constraints o Legislation constraints o Validation constraints q Constraints of costs, of delivery on the product 2/2
Stakeholders Needs Document template (2) 6 q Constraints of enabling systems or services o Implementation (and design) constraints o Transfer for use constraints o Disposal constraints o Logistics support and maintenance constraints o Production and Manufacturing constraints o Legislation constraints o Validation constraints q Constraints of costs, of delivery on the product 2/2
 STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 2 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 – CONCEPT OF NEED 7 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 1 - INTRODUCTION TO STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS 2 – SOME DEFINITIONS 3 – CONCEPT OF NEED 7 4 - DESCRIPTION OF THE STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DEFINITION PROCESS 5 – APPLICABLE MODELLING TECHNIQUES 6 - TEMPLATE OF A STAKEHOLDERS NEEDS DOCUMENT 7 - SUPPLEMENTS
 Verification and validation of the needs Verification of the characteristics of the needs : 7 Maturity = Is not the expression of the need too far from the perceived needs, from the expectations of the stakeholders ? Exhaustivity = Are all the stakeholders' needs expressed, including the malevolent? Accuracy = Do the stakeholders acknowledge an accurate expression of their needs? Feasible = Might concepts of operation be identified to assess the feasibility to solve the submitted problem? Translatable = Does the expression of the need allow to translate the need into technical requirements? Consistency = Does any conflict exist between the various expressed needs? Relevance = Does the expression of the needs allow to define the relevance of a solution to the submitted problem? Validation of the needs : Why these needs exist? (Justification) Which risks could make the needs disappeared? Which cause(s)?
Verification and validation of the needs Verification of the characteristics of the needs : 7 Maturity = Is not the expression of the need too far from the perceived needs, from the expectations of the stakeholders ? Exhaustivity = Are all the stakeholders' needs expressed, including the malevolent? Accuracy = Do the stakeholders acknowledge an accurate expression of their needs? Feasible = Might concepts of operation be identified to assess the feasibility to solve the submitted problem? Translatable = Does the expression of the need allow to translate the need into technical requirements? Consistency = Does any conflict exist between the various expressed needs? Relevance = Does the expression of the needs allow to define the relevance of a solution to the submitted problem? Validation of the needs : Why these needs exist? (Justification) Which risks could make the needs disappeared? Which cause(s)?
 Major risks that could be identified when defining the needs 7 q To take the wrong system : ¦ Level of abstraction too high (upper-system) or too low (sub system) Ä Stop the development and come back to the right level q Perimeter not well targeted : ¦ elements added or forgotten in the system (ex : roles of operators), Ä Unsuitable product or product rejected by the users ¦ interfaces forgotten (exchanges of matter, energy, information), ¦ physical connections forgotten (technological constraints) Ä not interoperable product q Lack or insufficiency of operational modes and scenarios Ä conflicting validation, backward transfer for use, backward development q Forgotten needs, forgotten stakeholders Ä backward development, conflicting validation q Wrong classification of the needs Ä Lost of time for the supplier, increasing development costs
Major risks that could be identified when defining the needs 7 q To take the wrong system : ¦ Level of abstraction too high (upper-system) or too low (sub system) Ä Stop the development and come back to the right level q Perimeter not well targeted : ¦ elements added or forgotten in the system (ex : roles of operators), Ä Unsuitable product or product rejected by the users ¦ interfaces forgotten (exchanges of matter, energy, information), ¦ physical connections forgotten (technological constraints) Ä not interoperable product q Lack or insufficiency of operational modes and scenarios Ä conflicting validation, backward transfer for use, backward development q Forgotten needs, forgotten stakeholders Ä backward development, conflicting validation q Wrong classification of the needs Ä Lost of time for the supplier, increasing development costs
 Practicing the needs definition Exercise : Expression of the stakeholders needs 7
Practicing the needs definition Exercise : Expression of the stakeholders needs 7
 SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Stakeholders' Needs Definition Process Hervé Panetto, Professor University of Lorraine, TELECOM Nancy Research Centre for Automatic Control (CRAN UMR 7039 CNRS) Chair of IFAC CC 5 « Manufacturing and Logistics Systems » Herve. Panetto@univ-Lorraine. fr Based on slides from Alain Faisandier (MAP Systems)
SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Stakeholders' Needs Definition Process Hervé Panetto, Professor University of Lorraine, TELECOM Nancy Research Centre for Automatic Control (CRAN UMR 7039 CNRS) Chair of IFAC CC 5 « Manufacturing and Logistics Systems » Herve. Panetto@univ-Lorraine. fr Based on slides from Alain Faisandier (MAP Systems)


