80b61cd624868c36daead27c5b7dc180.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

SWOC DAMA Master Data Management Peter Lamb January 24, 2007
Master Data Management with Kalido v MDM – The Context v Capabilities of Kalido MDM v Commonalities with DIW v MDM Capabilities v How is MDM Used v Types of problems customers are solving with MDM v Benefits customers are deriving through the use of MDM v Guidelines for an MDM Implementation v Importance of business involvement v Technology evaluation v Planning v Implementation v Questions 2 Copyright © Kalido 2006
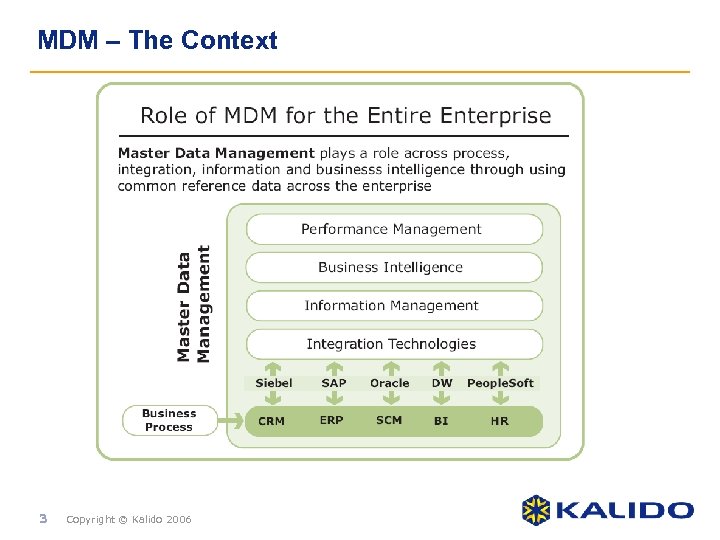
MDM – The Context 3 Copyright © Kalido 2006
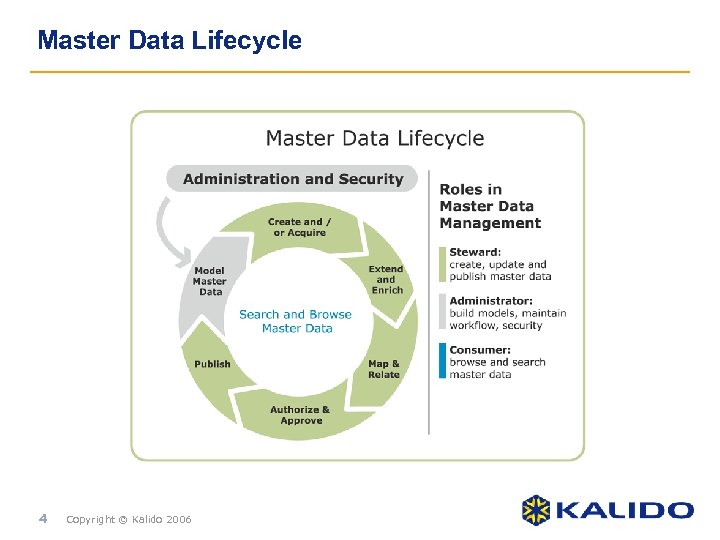
Master Data Lifecycle 4 Copyright © Kalido 2006
Enterprise Wide / Cross Functional Currencies Customers Regions Brand Families Cost Centers Package Types Market Segments Business Lines Hundreds of categories of master data Products Brands Branches Materials Sectors SKUs Suppliers Contribution Types Departments Product Groups KPI definitions Expense Types Organization Payees Copyright © Kalido 2006 Assets Units of Measurement Channels Sales Divisions 5 Employee Classes Supply Locations Tax Types
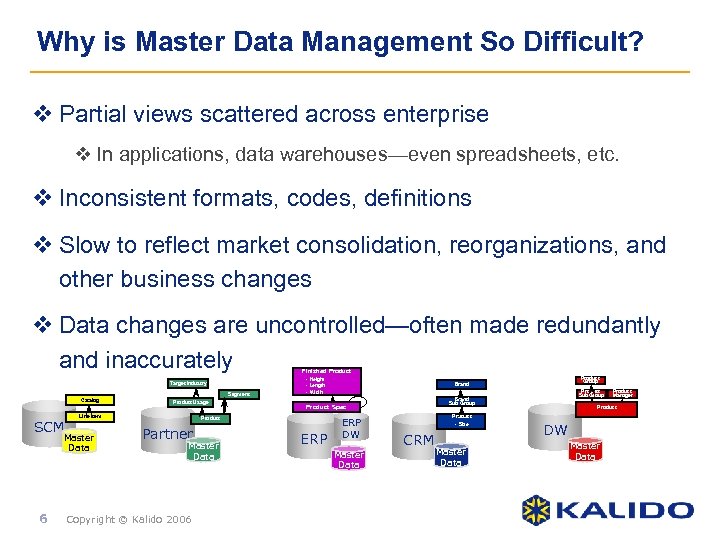
Why is Master Data Management So Difficult? v Partial views scattered across enterprise v In applications, data warehouses—even spreadsheets, etc. v Inconsistent formats, codes, definitions v Slow to reflect market consolidation, reorganizations, and other business changes v Data changes are uncontrolled—often made redundantly and inaccurately Finished Product Target Industry Segment Catalog SCM Line Item Master Data 6 Product Usage • Height • Length • Width Partner Master Data Copyright © Kalido 2006 ERP DW Master Data Product Sub Group Brand Sub Group Product Spec Product Group Brand Product • Size CRM Master Data Product Manager Product • Colour DW Master Data
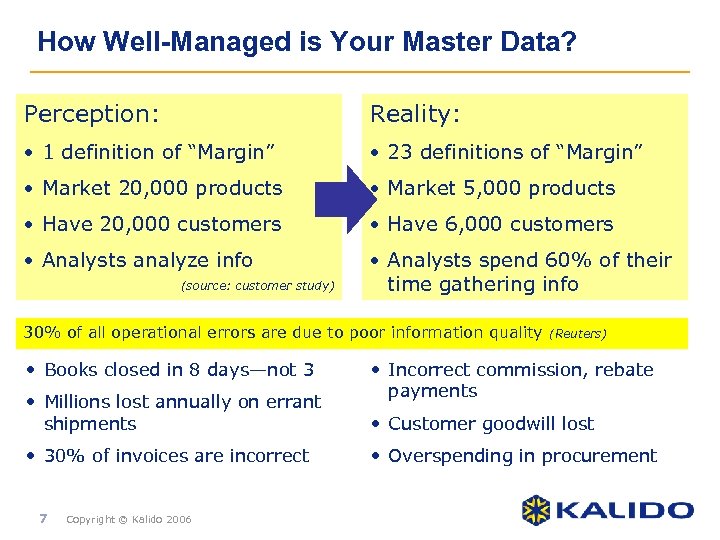
How Well-Managed is Your Master Data? Perception: Reality: • 1 definition of “Margin” • 23 definitions of “Margin” • Market 20, 000 products • Market 5, 000 products • Have 20, 000 customers • Have 6, 000 customers • Analysts analyze info • Analysts spend 60% of their time gathering info (source: customer study) 30% of all operational errors are due to poor information quality • Books closed in 8 days—not 3 • Millions lost annually on errant shipments • 30% of invoices are incorrect 7 Copyright © Kalido 2006 (Reuters) • Incorrect commission, rebate payments • Customer goodwill lost • Overspending in procurement
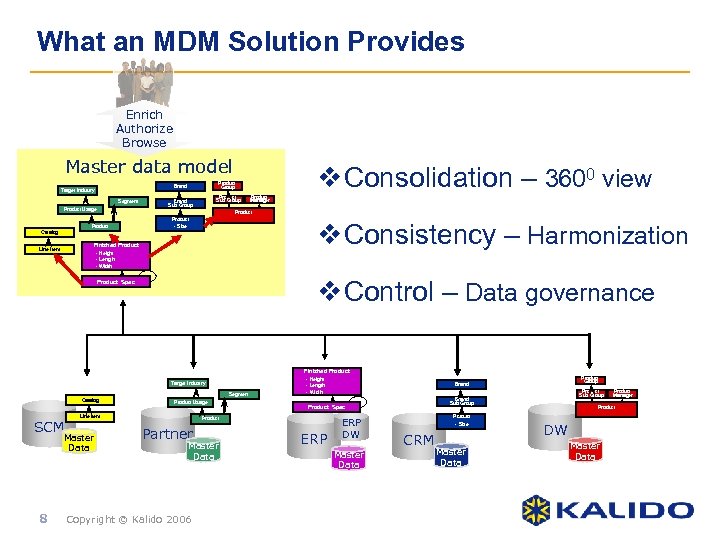
What an MDM Solution Provides Enrich Authorize Browse Master data model Segment Product Usage Product Sub Group Brand Sub Group Product Manager Product • Size • Colour Catalog Finished Product Line Item v Consolidation – 3600 view Product Group Brand Target Industry • Height • Length • Width v Consistency – Harmonization v Control – Data governance Product Spec Finished Product Target Industry Segment Catalog SCM Line Item Master Data 8 Product Usage • Height • Length • Width Partner Master Data Copyright © Kalido 2006 ERP DW Master Data Product Sub Group Brand Sub Group Product Spec Product Group Brand Product • Size CRM Master Data Product Manager Product • Colour DW Master Data
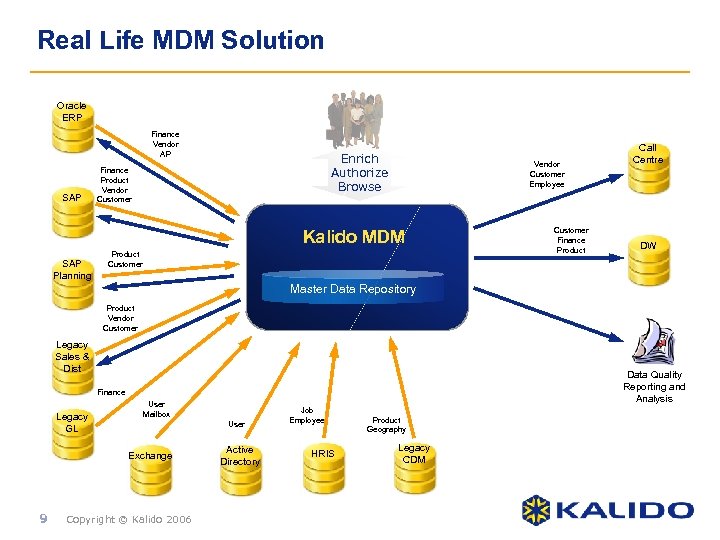
Real Life MDM Solution Oracle ERP Finance Vendor AP SAP Enrich Authorize Browse Finance Product Vendor Customer Employee Kalido MDM SAP Planning Product Customer Finance Product Call Centre DW Master Data Repository Product Vendor Customer Legacy Sales & Dist Data Quality Reporting and Analysis Finance Legacy GL User Mailbox User Exchange 9 Copyright © Kalido 2006 Active Directory Job Employee HRIS Product Geography Legacy CDM

Active Information Management DIW – Dynamic Information Warehouse MDM – Master Data Management
MDM and DIW – Sister Products v Capture and manage change over time v Audit log of all changes to master data v Define, hold and present business model v Change and extend business model with minimal impact v Publish master data for consumption by other applications 11 Copyright © Kalido 2006
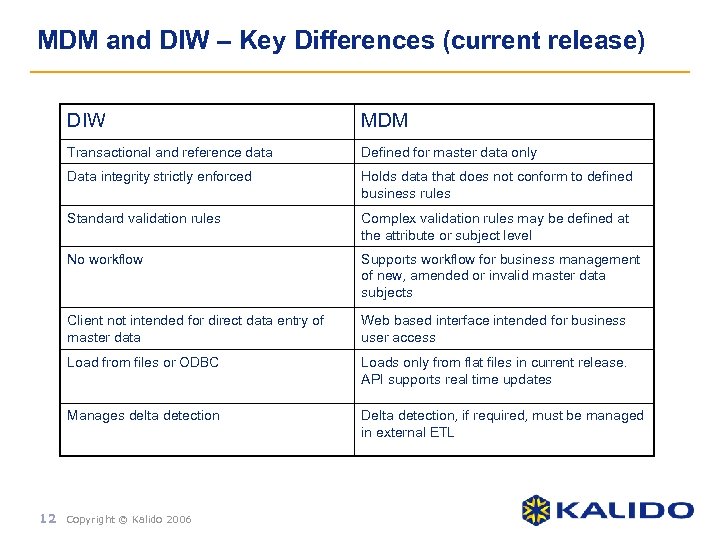
MDM and DIW – Key Differences (current release) DIW MDM Transactional and reference data Defined for master data only Data integrity strictly enforced Holds data that does not conform to defined business rules Standard validation rules Complex validation rules may be defined at the attribute or subject level No workflow Supports workflow for business management of new, amended or invalid master data subjects Client not intended for direct data entry of master data Web based interface intended for business user access Load from files or ODBC Loads only from flat files in current release. API supports real time updates Manages delta detection Delta detection, if required, must be managed in external ETL 12 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Key Capabilities of Kalido MDM
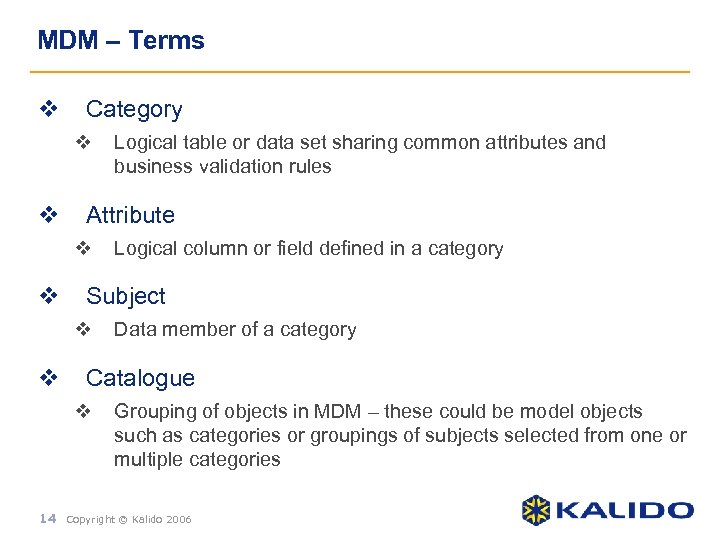
MDM – Terms v Category v v Attribute v v Logical column or field defined in a category Subject v v Logical table or data set sharing common attributes and business validation rules Data member of a category Catalogue v Grouping of objects in MDM – these could be model objects such as categories or groupings of subjects selected from one or multiple categories 14 Copyright © Kalido 2006
Key Capabilities - Model v Generic Model v Holds master data of any type as defined by the business v Hold and Present the Business Model v Define categories and attributes v Define relationships v Define complex business rules to identify non conforming data v Present the model to consuming application and to business users 15 Copyright © Kalido 2006
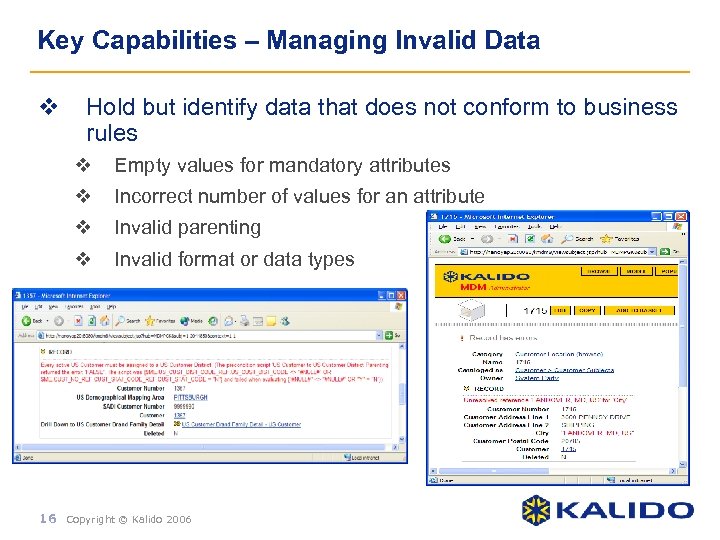
Key Capabilities – Managing Invalid Data v Hold but identify data that does not conform to business rules v Empty values for mandatory attributes v Incorrect number of values for an attribute v Invalid parenting v Invalid format or data types 16 Copyright © Kalido 2006
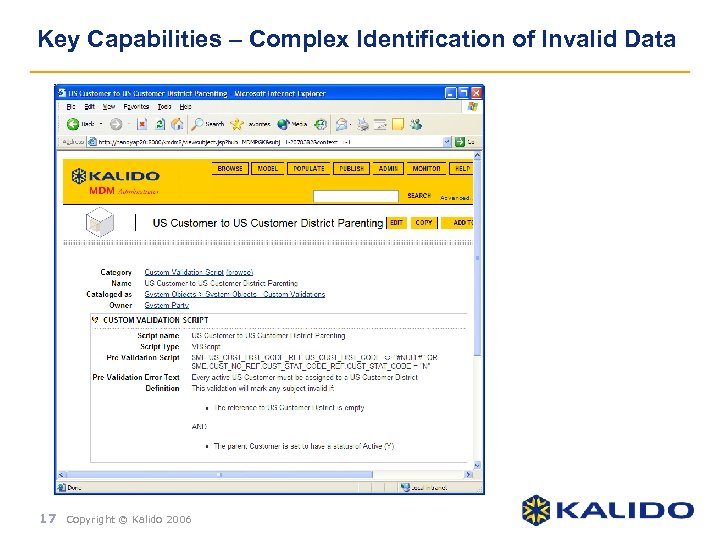
Key Capabilities – Complex Identification of Invalid Data 17 Copyright © Kalido 2006
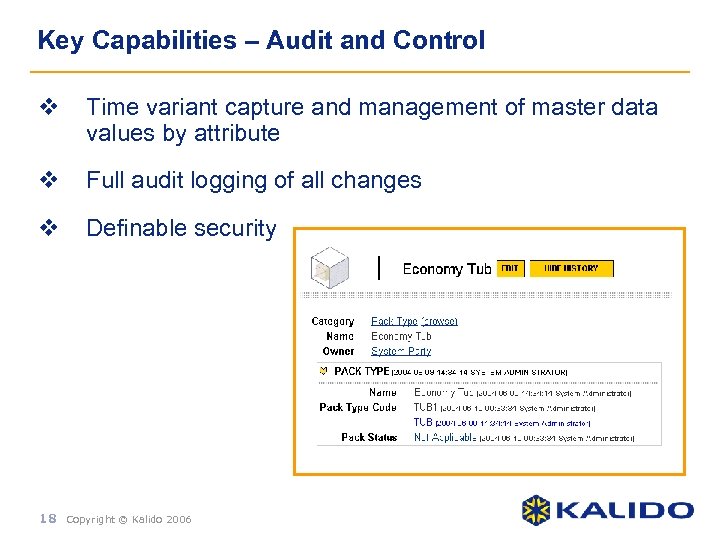
Key Capabilities – Audit and Control v Time variant capture and management of master data values by attribute v Full audit logging of all changes v Definable security 18 Copyright © Kalido 2006
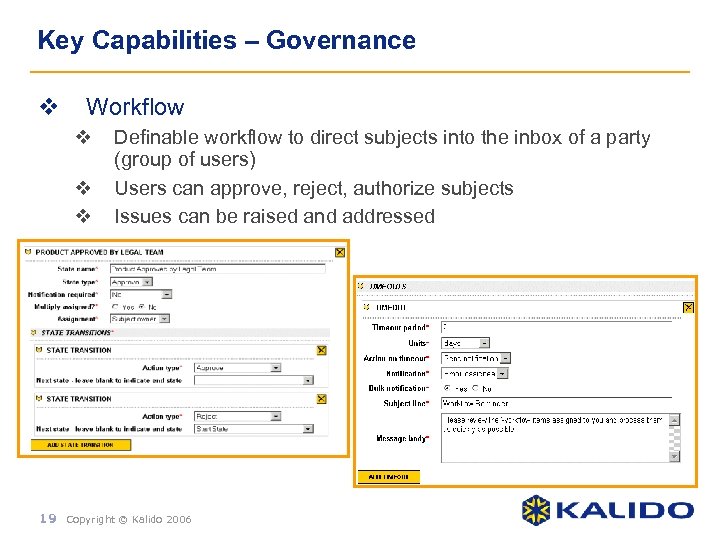
Key Capabilities – Governance v Workflow v v v Definable workflow to direct subjects into the inbox of a party (group of users) Users can approve, reject, authorize subjects Issues can be raised and addressed 19 Copyright © Kalido 2006
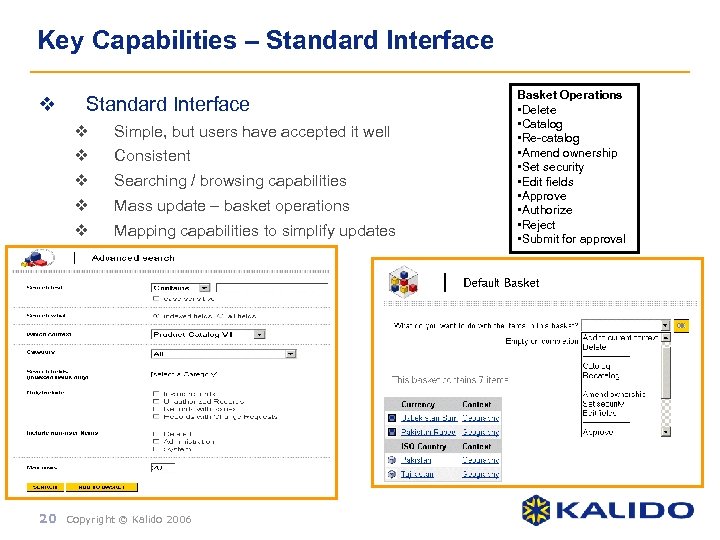
Key Capabilities – Standard Interface v Simple, but users have accepted it well v Consistent v Searching / browsing capabilities v Mass update – basket operations v Mapping capabilities to simplify updates 20 Copyright © Kalido 2006 Basket Operations • Delete • Catalog • Re-catalog • Amend ownership • Set security • Edit fields • Approve • Authorize • Reject • Submit for approval
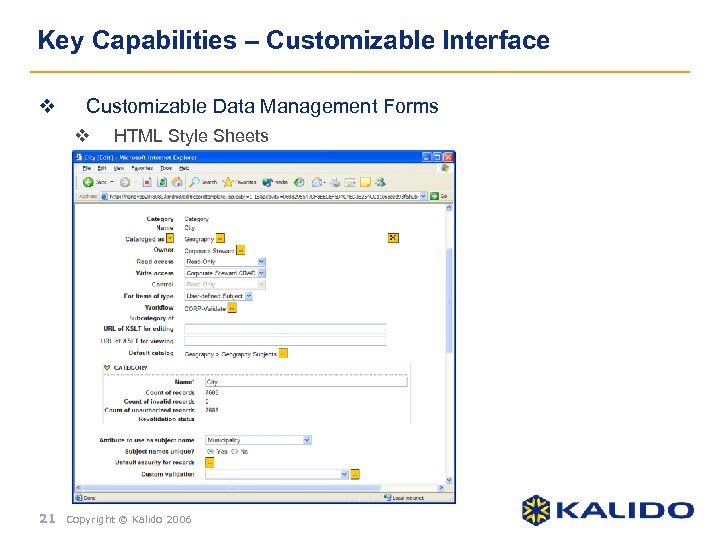
Key Capabilities – Customizable Interface v Customizable Data Management Forms v HTML Style Sheets 21 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Key Capabilities – Publishing / Implementation v Master Data Publishing v v Outbound publishing of non-conformant subject data for reporting v API access v v Category reporting scripts provide a simple and consistent presentation for consumption of master data Direct access possible to underlying tables Fast to Deliver v Simple to build v Simple to change v Prototyping an option Business Analysis, Not The Technology 22 Copyright © Kalido 2006
Benefits Derived from MDM v Cross functional data integration v Data quality v Data decoration v Audit logging v Workflow v Interface 23 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Implementation Guidelines

Guidelines / Best Practices - Business v Engage with the business early and at every step along the way v Business commitment is crucial v Not a ‘one-off’ project – success will drive more demand v Executive support v Definition of global master data standards v v v What constitutes master data in the organization Define standards Conflict resolution Business Must Lead Considerable Business Time Is Required 25 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Guidelines / Best Practices - Evaluation v Allow up to three months for the evaluation process v Interview reference customers v Consult Kalido P. S. to confirm suitability of MDM as the solution v Proof of Value v Prove the technology v Set realistic business expectations v Build confidence, interest and excitement Have Business Users Involved in the POV 26 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Guidelines / Best Practices - Planning v Set a clear scope v Limit scope, and extend as needs arise v Business prioritization for greatest return v Try to focus on a single subject area v Define the vision v Seek buy-in immediately v v v Refer to existing business processes Ensure commitment to new business processes Step by step approach 27 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Guidelines / Best Practices - Implementation v Training personnel fully v Focus where it is required – may need multiple sessions v Engage P. S. – coaching during development v Include key business users in training – model definition as well as interface v Get input from vendor consultants v Do not lose momentum v Iterative approach better than waterfall v Many lessons learned as first categories are implemented v Use real data and be ready for surprises that can change priorities 28 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Guidelines / Best Practices - Model v Business involvement is critical in defining the model v Aim to resolve ambiguity – do not add to it v Use business definitions v Use business names for categories and labels v Identify business owner for each object v Identify system of record for each object v Identify data that will be maintained in MDM and the business users that will be managing it v Define basic validation rules including unique identifiers v Publish the model for IT and business users v Graphic representation of category relationships v Detail on categories and attributes v Use MDM metadata 29 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Guidelines / Best Practices - Model v Understand where the business expects to be going – build for current requirements, but keep long term plans in mind v Expect to extend validation rules during the implementation phase v v v Keep in mind how the data quality can be improved How can value be added beyond initial requirements Identify security requirements v v v Sensitive data must be secure or business owner is not likely to make it available Build confidence by demonstrating security Split categories based on security if required to ensure control 30 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Guidelines / Best Practices – Data In and Out v Use real data during development v v Business will respond to real data and often ignore test data v Loading real data uncovers many conformance issues – do not wait for ETL to load the data v Confirm unique keys v v Load from spreadsheets rather than ETL for initial testing Expect model to change as data is loaded Determine Outbound Requirements v Generic – an approach for all data v Specific – what feeds to consumer systems must be delivered for the project to be successful v Define how invalid data will be handled – will it be published? 31 Copyright © Kalido 2006
Guidelines / Best Practices – Tracking and Purging v Track data - timestamp v Ideally, timestamp and track all data. This includes input feeds. v Normally multiple interfaces and sources, with many possibilities of failure v No one likes to admit to a data problem v v Source v v ETL MDM Define an approach for deleting subject data v Focus is to get data in – data may need to be removed v May be physical delete - purge v May be flag values v Be clear - ‘inactive’ and ‘deleted’ are not the same 32 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Guidelines / Best Practices – Validity & Governance v Continuously review validation rules v Define workflow requirements v v v Workflow requirements may be defined in the initial model, but clarity over data quality and ownership is likely to result in changes Monitor business processes that may be in place to integrate MDM workflow where possible Data volumes will have an impact 33 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Guidelines / Best Practices – Quality v Quality counts v v v Data and ETL quality is critical Do not risk a loss in confidence – be able to prove that the data is correct Modularize ETL v v v Solid process control including error messaging required Be prepared to restructure feeds – you may need to move from daily to hourly Outsourcing development not recommended 34 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Summary
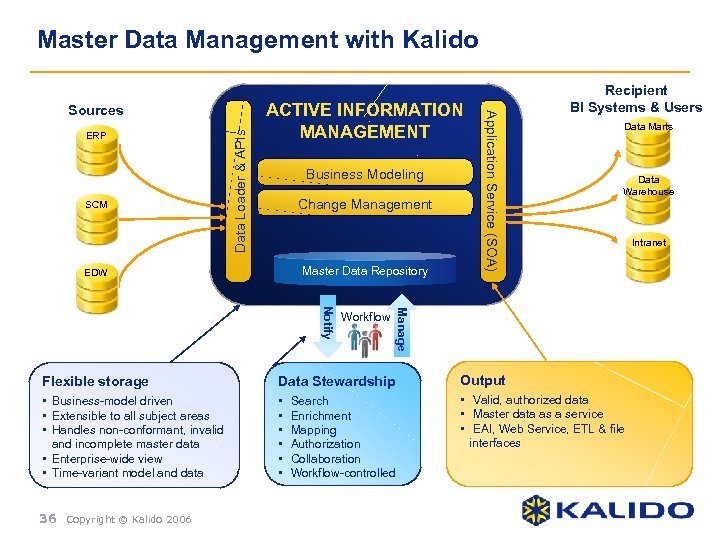
Master Data Management with Kalido SCM Data Loader & APIs ERP ACTIVE INFORMATION MANAGEMENT Business Modeling Change Management Master Data Repository EDW Data Marts Data Warehouse Manage Notify Workflow Application Service (SOA) Sources Recipient BI Systems & Users Flexible storage Data Stewardship Output • Business-model driven • Extensible to all subject areas • Handles non-conformant, invalid and incomplete master data • Enterprise-wide view • Time-variant model and data • • Valid, authorized data • Master data as a service • EAI, Web Service, ETL & file interfaces 36 Copyright © Kalido 2006 Search Enrichment Mapping Authorization Collaboration Workflow-controlled Intranet

Ventana Research Conclusions v All respondents felt KALIDO MDM was an excellent foundation on which to roll out master data management v They spoke highly of the service provided by Kalido consultants and commended their levels of commitment and expertise v Most were in the early stages of implementation and felt it was too early to quantify benefits. Nonetheless, all were convinced benefits were accruing and would eventually be realized and measured v Most organizations did not develop a formal business case but they saw implementing KALIDO MDM as an essential step toward effective information management 37 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Ventana Research – Why Kalido v Flexibility to accommodate business change v Effective dating – time dependency functionality v Fast to implement – low dependence on IT v Ability to build business rules and ensure compliance v Supports and helps enforce need to address master data ‘challenges’ v Very often no business case developed as such v v Often supported on basis of bigger initiative Is ‘self evident’ that its needed v Provides excellent ‘foundation’ for MDM v Early to have ‘quantified’ business benefits but all convinced they are there 38 Copyright © Kalido 2006

Questions… Peter Lamb +1 416 -538 -6231 peter. lamb@dataarch. ca
80b61cd624868c36daead27c5b7dc180.ppt