545590e6901b1155ef309746c82a1916.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 System Architecture Issues CSC 426
System Architecture Issues CSC 426
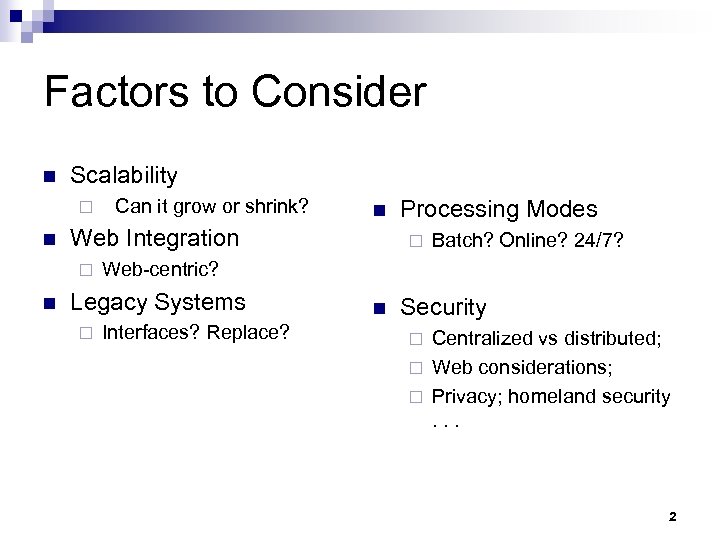 Factors to Consider n Scalability ¨ n n Web Integration ¨ n Can it grow or shrink? ¨ Batch? Online? 24/7? Web-centric? Legacy Systems ¨ Processing Modes Interfaces? Replace? n Security Centralized vs distributed; ¨ Web considerations; ¨ Privacy; homeland security. . . ¨ 2
Factors to Consider n Scalability ¨ n n Web Integration ¨ n Can it grow or shrink? ¨ Batch? Online? 24/7? Web-centric? Legacy Systems ¨ Processing Modes Interfaces? Replace? n Security Centralized vs distributed; ¨ Web considerations; ¨ Privacy; homeland security. . . ¨ 2
 The Big Picture Mainframe/centralized system n Stand-alone n LANs, WANs n 3
The Big Picture Mainframe/centralized system n Stand-alone n LANs, WANs n 3
 Client/Server vs. Mainframe – Let’s Not Be Biased. . . n Mainframes: ¨ ¨ n The Good ¨ ¨ n Centralized control. Single vendor (less finger-pointing). The Bad ¨ ¨ n Slow and stupid? Inflexible? Constrains the user (is this always bad? ). Single vendor (less flexibility). The Ugly ¨ Less sophisticated user interface. 4
Client/Server vs. Mainframe – Let’s Not Be Biased. . . n Mainframes: ¨ ¨ n The Good ¨ ¨ n Centralized control. Single vendor (less finger-pointing). The Bad ¨ ¨ n Slow and stupid? Inflexible? Constrains the user (is this always bad? ). Single vendor (less flexibility). The Ugly ¨ Less sophisticated user interface. 4
 Variations on the Client/Server Theme Database server n Transaction server n Object server n Web server n 5
Variations on the Client/Server Theme Database server n Transaction server n Object server n Web server n 5
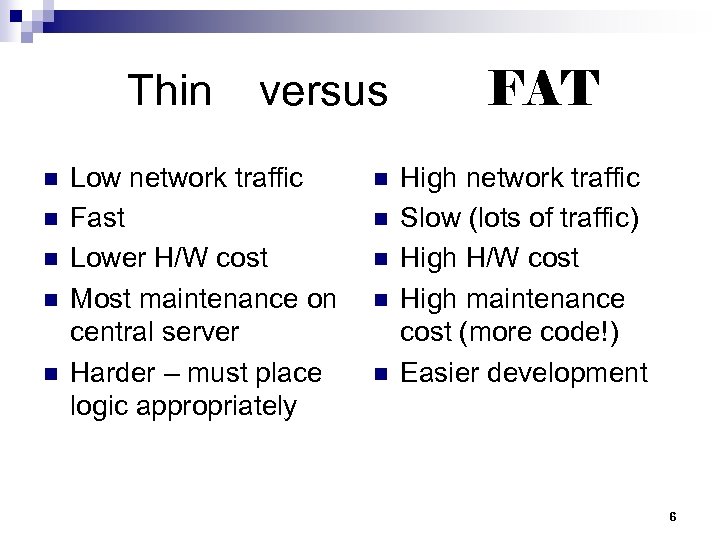 Thin n n versus Low network traffic Fast Lower H/W cost Most maintenance on central server Harder – must place logic appropriately n n n FAT High network traffic Slow (lots of traffic) High H/W cost High maintenance cost (more code!) Easier development 6
Thin n n versus Low network traffic Fast Lower H/W cost Most maintenance on central server Harder – must place logic appropriately n n n FAT High network traffic Slow (lots of traffic) High H/W cost High maintenance cost (more code!) Easier development 6
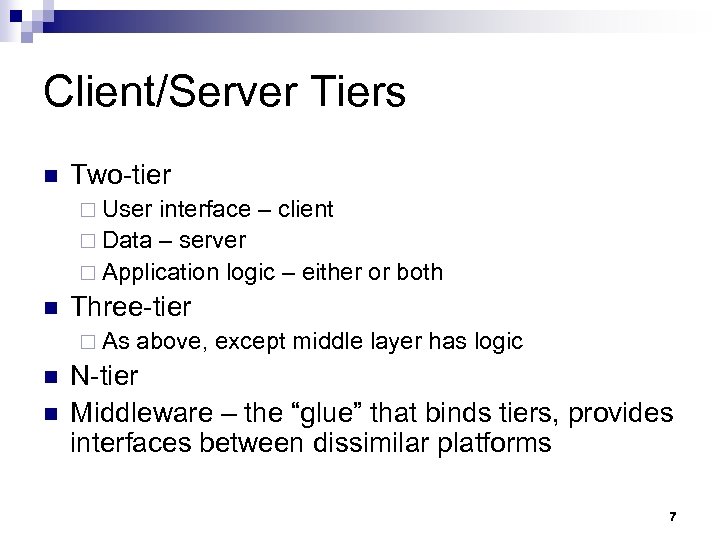 Client/Server Tiers n Two-tier ¨ User interface – client ¨ Data – server ¨ Application logic – either or both n Three-tier ¨ As n n above, except middle layer has logic N-tier Middleware – the “glue” that binds tiers, provides interfaces between dissimilar platforms 7
Client/Server Tiers n Two-tier ¨ User interface – client ¨ Data – server ¨ Application logic – either or both n Three-tier ¨ As n n above, except middle layer has logic N-tier Middleware – the “glue” that binds tiers, provides interfaces between dissimilar platforms 7
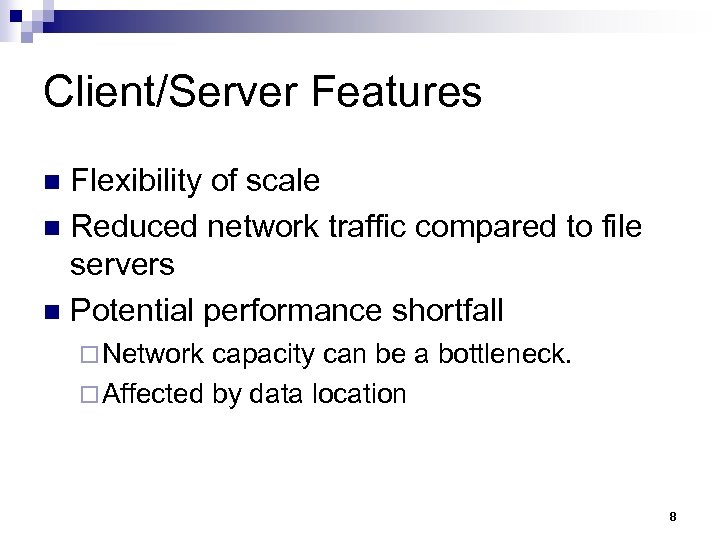 Client/Server Features Flexibility of scale n Reduced network traffic compared to file servers n Potential performance shortfall n ¨ Network capacity can be a bottleneck. ¨ Affected by data location 8
Client/Server Features Flexibility of scale n Reduced network traffic compared to file servers n Potential performance shortfall n ¨ Network capacity can be a bottleneck. ¨ Affected by data location 8
 Next: The Internet’s Effect on System Architecture
Next: The Internet’s Effect on System Architecture
 The Web: A Different Environment n Internet ¨ Allows even a small, local business to establish a world-wide presence. ¨ Lots of bang for the buck. n Intranet ¨ Facilitates internal systems and communications. 10
The Web: A Different Environment n Internet ¨ Allows even a small, local business to establish a world-wide presence. ¨ Lots of bang for the buck. n Intranet ¨ Facilitates internal systems and communications. 10
 Choices in Internet Commerce n Site preparation and maintenance. ¨ Build your own. ¨ Purchase packaged solution. ¨ Pay for service from e-commerce service provider. n Hosting. ¨ Internal ¨ External. 11
Choices in Internet Commerce n Site preparation and maintenance. ¨ Build your own. ¨ Purchase packaged solution. ¨ Pay for service from e-commerce service provider. n Hosting. ¨ Internal ¨ External. 11
 Networks n Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model ¨ Seven functional layers. ¨ Logical model. 12
Networks n Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model ¨ Seven functional layers. ¨ Logical model. 12
 Network Topologies Hierarchical n Star n Bus n Ring n 13
Network Topologies Hierarchical n Star n Bus n Ring n 13
 Network Topologies n Hierarchical ¨ One computer controls computers at the next lower level. ¨ At each lower level in the hierarchy, each computer on that level controls computers at the next level. 14
Network Topologies n Hierarchical ¨ One computer controls computers at the next lower level. ¨ At each lower level in the hierarchy, each computer on that level controls computers at the next level. 14
 Network Topologies q Star q A hub computer controls the network and all traffic flows through it. 15
Network Topologies q Star q A hub computer controls the network and all traffic flows through it. 15
 Network Topologies n Bus All devices are attached to a single bus (communication channel). ¨ Two-way traffic. ¨ 16
Network Topologies n Bus All devices are attached to a single bus (communication channel). ¨ Two-way traffic. ¨ 16
 Network Topologies ■ Ring ■ Devices are connected to the same communication channel. ■ One-way traffic. ■ A failed device stops traffic. 17
Network Topologies ■ Ring ■ Devices are connected to the same communication channel. ■ One-way traffic. ■ A failed device stops traffic. 17
 Network Protocols ■ Protocol? ■ An agreed-upon method of controlling data transmission. ■ Popular type: TCP/IP (What does this mean? ) 18
Network Protocols ■ Protocol? ■ An agreed-upon method of controlling data transmission. ■ Popular type: TCP/IP (What does this mean? ) 18
 Wireless n IEEE Protocols ¨ 802. 11 b, 802. 11 g Security issues. n Very flexible. n Relatively inexpensive to set up a network. n 19
Wireless n IEEE Protocols ¨ 802. 11 b, 802. 11 g Security issues. n Very flexible. n Relatively inexpensive to set up a network. n 19
 More Choices for the Designer! Oh, for the simple mainframe world. . . n Systems analyst n ¨ More complex knowledge and skill sets required. ¨ More flexibility in solutions. 20
More Choices for the Designer! Oh, for the simple mainframe world. . . n Systems analyst n ¨ More complex knowledge and skill sets required. ¨ More flexibility in solutions. 20


