syllable.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

SYLLABIC STRUCTURE By Elena A. Filimonova

the notion of syllable Being the smallest pronounceable units, the syllables form language units of greater magnitude, that is morphemes, words and phrases.

There exist two points of view: n n =a purely articulatory unit which lacks any functional value the boundaries of the syllable do not always coincide with those of the morphemes. =the smallest pronounceable unit which can reveal some linguistic function.

a) a syllable is a chain of phonemes of varying length; b) a syllable is constructed on the basis of contrast of its constituents (which is usually of vowel-consonant type); c) the nucleus of a syllable is a vowel, the presence of consonants is optional; d) the distribution of phonemes in the syllabic structure follows the rules which are specific enough for a particular language.

What forms a syllable? n n any vowel (monophthong or diphthong) alone or in combination with 1 or more consonants (are, he, man); a word-final sonorant (lateral or nasal) immediately preceded by a consonant (table, rhythm, garden). phonological opposition vowel — consonant. Which sounds are syllabic in English?

Expiratory/ chest pulse or pressure theory (R H. Stetson) expiration = syllable instrumental techniques: electromyography, to record the lip, tongue and chest movements, and to measure variations in the lung and subglottic air pressure during phonation. Criticism: G. P. Torsuev: in a phrase a number of words and consequently syllables can be pronounced with a single expiration.
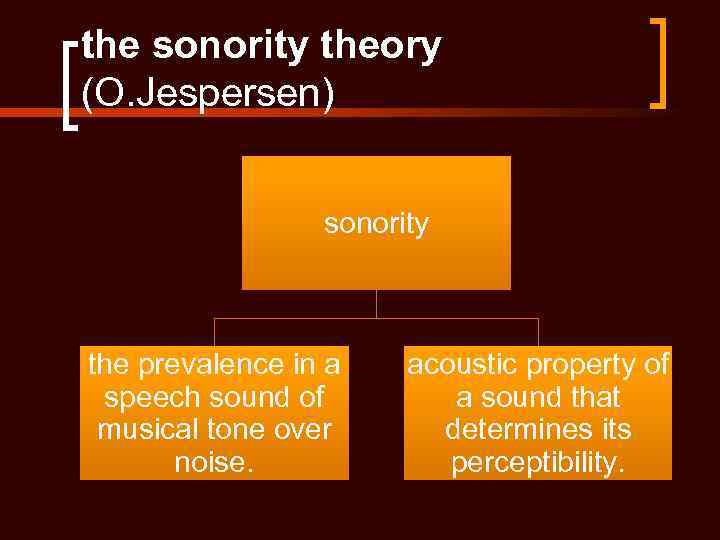
the sonority theory (O. Jespersen) sonority the prevalence in a speech sound of musical tone over noise. acoustic property of a sound that determines its perceptibility.
![Sonority theory n n n n VOICELESS PLOSIVES [p, t, k]------------VOICELESS FRICATIVES [f, s]-------------VOICED Sonority theory n n n n VOICELESS PLOSIVES [p, t, k]------------VOICELESS FRICATIVES [f, s]-------------VOICED](https://present5.com/presentation/263725264_438337287/image-8.jpg)
Sonority theory n n n n VOICELESS PLOSIVES [p, t, k]------------VOICELESS FRICATIVES [f, s]-------------VOICED PLOSIVES [b, d, g]------------VOICED FRICATIVES [v, z]-------------SONORANTS [w, j]----CLOSE VOWELS------OPEN VOWELS------

plant

Criticism VA. Vassilyev: - it fails to explain the actual mechanism of syllable formation and syllable division. -fails to determine the position of the syllabic boundary /aneim/ : /a ‘nem/ and /an ‘eim/
the theory of muscular tension L. V. Shcherba

Modifications by V. A. Vassilyev -the syllable like any other pronounceable unit can be characterized by three physical parameters: pitch, intensity and length. - these parameters vary from minimum on the prevocalic consonants to maximum on the centre of the syllable, and then there is another decrease within the postvocalic consonants.
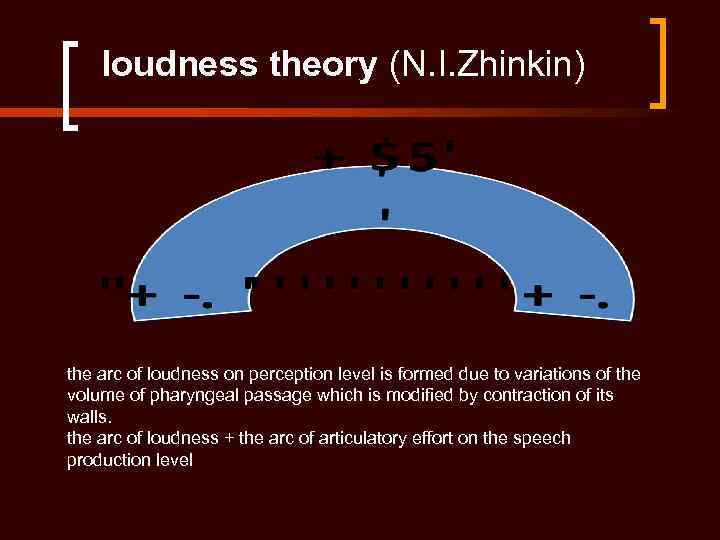
loudness theory (N. I. Zhinkin) the arc of loudness on perception level is formed due to variations of the volume of pharyngeal passage which is modified by contraction of its walls. the arc of loudness + the arc of articulatory effort on the speech production level
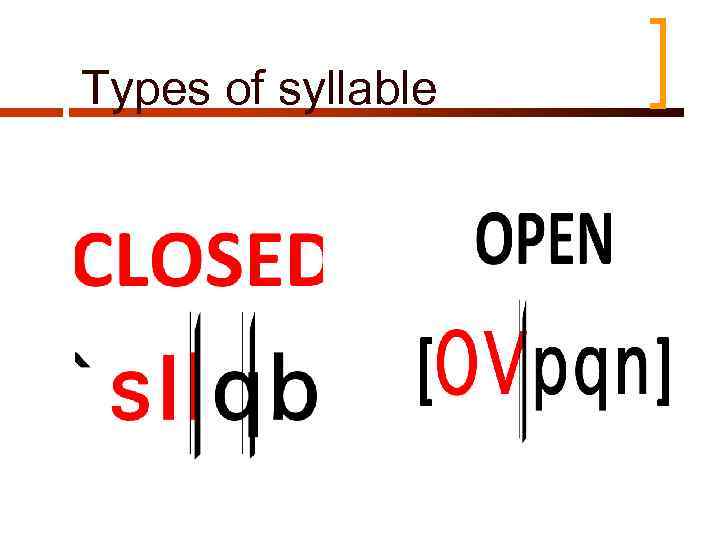
Types of syllable

![syllable division Phonotactics n intervocalic consonants and their clusters like in the words ['siti] syllable division Phonotactics n intervocalic consonants and their clusters like in the words ['siti]](https://present5.com/presentation/263725264_438337287/image-17.jpg)
syllable division Phonotactics n intervocalic consonants and their clusters like in the words ['siti] city, [a'gri: ] agree, ['ekstra] extra and others a) ['ek-stra] — back street b) ['eks-tra]— six try c) ['ekst-ra] — mixed ray n 2 ways of syllable division and, as a result, 2 ways of pronunciation: without [wi’ðaut] and [wið’aut]
![functions of syllables n n constitutive function distinctive function [nai-'treit] nitrate — [nait'reit] night-rate functions of syllables n n constitutive function distinctive function [nai-'treit] nitrate — [nait'reit] night-rate](https://present5.com/presentation/263725264_438337287/image-18.jpg)
functions of syllables n n constitutive function distinctive function [nai-'treit] nitrate — [nait'reit] night-rate a) the degree of aspiration of [t] sounds which is greater in the first member of the opposition than in the second; b) allophonic difference of [r]: in the first member of the opposition it is slightly devoiced under the influence of the initial [t]; c) the length of the diphthong [ai]: in the second member of the opposition it is shorter because the syllable is closed by a voiceless plosive [t].

— a name - an aim — my skill - mice kill — a nice house - an ice house — pea stalks (стебли) - peace talks — play track - plate - I saw her eyes. — I saw her rise. I saw the meat. — I saw them eat.

rules of division of English words into syllables 1) the English long monophthongs, diphthongs and the unstressed short vowels [ı, ə, υ] always occur in a phonetically open syllable : mee-ting, voi-ces, hau-sing, peo-ple, gar-den. 2) a short stressed vowel when separated from a following syllabic sound by only 1 consonant, always occurs in a closed syllable: city, many, Spanish, body, little, 3) the sonorants [1], [m], [n] are syllabic if they are preceded by noise consonants, for example: little, blossom, sadden; 4) there cannot be more than one vowel (a diphthong or a monophthong) within one syllable; 5) the typical and most fundamental syllabic structure is of (C)VC type; 6) word final consonants are normally of weak-end type.

Thank you for your attention!
syllable.ppt