consumerism.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 7

sustainable Consumerism

Points to be discussed • Definition • Pros • Consumer types

Definition • Oslo Symposium on Sustainable Consumption defines it as "the use of services and related products which respond to basic needs and bring a better quality of life while minimizing the use of natural resources and toxic materials as well as emissions of waste and pollutants over the life cycle of the service or product so as not to jeopardize the needs of future generations. "
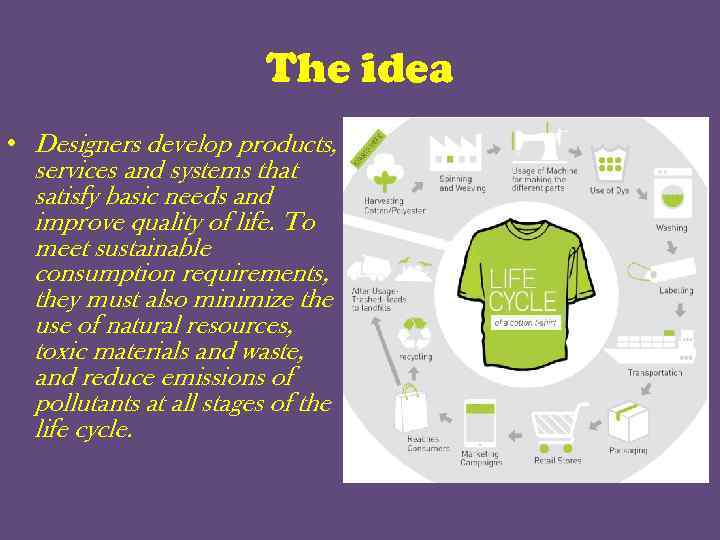
The idea • Designers develop products, services and systems that satisfy basic needs and improve quality of life. To meet sustainable consumption requirements, they must also minimize the use of natural resources, toxic materials and waste, and reduce emissions of pollutants at all stages of the life cycle.

Disadvantages • As market shares of "green" products grow, so does debate about their true impacts. Certification and labeling of environmentally and socially sustainable goods have exploded in the last 10 years, coinciding with hotter, more extreme weather, continued deforestation and biodiversity loss, and accelerated depletion of many natural resources. So it’s fair to ask, is green consumerism working?
Consumer types Consumer attitudes and behaviours towards sustainability can be classified into 4 groups. • Eco-warriors: Actively demonstrate on environmental issues. • Eco-champions: Individuals or groups that champion environmental issues within organizations. • Eco-fans: Individuals or groups that champion environmental issues within organizations. • Eco-phobes: Actively resent talk of environmental protection.

thank you for your attention!
consumerism.ppt