SP_01_Lec_engl_00.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

System programming Lecture #1 Artamonov E. B.

Language С: the general characteristic, historical information, the basic advantages l Language С is the general purpose programming language. Occurrence of him is closely connected to creation of operational system UNIX for he was developed specially for this system and on him the most part of system software UNIX is written. However language С is not focused on work only in one operational system or by any concrete machine.

Basic properties of language С: a wide set of managing designs for the organization of cycles and the conditional transitions providing an opportunity of a spelling of flexible and well structured programs; l the big set of operators and operations, many of which suppose direct translation in a machine code; l variety of primitive types of the data, including an opportunity of management in length of integer and material variables; l presence of means for designing new aggregated types of the data; l

Basic properties of language С: an opportunity of direct work with machine addresses through the device of indexes; l presence of the preprocessor, allowing to make change to the text of the program directly ahead of its compilation; l block structure of a program code, an opportunity of work with various classes of memory and means for modular programming l

Preparation for performance and performance of programs l Language C concerns to number compiling programming languages. It means, that preparation for performance of the С-program includes the following stages: l l l input of the initial text of the program in a file by means of any editor of texts (the name of a file, as a rule, has standard expansion); compilation of the program, i. e. transformation of her description in the source language in a semantic equivalent on a computer language, named the objective module (the name of a file in which the result of compilation is located, usually has expansion "OBJ"); construction of the loading module ready to performance from objective modules, including modules from external libraries (the file containing the ready program, has a name with expansion "EXE").

Elements of language C THE ALPHABET Letters and figures - the big letters of the latin alphabet ABCDEFGHIJKLM NOPQRSTUVWXYZ - small letters of the latin alphabet abcdefghijklm nopqrstuvwxyz l decimal figures 0123456789 l

Elements of language C THE ALPHABET Special symbols blank! " * % and ' () * +, -. /: ; <=>? [] ^ _ {|} ~ l Names of objects programs (identifiers) l Identifiers in language С are sequences of letters and the figures, beginning with the letter, and the symbol of underlining (_) is considered by the compiler as the letter. The big and small letters of the latin alphabet are considered various. Length of the identifier be formal can any.

Elements of language C Key words are the predetermined identifiers having special values. Names of any objects of the program should not coincide with the following reserved key words: l types of the data char float short typedef void double int signed union enum long struct unsigned l classes of memory auto extern register static l

Elements of language C Key words operators break default for return while case do goto sizeof continue else if switch l special const far huge pascal cdecl fortran near volatile l

Elements of language C Comments are understood as the sequences of symbols ignored by the compiler. Comments have the following form: /* Characters */ l where Characters there is an any combination of any printed symbols ASCII. l

Elements of language C Constants l Constants in language С can be numbers (the whole and material), symbols and lines of symbols which is allowable to use in the program in sense of their values. Value of any constant cannot be changed during work of the program. Special instructions of language enable to give to constants of any type symbolical names.

Elements of language C Operations and expressions l It is necessary to understand the actions which are carried out by the program above objects determined in her as operations. For a designation of operations some standard combinations of special symbols from the alphabet of language are used. The objects of the program participating in operation, refer to as operands. Any combination of one or greater number of operands and symbols of the operations, giving a unique value, forms expression. Any expression, coming to an end a semicolon, is the operator. The set of all operations of language С is convenient for dividing into eight following groups:

Elements of language C arithmetic operations + - * / % ++-l operations of the relation ==! = <> <=> = l logic operations ! || && l bit-by-bit operations ~ <>> & | ^ l operations of giving = + = - = * = / = % = <<=>> = and = ^ = | = l
![Elements of language C operations above files [] l operations above structures and associations Elements of language C operations above files [] l operations above structures and associations](https://present5.com/presentation/-101139455_437940004/image-14.jpg)
Elements of language C operations above files [] l operations above structures and associations -> l other operations ? : , syzeof (type specifier) () l

Elements of language C Operators l The elementary operator of language С is any expression, coming to an end a semicolon. In particular, separately worth semicolon is interpreted by the compiler as the zero - operator. The most significant group of operators is formed with instructions (operators) of management of process of performance of the program. To them concern:

Elements of language C - operators of a cycle l for (<init-expr>; <cond-expr>; <loop-expr>) statement; l while (expression) statement; l do statement while (expression);
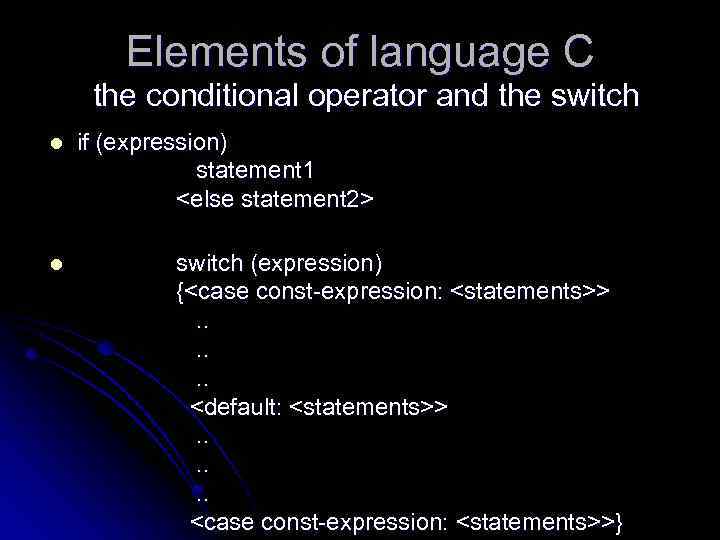
Elements of language C the conditional operator and the switch l l if (expression) statement 1 <else statement 2> switch (expression) {<case const-expression: <statements>>. . . <default: <statements>>. . . <case const-expression: <statements>>}

Elements of language C operators of transfer of management l goto break continue return Here expression there is an any correct expression of language С (C++), and through statement it is designated simple or compound the operator whom, in particular, can be and any operator of management (see lower). The last means, that the investment of operators of management each other is allowable. Elements of designs of language, prisoners in angular brackets (<>), are not obligatory and can be lowered. One or several operators made in braces, the compound operator or the block form. The semicolon after a closing bracket thus is not put.

Elements of language C Descriptions l Descriptions in language С are the lines of the program determining names and the characteristics of functions, variable, types and the symbolical constants used in the program. General structure of the program l Any program in language С represents set of the functions which are carrying out the basic work on realization of some algorithm. Each of these functions, in turn, is an independent set of descriptions and the operators made between heading of function and her end. That function with which performance of the program begins, refers to as the main function. She should have the predetermined name main ().
SP_01_Lec_engl_00.ppt