b388697a54d61c201a08657a3615b23e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
SYNTHESIS BY EXAMPLE Creation of sound synthesis algorithms using evolutionary methods By: Ricardo A. García rago@media. mit. edu MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group © 2001

INTRODUCTION z How is that sound coming out of your soundcard being generated? z Is that a real violin? z What kind of controls do we have over it? • pitch, length, other performance parameters • sound attributes: brightness, harmonic content, etc The questions: z How are those sound synthesis algorithms conceived? z Can this design process be automated? MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
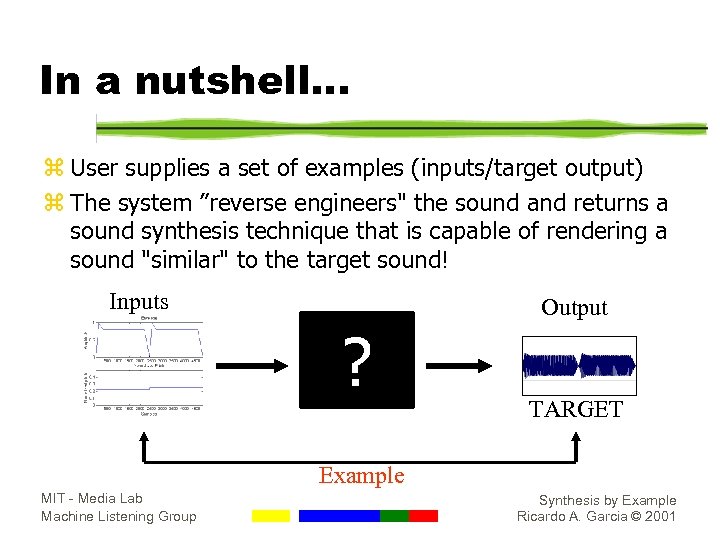
In a nutshell. . . z User supplies a set of examples (inputs/target output) z The system ”reverse engineers" the sound and returns a sound synthesis technique that is capable of rendering a sound "similar" to the target sound! Inputs Output ? TARGET Example MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
Talk outline z Introduction z Sound Synthesizers z Design of Sound Synthesis Techniques (SST) z Proposed approach for design z Genetic Programming z Automatic Generation of Sound Synthesizers (AGe. SS) system z Examples MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
What is a sound synthesizer? z Any method or device used to produce sound z Sound Synthesis Technique (SST): Algorithm that produces sound samples, usually implemented in a digital computer x. Inputs: – internal parameters (init time) – control signals (time varying) x. Output: – sound samples (Waveform) z Structured audio, symbolic representation Model analysis MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
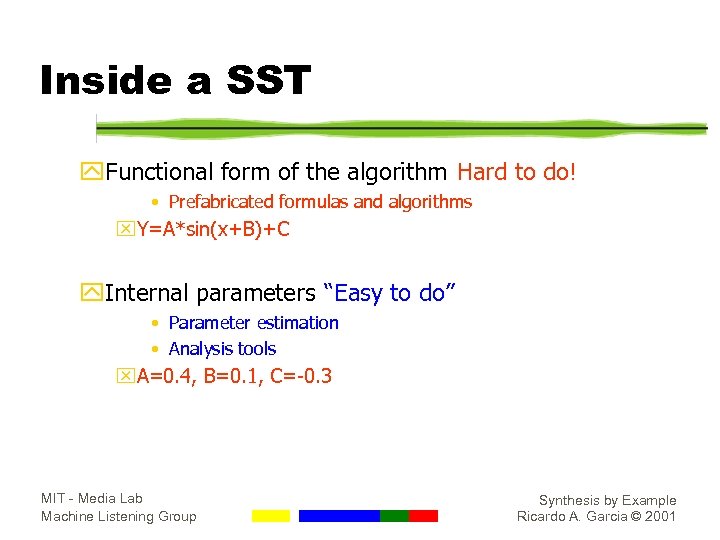
Inside a SST y. Functional form of the algorithm Hard to do! • Prefabricated formulas and algorithms x. Y=A*sin(x+B)+C y. Internal parameters “Easy to do” • Parameter estimation • Analysis tools x. A=0. 4, B=0. 1, C=-0. 3 MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
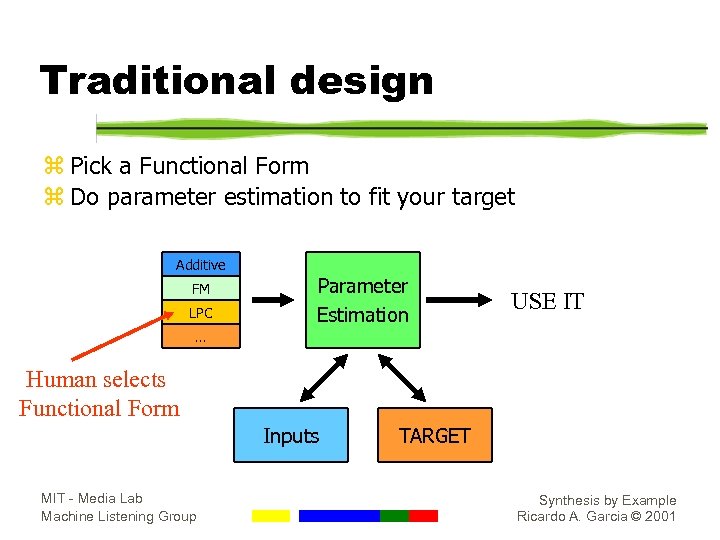
Traditional design z Pick a Functional Form z Do parameter estimation to fit your target Additive FM LPC Parameter Estimation USE IT … Human selects Functional Form Inputs MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group TARGET Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
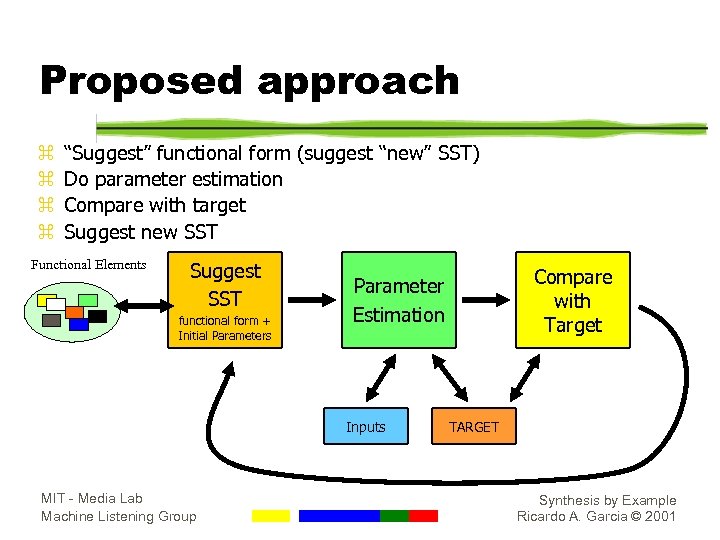
Proposed approach z z “Suggest” functional form (suggest “new” SST) Do parameter estimation Compare with target Suggest new SST Functional Elements Suggest SST functional form + Initial Parameters Inputs MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Compare with Target Parameter Estimation TARGET Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
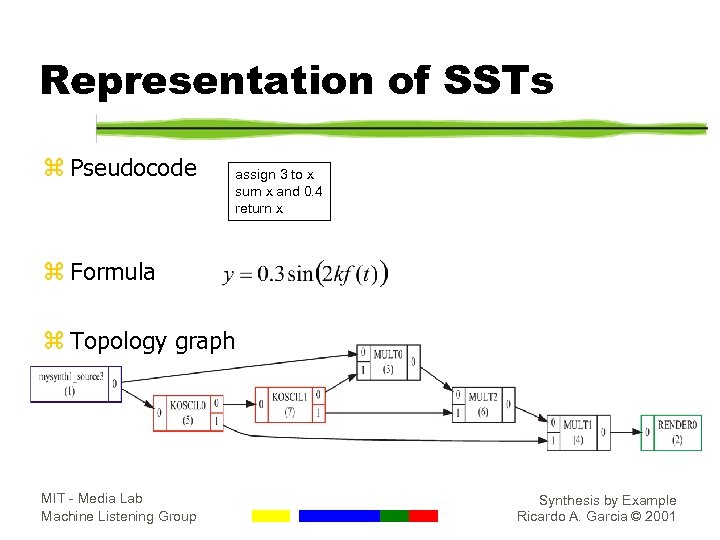
Representation of SSTs z Pseudocode assign 3 to x sum x and 0. 4 return x z Formula z Topology graph MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
SST space z. SST space: all the possible valid combinations of a set of functional elements and their connections! HUGE! z. Hypothesis: ”given a set of inputs, target and fitness metrics, it is possible to find the functional-form and internal parameters of a SST capable of synthesizing a sound “close” to the target”. MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
Design of SST as a search z Specs: x. Inputs EXAMPLE xoutput (TARGET) x. Fitness metric z Search: find a point (SST, Functional form + internal parameters) that fulfills the specs MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
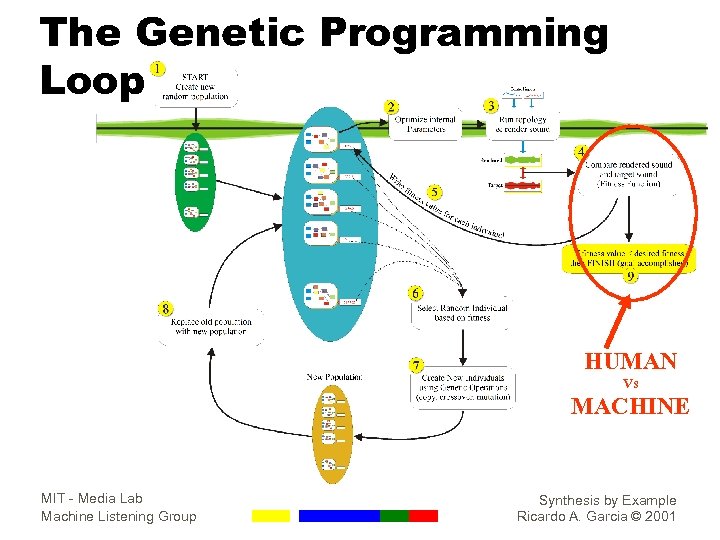
The Genetic Programming Loop HUMAN Vs MACHINE MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
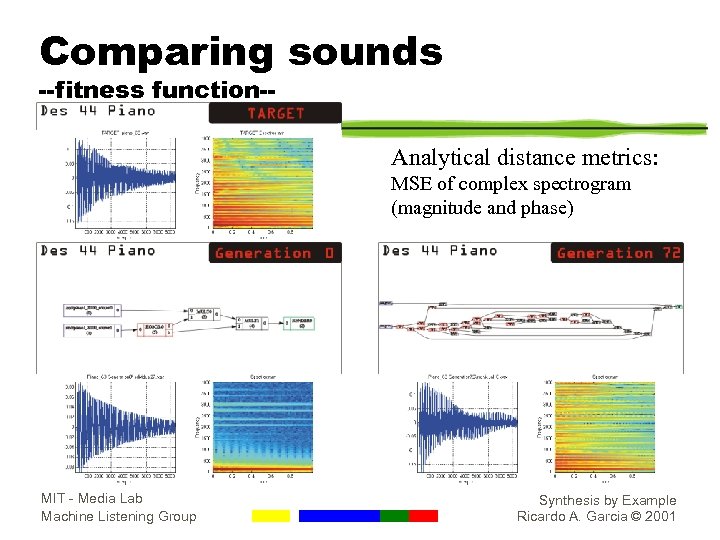
Comparing sounds --fitness function-- Analytical distance metrics: MSE of complex spectrogram (magnitude and phase) MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001

Perceptual Fitness Function z A perceptual distance metrics x. Perceptually relevant components: full error x. Above masking threshold: error up to M. T. x. Below masking threshold: no error MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
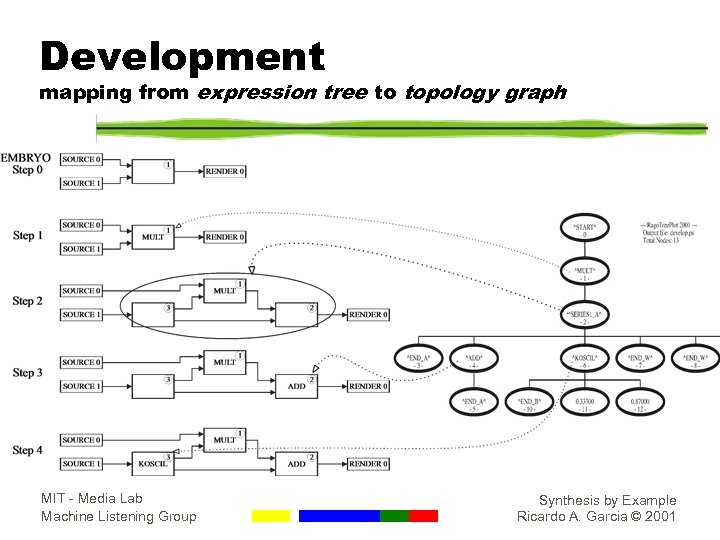
Development mapping from expression tree to topology graph MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
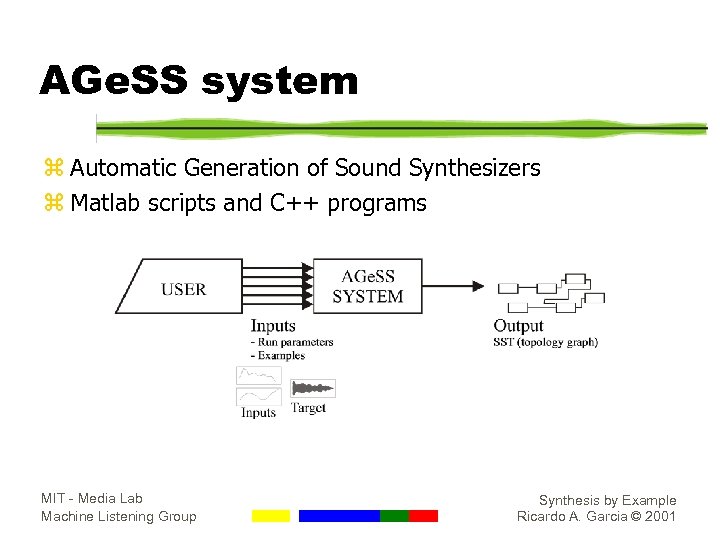
AGe. SS system z Automatic Generation of Sound Synthesizers z Matlab scripts and C++ programs MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
Examples z. A synthetic tone (des 35 comp 2. avi) z. A piano note (des 44 comp 2. avi) z. FM synthesizer (chow 727. avi) MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
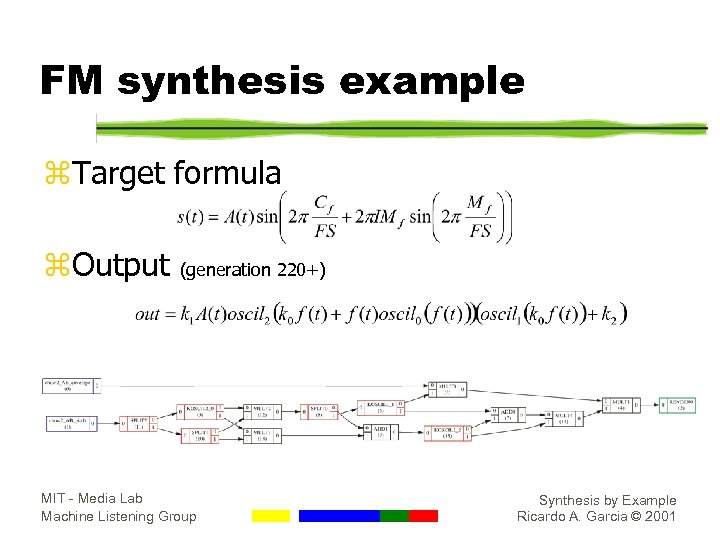
FM synthesis example z. Target formula z. Output (generation 220+) MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
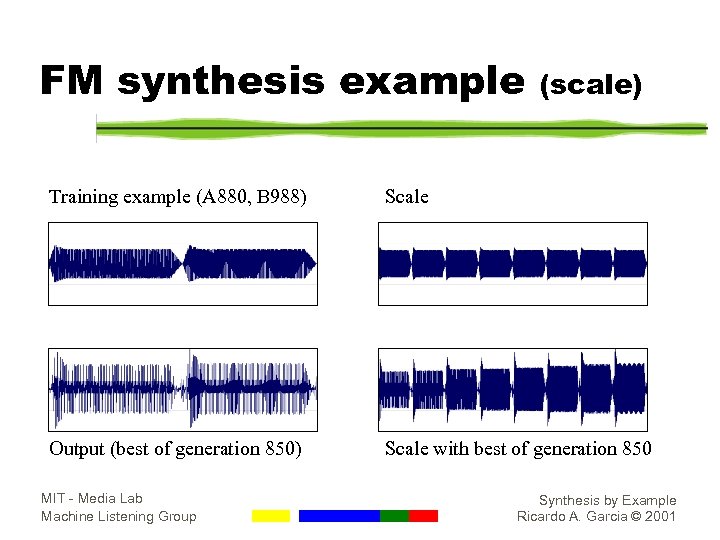
FM synthesis example (scale) Training example (A 880, B 988) Scale Output (best of generation 850) Scale with best of generation 850 MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001

For more information… Ricardo A. Garcia Email: rago@media. mit. edu Web: http: //www. media. mit. edu/~rago MIT - Media Lab Machine Listening Group Synthesis by Example Ricardo A. Garcia © 2001
b388697a54d61c201a08657a3615b23e.ppt