311e4b5e9e2ac9c43be06b0b0433bbad.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Symposium on Knowledge Management – Towards Organisational Excellence, 8 th July 05 Development and Application of Knowledge Management in CLP Power Paul Poon Director – Power Systems CLP Power Hong Kong Limited 1
Symposium on Knowledge Management – Towards Organisational Excellence, 8 th July 05 Development and Application of Knowledge Management in CLP Power Paul Poon Director – Power Systems CLP Power Hong Kong Limited 1
 Agenda l l l Business Background Needs for KM KM Vision, Mission & Strategies Current Developments and Applications Critical Success Factors & Experiences Way Forward 2
Agenda l l l Business Background Needs for KM KM Vision, Mission & Strategies Current Developments and Applications Critical Success Factors & Experiences Way Forward 2
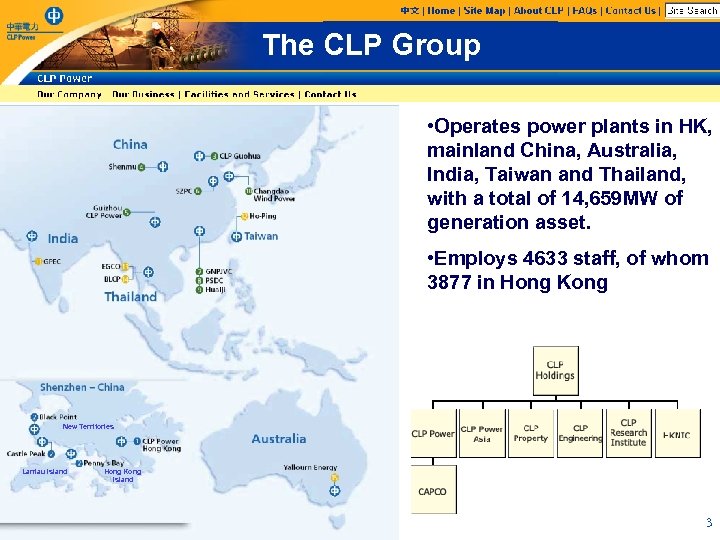 The CLP Group • Operates power plants in HK, mainland China, Australia, India, Taiwan and Thailand, with a total of 14, 659 MW of generation asset. • Employs 4633 staff, of whom 3877 in Hong Kong New Territories Lantau Island Hong Kong Island 3
The CLP Group • Operates power plants in HK, mainland China, Australia, India, Taiwan and Thailand, with a total of 14, 659 MW of generation asset. • Employs 4633 staff, of whom 3877 in Hong Kong New Territories Lantau Island Hong Kong Island 3
 CLP Power in Hong Kong Electricity Supply since 1903 4
CLP Power in Hong Kong Electricity Supply since 1903 4
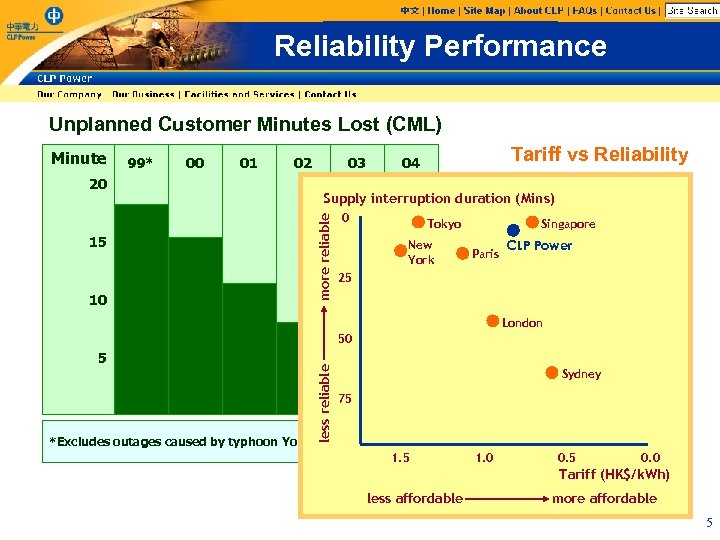 Reliability Performance Unplanned Customer Minutes Lost (CML) 99* 00 01 02 20 15 10 03 Tariff vs Reliability 04 Supply interruption duration (Mins) more reliable Minute 0 Tokyo New York Singapore Paris CLP Power 25 London 5 *Excludes outages caused by typhoon York less reliable 50 Sydney 75 1. 0 0. 5 0. 0 Tariff (HK$/k. Wh) less affordable more affordable 5
Reliability Performance Unplanned Customer Minutes Lost (CML) 99* 00 01 02 20 15 10 03 Tariff vs Reliability 04 Supply interruption duration (Mins) more reliable Minute 0 Tokyo New York Singapore Paris CLP Power 25 London 5 *Excludes outages caused by typhoon York less reliable 50 Sydney 75 1. 0 0. 5 0. 0 Tariff (HK$/k. Wh) less affordable more affordable 5
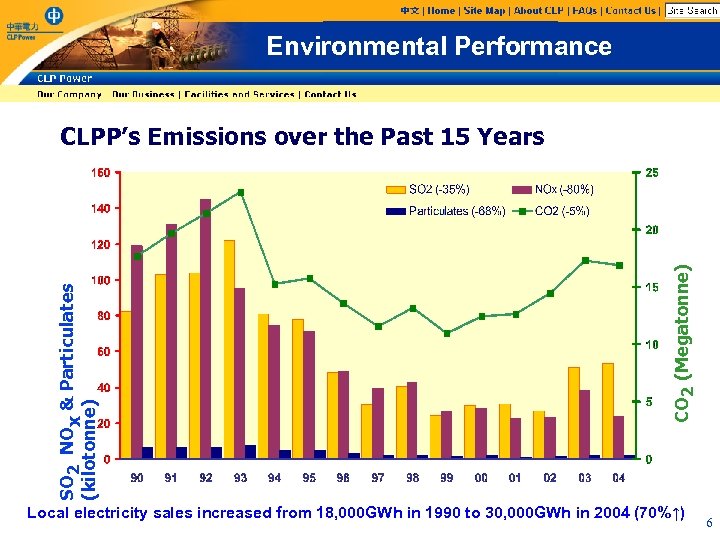 Environmental Performance CO 2 (Megatonne) SO 2 NOx & Particulates (kilotonne) CLPP’s Emissions over the Past 15 Years Local electricity sales increased from 18, 000 GWh in 1990 to 30, 000 GWh in 2004 (70%↑) 6
Environmental Performance CO 2 (Megatonne) SO 2 NOx & Particulates (kilotonne) CLPP’s Emissions over the Past 15 Years Local electricity sales increased from 18, 000 GWh in 1990 to 30, 000 GWh in 2004 (70%↑) 6
 Other Key Business Performance • Productivity: increased by 127% in the past 10 years • Tariff: frozen since 1998 and rebated HK$3 B in the past 6 years • Overall winner of the HKMA Quality Award in 2004 • Best Managed Companies Poll 2004 (HK Region) – by Asiamoney • Corporate Governance Asia Recognition Awards 2004 – by Corporate Governance Asia Journal 7
Other Key Business Performance • Productivity: increased by 127% in the past 10 years • Tariff: frozen since 1998 and rebated HK$3 B in the past 6 years • Overall winner of the HKMA Quality Award in 2004 • Best Managed Companies Poll 2004 (HK Region) – by Asiamoney • Corporate Governance Asia Recognition Awards 2004 – by Corporate Governance Asia Journal 7
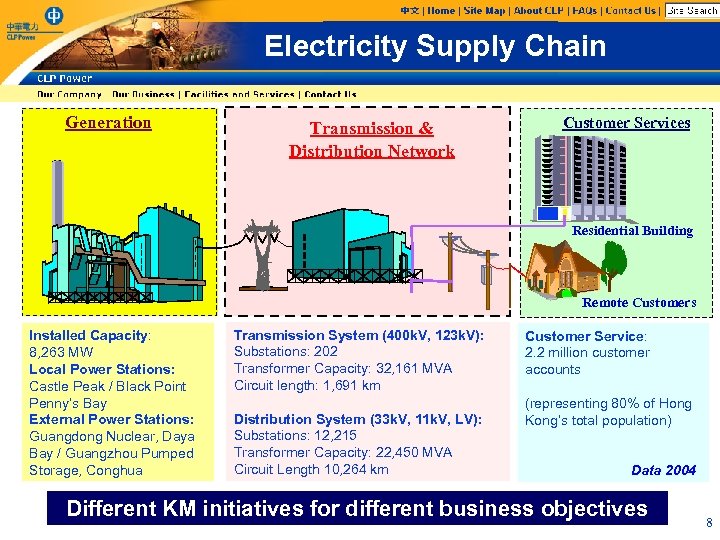 Electricity Supply Chain Generation Transmission & Distribution Network Customer Services Residential Building Remote Customers Installed Capacity: 8, 263 MW Local Power Stations: Castle Peak / Black Point Penny’s Bay External Power Stations: Guangdong Nuclear, Daya Bay / Guangzhou Pumped Storage, Conghua Transmission System (400 k. V, 123 k. V): Substations: 202 Transformer Capacity: 32, 161 MVA Circuit length: 1, 691 km Distribution System (33 k. V, 11 k. V, LV): Substations: 12, 215 Transformer Capacity: 22, 450 MVA Circuit Length 10, 264 km Customer Service: 2. 2 million customer accounts (representing 80% of Hong Kong’s total population) Data 2004 Different KM initiatives for different business objectives 8
Electricity Supply Chain Generation Transmission & Distribution Network Customer Services Residential Building Remote Customers Installed Capacity: 8, 263 MW Local Power Stations: Castle Peak / Black Point Penny’s Bay External Power Stations: Guangdong Nuclear, Daya Bay / Guangzhou Pumped Storage, Conghua Transmission System (400 k. V, 123 k. V): Substations: 202 Transformer Capacity: 32, 161 MVA Circuit length: 1, 691 km Distribution System (33 k. V, 11 k. V, LV): Substations: 12, 215 Transformer Capacity: 22, 450 MVA Circuit Length 10, 264 km Customer Service: 2. 2 million customer accounts (representing 80% of Hong Kong’s total population) Data 2004 Different KM initiatives for different business objectives 8
 Needs for KM l Unique business nature: Ø Ø l Unique expertise - one of the 2 power utilities in HK; no power system equipment suppliers in HK Knowledge intensive organisation - not easy to replenish experienced staff from the market Prepare for future growth and challenges: Ø Ø Ø Expedite job rotations program for staff development and growth Experienced staff retirement - require systematic approach to retain critical knowledge Adoption of new advanced technologies need to acquire knowledge (breadth & depth) in a short time 9
Needs for KM l Unique business nature: Ø Ø l Unique expertise - one of the 2 power utilities in HK; no power system equipment suppliers in HK Knowledge intensive organisation - not easy to replenish experienced staff from the market Prepare for future growth and challenges: Ø Ø Ø Expedite job rotations program for staff development and growth Experienced staff retirement - require systematic approach to retain critical knowledge Adoption of new advanced technologies need to acquire knowledge (breadth & depth) in a short time 9
 We have a long tradition of knowledge sharing…. KM activities in the past: l l l l Instructions, codes of practices, policies Electronic Document Management System Quality Circle Convention (QCC) Lessons Learnt/ Project Review Documents E-learning Experience sharing Sessions Best Practices Benchmarking …. 10
We have a long tradition of knowledge sharing…. KM activities in the past: l l l l Instructions, codes of practices, policies Electronic Document Management System Quality Circle Convention (QCC) Lessons Learnt/ Project Review Documents E-learning Experience sharing Sessions Best Practices Benchmarking …. 10
 PSBG KM Strategies Now, we adopt a more systematic and integrated approach in KM “To be a leading organization in managing the knowledge resources to assure effective delivery of electrical energy” KM Vision & Mission Key Strategies l l Identify & Retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge 11
PSBG KM Strategies Now, we adopt a more systematic and integrated approach in KM “To be a leading organization in managing the knowledge resources to assure effective delivery of electrical energy” KM Vision & Mission Key Strategies l l Identify & Retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge 11
 Current Developments and Applications 12
Current Developments and Applications 12
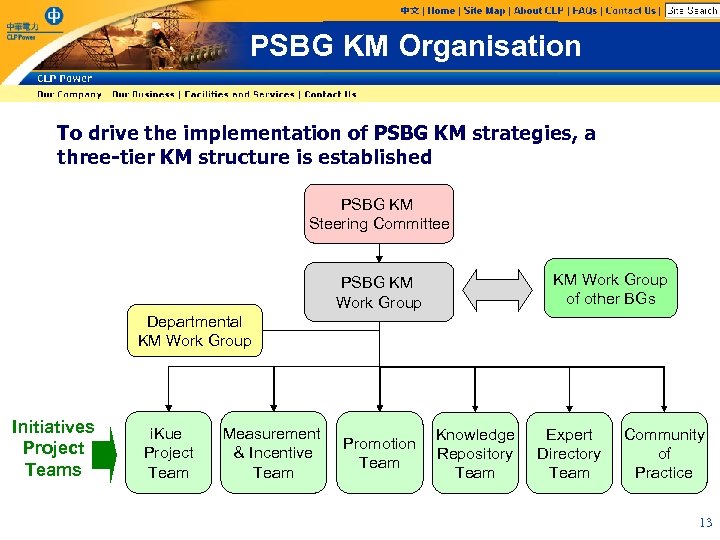 PSBG KM Organisation To drive the implementation of PSBG KM strategies, a three-tier KM structure is established PSBG KM Steering Committee KM Work Group of other BGs PSBG KM Work Group Departmental KM Work Group Initiatives Project Teams i. Kue Project Team Measurement & Incentive Team Promotion Team Knowledge Repository Team Expert Directory Team Community of Practice 13
PSBG KM Organisation To drive the implementation of PSBG KM strategies, a three-tier KM structure is established PSBG KM Steering Committee KM Work Group of other BGs PSBG KM Work Group Departmental KM Work Group Initiatives Project Teams i. Kue Project Team Measurement & Incentive Team Promotion Team Knowledge Repository Team Expert Directory Team Community of Practice 13
 i. Kue Project Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Project Scope: • Capture mission critical knowledge • Establish 10 critical knowledge themes Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge 14
i. Kue Project Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Project Scope: • Capture mission critical knowledge • Establish 10 critical knowledge themes Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge 14
 i. Kue Project Identify and retain critical knowledge Project Scope: • • Project Schedule: 2004 ~ 2007 Leverage on i. Kue platform Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge 15
i. Kue Project Identify and retain critical knowledge Project Scope: • • Project Schedule: 2004 ~ 2007 Leverage on i. Kue platform Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge 15
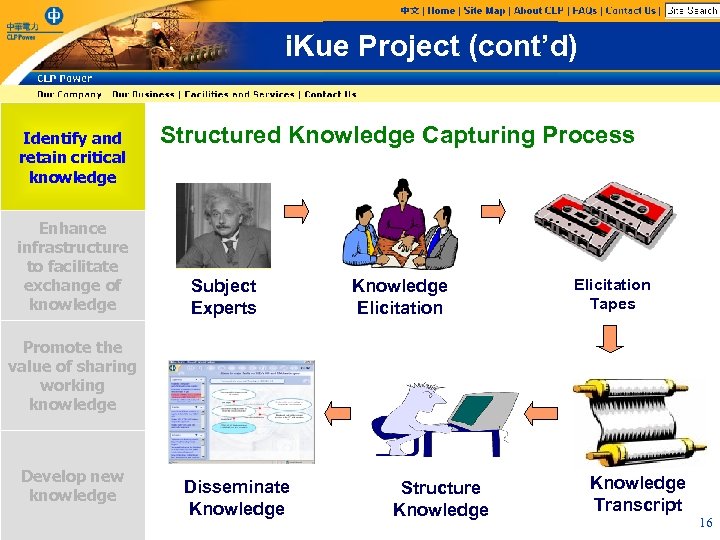 i. Kue Project (cont’d) Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Structured Knowledge Capturing Process Subject Experts Knowledge Elicitation Tapes Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge Disseminate Knowledge Structure Knowledge Transcript 16
i. Kue Project (cont’d) Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Structured Knowledge Capturing Process Subject Experts Knowledge Elicitation Tapes Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge Disseminate Knowledge Structure Knowledge Transcript 16
 i. Kue Project (cont’d) Identify and retain critical knowledge How can i. Kue be used? Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Current i. Kue Project status • 1 knowledge theme rolled out in 2004 • 3 knowledge themes being developed in 2005 Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge 17
i. Kue Project (cont’d) Identify and retain critical knowledge How can i. Kue be used? Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Current i. Kue Project status • 1 knowledge theme rolled out in 2004 • 3 knowledge themes being developed in 2005 Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge 17
 Community of Practices Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge • Formation of Community of Practices (Co. P) to review and update the knowledge themes • Maintain the contents accurate and include upto-date info into the knowledge themes • First Co. P established in Q 1 2005 Develop new knowledge 18
Community of Practices Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge • Formation of Community of Practices (Co. P) to review and update the knowledge themes • Maintain the contents accurate and include upto-date info into the knowledge themes • First Co. P established in Q 1 2005 Develop new knowledge 18
 KM Portal Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge Continue to upgrade and maintain KM Portal • Rolled out in July 04 • Single entry point for various knowledge items • Contents arranged in logical structure for easy navigation and information retrieval • • Provides website search engine and glossary Continuous improvement based on the results of the knowledge audit 19
KM Portal Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge Continue to upgrade and maintain KM Portal • Rolled out in July 04 • Single entry point for various knowledge items • Contents arranged in logical structure for easy navigation and information retrieval • • Provides website search engine and glossary Continuous improvement based on the results of the knowledge audit 19
 Expert Directory Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge l l l A web application that allows user to search for Subject Experts being nominated to provide advices on technical enquiries Criteria for nomination into the Expert Directory includes: • Experience in the field • Communications skills • Knowledge sharing inclination Develop new knowledge 20
Expert Directory Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge l l l A web application that allows user to search for Subject Experts being nominated to provide advices on technical enquiries Criteria for nomination into the Expert Directory includes: • Experience in the field • Communications skills • Knowledge sharing inclination Develop new knowledge 20
 Knowledge Sharing Culture Promotion Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge a. Knowledge-sharing culture development: • KM Team Building Workshops • Quarterly KM newsletter • Competitions • E-games • Roadshows • KM Workshops / Seminars • Communication via Departmental KM Representatives Develop new knowledge 21
Knowledge Sharing Culture Promotion Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge a. Knowledge-sharing culture development: • KM Team Building Workshops • Quarterly KM newsletter • Competitions • E-games • Roadshows • KM Workshops / Seminars • Communication via Departmental KM Representatives Develop new knowledge 21
 Measurement & Incentive Systems Identify and retain critical knowledge Measurement and incentive systems • • Develop new knowledge KM cultural survey • Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Planned assessment on i. Kue system by Co. P • Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Recognition ceremonies KM awards Contribu tion Culture Effectiv eness 22
Measurement & Incentive Systems Identify and retain critical knowledge Measurement and incentive systems • • Develop new knowledge KM cultural survey • Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Planned assessment on i. Kue system by Co. P • Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Recognition ceremonies KM awards Contribu tion Culture Effectiv eness 22
 Knowledge Audit & Knowledge Repository Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Knowledge Audit Business Objectives • Assess knowledge possessed and gaps • Prioritize knowledge areas to be further Process captured/developed Flow • Focus on business needs Codified • Use the Knowledge Audit to derive Technology Knowledge the framework of the Knowledge Non-codified Repository People Knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge Knowledge Repository Roadmap • Positioned as a “Corporate Memory”, comprising: • Codified Knowledge (tacit & explicit) • Links to subject matter experts / Co. Ps • The Codified knowledge should also include Audio/video recordings, best practices documentation, lessons learnt, etc • Contents of the Repository are to be furnished by line units 23
Knowledge Audit & Knowledge Repository Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Knowledge Audit Business Objectives • Assess knowledge possessed and gaps • Prioritize knowledge areas to be further Process captured/developed Flow • Focus on business needs Codified • Use the Knowledge Audit to derive Technology Knowledge the framework of the Knowledge Non-codified Repository People Knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge Develop new knowledge Knowledge Repository Roadmap • Positioned as a “Corporate Memory”, comprising: • Codified Knowledge (tacit & explicit) • Links to subject matter experts / Co. Ps • The Codified knowledge should also include Audio/video recordings, best practices documentation, lessons learnt, etc • Contents of the Repository are to be furnished by line units 23
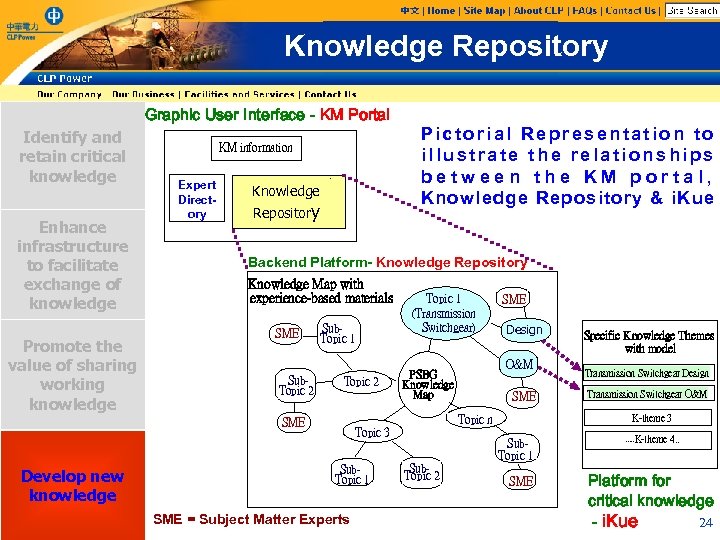 Knowledge Repository Graphic User Interface - KM Portal Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge KM information Expert Directory Knowledge Repository Backend Platform- Knowledge Repository Knowledge Map with experience-based materials SME Sub. Topic 2 Sub. Topic 1 Topic 2 Topic 1 (Transmission Switchgear) SME Design O&M PSBG Knowledge Map SME Topic 3 Sub. Topic 1 SME = Subject Matter Experts Sub. Topic 1 Sub. Topic 2 Specific Knowledge Themes with model Transmission Switchgear Design Transmission Switchgear O&M K-theme 3 Topic n SME Develop new knowledge Pictorial Representation to illustrate the relationships between the KM portal, Knowledge Repository & i. Kue SME . . . K-theme 4. . K-theme 2 Platform for critical knowledge 24 - i. Kue
Knowledge Repository Graphic User Interface - KM Portal Identify and retain critical knowledge Enhance infrastructure to facilitate exchange of knowledge Promote the value of sharing working knowledge KM information Expert Directory Knowledge Repository Backend Platform- Knowledge Repository Knowledge Map with experience-based materials SME Sub. Topic 2 Sub. Topic 1 Topic 2 Topic 1 (Transmission Switchgear) SME Design O&M PSBG Knowledge Map SME Topic 3 Sub. Topic 1 SME = Subject Matter Experts Sub. Topic 1 Sub. Topic 2 Specific Knowledge Themes with model Transmission Switchgear Design Transmission Switchgear O&M K-theme 3 Topic n SME Develop new knowledge Pictorial Representation to illustrate the relationships between the KM portal, Knowledge Repository & i. Kue SME . . . K-theme 4. . K-theme 2 Platform for critical knowledge 24 - i. Kue
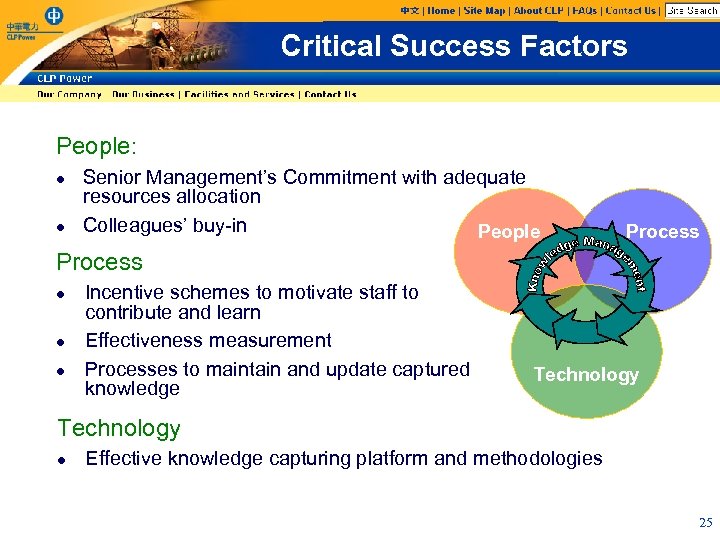 Critical Success Factors People: l l Senior Management’s Commitment with adequate resources allocation Colleagues’ buy-in People Process l l l Incentive schemes to motivate staff to contribute and learn Effectiveness measurement Processes to maintain and update captured knowledge Technology l Effective knowledge capturing platform and methodologies 25
Critical Success Factors People: l l Senior Management’s Commitment with adequate resources allocation Colleagues’ buy-in People Process l l l Incentive schemes to motivate staff to contribute and learn Effectiveness measurement Processes to maintain and update captured knowledge Technology l Effective knowledge capturing platform and methodologies 25
 Further Examples of the benefits of KM Knowledge elicitation of an Engineer with 30 years of Service Experience • Capturing the colleague’s experience on Transmission Switchgear and Transformer Design before retirement • Documented the rationale (or tacit knowledge) behind the clauses in the technical specifications: – Transformer blowers - Galvanized wire-mesh guards, with a mesh not greater than 13 mm, shall be provided…. – The 132 k. V/11 k. V transformer’s tap changer rated step voltage should be about 3000 V……. 26
Further Examples of the benefits of KM Knowledge elicitation of an Engineer with 30 years of Service Experience • Capturing the colleague’s experience on Transmission Switchgear and Transformer Design before retirement • Documented the rationale (or tacit knowledge) behind the clauses in the technical specifications: – Transformer blowers - Galvanized wire-mesh guards, with a mesh not greater than 13 mm, shall be provided…. – The 132 k. V/11 k. V transformer’s tap changer rated step voltage should be about 3000 V……. 26
 Further Examples of the benefits of KM Knowledge elicitation on Overhead Line O&M Knowledge Theme • Capturing various colleagues’ knowledge on Overhead Line Operations & Maintenance • Information scattered; locations of relevant information not clear • By capturing the knowledge into i. Kue, as well as codifying the relevant tacit knowledge, also provides a systematic central platform for searching / retrieving knowledge 27
Further Examples of the benefits of KM Knowledge elicitation on Overhead Line O&M Knowledge Theme • Capturing various colleagues’ knowledge on Overhead Line Operations & Maintenance • Information scattered; locations of relevant information not clear • By capturing the knowledge into i. Kue, as well as codifying the relevant tacit knowledge, also provides a systematic central platform for searching / retrieving knowledge 27
 Our Experience • No winning strategy, every organisation’s situation is different • Need to educate staff on KM • Recognize on-going maintenance efforts • Should have a comprehensive & sustainable implementation plan 28
Our Experience • No winning strategy, every organisation’s situation is different • Need to educate staff on KM • Recognize on-going maintenance efforts • Should have a comprehensive & sustainable implementation plan 28
 Way Forward Near Term (within 1~2 year): • • Complete the critical knowledge themes in i. Kue Establish Co. Ps for critical knowledge themes Gradually build up the Knowledge Repository Further devise incentive schemes and design systematic programmes to motivate staff to contribute and make use of KM • Conduct workshops, broadcast newsletters, and organize functions to foster knowledge sharing culture Longer Term (3~5 years): • Expand the application of Co. P • Establish system to measure effectiveness of KR • Conduct regular survey on knowledge culture 29
Way Forward Near Term (within 1~2 year): • • Complete the critical knowledge themes in i. Kue Establish Co. Ps for critical knowledge themes Gradually build up the Knowledge Repository Further devise incentive schemes and design systematic programmes to motivate staff to contribute and make use of KM • Conduct workshops, broadcast newsletters, and organize functions to foster knowledge sharing culture Longer Term (3~5 years): • Expand the application of Co. P • Establish system to measure effectiveness of KR • Conduct regular survey on knowledge culture 29
 Slogan 知識管理齊獻力 薪火相傳互得益 30
Slogan 知識管理齊獻力 薪火相傳互得益 30
 132 k. V oil-filled cable damaged by an excavation contractor … 31
132 k. V oil-filled cable damaged by an excavation contractor … 31
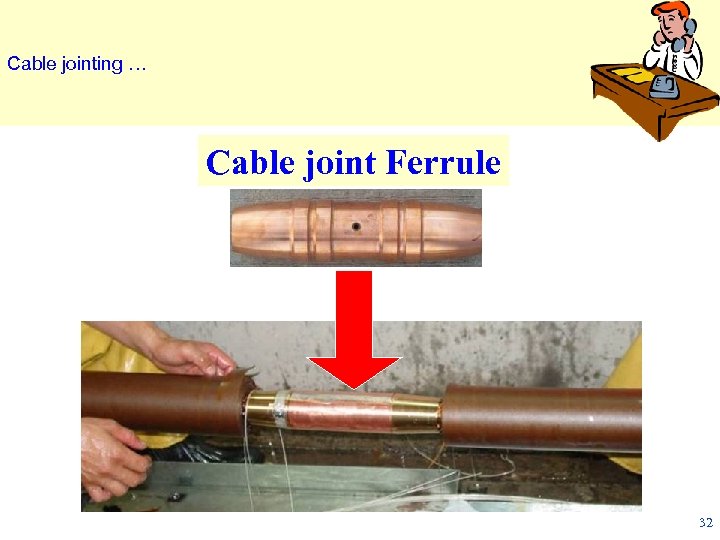 Cable jointing … Cable joint Ferrule 32
Cable jointing … Cable joint Ferrule 32
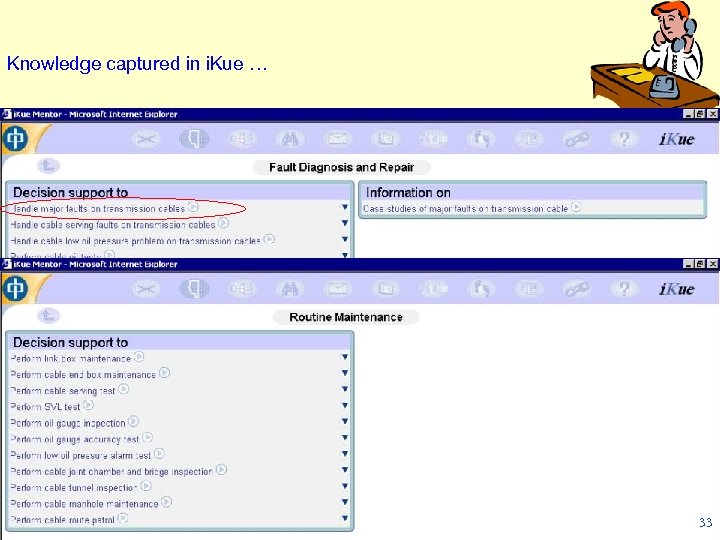 Knowledge captured in i. Kue … 33
Knowledge captured in i. Kue … 33
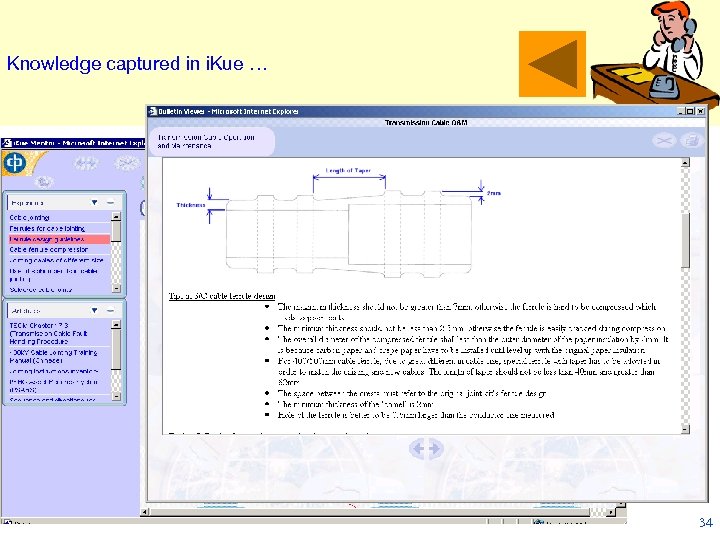 Knowledge captured in i. Kue … 34
Knowledge captured in i. Kue … 34


