3f1041a5d3467c1d3f040f577a38ceb7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Sweden Land of legends – home of kings
Sweden Land of legends – home of kings
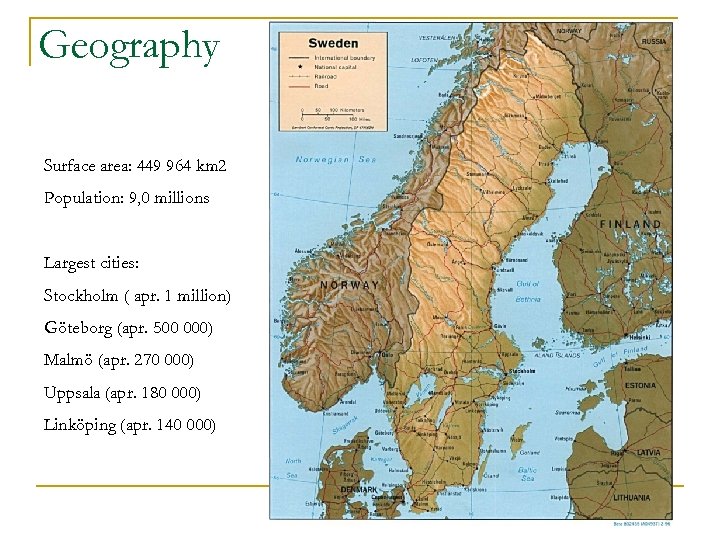 Geography Surface area: 449 964 km 2 Population: 9, 0 millions Largest cities: Stockholm ( apr. 1 million) Göteborg (apr. 500 000) Malmö (apr. 270 000) Uppsala (apr. 180 000) Linköping (apr. 140 000)
Geography Surface area: 449 964 km 2 Population: 9, 0 millions Largest cities: Stockholm ( apr. 1 million) Göteborg (apr. 500 000) Malmö (apr. 270 000) Uppsala (apr. 180 000) Linköping (apr. 140 000)
 Geography (cont. ) Population density: 20/km 2 Compare with e. g. India: 324/km 2 About 80% of population live south of Uppsala
Geography (cont. ) Population density: 20/km 2 Compare with e. g. India: 324/km 2 About 80% of population live south of Uppsala
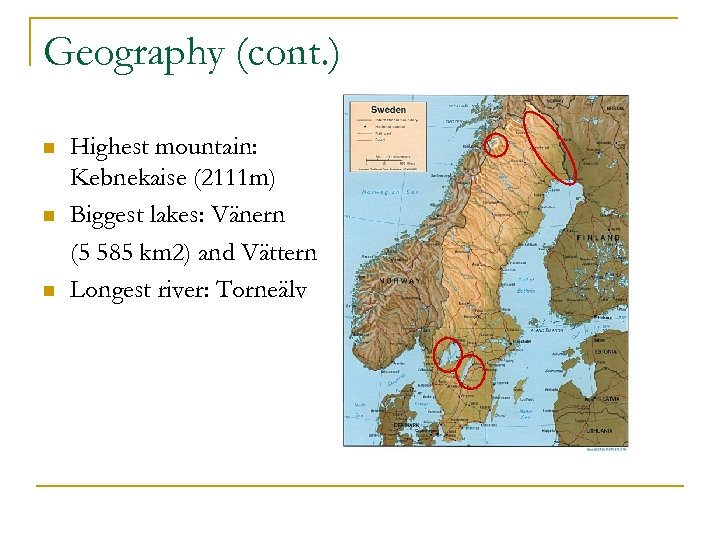 Geography (cont. ) n n n Highest mountain: Kebnekaise (2111 m) Biggest lakes: Vänern (5 585 km 2) and Vättern Longest river: Torneälv
Geography (cont. ) n n n Highest mountain: Kebnekaise (2111 m) Biggest lakes: Vänern (5 585 km 2) and Vättern Longest river: Torneälv
 Geography (cont. ) n n Sweden is relatively close to the north pole. This means long days in the summer, short in the winter North of the arctic circle, the sun won’t rise at all at the end of December and it will never set at the end of June
Geography (cont. ) n n Sweden is relatively close to the north pole. This means long days in the summer, short in the winter North of the arctic circle, the sun won’t rise at all at the end of December and it will never set at the end of June
 Flag etc. Swedens flag Origin and symbolism debated, but the flag has been the same since about 16 th century National coat of arms Symbols for different kings and rulers between 13 th and 16 th century
Flag etc. Swedens flag Origin and symbolism debated, but the flag has been the same since about 16 th century National coat of arms Symbols for different kings and rulers between 13 th and 16 th century
 The monarchy n n n Sweden is a constitutional monarchy King: Carl XVI Gustav Queen: Silvia Princesses Victoria (crown princess) and Madeleine Prince Carl Philip
The monarchy n n n Sweden is a constitutional monarchy King: Carl XVI Gustav Queen: Silvia Princesses Victoria (crown princess) and Madeleine Prince Carl Philip
 Government n n n Parliamentary system with one chamber: Riksdagen (349 delegates) No president, King official head of state but the ”Statsminister” (Prime minister) holds actual power. Elections every 4 th year
Government n n n Parliamentary system with one chamber: Riksdagen (349 delegates) No president, King official head of state but the ”Statsminister” (Prime minister) holds actual power. Elections every 4 th year
 Government (cont. ) n n Government parties: Moderaterna (Right-wing), Folkpartiet (Liberal Party), Centern (Centre Party) and Kristdemokraterna (Cristian Democrats) Other big parties: q q q Socialdemokraterna (Social democrats). Vänsterpartiet (Left-wing) Miljöpartiet
Government (cont. ) n n Government parties: Moderaterna (Right-wing), Folkpartiet (Liberal Party), Centern (Centre Party) and Kristdemokraterna (Cristian Democrats) Other big parties: q q q Socialdemokraterna (Social democrats). Vänsterpartiet (Left-wing) Miljöpartiet
 Government (cont. ) n Statsminister: Fredrik Reinfeldt (Moderaterna)
Government (cont. ) n Statsminister: Fredrik Reinfeldt (Moderaterna)
 Government (cont. ) n State body devided into three levels: q q q Stat (national) Landsting (regional, 21 in all of Sweden) Linköping belongs to Östergötlands län Kommun (city, county, 290 in all of Sweden) We live in Linköpings kommun
Government (cont. ) n State body devided into three levels: q q q Stat (national) Landsting (regional, 21 in all of Sweden) Linköping belongs to Östergötlands län Kommun (city, county, 290 in all of Sweden) We live in Linköpings kommun
 European Union n Sweden has belonged to the European Union (EU) since 1994 In a 2004 referendum we voted not to join the European Monetary Union (EMU). Sweden is one of the EU-countries where the EU has lowest rate of popularity
European Union n Sweden has belonged to the European Union (EU) since 1994 In a 2004 referendum we voted not to join the European Monetary Union (EMU). Sweden is one of the EU-countries where the EU has lowest rate of popularity
 Currency n n Krona (SEK) Aprox. 9 Euros, or 6. 2 US$ 100 öre = 1 krona, only pieces of 50 öre are used Bills of 20, 50, 100, 500 and 1000 kronor Famous swedes on bills include: q q q Carl Von Linné (botanist and naturalist, 100 kronor bill) Jenny Lind (soprano singer, 50 kronor bill) Selma Lagerlöf (writer, 20 kronor bill)
Currency n n Krona (SEK) Aprox. 9 Euros, or 6. 2 US$ 100 öre = 1 krona, only pieces of 50 öre are used Bills of 20, 50, 100, 500 and 1000 kronor Famous swedes on bills include: q q q Carl Von Linné (botanist and naturalist, 100 kronor bill) Jenny Lind (soprano singer, 50 kronor bill) Selma Lagerlöf (writer, 20 kronor bill)
 Religion n n Official religion is Lutheran church About 82% belong to this church but Sweden is a highly secularised society and church attendance is generally low Catholic church: about 180 000 members Muslim communities: about 130 000 members (estimated in 2003) Orthodox church: about 100 000 members
Religion n n Official religion is Lutheran church About 82% belong to this church but Sweden is a highly secularised society and church attendance is generally low Catholic church: about 180 000 members Muslim communities: about 130 000 members (estimated in 2003) Orthodox church: about 100 000 members
 Religion (cont. ) n n Small comunties of almost every other faith in the world: Jewish, Hindu, Buddist etc. In religious terms, Sweden is a very tolerant society
Religion (cont. ) n n Small comunties of almost every other faith in the world: Jewish, Hindu, Buddist etc. In religious terms, Sweden is a very tolerant society
 Demography (cont. ) n Average life expectancy q q n n 77 years for men (3 rd highest in the world) 82 years for women (5 th highest in the world) Mortality and fertility is generally low (on average, every woman gives birth to 1. 7 children) Population increase almost exclusively due to immigration
Demography (cont. ) n Average life expectancy q q n n 77 years for men (3 rd highest in the world) 82 years for women (5 th highest in the world) Mortality and fertility is generally low (on average, every woman gives birth to 1. 7 children) Population increase almost exclusively due to immigration
 Festivites n Christmas - Jul q q 24 th of December most important, that’s when Santa Claus shows up with present for the kids 25 th and 26 th of December also national holidays Originally celebrated to commemorate the birth of Jesus Christ in Bethlehem Christmas dinners usually include ham, swedish meatballs, sill and porridge.
Festivites n Christmas - Jul q q 24 th of December most important, that’s when Santa Claus shows up with present for the kids 25 th and 26 th of December also national holidays Originally celebrated to commemorate the birth of Jesus Christ in Bethlehem Christmas dinners usually include ham, swedish meatballs, sill and porridge.
 The snaps n n n Snaps is a traditional swedish strong liquor, similar to vodka but with spices. Every region and many destilleries have their own way of making snaps and there are literally hundres of different kinds. We drink it at most of the traditional festivities
The snaps n n n Snaps is a traditional swedish strong liquor, similar to vodka but with spices. Every region and many destilleries have their own way of making snaps and there are literally hundres of different kinds. We drink it at most of the traditional festivities
 Festivities (cont. ) n New years eve - Nyårsafton q q q Celebrated on the 31 th of December People dress up, have dinner or party. When the clock strikes 24. 00, fireworks are shot off and we toast in champagne
Festivities (cont. ) n New years eve - Nyårsafton q q q Celebrated on the 31 th of December People dress up, have dinner or party. When the clock strikes 24. 00, fireworks are shot off and we toast in champagne
 Festivities (cont. ) n Easter - Påsk q q q Dates change from year to year. In 2008 easter week is 20 th to 24 th of March with the most important night, Påskafton on the 22 th of March People get together and eat easter dinner consisting of, among other things eggs, Janssons frestelse and sill For the kids, parents hide eastereggs filled with candy in the house or garden.
Festivities (cont. ) n Easter - Påsk q q q Dates change from year to year. In 2008 easter week is 20 th to 24 th of March with the most important night, Påskafton on the 22 th of March People get together and eat easter dinner consisting of, among other things eggs, Janssons frestelse and sill For the kids, parents hide eastereggs filled with candy in the house or garden.
 Festivities (cont. ) n Valpurgis Night q q On the 30 th of April Bonfires are lit and songs are sung to commemorate the conquest of spring over winter
Festivities (cont. ) n Valpurgis Night q q On the 30 th of April Bonfires are lit and songs are sung to commemorate the conquest of spring over winter
 Festivities (cont. ) n National day – Nationaldagen q q q 6 th of June Not widely celebrated but it is a national holiday Origin: among other things, Gustav Vasa, a famous swedish king in the 16 th century, was coronated on the 6 th of june 1523
Festivities (cont. ) n National day – Nationaldagen q q q 6 th of June Not widely celebrated but it is a national holiday Origin: among other things, Gustav Vasa, a famous swedish king in the 16 th century, was coronated on the 6 th of june 1523
 Festivities (cont. ) n Midsummer’s eve – Midsommarafton q q Always on the Friday closest to the longest day of the year. In 2008 that happens on the 20 th of June Based on old heathen tradition and fertility rituals In olden days, this night had a number of magical properties (compare to e. g. ”A midsummer nights dream” by William Shakespeare) People get together, eat the new seasons’ potatoes, sill and drink snaps. Also, we dance silly dances imitating frogs.
Festivities (cont. ) n Midsummer’s eve – Midsommarafton q q Always on the Friday closest to the longest day of the year. In 2008 that happens on the 20 th of June Based on old heathen tradition and fertility rituals In olden days, this night had a number of magical properties (compare to e. g. ”A midsummer nights dream” by William Shakespeare) People get together, eat the new seasons’ potatoes, sill and drink snaps. Also, we dance silly dances imitating frogs.
 Festivities (cont. ) n Kräftskiva q q No specific date but parties are held during the crayfish season in the end of August We eat crayfish, sing songs and drink snaps
Festivities (cont. ) n Kräftskiva q q No specific date but parties are held during the crayfish season in the end of August We eat crayfish, sing songs and drink snaps
 Famous Swedes n n n n Alfred Nobel q Inventor of dynamite whose fortune is the basis for the Nobel prize Ingrid Bergman Hollywood ABBA q Popgroup with international successes in the 1970’s Olof Palme q Politician and statsminister with many international ties, assasinated in 1986 Ingvar Kamprad q Founder of IKEA Björn Borg q Famous tennisplayer in the 1970’s Selma Lagerlöf Nobel Prize winner in literature
Famous Swedes n n n n Alfred Nobel q Inventor of dynamite whose fortune is the basis for the Nobel prize Ingrid Bergman Hollywood ABBA q Popgroup with international successes in the 1970’s Olof Palme q Politician and statsminister with many international ties, assasinated in 1986 Ingvar Kamprad q Founder of IKEA Björn Borg q Famous tennisplayer in the 1970’s Selma Lagerlöf Nobel Prize winner in literature


