The analysis Heineken case_example.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Swiss business school Marketing Management The Analysis Report For the Case “Heineken N. V. : Global Branding and Advertising”

Introduction q Heineken the world’s leading international premium beer brand q. The leading brewer in Europe q One of top-3 brewers in the world by volume with annualized ~150 m hectoliters q Strong portfolio of superior local and international premium brands, including Heineken® q International spread: Stable core markets in Europe and North America and strong positions in Central Eastern Europe, South East Asia, India and Africa q Present in over 170 countries q Largest beer and beverage distributor in Western Europe

Introduction q. The Heineken brewery was founded in Amsterdam in 1863 by Gerard Adriaan Heineken q Heineken beer won a gold medal at the 1889 Paris World’s Fair and, by 1893, was one of the largest selling beers in the Netherlands q In 1993, beer accounted for 82% of sales of Heineken, the remainder being derived from soft drinks, spirits and wine q In 1993, sales of beer brewed under Heineken’s supervision reached 5, 6 billion liters, second in the world only to Anheuser. Busch with 10 billion liters
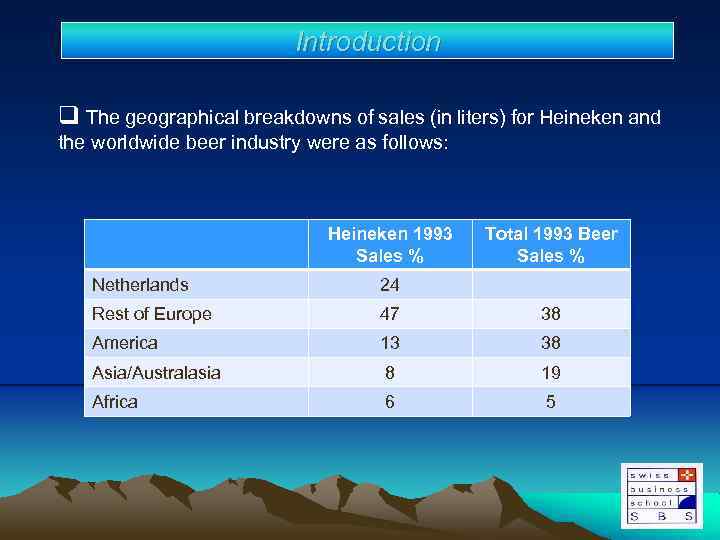
Introduction q The geographical breakdowns of sales (in liters) for Heineken and the worldwide beer industry were as follows: Heineken 1993 Sales % Total 1993 Beer Sales % Netherlands 24 Rest of Europe 47 38 America 13 38 Asia/Australasia 8 19 Africa 6 5
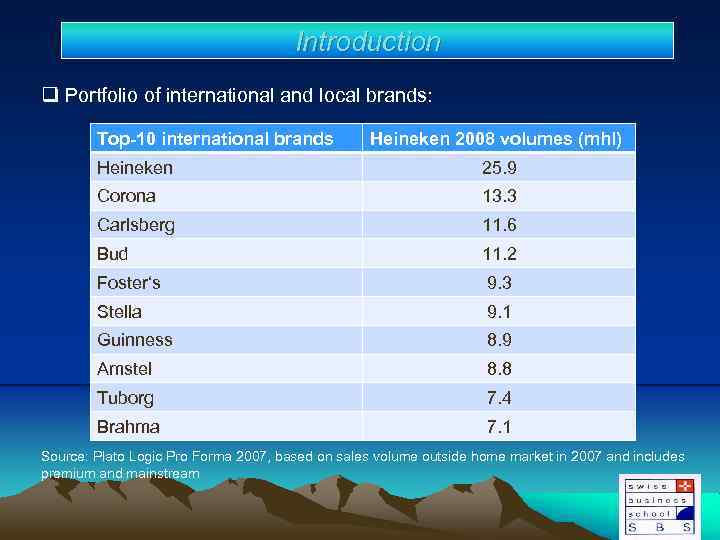
Introduction q Portfolio of international and local brands: Top-10 international brands Heineken 2008 volumes (mhl) Heineken 25. 9 Corona 13. 3 Carlsberg 11. 6 Bud 11. 2 Foster‘s 9. 3 Stella 9. 1 Guinness 8. 9 Amstel 8. 8 Tuborg 7. 4 Brahma 7. 1 Source: Plato Logic Pro Forma 2007, based on sales volume outside home market in 2007 and includes premium and mainstream

Introduction q Heineken was the most heavily advertised premium brand in Europe and worldwide. q Comparative Heineken Usage Data for Seven European Markets: Netherl ands France Greece Ireland Italy Spain UK Main brand usage, % 17 14 44 25 7 5 11 Trial/awareness ratio, % 92 89 99 91 86 66 90 Market share position 1 2 3 7 7 Advertising share of voice position 1 2 4 5 4 6 6 Per capita beer consumption (liters) 90 41 40 123 24 71 103

Problem Statement q Building strong brand portfolios that combines the power of local and international brands and which has Heineken at its centre q How far Heineken’s brand image should or could be standardized

Issues and Analysis PESTEL ANALYSIS q. The worldwide beer consumption is expected to grow by 2%-3 % annually. q. In the developed markets (Western Europe, the United States, Australia and Japan), the overall growth rate is forecast to be close to zero. Growth in these markets will be mainly realized in the premium/import and specialty segments, which will grow annually by approximately 4%, at the expense of mainstream beers. q. Within the premium segment the international premium segment is expected to grow over 6% annually. q. In the developing regions; Central Eastern Europe, Latin America, Asia and Africa, beer consumption is growing at the solid rate of 34%. q. Increased beer consumption is driven by a growing population, an increase in personal income and the shift from the consumption of traditional (hard) liquors towards beer.

Issues and Analysis SWOT ANALYSIS Strengths: §Heineken is positioned as a premium brand, except for home market in the Netherlands §Heineken has wide international presence through a global network of distributors and breweries §Heineken’s unique, unrivalled recipe has not changed §High quality of Heineken beer is the same all around the world §Creative brand management, which is coordinated centrally §Quality ingredients §A perfectly controlled brewing process Weaknesses: §Weak flexibility Heineken as a multinational corporation §High product costs

Issues and Analysis SWOT ANALYSIS Opportunities: §Developing international markets §Mergers, joint ventures, or strategic alliance §Removal an international trade barriers Threats: §High activity of competitors §Price war §World crisis

Selected Strategies q Project Comet was established in 1991 to recommend how to enhance Heineken’s competitive advantage by more consistently the brand as “the world’s leading premium beer” q The project team concluded that Heineken’s desired brand image was “good taste” q. The brand’s good taste image would be built on five core brand values: § Taste § Premiumness § Tradition § Winning spirit § Friendship

Selected Strategies Pros of the Comet project: q The project team detailed how each of the core brand values should be portrayed in Heineken brand commercials q The project team next tried to develop guidelines for the visual images – the people, the relationships and the settings – to be included in Heineken commercials q Development of the impactful advertising through audit and deep development of strong brand

Selected Strategies q In late 1993 project Mosa was established, in the project Heineken commissioned focus groups in eight countries to understand: a) What male drinkers meant by taste and friendship in relation to premium beer drinking b) Which expressions of taste and friendship could be used by the Heineken brand in advertising

Selected Strategies Pros of the Mosa project: q The project team identify which of several factors consumers perceived as strong or weak indicator of beer taste q The different social occasions when a standard versus a premium beer would be appropriate were discussed q Appropriate taste and friendship expressions were ranking q. Concentration on the one brand Heineken forgoes the chance to create

Selected Strategies Cons of the both projects: q. Concentration on the one brand the company forgoes the chance to create a new brand with its own unique image and equity q. Any one brand is not viewed equally favorably by all the different market segments that the firm would like to target q. Concentration on the one brand Heineken forgoes the chance to attract consumers seeking variety who may otherwise have switched to another brand

Lessons learnt q How to identify and establish brand positioning q How to plan and implement brand marketing q How to measure and interpret brand performance q What are the important decisions in developing a branding strategy
Conclusion q In general, the basic principle in designing a brand portfolio is to maximize market coverage, so that no potential customers are being ignored, but to minimize brand overlap, so brands are not competing to gain customer approval Thanks for your attention!
The analysis Heineken case_example.ppt