8f580ab5caa1ff1cece6e5bf92bab825.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38

Sustainable Development Programme University of St Andrews Rehema White Department of Geography & Sustainable Development

Contents • • Principles of the SD Programme Past and present structure of the SD Programme Threats to interdisciplinary HE teaching Conclusions

PRINCIPLES
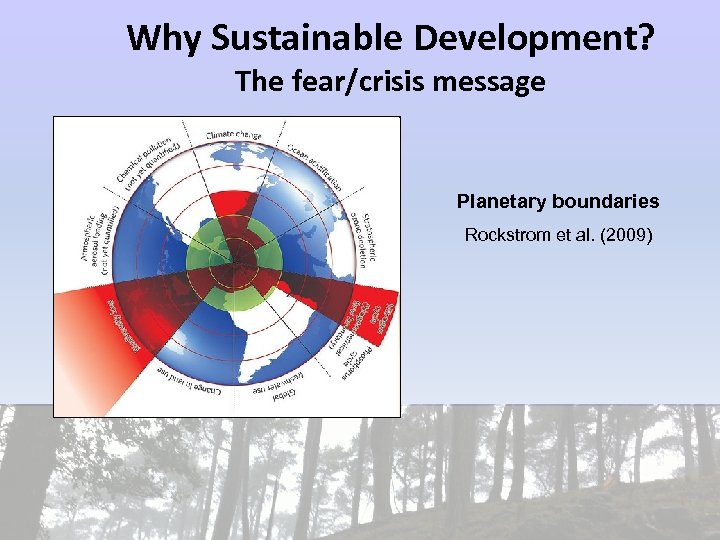
Why Sustainable Development? The fear/crisis message Planetary boundaries Rockstrom et al. (2009)

Why Sustainable Development? The alternative futures (hope) message

Rationale for Sustainable Development Meet needs of future generations Social justice Environmental integrity

What is Sustainable Development? ‘Sustainable Development is development that meets the needs of present generations without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs’ (Brundtland Report, 1987). Key features: • Social justice within environmental limits; • A process • Multiple pathways towards alternative futures • Recognition of a diversity of perspectives • Recognition of new models of knowledge production and exchange.

Aim of SD Programme Enable students to critically interrogate the principles, practice and plurality of sustainable development and contribute to the evolution of innovative, interdisciplinary thinking and action necessary to move towards more sustainable futures

Principles of SD degree 1. Critical interrogation of SD 2. Interdisciplinarity 3. Transformative vs. Transmissive learning 4. Academia as if the world matters 5. Local focus and global perspective

1. Critical interrogation “We can’t solve problems by using the same kind of thinking we used when we created them” Albert Einstein “Let him that would move the world first move himself” Socrates
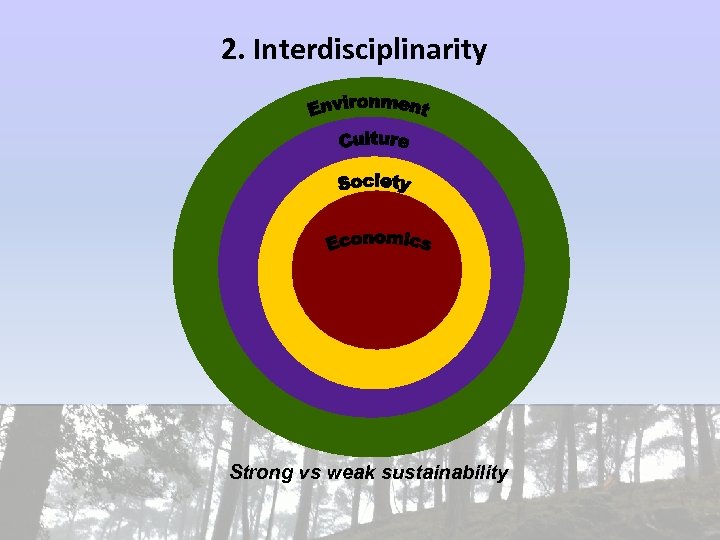
2. Interdisciplinarity Strong vs weak sustainability
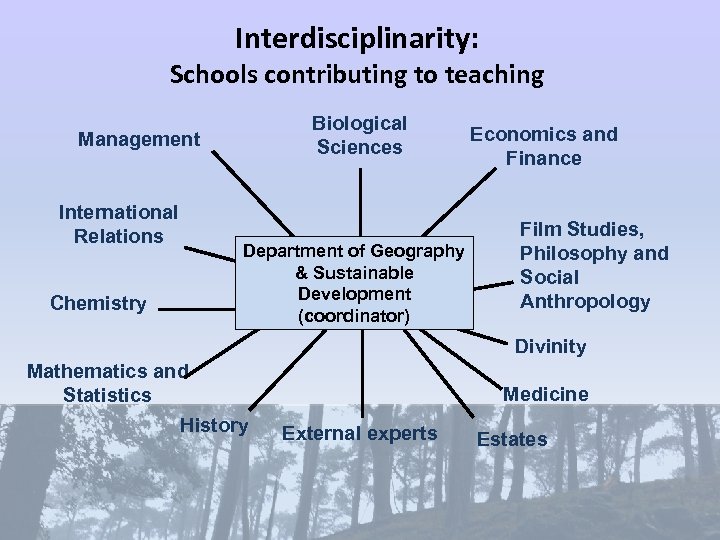
Interdisciplinarity: Schools contributing to teaching Biological Sciences Management International Relations Chemistry Department of Geography & Sustainable Development (coordinator) Economics and Finance Film Studies, Philosophy and Social Anthropology Divinity Mathematics and Statistics History Medicine External experts Estates

3. Pedagogy - Transformative learning & multiple skills Educational display Group work Design Essays Visiting speakers Dissertation Marketing Debate Exams Reports Popular articles Careers support Independent research Presentations Time Reflective management assignments External linkages Fieldtrips
4. Curriculum: Academia as if the world matters: Contemporary issues framework UN’s five priority areas: • Water and sanitation • Energy • Health • Agriculture • Biodiversity Cross cutting themes: • Research and education • Policy, decision making and governance • Markets and institutions • Changing behaviour • Values, philosophies and ethics • Gender and equity

Contemporary sustainability issues matrix 2016 Topics: • Poverty • Health and wellbeing • Water and sanitation • Climate change and energy • Prosperity and responsible consumption and production • Sustainable communities and cities • Biodiversity and ecosystems Cross cutting themes: • Knowledge for research, learning and practice • Policy, decision making and governance • Partnership and diversity • Sustainable behaviours • Values, philosophies and ethics • Equity and Gender
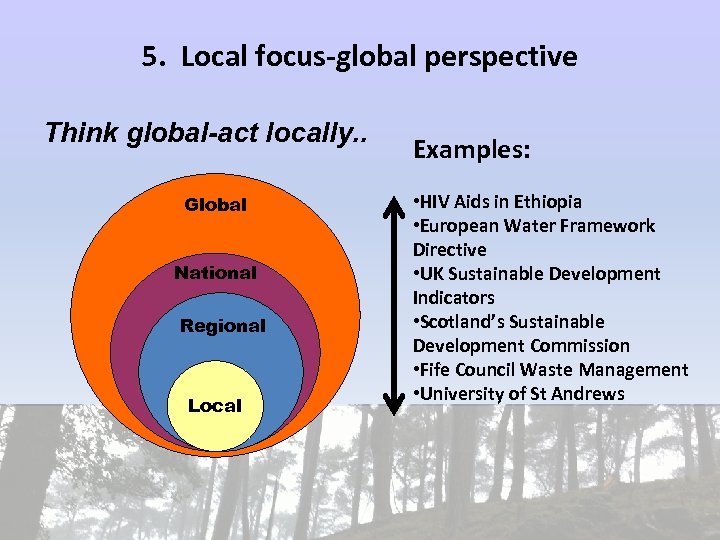
5. Local focus-global perspective Think global-act locally. . Global National Global Regional National Local Examples: • HIV Aids in Ethiopia • European Water Framework Directive • UK Sustainable Development Indicators • Scotland’s Sustainable Development Commission • Fife Council Waste Management • University of St Andrews

SD PROGRAMME - PAST
How is the SD Programme taught? Students tailor individual SD Pathways with partner disciplines to at match their skills, interests and career goals SD Interdisciplinary core modules + specialism modules At every level students combine core SD modules with modules from other disciplines (both MA and BSc) e. g. geography, biology, management, modern history, social anthropology, economics, philosophy, chemistry.

SD Pathways Climate change International development Environmental management Sustainable technologies Social justice Knowledge and education for sustainability • Business and corporate social responsibility • Policy for sustainable development • • •
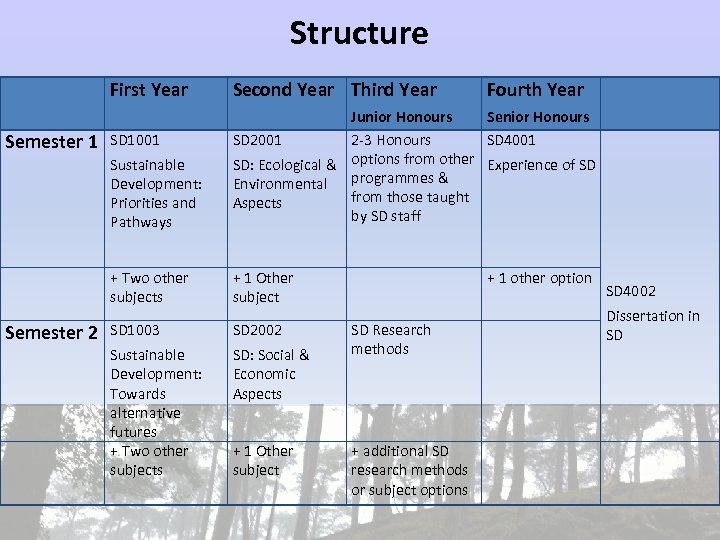
Structure First Year Second Year Third Year Fourth Year Sustainable Development: Priorities and Pathways + Two other subjects Semester 1 Semester 2 Junior Honours Senior Honours SD 2001 2 -3 Honours SD 4001 SD: Ecological & options from other Experience of SD Environmental programmes & from those taught Aspects by SD staff + 1 Other subject SD 1003 SD 2002 Sustainable Development: Towards alternative futures + Two other subjects SD: Social & Economic Aspects SD 1001 + 1 Other subject + 1 other option SD Research methods + additional SD research methods or subject options SD 4002 Dissertation in SD
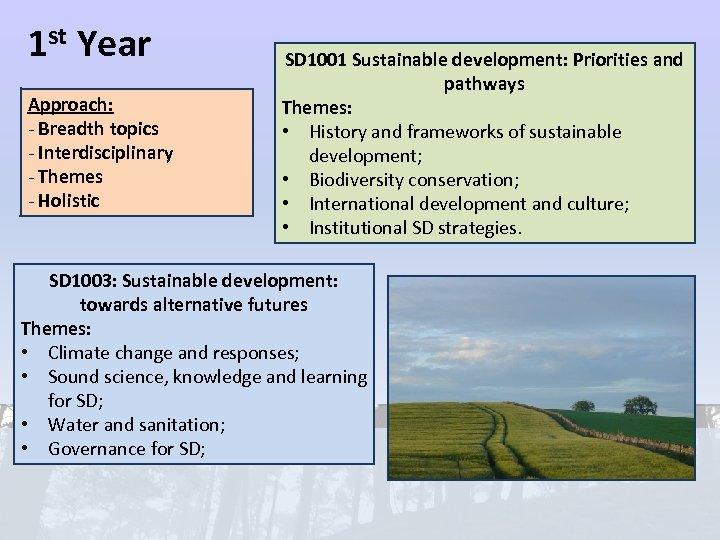
1 st Year Approach: - Breadth topics - Interdisciplinary - Themes - Holistic SD 1001 Sustainable development: Priorities and pathways Themes: • History and frameworks of sustainable development; • Biodiversity conservation; • International development and culture; • Institutional SD strategies. SD 1003: Sustainable development: towards alternative futures Themes: • Climate change and responses; • Sound science, knowledge and learning for SD; • Water and sanitation; • Governance for SD;

2 nd Year Approach: - Separate and more in-depth focus on environmental and social aspects - Maintains interdisciplinarity & holism SD 2001: SD: Ecological & Environmental Aspects Themes: • Ecosystem functions & services • Anthropogenic effects on ecosystem functions & services • Technology & the environment • Environmental monitoring & assessment • Conservation & protection strategies SD 2002: SD Social and Economic Aspects Themes: • Values, philosophy and history of SD • Policy, decision making and governance • Markets and institutions • Development, cultures and social justice Presentations Social audit Essays Posters Statistics workshops Field trips Displays

3 rd Year Research Methods Training 30, 40 or 60 Credits from the following: 10 credits compulsory 10 credits UNIT 1: Interdisciplinary Research Methodology/Design UNIT 2: Qualitative Methods for Social Science 10 credits 10+10 credits 20 credits compulsory UNIT 3: Quantitative Methods for Social Science UNIT 4: Physical Science Methods UNIT 5: Field Course – group research exercise/future scenarios planning

4 th Year Independent research dissertations Example titles: • A Framework Analysis of the European Union Emission Trading Scheme • Limitations Facing Behavioural Change in Light of Global Climate Change • How the media's portrayal of climate change influences public opinion and political response • The future of commercial fishing in Scotland • Post Deep-water Horizon: BP's reputation management in relation to its corporate social responsibility • Assessing the economic, environmental and social effectiveness of a microloans project for women and sustainable agriculture in rural Zambia • Sustainable Building Design: Reconciling New and Traditional Methods with Sustainability • Drivers and benefits of the recent urban farm movement in Chicago • An analysis of commercial wind farm contributions to community benefit schemes in Scotland • The implications of bee decline in Fife • How can Sustainable Development be considered by NGOs in post-natural disaster redevelopment? • Rocky Road to Recovery: The role of NGOs in Paving Kenya's Path to Sustainable Development in the Aftermath of the 2007 Election Crisis • People & Power: A case study of health & health care in an Indian Tea Garden • Barriers and opportunities for domestic microrenewables to contribute to reduction in carbon emissions • Acting like it matters: Using the Dramatic Arts for Sustainability Education in Scottish Primary Schools

Doing interdisciplinarity well… Reconciling epistemological incompatibilities! Linking teaching staff (harder than-) Explicitly discussing it with students Synthesis lectures Framework for modules, assignments, programme… Themes and case studies Assignments: learning by doing, critical reflection, discussion and dialogical pedagogy • Making it real – linking to practical initiatives • •

Reconciling our epistemological incompatibilities • How do we reconcile our epistemological incompatibilities as individuals or collectively? • Do our methodologies align with our epistemological position?

Carbon emission reduction SD 1003 • • Calculate personal carbon emissions for semester 1 Make a plan to reduce carbon by 20% for semester 2 Record carbon emissions semester 2 Write a reflective essay explaining whether target was met and if not why, critically analysing results in relation to literature on climate change mitigation and behaviour change

Sustainable Development Programme ‘Willow weaving’ material based practice in SD 2002

4 th Year Fieldtrip Findhorn ecovillage Findhorn

wards a sustainable university? University of St Andrews Teaching Estates Research Governance Students Community White 2013; White and Harde 2013; White 2014

wards a sustainable university? University of St Andrews Teaching Research Estates Transition USt. A Governance Students Wider Community White 2013; White and Harde 2013; White 2014

Successes……. üUniversities that Count recognition for teaching and research in SD üGreen Gown Award 2009 Best UK Sustainability Course üScotland’s flagship Higher Education case study for the UN Decade for Education in Sustainable Development üTimes Higher Education Award for Outstanding Contribution to Sustainable Development 2006 üFirst class status for People and Planet Green League Environmental Performance 2007 and 2008 (top Scottish University) üBREEAM Excellent 2009 for new medical building üGreen Tourism Award

SD PROGRAMME - PRESENT

CHALLENGES FOR INTERDISCIPLINARY PROGRAMMES

Challenges • Need senior and local buy in • Need to be formally embedded in wider University structures • Need sufficient resourcing – interdisciplinarity takes time, trust, relationships, commitment • Need to permit innovation • Recognise stages – pioneer, growth, stable, erosion…. . ?

Conclusions • Interdisciplinarity in sustainability programmes is necessary and exhilarating, but requires resource, time and commitment • It can occur within modules or across modules and will look very different depending on your institutional interest • Essential to consider curriculum and pedagogy • Develop a theoretical underpinning • Engage with practice within and beyond the institution • Beware of the challenges even when established!

8f580ab5caa1ff1cece6e5bf92bab825.ppt