Лекция 16 Ревматические болезни 2011.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64
 Systemic diseases of connective tissue - Rheumatic diseases (collagenoses) Lecture
Systemic diseases of connective tissue - Rheumatic diseases (collagenoses) Lecture
 Rheumatic diseases a group of chronic diseases with systemic progressive disorganization of connective tissue and vessels, as well as immune derangements.
Rheumatic diseases a group of chronic diseases with systemic progressive disorganization of connective tissue and vessels, as well as immune derangements.
 Rheumatic diseases u Disease nature: infection-allergic. u Risk factors: heredity, infection, hypothermia, medicaments (drugs).
Rheumatic diseases u Disease nature: infection-allergic. u Risk factors: heredity, infection, hypothermia, medicaments (drugs).
 Common signs of diseases u Presence of chronic infection foci; u Immunologic homeostasis derangements; u Generalized vasculitis; u Chronic undulating course; u Systemic progressive disorganization of connective tissue.
Common signs of diseases u Presence of chronic infection foci; u Immunologic homeostasis derangements; u Generalized vasculitis; u Chronic undulating course; u Systemic progressive disorganization of connective tissue.
 Nosologic forms u Rheumatism; u Rheumatoid arthritis; u Systemic lupus erythematosus; u Scleroderma; u Nodular periarteritis; u Bechterew`s disease; u Dermatomyositis.
Nosologic forms u Rheumatism; u Rheumatoid arthritis; u Systemic lupus erythematosus; u Scleroderma; u Nodular periarteritis; u Bechterew`s disease; u Dermatomyositis.
 Stages of connective tissue disorganization u Mucoid swelling, u Fibrinoid changes: (fibrinoid swelling, fibrinoid necrosis), u Inflammatory-cellular reactions, u Sclerosis.
Stages of connective tissue disorganization u Mucoid swelling, u Fibrinoid changes: (fibrinoid swelling, fibrinoid necrosis), u Inflammatory-cellular reactions, u Sclerosis.
 Predominant localization of affections Rheumatism – heart and vessels; Rheumatoid arthritis – joints; Systemic lupus erythematosus – skin, kidneys; Scleroderma – skin; Nodular periarteritis – arteries wall; Bechterew`s disease – articularligamentous apparatus of the spine; Dermatomyositis – skeletal muscular system.
Predominant localization of affections Rheumatism – heart and vessels; Rheumatoid arthritis – joints; Systemic lupus erythematosus – skin, kidneys; Scleroderma – skin; Nodular periarteritis – arteries wall; Bechterew`s disease – articularligamentous apparatus of the spine; Dermatomyositis – skeletal muscular system.
 Rheumatism Rheumatic endocarditis – is a chronic disease of infection-allergic nature with the progressive disorganization of connective tissue and vessels Etiology: β-hemolytic streptococcus of А group
Rheumatism Rheumatic endocarditis – is a chronic disease of infection-allergic nature with the progressive disorganization of connective tissue and vessels Etiology: β-hemolytic streptococcus of А group
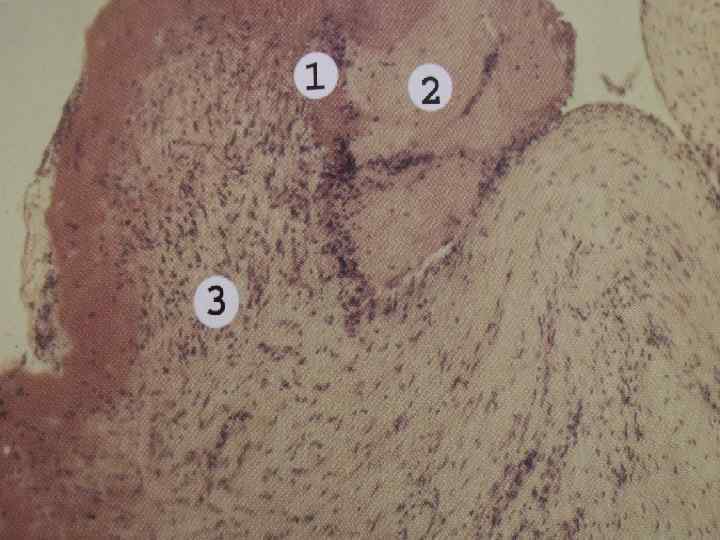
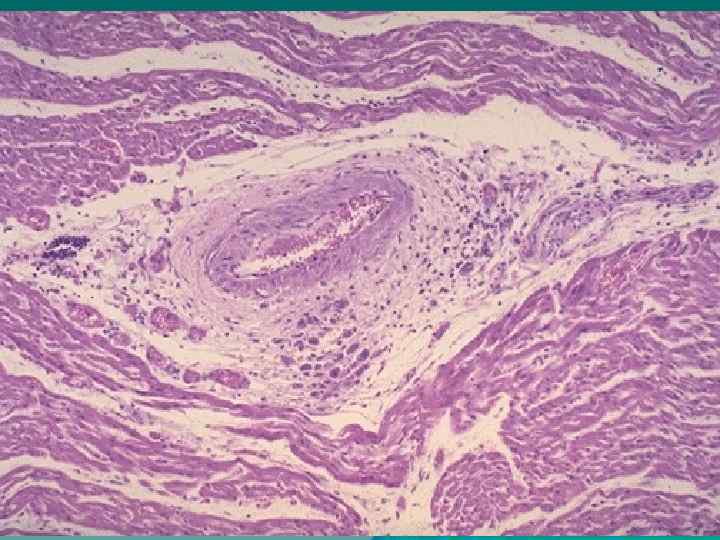
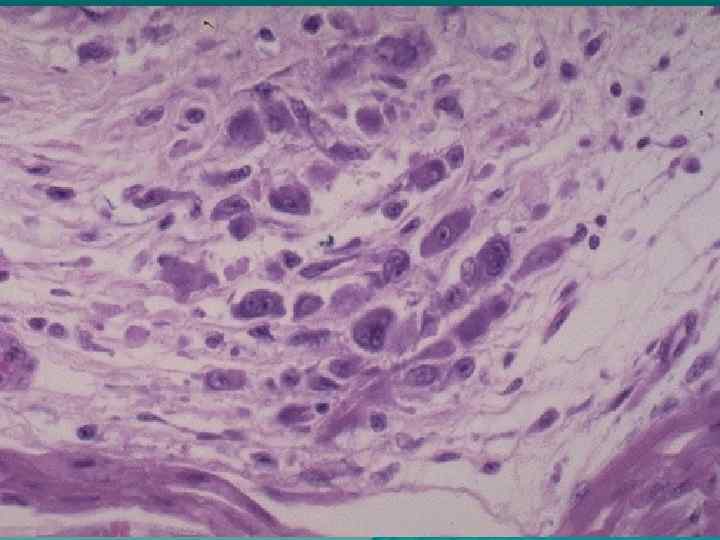
 Connective tissue disorganization stages in case of rheumatism: u Mucoid swelling, u Fibrinoid changes: (fibrinoid swelling, fibrinoid necrosis), u Cellular reactions (formation of granulomas: blooming, fading, sclerosing – Aschoff-Talalaev`s nodules), u Sclerosis.
Connective tissue disorganization stages in case of rheumatism: u Mucoid swelling, u Fibrinoid changes: (fibrinoid swelling, fibrinoid necrosis), u Cellular reactions (formation of granulomas: blooming, fading, sclerosing – Aschoff-Talalaev`s nodules), u Sclerosis.
 Clinicoanatomical forms of rheumatism: u Cardiovascular: predominant affection of the heart and vessels. u Polyarthritic: affection of the heart, vessels and joints. u Cerebral: affection of the heart, vessels and brain. u Nodose: affection of the heart, vessels and skin.
Clinicoanatomical forms of rheumatism: u Cardiovascular: predominant affection of the heart and vessels. u Polyarthritic: affection of the heart, vessels and joints. u Cerebral: affection of the heart, vessels and brain. u Nodose: affection of the heart, vessels and skin.
 Cardiovascular form u Vessels – vasculitis; u Endocardium – endocarditis; u Myocardium – myocarditis: u Pericardium – pericarditis; u Rheumatic heart disease: combined affection of endocardium and myocardium; u Pancarditis: inflammation of all cardiac membranes (coats).
Cardiovascular form u Vessels – vasculitis; u Endocardium – endocarditis; u Myocardium – myocarditis: u Pericardium – pericarditis; u Rheumatic heart disease: combined affection of endocardium and myocardium; u Pancarditis: inflammation of all cardiac membranes (coats).
 Endocarditis According to localization: parietal, chordal, valvular; u According to morphology: diffuse (valvulitis), acute verrucous, fibroplastic, recurrent-verrucous. u Outcome – heart disease formation. u
Endocarditis According to localization: parietal, chordal, valvular; u According to morphology: diffuse (valvulitis), acute verrucous, fibroplastic, recurrent-verrucous. u Outcome – heart disease formation. u
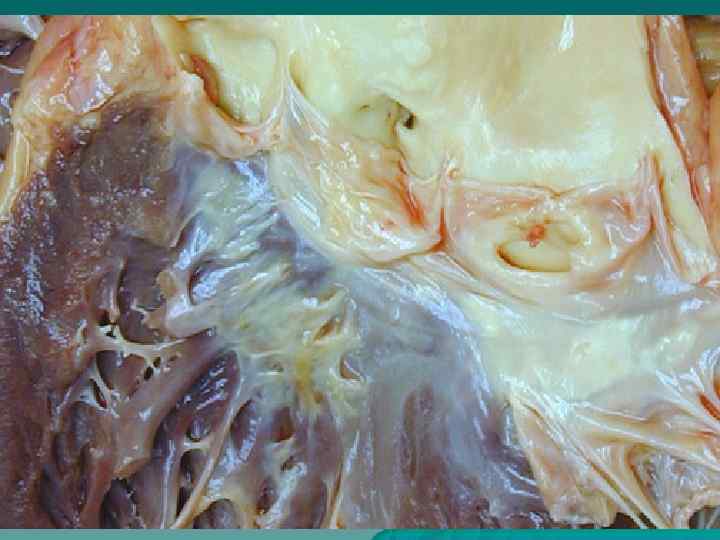
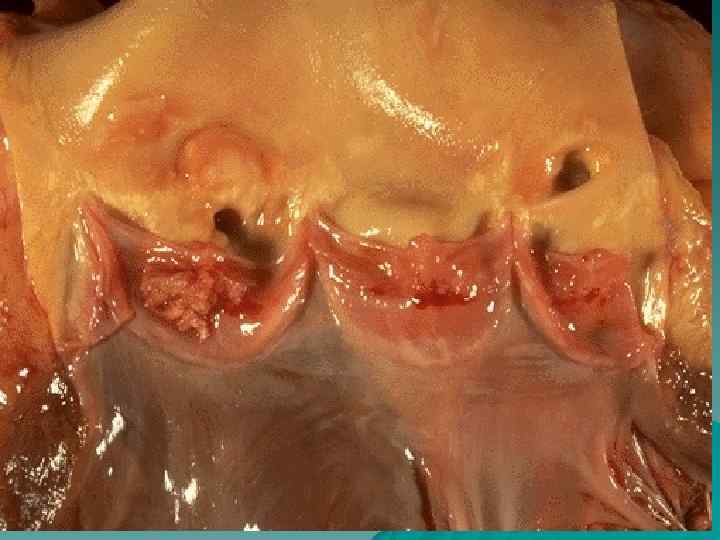
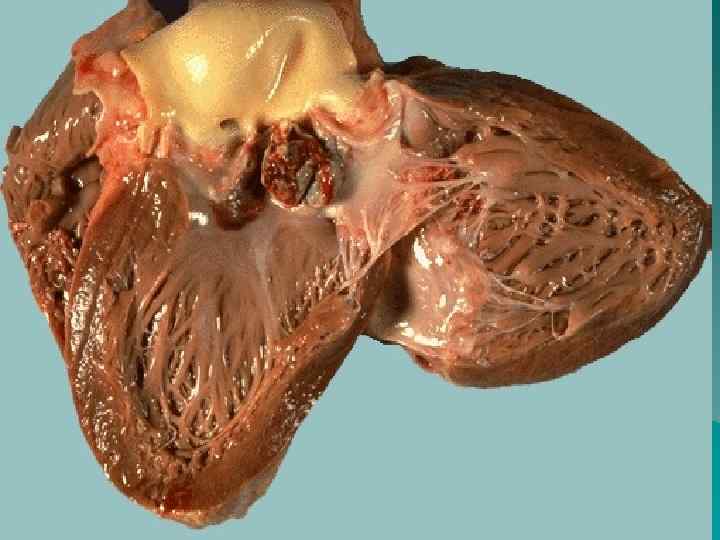
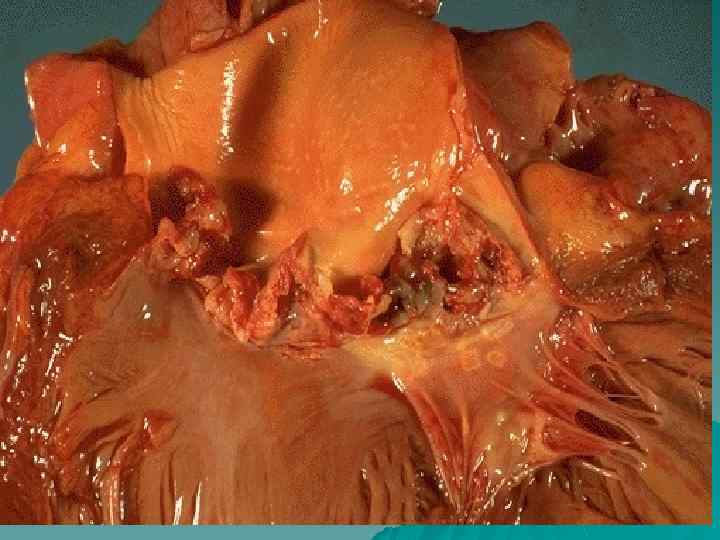
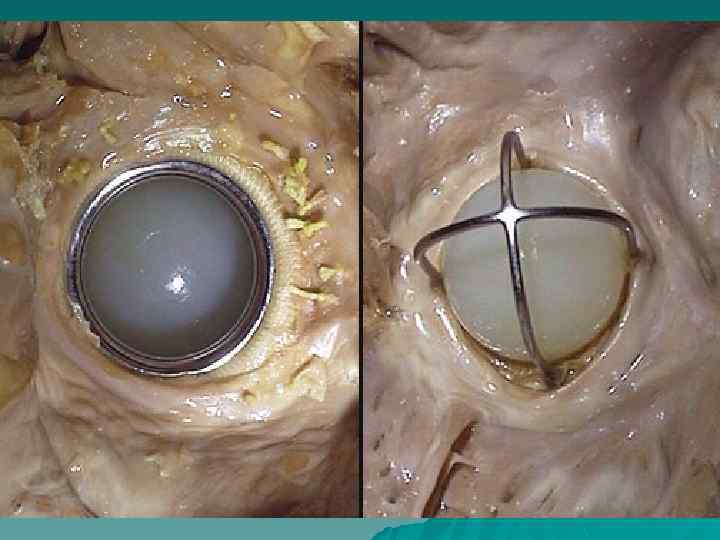
 Heart diseases u According to the origin: congenital and acquired; u According to morphology: stenosis, insufficiency, combined heart disease; u Isolated, associated heart disease.
Heart diseases u According to the origin: congenital and acquired; u According to morphology: stenosis, insufficiency, combined heart disease; u Isolated, associated heart disease.
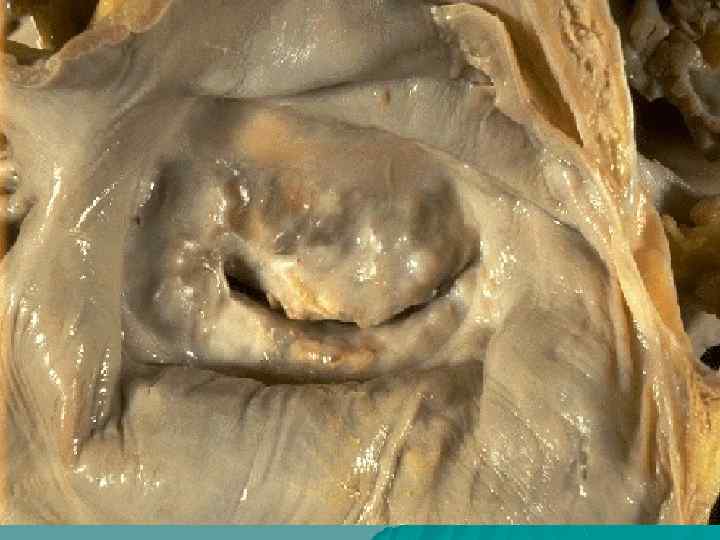
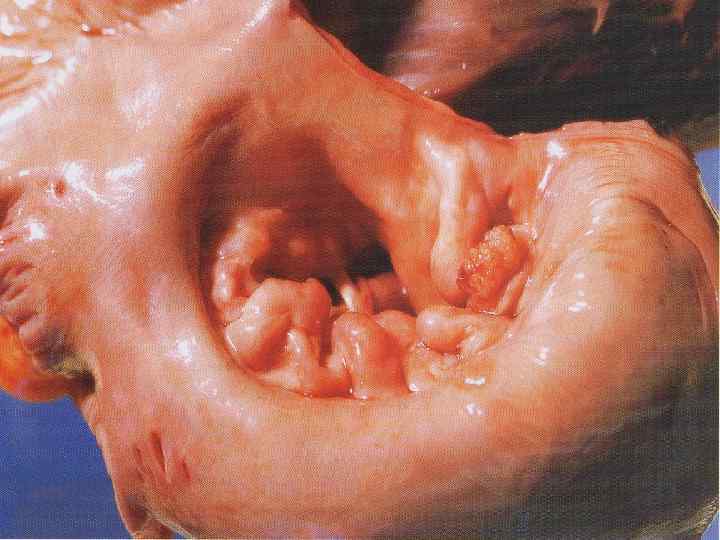 Стеноз митрального клапана
Стеноз митрального клапана
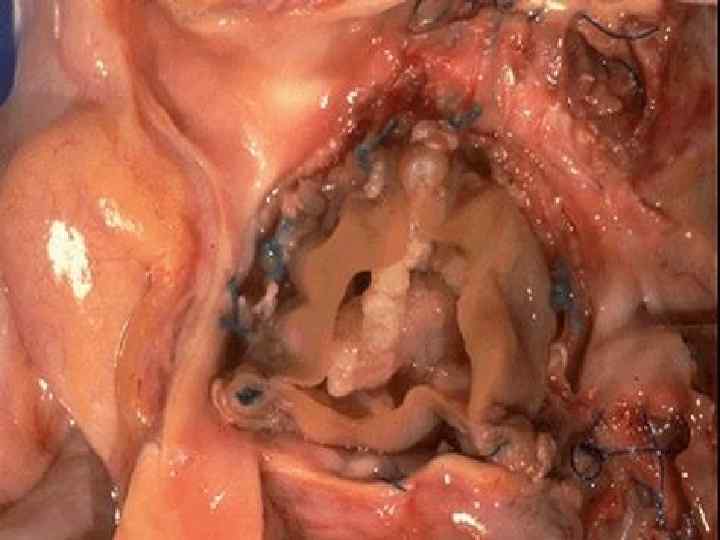
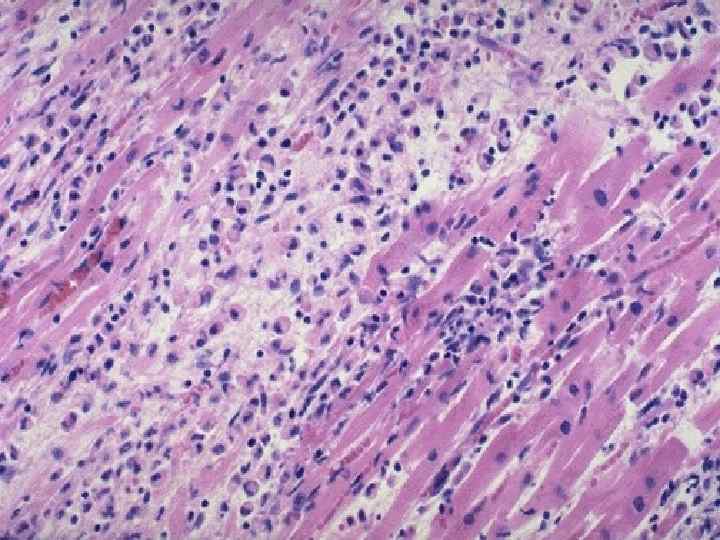
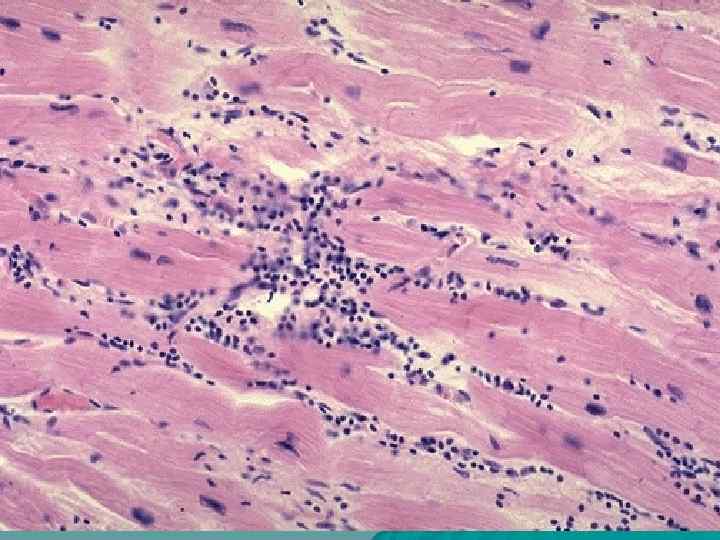
 Myocarditis u Productive (granulomatous), u Interstitial, exudative, diffuse, u Interstitial, exudative, focal. Outcome - cardiosclerosis
Myocarditis u Productive (granulomatous), u Interstitial, exudative, diffuse, u Interstitial, exudative, focal. Outcome - cardiosclerosis
 Pericarditis According to morphology: u Serous, u Fibrinous, u Serofibrinous. u Outcome – commissures and pericardial cavity obliteration.
Pericarditis According to morphology: u Serous, u Fibrinous, u Serofibrinous. u Outcome – commissures and pericardial cavity obliteration.
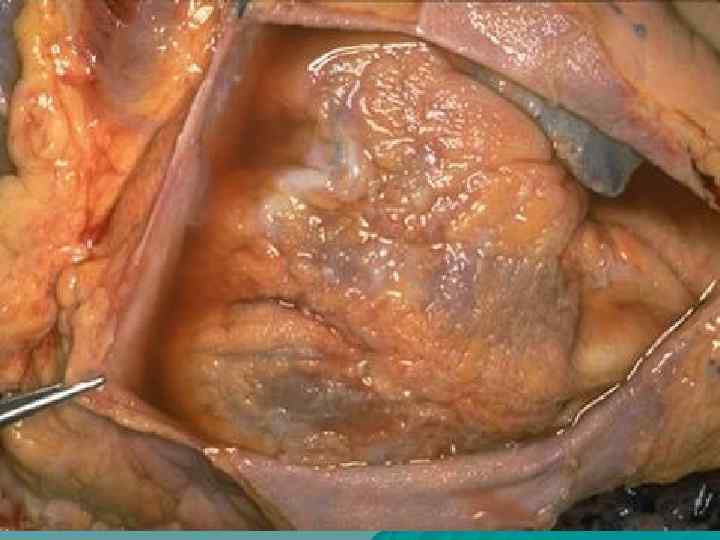
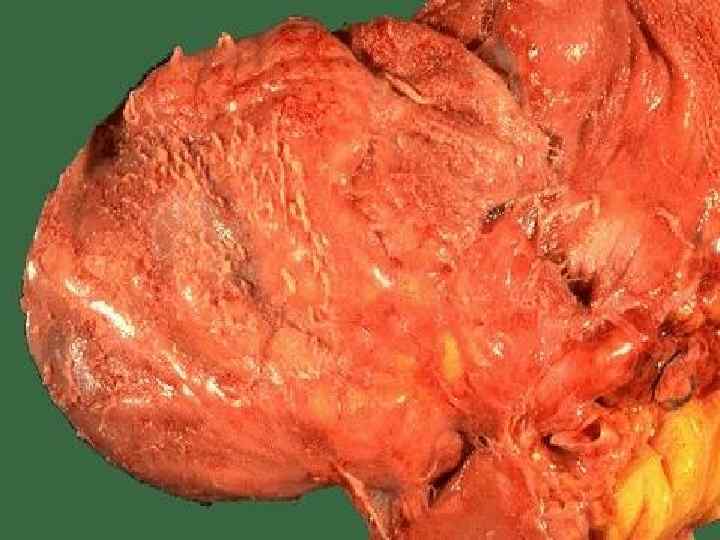
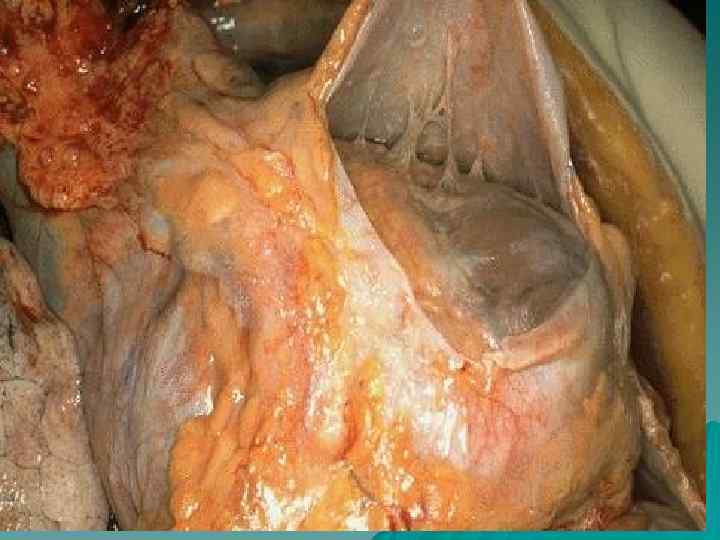
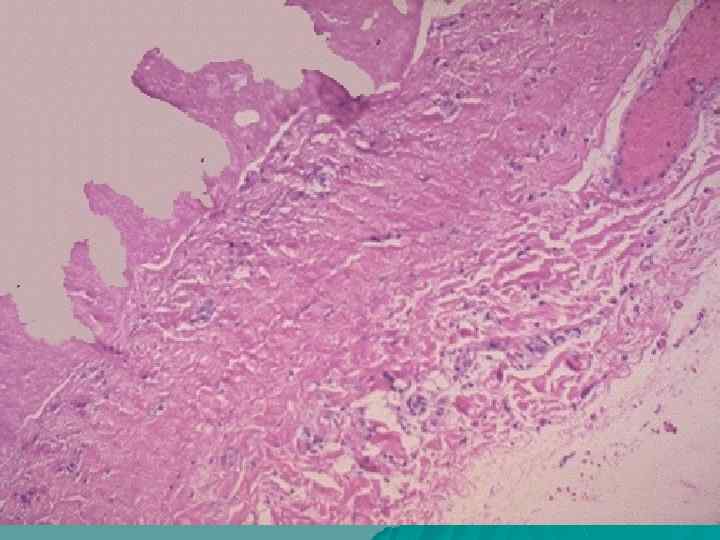
 Cardiovascular form u Complications: thromboembolism, vascular thrombosis, infarctions of kidneys, spleen, brain; cirrhosis, banal pneumonia. u Death causes: cardiac decompensation and general blood circulation disturbance, specific and nonspecific pneumonia, cerebral hemorrhage, intercurrent
Cardiovascular form u Complications: thromboembolism, vascular thrombosis, infarctions of kidneys, spleen, brain; cirrhosis, banal pneumonia. u Death causes: cardiac decompensation and general blood circulation disturbance, specific and nonspecific pneumonia, cerebral hemorrhage, intercurrent
 Polyarthritic form of rheumatism u Is found in 10 -15% of patients; u Large joints are chiefly affected; u Inflammation pattern: serous, without the lesion of articular cartilage; u Heart and vessels are affected to a lesser degree. u Important! Has to be differentiated with rheumatoid arthritis!
Polyarthritic form of rheumatism u Is found in 10 -15% of patients; u Large joints are chiefly affected; u Inflammation pattern: serous, without the lesion of articular cartilage; u Heart and vessels are affected to a lesser degree. u Important! Has to be differentiated with rheumatoid arthritis!
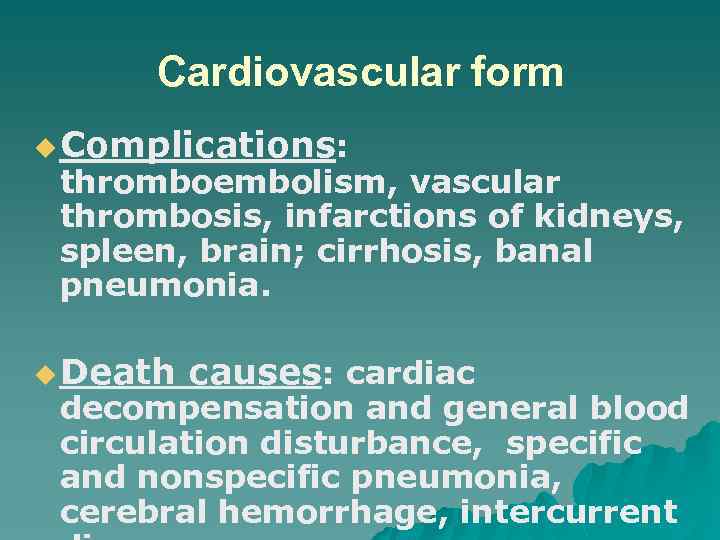
 Nodose (nodular) form of rheumatism u More often is found in children; u Connective tissue disorganization along the tendons; u Development of nodose erythema; u Outcome - scarring; u There are similar changes in other organs, but without the clinical manifestations.
Nodose (nodular) form of rheumatism u More often is found in children; u Connective tissue disorganization along the tendons; u Development of nodose erythema; u Outcome - scarring; u There are similar changes in other organs, but without the clinical manifestations.
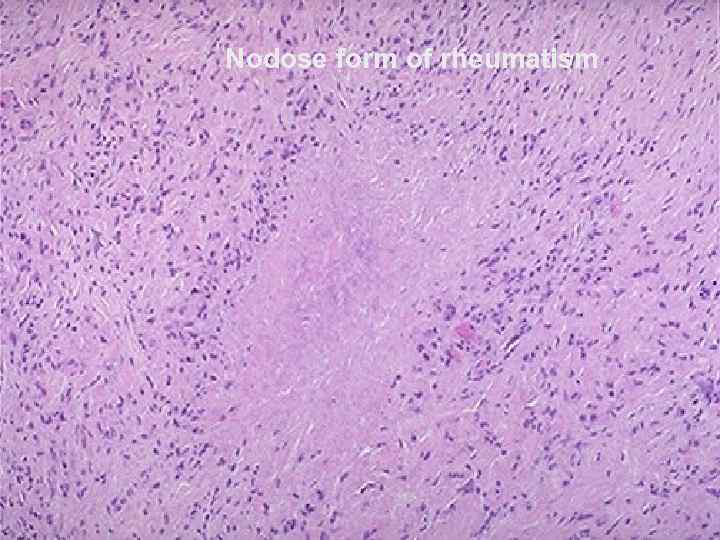 Nodose form of rheumatism
Nodose form of rheumatism
 Cerebral form of rheumatism u Is found in children (juvenile chorea); u Vasculitis, degenerative changes of brain cells; u Other organs are changing less.
Cerebral form of rheumatism u Is found in children (juvenile chorea); u Vasculitis, degenerative changes of brain cells; u Other organs are changing less.
 RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
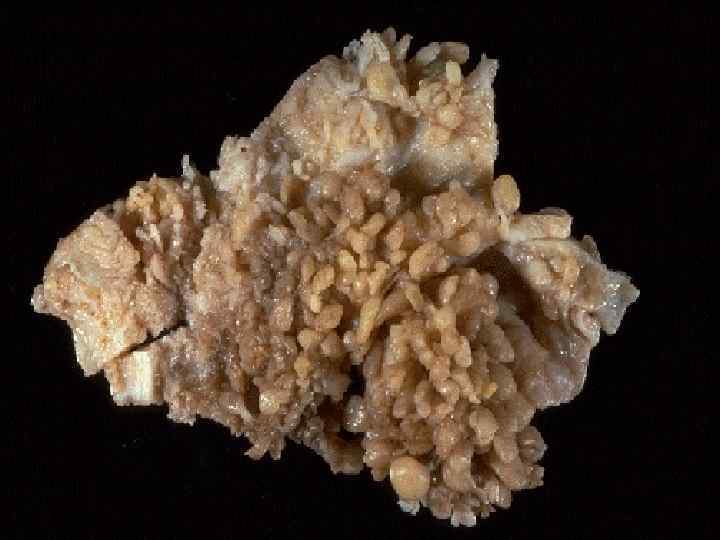
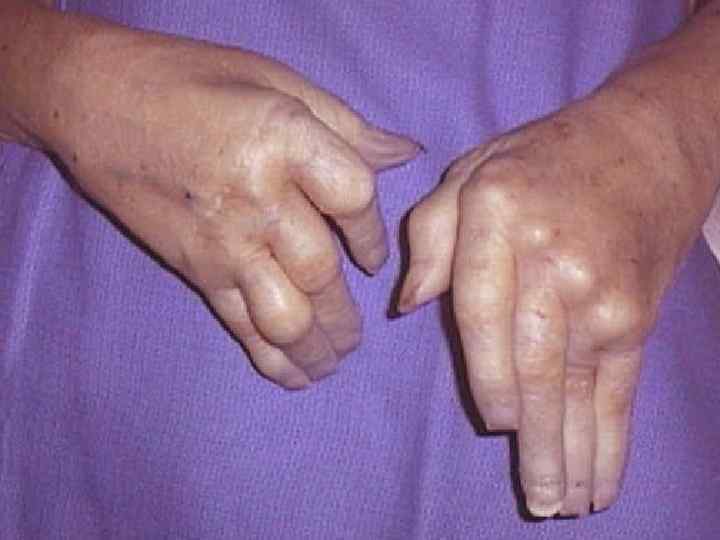
 Rheumatoid arthritis u More often is found in women and children; u Etiology – β-hemolytic streptococcus of В group u Rheumatoid factor – Ig М, G, A, is found in the blood u Small joints of hands and feet (more rarely) are affected
Rheumatoid arthritis u More often is found in women and children; u Etiology – β-hemolytic streptococcus of В group u Rheumatoid factor – Ig М, G, A, is found in the blood u Small joints of hands and feet (more rarely) are affected
 Anatomical pathology of rheumatoid arthritis 1. 2. 3 stages are distinguished: In the joint cavity - nebulous fluid, the cartilage is extant, areas of mucoid and fibrinoid swelling, necrosis, villi (compact casts) - «rice bodies» - are formed Villi overgrowth and cartilage destruction, excrescence of granulation tissue – formation of pannus Formation of fibro-osseous ankylosis
Anatomical pathology of rheumatoid arthritis 1. 2. 3 stages are distinguished: In the joint cavity - nebulous fluid, the cartilage is extant, areas of mucoid and fibrinoid swelling, necrosis, villi (compact casts) - «rice bodies» - are formed Villi overgrowth and cartilage destruction, excrescence of granulation tissue – formation of pannus Formation of fibro-osseous ankylosis
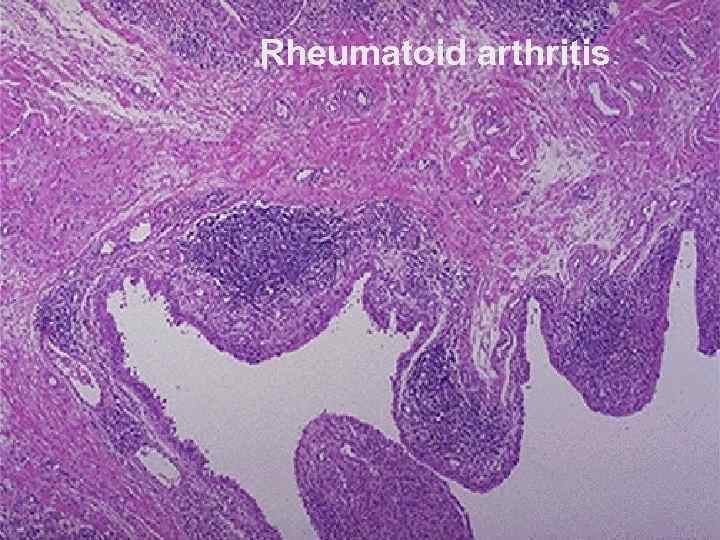 Rheumatoid arthritis Ревматоидный артрит
Rheumatoid arthritis Ревматоидный артрит

 SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
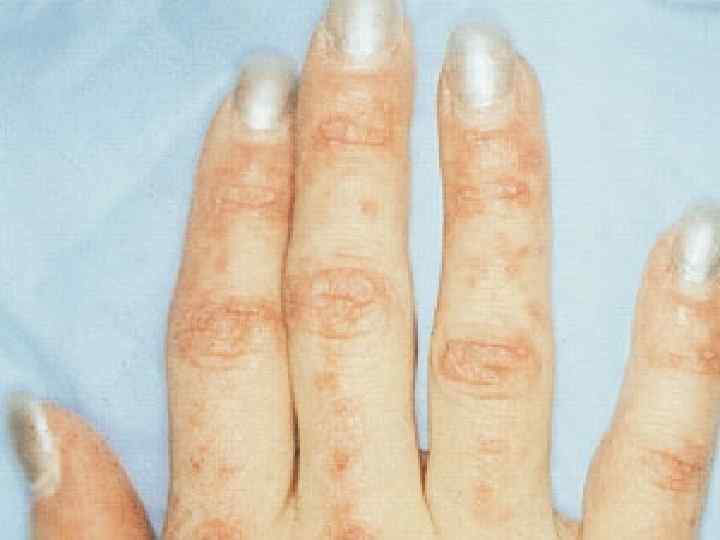
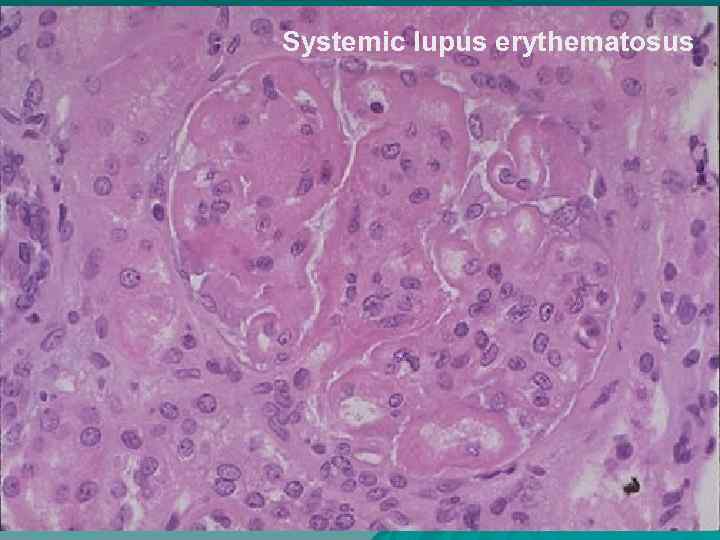
 Systemic lupus erythematosus u u u u More often is found in young women and children; Etiology – viruses; Skin, vessels and kidneys are affected; Skin – subacute dermatitis ( «butterfly» ); Kidneys- «lupous nephritis» ; Vessels – vasculitis of microcirculatory bed vessels; Heart – abacterial verrucous endocarditis.
Systemic lupus erythematosus u u u u More often is found in young women and children; Etiology – viruses; Skin, vessels and kidneys are affected; Skin – subacute dermatitis ( «butterfly» ); Kidneys- «lupous nephritis» ; Vessels – vasculitis of microcirculatory bed vessels; Heart – abacterial verrucous endocarditis.
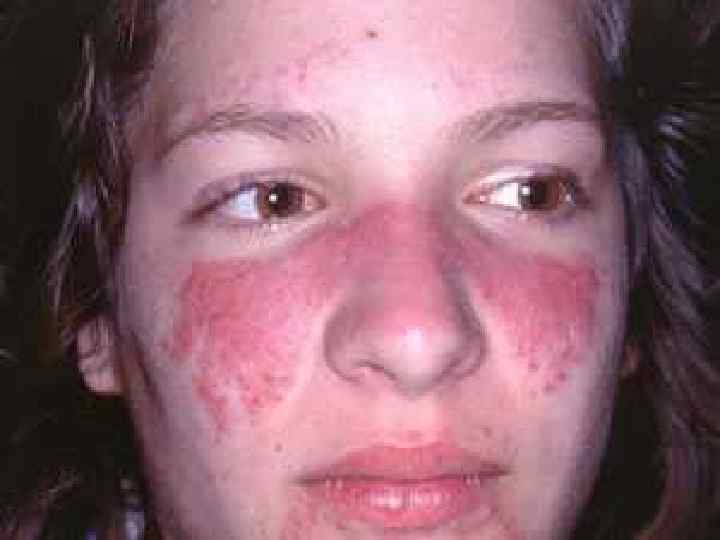
 Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
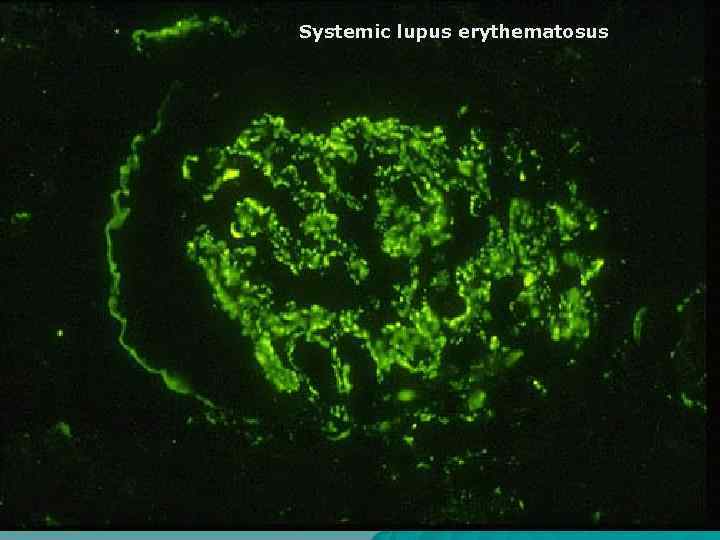 Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
 BECHTEREW`S DISEASE
BECHTEREW`S DISEASE
 Bechterew`s disease o o o Mainly young men suffer from it Etiology – heredity, clamydia Articuloligamentous apparatus of the spine is affected Formation of anchylosis, the spinal column is getting similar to «bamboo cane» Besides, the heart and lungs can be affected, with formation of sclerosis in these organs
Bechterew`s disease o o o Mainly young men suffer from it Etiology – heredity, clamydia Articuloligamentous apparatus of the spine is affected Formation of anchylosis, the spinal column is getting similar to «bamboo cane» Besides, the heart and lungs can be affected, with formation of sclerosis in these organs
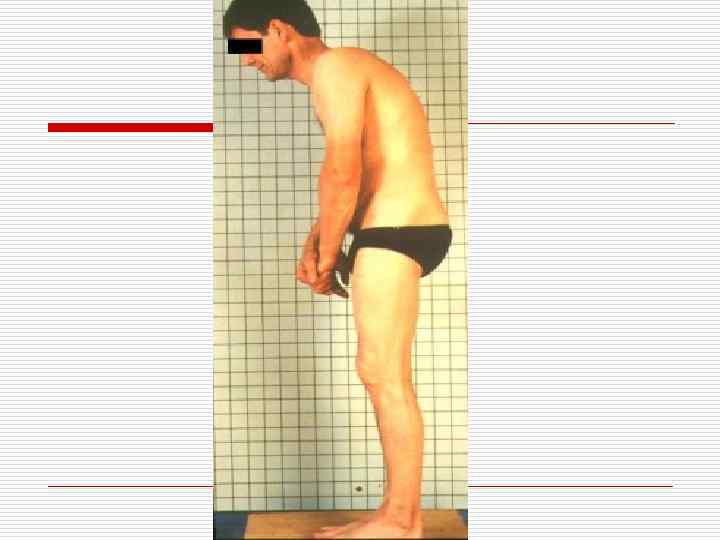
 SYSTEMIC SCLERODERMA
SYSTEMIC SCLERODERMA
 Systemic scleroderma o o o Etiology – heredity, viruses Skin and internal organs (joints, renal vessels, heart, lungs) are affected Formation of sclerosis with the following insufficiency of the organ, where sclerosis has developed to the maximum
Systemic scleroderma o o o Etiology – heredity, viruses Skin and internal organs (joints, renal vessels, heart, lungs) are affected Formation of sclerosis with the following insufficiency of the organ, where sclerosis has developed to the maximum
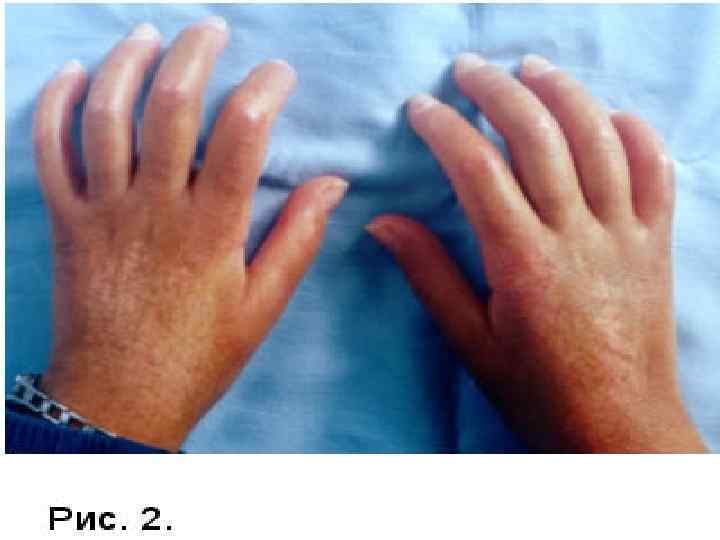
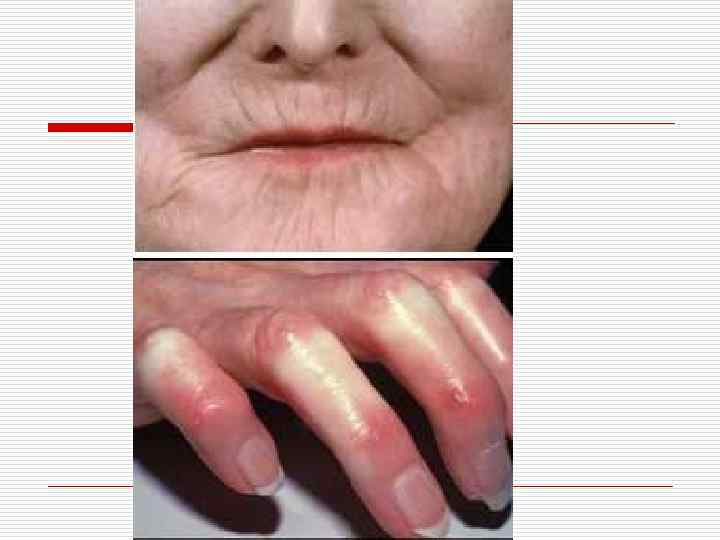
 NODULAR PERIARTERITIS
NODULAR PERIARTERITIS
 Nodular periarteritis o o Etiology is of unknown origin Arteries are affected: renal (90100%), coronary (88 -90%), mesenteric (60%), hepatic and cerebral (50%) The disease basis is vasculitis, outcome - sclerosis Course: acute, subacute and chronic
Nodular periarteritis o o Etiology is of unknown origin Arteries are affected: renal (90100%), coronary (88 -90%), mesenteric (60%), hepatic and cerebral (50%) The disease basis is vasculitis, outcome - sclerosis Course: acute, subacute and chronic
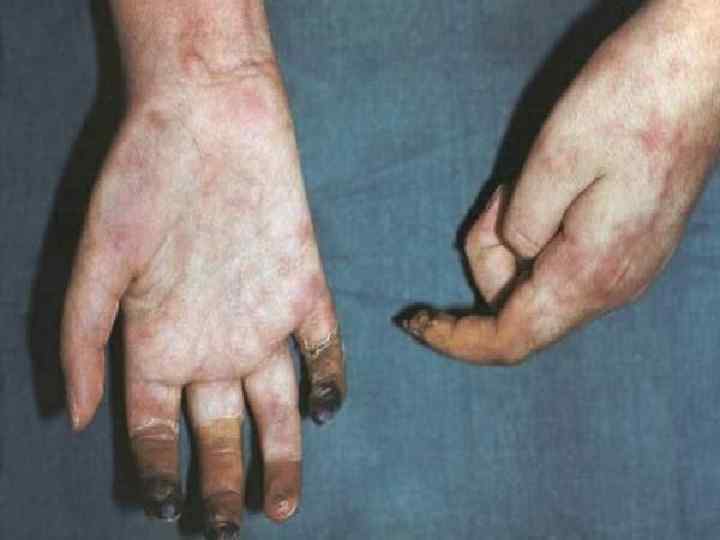
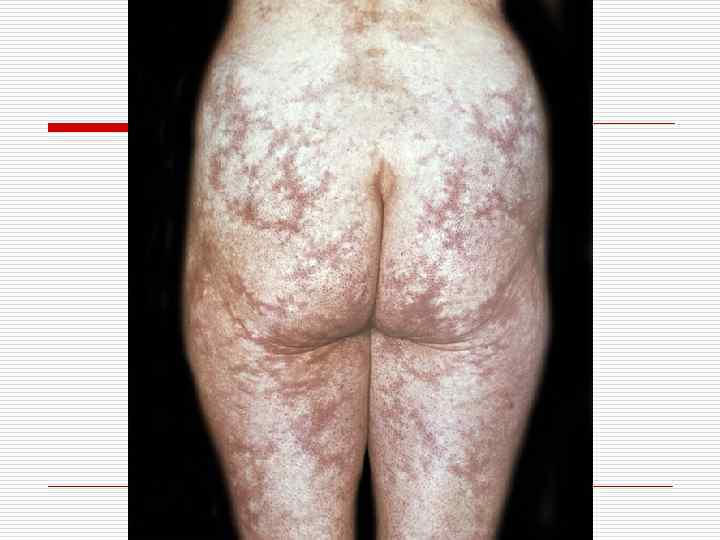
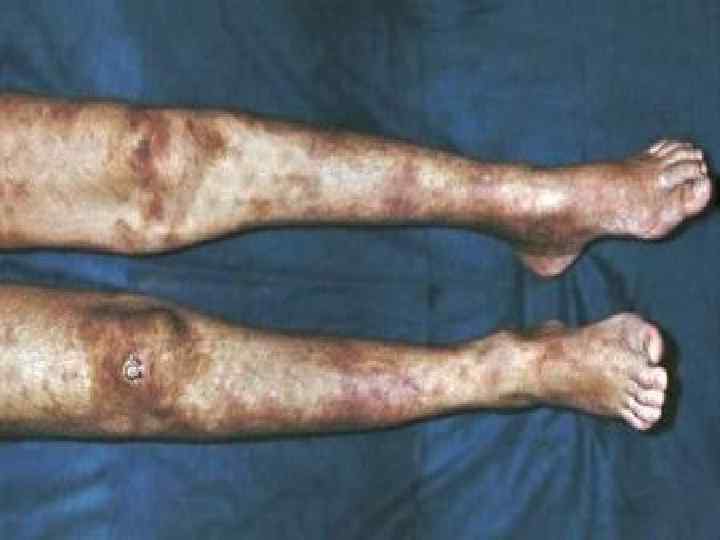
 DERMATOMYOSITIS
DERMATOMYOSITIS