
SYLLABLE

SYLLABLE • the smallest units, into which the speech continuum is divided • phonologically, the syllable is a structural unit, which consists of a vowel alone or of a vowel (or a syllabic sonorant) surrounded by consonants in the numbers and arrangements permitted by a given language.

SYLLABLE • a single word: chair /ʧeə/ • a part of a word: English /ˈɪŋ - ɡlɪʃ/ • a part of the grammatical form of a word: later /ˈleɪ - tə/

TYPES OF SYLLABLES • V (vowel)-types of syllable - uncovered open • VC (vowel-consonant)-types of syllable - uncovered closed • CV (consonant-vowel)-types of syllable - covered open • CVC-types of syllable - covered closed

PHONETIC THEORIES • the expiratory, or chest pulse theory • the relative sonority theory • the muscular tensiоn (or the articulatory effort) theory • loudness theory
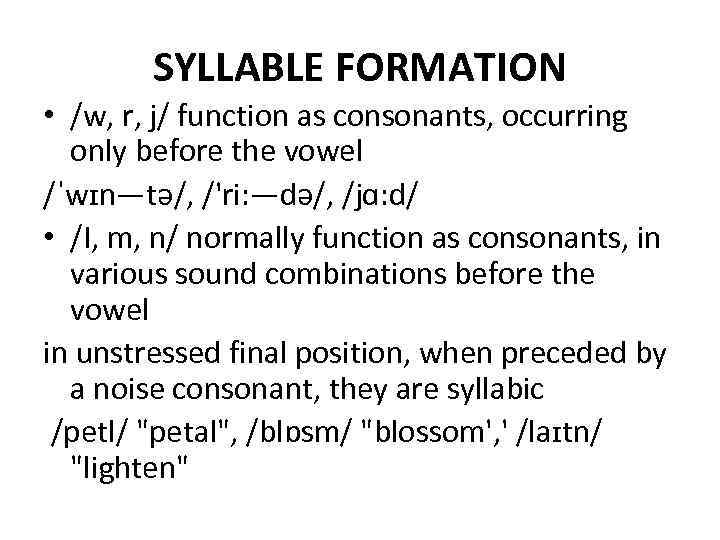
SYLLABLE FORMATION • /w, r, j/ function as consonants, occurring only before the vowel /ˈwɪn—tǝ/, /'ri: —dǝ/, /jɑ: d/ • /I, m, n/ normally function as consonants, in various sound combinations before the vowel in unstressed final position, when preceded by a noise consonant, they are syllabic /petl/ "petal", /blɒsm/ "blossom', ' /laɪtn/ "lighten"

SYLLABLE FORMATION • short English vowels /ɪ, e, æ, ʌ, ɒ, ʊ, ǝ/ never occur in stressed final position without the following consonant • in unstressed position the vowels /ɪ, ǝ/ саn occur as final • in initial position, i. e. before the vowel, there can be any consonant except /ŋ/ • no consonant combinations are possible with /ð, z/ • consonant clusters /mh, sr, spw, fs, hr, stl/ cannot occur initially

PHONETIC SYLLABLES • • • /ˈpeər - ənts/ /aɪ—ˈdɪǝ/ /kɑ: —ˈtu: n/ /ǝ—ˈgri: / /rɪ—ˈgret/ /ǝd—'maɪǝ/ /ed -ˈvaɪs/ /ˈekstrə/ /ˈsaɪ—əns/ /ˈflaʊ - ǝ/

FUNCTIONS OF THE SYLLABLE • constitutive function • distinctive function

SYLLABLE JUNCTURE CLOSE JUNCTURE OPEN JUNCTURE • occurs between sounds within one syllable • occurs between syllables we'll own /wi|l ˈəʊn/ we'll own /wil |ˈəʊn/ we loan /wi ˈl|əʊn/ we loan /wi |ˈləʊn/