fee3f595d8802d1122bf0584428f925d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Systems Engineering Part 2 Product Architectures 1
Systems Engineering Part 2 Product Architectures 1
 What is Product Architecture? • Three related parts – The definition and the arrangement of functional elements – The mapping of these elements to physical components – The specification of interfaces among interacting physical components 2
What is Product Architecture? • Three related parts – The definition and the arrangement of functional elements – The mapping of these elements to physical components – The specification of interfaces among interacting physical components 2
 Some System Engineer Roles. . . Formulate and structure the System • Architectural Structure • create a schematic of the product reflects the teams best understanding of the product’s functionality • cluster the elements of the schematic reflect geometric integration, function sharing, vendor expertise considerations, localization of change accommodate variety, enable standardization, portability of interfaces (laser light, electrical vs mechanical) • create a rough geometric layout • identify the fundamental and incidental interactions between clusters • define secondary sub-systems 3
Some System Engineer Roles. . . Formulate and structure the System • Architectural Structure • create a schematic of the product reflects the teams best understanding of the product’s functionality • cluster the elements of the schematic reflect geometric integration, function sharing, vendor expertise considerations, localization of change accommodate variety, enable standardization, portability of interfaces (laser light, electrical vs mechanical) • create a rough geometric layout • identify the fundamental and incidental interactions between clusters • define secondary sub-systems 3
 • Define subsystems from clusters • Subsystem Architecture • repeat above at the subsystem level • Optimizing design across sub-system interfaces consider migration of components • Trade Studies • Alternative technologies • Create detailed Specifications • Planned Evolutionary Changes including Technology transparency • Establishing Error Budgets, weight budgets, power budgets, etc. 4
• Define subsystems from clusters • Subsystem Architecture • repeat above at the subsystem level • Optimizing design across sub-system interfaces consider migration of components • Trade Studies • Alternative technologies • Create detailed Specifications • Planned Evolutionary Changes including Technology transparency • Establishing Error Budgets, weight budgets, power budgets, etc. 4
 A Function Structure for a Trailer What other functions are possible? 5
A Function Structure for a Trailer What other functions are possible? 5
 Functional Elements Components Modular Architecture 6
Functional Elements Components Modular Architecture 6
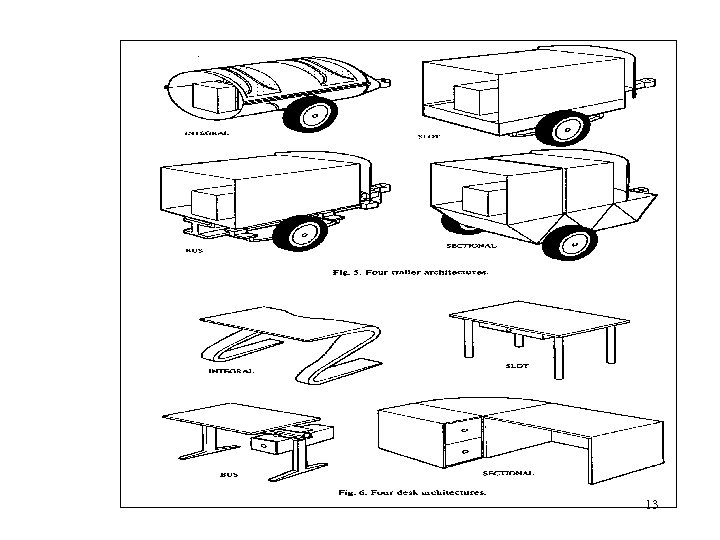
 Types of Modular Architectures • Slot – each component has a different coupling so cannot be interchanged (instrument panel of some airplanes, some parts of back plane of computers) • Bus – Common element which all components can connect to (track lighting, Ethernet, ) • Sectional – All interfaces are the same type (set of blocks) 7
Types of Modular Architectures • Slot – each component has a different coupling so cannot be interchanged (instrument panel of some airplanes, some parts of back plane of computers) • Bus – Common element which all components can connect to (track lighting, Ethernet, ) • Sectional – All interfaces are the same type (set of blocks) 7
 What are the advantages and disadvantages of a modular architecture ? 8
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a modular architecture ? 8
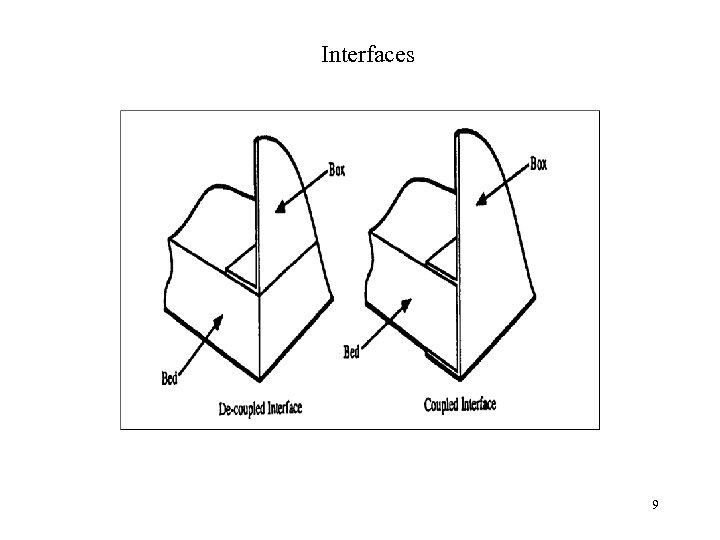 Interfaces 9
Interfaces 9
 Integral Architecture 10
Integral Architecture 10
 Examples of Integral Architecture • • • Fully custom VLSI chip One piece “monkey suit’ One room studio apartment? All in one printer/fax/scanner? Other? 11
Examples of Integral Architecture • • • Fully custom VLSI chip One piece “monkey suit’ One room studio apartment? All in one printer/fax/scanner? Other? 11
 What are the advantages and disadvantages of a integral architecture? 12
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a integral architecture? 12
 13
13
 14
14
 Product Evolution • • Upgrade Add-ons Adaptation Wear Consumption Flexibility Maintainability Feature bundling Well-designed product architectures accommodate these life cycle changes 15
Product Evolution • • Upgrade Add-ons Adaptation Wear Consumption Flexibility Maintainability Feature bundling Well-designed product architectures accommodate these life cycle changes 15
 Product Families • Spin out a variety of products from a common set of modules • Reuse extensively • Fast turn-around experiments to test market acceptance of features and to satisfy different segments • Change Technology platforms infrequently 16
Product Families • Spin out a variety of products from a common set of modules • Reuse extensively • Fast turn-around experiments to test market acceptance of features and to satisfy different segments • Change Technology platforms infrequently 16
 Trailer Example • Different load strength trailer beds (modularized) • normal or heavy duty environmental protection? • Three sets of suspension springs • Air drag streamlining or standard 17
Trailer Example • Different load strength trailer beds (modularized) • normal or heavy duty environmental protection? • Three sets of suspension springs • Air drag streamlining or standard 17
 Electronic Example • Consider Digital Design Alternatives – – – Breadboard SSI Microprocessor/Microcomputer Full Custom (Transistor by transistor) Standard Macrocell Gate Array Field Programmable Logic Array 18
Electronic Example • Consider Digital Design Alternatives – – – Breadboard SSI Microprocessor/Microcomputer Full Custom (Transistor by transistor) Standard Macrocell Gate Array Field Programmable Logic Array 18
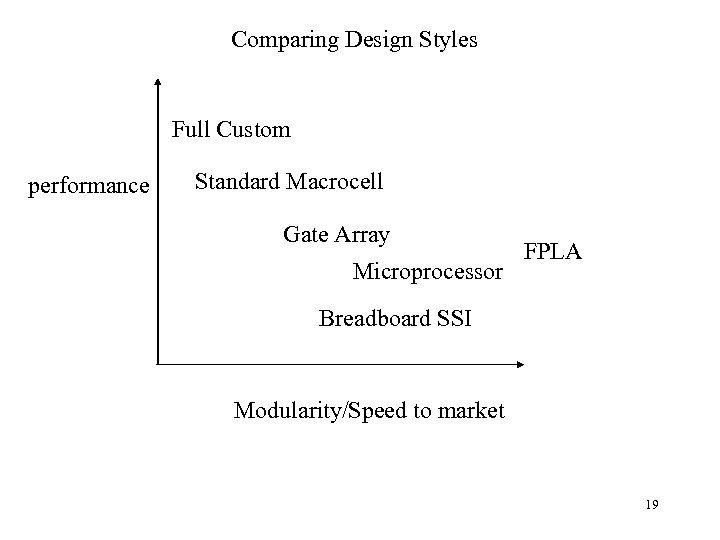 Comparing Design Styles Full Custom performance Standard Macrocell Gate Array Microprocessor FPLA Breadboard SSI Modularity/Speed to market 19
Comparing Design Styles Full Custom performance Standard Macrocell Gate Array Microprocessor FPLA Breadboard SSI Modularity/Speed to market 19
 Modular/Integral Which is preferred? • • • Feature Performance Time to Market Cost Upgrade Competitive defense Developing World M I 20
Modular/Integral Which is preferred? • • • Feature Performance Time to Market Cost Upgrade Competitive defense Developing World M I 20
 How to achieve product variety 21
How to achieve product variety 21
 Developing World Architectures Given conditions in Guatemala is there a bias for any particular architectural style? • Condition • Drives style 22
Developing World Architectures Given conditions in Guatemala is there a bias for any particular architectural style? • Condition • Drives style 22


