a30664b88c3318924b9c6d29e1674f99.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, Fourth Edition Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2
Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, Fourth Edition Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2
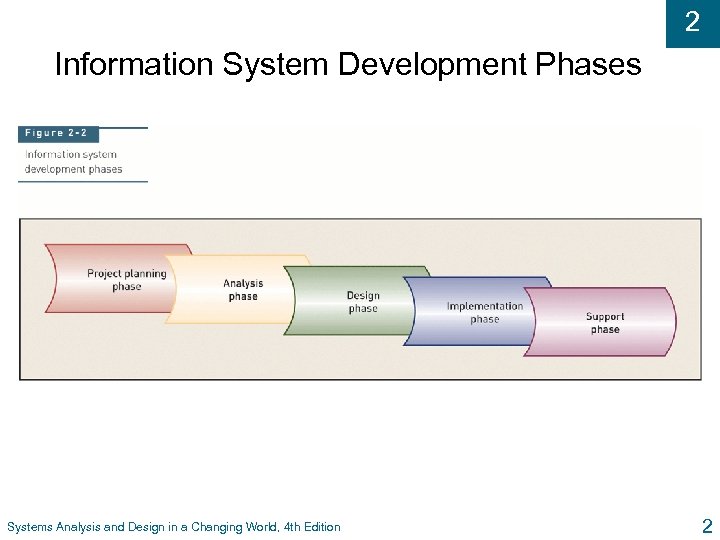 2 Information System Development Phases Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2
2 Information System Development Phases Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2
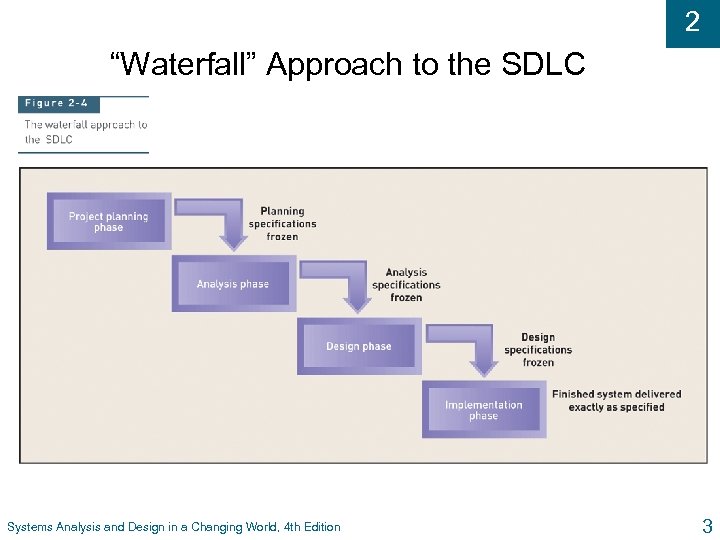 2 “Waterfall” Approach to the SDLC Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 3
2 “Waterfall” Approach to the SDLC Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 3
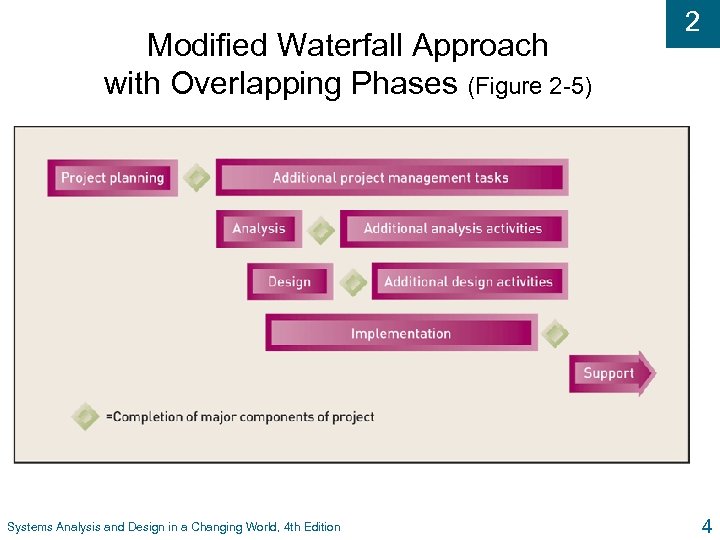 Modified Waterfall Approach with Overlapping Phases (Figure 2 -5) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 4
Modified Waterfall Approach with Overlapping Phases (Figure 2 -5) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 4
 2 Newer Adaptive Approaches to the SDLC u Based on spiral model l l Prototype created by end of each cycle l u Project cycles through development activities over and over until project is complete Focuses on mitigating risk Iteration – Work activities are repeated l Each iteration refines previous result l Approach assumes no one gets it right the first time l There a series of mini projects for each iteration Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 5
2 Newer Adaptive Approaches to the SDLC u Based on spiral model l l Prototype created by end of each cycle l u Project cycles through development activities over and over until project is complete Focuses on mitigating risk Iteration – Work activities are repeated l Each iteration refines previous result l Approach assumes no one gets it right the first time l There a series of mini projects for each iteration Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 5
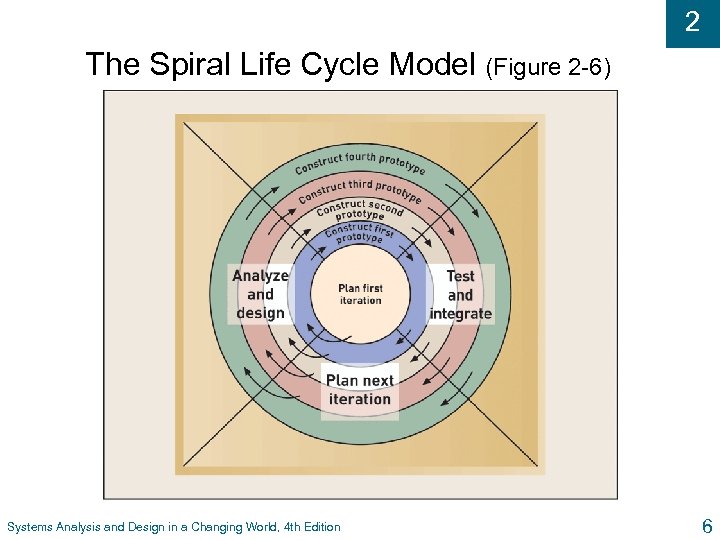 2 The Spiral Life Cycle Model (Figure 2 -6) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 6
2 The Spiral Life Cycle Model (Figure 2 -6) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 6
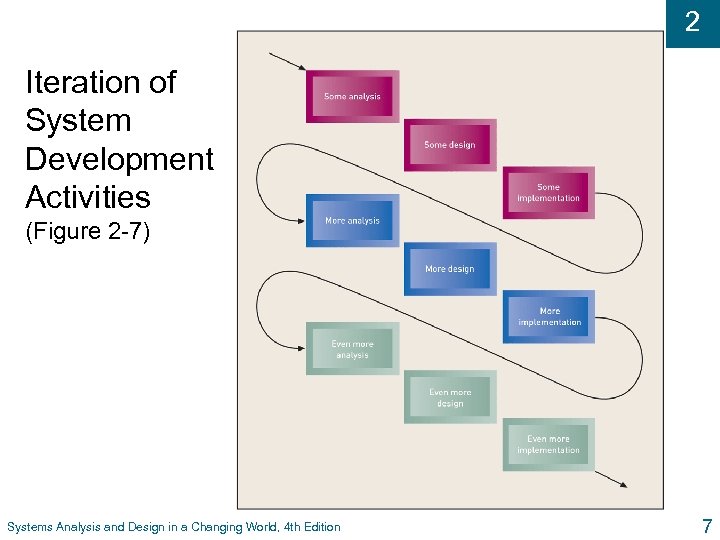 2 Iteration of System Development Activities (Figure 2 -7) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 7
2 Iteration of System Development Activities (Figure 2 -7) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 7
 2 Activities of Planning Phase of SDLC u Define business problem and scope u Produce detailed project schedule u Confirm project feasibility l Economic, organizational, technical, resource, and schedule u Staff the project (resource management) u Launch project official announcement Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 8
2 Activities of Planning Phase of SDLC u Define business problem and scope u Produce detailed project schedule u Confirm project feasibility l Economic, organizational, technical, resource, and schedule u Staff the project (resource management) u Launch project official announcement Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 8
 2 Activities of Analysis Phase of SDLC u Gather information to learn problem domain u Define system requirements u Build prototypes for discovery of requirements u Prioritize requirements u Generate u Review and evaluate alternatives recommendations with management Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 9
2 Activities of Analysis Phase of SDLC u Gather information to learn problem domain u Define system requirements u Build prototypes for discovery of requirements u Prioritize requirements u Generate u Review and evaluate alternatives recommendations with management Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 9
 2 Activities of Design Phase of SDLC u Design and integrate the network u Design the application architecture u Design the user interfaces u Design the system interfaces u Design and integrate the database u Prototype u Design for design details and integrate system controls Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 10
2 Activities of Design Phase of SDLC u Design and integrate the network u Design the application architecture u Design the user interfaces u Design the system interfaces u Design and integrate the database u Prototype u Design for design details and integrate system controls Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 10
 Activities of Implementation Phase of SDLC u Construct u Verify software components and test u Convert u Train 2 data users and document the system u Install the system Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 11
Activities of Implementation Phase of SDLC u Construct u Verify software components and test u Convert u Train 2 data users and document the system u Install the system Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 11
 2 Activities of Support Phase of SDLC u Maintain l system Small patches, repairs, and updates u Enhance system l Small upgrades or enhancements to expand system capabilities l Larger enhancements may require separate development project u Support l users Help desk and/or support team Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 12
2 Activities of Support Phase of SDLC u Maintain l system Small patches, repairs, and updates u Enhance system l Small upgrades or enhancements to expand system capabilities l Larger enhancements may require separate development project u Support l users Help desk and/or support team Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 12
 2 Methodologies and Models u Methodologies l Comprehensive guidelines to follow for completing every SDLC activity l Collection of models, tools, and techniques u Models l Representation of an important aspect of real world, but not same as real thing l Abstraction used to separate out aspect l Diagrams and charts l Project planning and budgeting aids Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 13
2 Methodologies and Models u Methodologies l Comprehensive guidelines to follow for completing every SDLC activity l Collection of models, tools, and techniques u Models l Representation of an important aspect of real world, but not same as real thing l Abstraction used to separate out aspect l Diagrams and charts l Project planning and budgeting aids Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 13
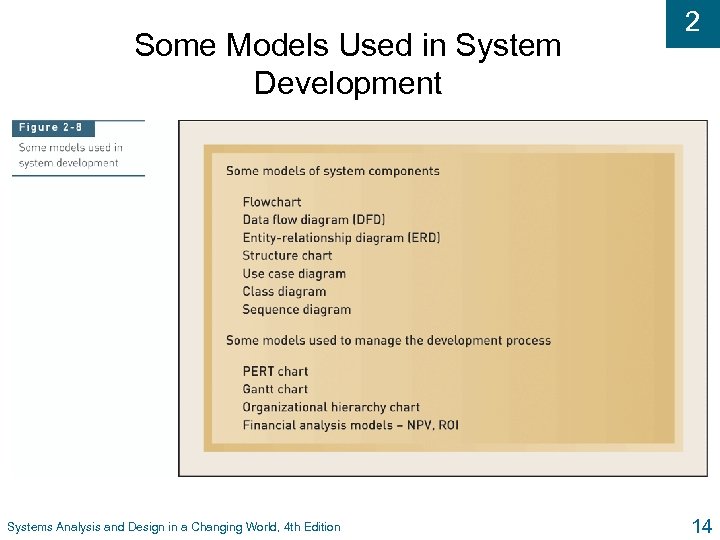 Some Models Used in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 14
Some Models Used in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 14
 2 Some Tools Used in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 16
2 Some Tools Used in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 16
 Some Techniques Used in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 17
Some Techniques Used in System Development Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 17
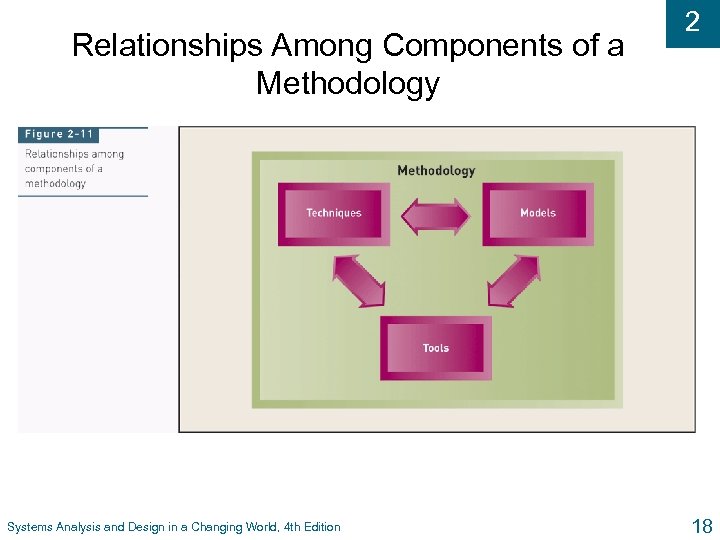 Relationships Among Components of a Methodology Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 18
Relationships Among Components of a Methodology Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 18
 2 Two Approaches to System Development u Traditional approach l Also called structured system development l Structured analysis and design technique (SADT) l Includes information engineering (IE) u Object-oriented approach l Also called OOA, OOD, and OOP l Views information system as collection of interacting objects that work together to accomplish tasks Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 19
2 Two Approaches to System Development u Traditional approach l Also called structured system development l Structured analysis and design technique (SADT) l Includes information engineering (IE) u Object-oriented approach l Also called OOA, OOD, and OOP l Views information system as collection of interacting objects that work together to accomplish tasks Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 19
 2 Traditional Approach u Structured programming l Improves computer program quality l Allows other programmers to easily read and modify code l Each program module has one beginning and one ending l Three programming constructs (sequence, decision, repetition) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 20
2 Traditional Approach u Structured programming l Improves computer program quality l Allows other programmers to easily read and modify code l Each program module has one beginning and one ending l Three programming constructs (sequence, decision, repetition) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 20
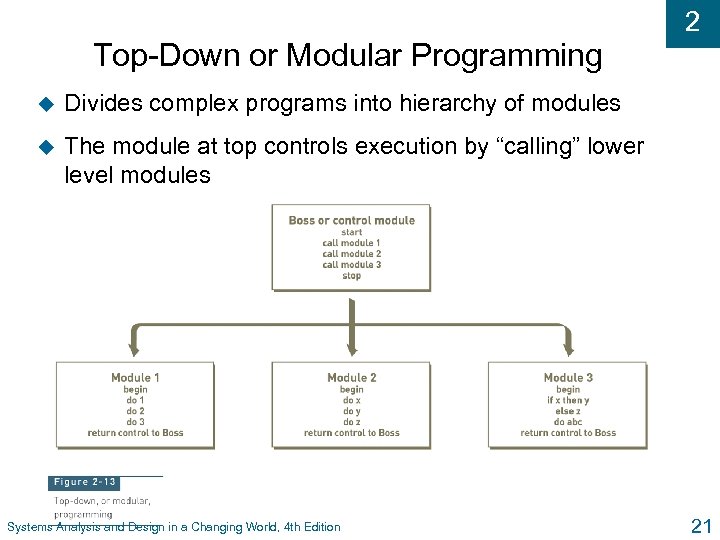 2 Top-Down or Modular Programming u Divides complex programs into hierarchy of modules u The module at top controls execution by “calling” lower level modules Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 21
2 Top-Down or Modular Programming u Divides complex programs into hierarchy of modules u The module at top controls execution by “calling” lower level modules Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 21
 2 Structured Design u Technique guidelines developed to provide design l What set of programs should be l What program should accomplish l How programs should be organized into a hierarchy u Modules u Main are shown with structure chart principle of program modules l Loosely coupled – module is independent of other modules l Highly cohesive – module has one clear task Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 22
2 Structured Design u Technique guidelines developed to provide design l What set of programs should be l What program should accomplish l How programs should be organized into a hierarchy u Modules u Main are shown with structure chart principle of program modules l Loosely coupled – module is independent of other modules l Highly cohesive – module has one clear task Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 22
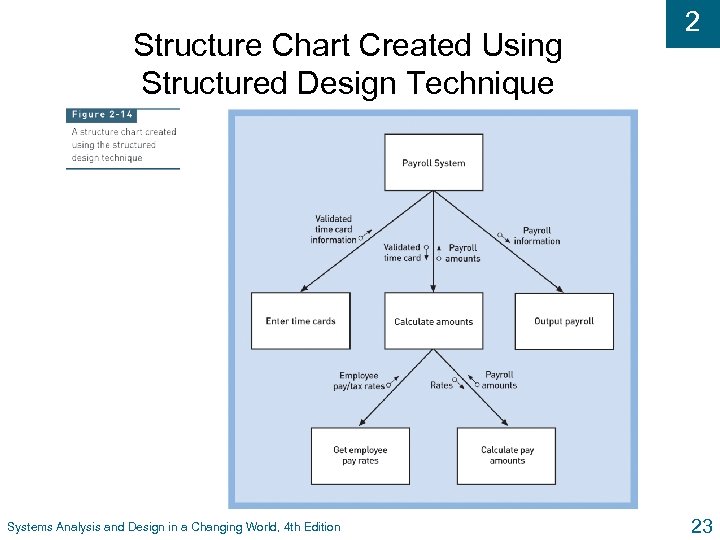 Structure Chart Created Using Structured Design Technique Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 23
Structure Chart Created Using Structured Design Technique Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 23
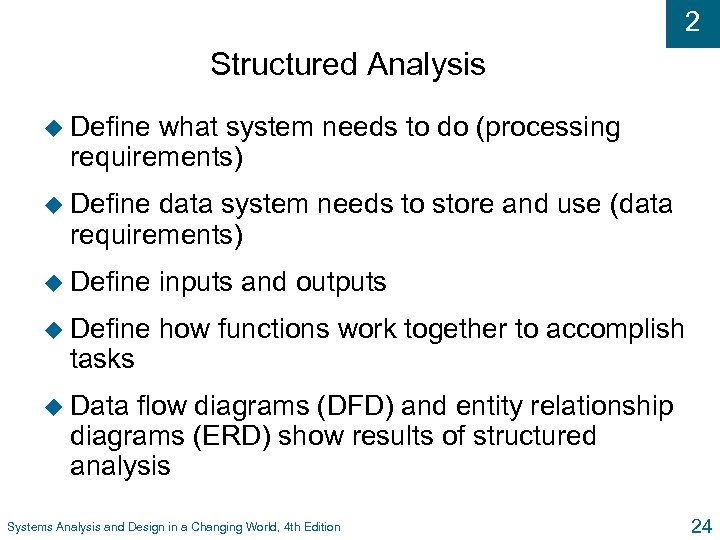 2 Structured Analysis u Define what system needs to do (processing requirements) u Define data system needs to store and use (data requirements) u Define inputs and outputs u Define how functions work together to accomplish tasks u Data flow diagrams (DFD) and entity relationship diagrams (ERD) show results of structured analysis Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 24
2 Structured Analysis u Define what system needs to do (processing requirements) u Define data system needs to store and use (data requirements) u Define inputs and outputs u Define how functions work together to accomplish tasks u Data flow diagrams (DFD) and entity relationship diagrams (ERD) show results of structured analysis Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 24
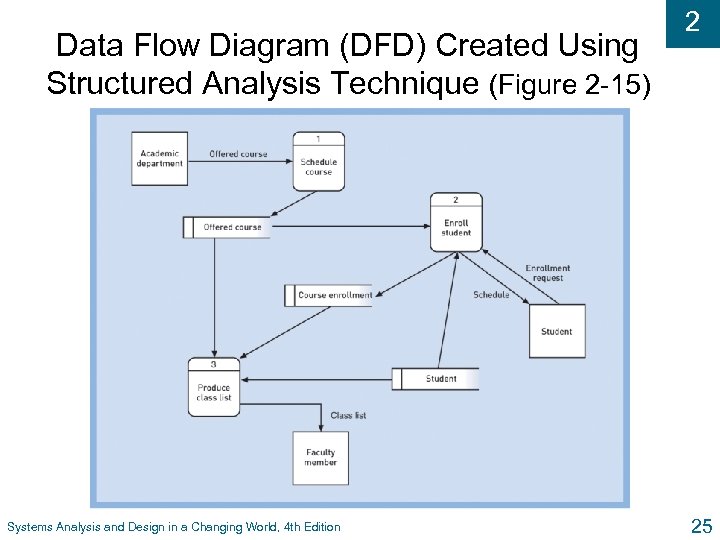 Data Flow Diagram (DFD) Created Using Structured Analysis Technique (Figure 2 -15) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 25
Data Flow Diagram (DFD) Created Using Structured Analysis Technique (Figure 2 -15) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 25
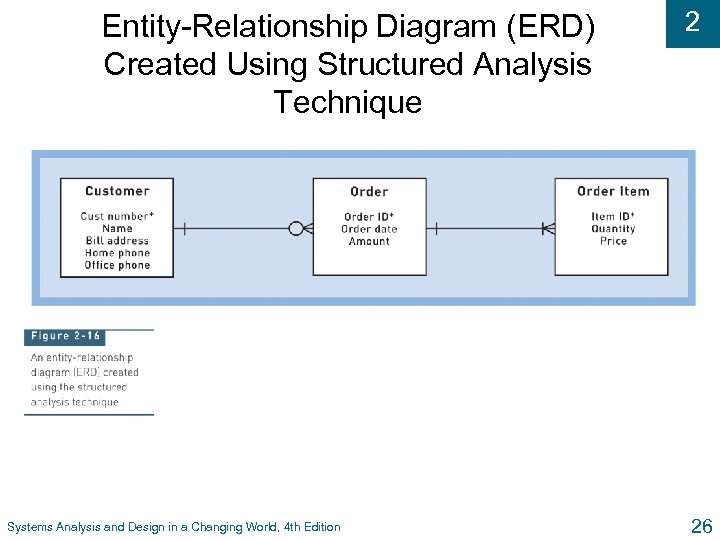 Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) Created Using Structured Analysis Technique Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 26
Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) Created Using Structured Analysis Technique Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 26
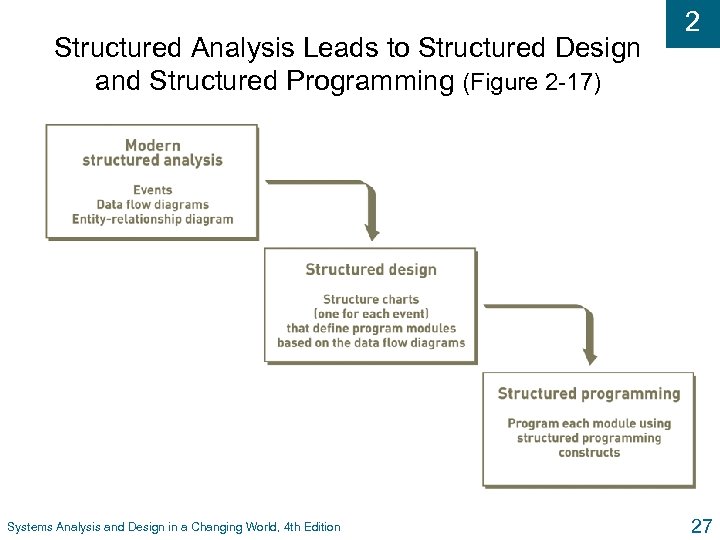 Structured Analysis Leads to Structured Design and Structured Programming (Figure 2 -17) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 27
Structured Analysis Leads to Structured Design and Structured Programming (Figure 2 -17) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 27
 2 Information Engineering (IE) u Refinement to structured development u Methodology with strategic planning, data modeling, automated tools focus u More rigorous and complete than SADT u Industry merged key concepts from structured development and information engineering approaches into traditional approach Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 28
2 Information Engineering (IE) u Refinement to structured development u Methodology with strategic planning, data modeling, automated tools focus u More rigorous and complete than SADT u Industry merged key concepts from structured development and information engineering approaches into traditional approach Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 28
 2 Object-Oriented Approach u Completely systems different approach to information u Views information system as collection of interacting objects that work together to accomplish tasks l Objects – things in computer system that can respond to messages l Conceptually, no processes, programs, data entities, or files are defined – just objects u OO languages: Java, C++, C#. NET, VB. NET Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 29
2 Object-Oriented Approach u Completely systems different approach to information u Views information system as collection of interacting objects that work together to accomplish tasks l Objects – things in computer system that can respond to messages l Conceptually, no processes, programs, data entities, or files are defined – just objects u OO languages: Java, C++, C#. NET, VB. NET Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 29
 2 Stop Here 1/29/07 Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 30
2 Stop Here 1/29/07 Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 30
 2 Object-Oriented Approach (continued) u Object-oriented analysis (OOA) l l u Defines types of objects users deal with Shows use cases are required to complete tasks Object-oriented design (OOD) l l Shows how objects interact to complete tasks l u Defines object types needed to communicate with people and devices in system Refines each type of object for implementation with specific language of environment Object-oriented programming (OOP) l Writing statements in programming language to define what each type of object does Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 31
2 Object-Oriented Approach (continued) u Object-oriented analysis (OOA) l l u Defines types of objects users deal with Shows use cases are required to complete tasks Object-oriented design (OOD) l l Shows how objects interact to complete tasks l u Defines object types needed to communicate with people and devices in system Refines each type of object for implementation with specific language of environment Object-oriented programming (OOP) l Writing statements in programming language to define what each type of object does Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 31
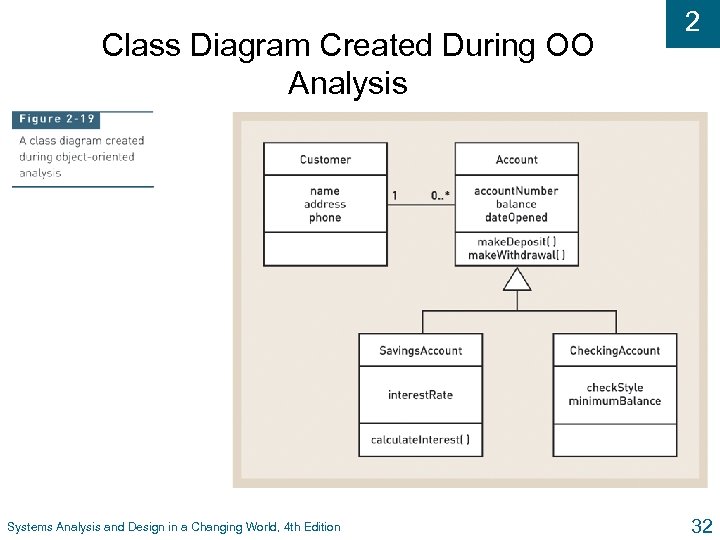 Class Diagram Created During OO Analysis Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 32
Class Diagram Created During OO Analysis Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 32
 2 SDLC Variations u Many variations of SDLC in practice l Based on variation of names for phases l No matter which one, activities/tasks are similar u Some increase emphasis on people l User-centered design, participatory design l Sociotechnical systems u Some increase speed of development l Rapid application development (RAD) l Prototyping Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 33
2 SDLC Variations u Many variations of SDLC in practice l Based on variation of names for phases l No matter which one, activities/tasks are similar u Some increase emphasis on people l User-centered design, participatory design l Sociotechnical systems u Some increase speed of development l Rapid application development (RAD) l Prototyping Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 33
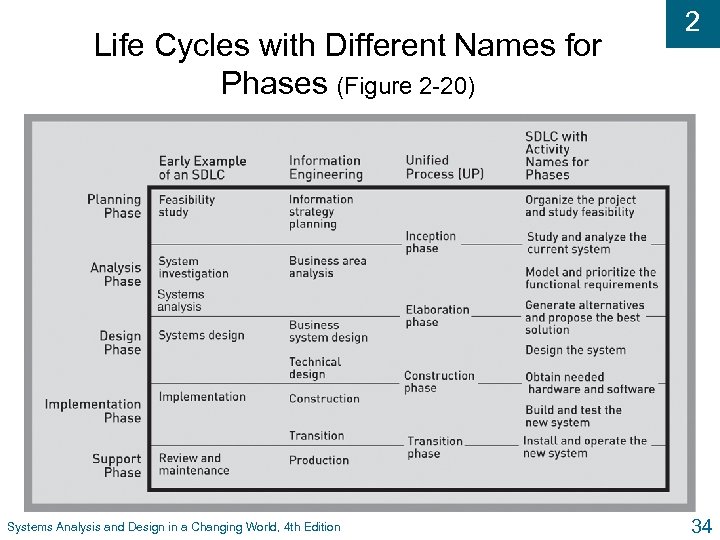 Life Cycles with Different Names for Phases (Figure 2 -20) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 34
Life Cycles with Different Names for Phases (Figure 2 -20) Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 34
 2 Tools to Support System Development u Computer-aided system engineering (CASE) l Automated tools to improve the speed and quality of system development work l Contains database of information about system called repository u Upper CASE – support for analysis and design u Lower CASE – support for implementation u ICASE – integrated CASE tools u Now called visual modeling tools, integrated application development tools, and round-trip engineering tools Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 35
2 Tools to Support System Development u Computer-aided system engineering (CASE) l Automated tools to improve the speed and quality of system development work l Contains database of information about system called repository u Upper CASE – support for analysis and design u Lower CASE – support for implementation u ICASE – integrated CASE tools u Now called visual modeling tools, integrated application development tools, and round-trip engineering tools Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 35
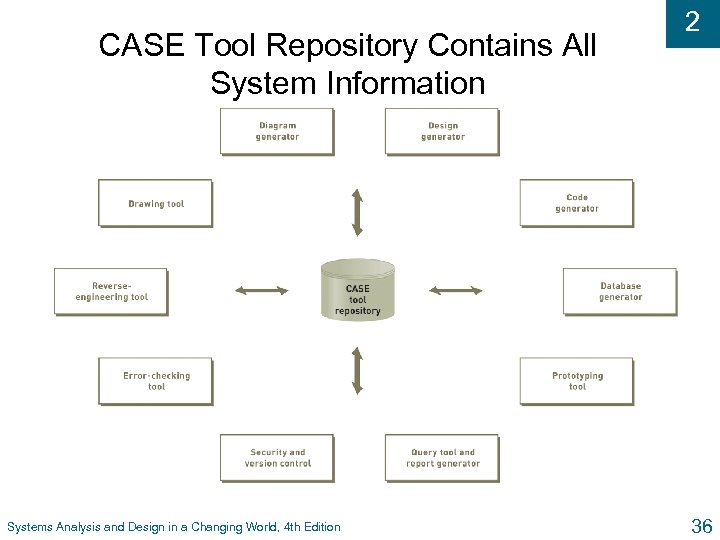 CASE Tool Repository Contains All System Information Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 36
CASE Tool Repository Contains All System Information Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 2 36
 2 Summary u System development projects are organized around the systems development life cycle (SDLC) u Some projects use a predictive approach to the SDLC, and others use a more adaptive approach to the SDLC u SDLC phases include project planning, analysis, design, implementation, and support Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 37
2 Summary u System development projects are organized around the systems development life cycle (SDLC) u Some projects use a predictive approach to the SDLC, and others use a more adaptive approach to the SDLC u SDLC phases include project planning, analysis, design, implementation, and support Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 37
 2 Summary (continued) u In practice, phases overlap, and projects contain many iterations of analysis, design, and implementation u Models, techniques, and tools make up a system development methodology u System development methodology provides guidelines to complete every activity in the SDLC Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 38
2 Summary (continued) u In practice, phases overlap, and projects contain many iterations of analysis, design, and implementation u Models, techniques, and tools make up a system development methodology u System development methodology provides guidelines to complete every activity in the SDLC Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 38
 2 Summary (continued) u System development methodologies are based on traditional approach or object-oriented approach u CASE tools are designed to help analysts complete system development tasks Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 39
2 Summary (continued) u System development methodologies are based on traditional approach or object-oriented approach u CASE tools are designed to help analysts complete system development tasks Systems Analysis and Design in a Changing World, 4 th Edition 39


