b75a64a1dea3f306bb79e0b32304d395.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Surviving the Silicon Pipeline 2006. 11. 27
Surviving the Silicon Pipeline 2006. 11. 27
 Silicon Cycle
Silicon Cycle
 Frequently encountered problems during chip design project • (Quality of Starter Package ; Qo. SP) How do I know I am working on a right product in a right way? – Is the specification justified in terms of target customers’ demand (request, delivery time), resource I have (money, man power, tools)? • (Timeliness of Handshaking ; Ho. S) How do I make sure I can move to the next stage? • (Overhead) How much overhead is acceptable for each DFX (X=V, M, T)? • (Self-Adjustment) How do I know when and how to make/change the decision (on product specification, design flow, job assignment)?
Frequently encountered problems during chip design project • (Quality of Starter Package ; Qo. SP) How do I know I am working on a right product in a right way? – Is the specification justified in terms of target customers’ demand (request, delivery time), resource I have (money, man power, tools)? • (Timeliness of Handshaking ; Ho. S) How do I make sure I can move to the next stage? • (Overhead) How much overhead is acceptable for each DFX (X=V, M, T)? • (Self-Adjustment) How do I know when and how to make/change the decision (on product specification, design flow, job assignment)?
 FEP’s in pipeline terms • Imbalance of resource among pipeline stages – Needs constant monitoring of stable job flow – In case of imbalance, pipeline stalls. • Some overloaded, while others idle. • Expensive resource conflicts/under-utilization – Needs augmentation by finer pipelining or more parallelism • Proper overhead and transfer timing – Excessive overhead -> Current stage takes too long. – Too little overhead -> Subsequent stage takes too long. – Needs to set up a strategy for bug population control throughout the pipeline • Wrong guys (tools, IP’s, spec. , designs. . ) stay too long in the pipeline -> detect and kill early
FEP’s in pipeline terms • Imbalance of resource among pipeline stages – Needs constant monitoring of stable job flow – In case of imbalance, pipeline stalls. • Some overloaded, while others idle. • Expensive resource conflicts/under-utilization – Needs augmentation by finer pipelining or more parallelism • Proper overhead and transfer timing – Excessive overhead -> Current stage takes too long. – Too little overhead -> Subsequent stage takes too long. – Needs to set up a strategy for bug population control throughout the pipeline • Wrong guys (tools, IP’s, spec. , designs. . ) stay too long in the pipeline -> detect and kill early
 What is Specification? • Most basically, it is Requirement. • Requirement in terms of – Functionality – Performance (speed) – Power consumption – Cost (NRE, manufacturing) – And … Delivery time
What is Specification? • Most basically, it is Requirement. • Requirement in terms of – Functionality – Performance (speed) – Power consumption – Cost (NRE, manufacturing) – And … Delivery time
 Essential Components of Specification 1. Requirement ; – Specification must clarify what are wanted. 2. Implementation Readiness ; – Specification must be implementable. If so, how easy? 3. Scenario for getting it through ; – Strategies for • • • Confirming its completeness Finding/correcting design errors Maximizing yield through manufacturing
Essential Components of Specification 1. Requirement ; – Specification must clarify what are wanted. 2. Implementation Readiness ; – Specification must be implementable. If so, how easy? 3. Scenario for getting it through ; – Strategies for • • • Confirming its completeness Finding/correcting design errors Maximizing yield through manufacturing
 Platform-Based Design • Combining two levels (1+2) ; – considering both ‘What are wanted? ’ and ‘Are they implementable? ’ • Middle-out, or dual negotiation approach ; A compromise between Top-Down and Bottom-Up – Target hit probability is nearly doubled. – Limited to a given range of applications – Traversal time, or design time is reduced by ½ compared either to TD or BU
Platform-Based Design • Combining two levels (1+2) ; – considering both ‘What are wanted? ’ and ‘Are they implementable? ’ • Middle-out, or dual negotiation approach ; A compromise between Top-Down and Bottom-Up – Target hit probability is nearly doubled. – Limited to a given range of applications – Traversal time, or design time is reduced by ½ compared either to TD or BU
 Specification coverage expands • Depending on the scope of your interest – Barely working design (of a product) – A profitable product (DFM, DFY) – Series of products (derivatives) – Company (company image, investor relations, early market entry…)
Specification coverage expands • Depending on the scope of your interest – Barely working design (of a product) – A profitable product (DFM, DFY) – Series of products (derivatives) – Company (company image, investor relations, early market entry…)
 Pipeline Loss = Loss of Value through the Pipeline • • • Specification error Design error Verification error Manufacturing error Testing error
Pipeline Loss = Loss of Value through the Pipeline • • • Specification error Design error Verification error Manufacturing error Testing error
 Specification error • Specification error = 1 -Ps, or 1 -Qs – Ps=probability of specification to be correct – Qs=quality of specification • Cost of specification error = Cs – Cs= 1) cost of extra silicon area due to over-design 2) price lowering due to speed degradation
Specification error • Specification error = 1 -Ps, or 1 -Qs – Ps=probability of specification to be correct – Qs=quality of specification • Cost of specification error = Cs – Cs= 1) cost of extra silicon area due to over-design 2) price lowering due to speed degradation
 Design error • Logical error during horizontal translation • Conflict with specification due to vertical (Downward) implementation – Library mapping = logical equivalence accompanied by such physical constraints as timing, power, and area. – Open-loop design complemented by backannotation (to be zero-in by iteration) • Ex ; 1) Physical layout (Placement & Routing) after logic synthesis, 2) Component-based design followed by physical interconnect
Design error • Logical error during horizontal translation • Conflict with specification due to vertical (Downward) implementation – Library mapping = logical equivalence accompanied by such physical constraints as timing, power, and area. – Open-loop design complemented by backannotation (to be zero-in by iteration) • Ex ; 1) Physical layout (Placement & Routing) after logic synthesis, 2) Component-based design followed by physical interconnect
 Verification error • Verification error = 1 -Pv, or 1 -Qv – Pv=probability of verification to be correct = 1 -probability of design error go unnoticed – Qv=quality of verification • Verification efficiency = Qv/(1+Cv) – Cv = verification overhead, or additional cost due to DFV (design for verification)
Verification error • Verification error = 1 -Pv, or 1 -Qv – Pv=probability of verification to be correct = 1 -probability of design error go unnoticed – Qv=quality of verification • Verification efficiency = Qv/(1+Cv) – Cv = verification overhead, or additional cost due to DFV (design for verification)
 Pitfalls in Specification • Over-specification/over-design ; miss market window. • Too-long term, too conservative design project ; components obsolete at launch time. ex) military design • Too many external IP’s with insufficient 2 nd sources or little room for royalty negotiation
Pitfalls in Specification • Over-specification/over-design ; miss market window. • Too-long term, too conservative design project ; components obsolete at launch time. ex) military design • Too many external IP’s with insufficient 2 nd sources or little room for royalty negotiation
 Give and Takes of each DFX • DFV (Design for Verification) ; Design time for design time, code size for number of iterations, intra computing effort for inter communication hassle • DFT (Design for Testing) ; Area for reputation, good chips rejected is a physical loss, while bad chips with latent bugs is a strategic loss (X-factor) • DFM (Design for Manufacturability) ; More NRE cost (tool cost, extra preprocessing step) for less unit cost • DFY (Design for Yield) ; more parametric extraction and simulation time for higher yield
Give and Takes of each DFX • DFV (Design for Verification) ; Design time for design time, code size for number of iterations, intra computing effort for inter communication hassle • DFT (Design for Testing) ; Area for reputation, good chips rejected is a physical loss, while bad chips with latent bugs is a strategic loss (X-factor) • DFM (Design for Manufacturability) ; More NRE cost (tool cost, extra preprocessing step) for less unit cost • DFY (Design for Yield) ; more parametric extraction and simulation time for higher yield
 Area, delivery time, reputation, cost, speed, power
Area, delivery time, reputation, cost, speed, power
 World of pipelines Silicon pipeline
World of pipelines Silicon pipeline
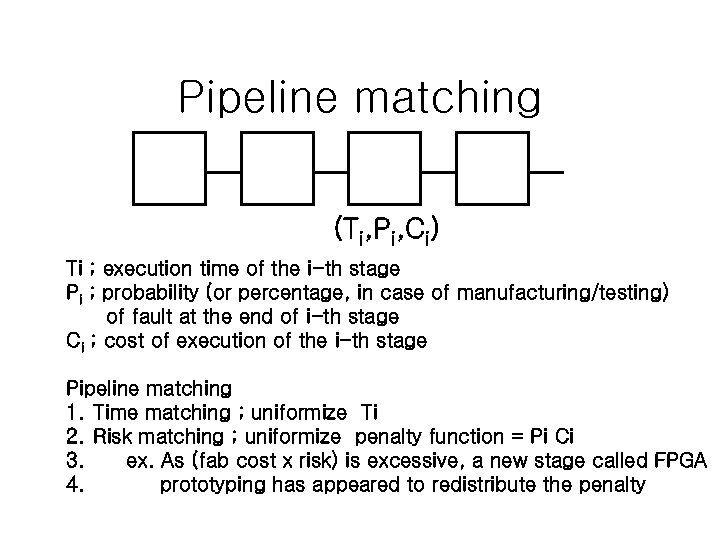 Pipeline matching (Ti, Pi, Ci) Ti ; execution time of the i-th stage Pi ; probability (or percentage, in case of manufacturing/testing) of fault at the end of i-th stage Ci ; cost of execution of the i-th stage Pipeline matching 1. Time matching ; uniformize Ti 2. Risk matching ; uniformize penalty function = Pi Ci 3. ex. As (fab cost x risk) is excessive, a new stage called FPGA 4. prototyping has appeared to redistribute the penalty
Pipeline matching (Ti, Pi, Ci) Ti ; execution time of the i-th stage Pi ; probability (or percentage, in case of manufacturing/testing) of fault at the end of i-th stage Ci ; cost of execution of the i-th stage Pipeline matching 1. Time matching ; uniformize Ti 2. Risk matching ; uniformize penalty function = Pi Ci 3. ex. As (fab cost x risk) is excessive, a new stage called FPGA 4. prototyping has appeared to redistribute the penalty
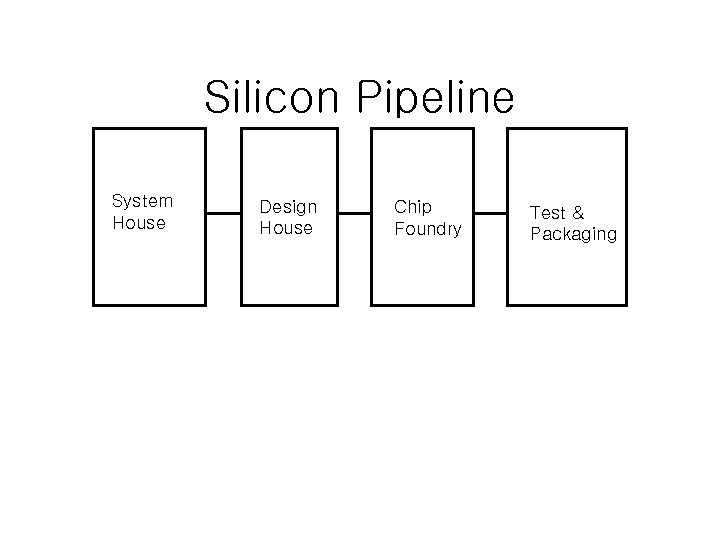 Silicon Pipeline System House Design House Chip Foundry Test & Packaging
Silicon Pipeline System House Design House Chip Foundry Test & Packaging
 Summit Attack summit C 4 C 3 C 1 Base Camp C 2
Summit Attack summit C 4 C 3 C 1 Base Camp C 2
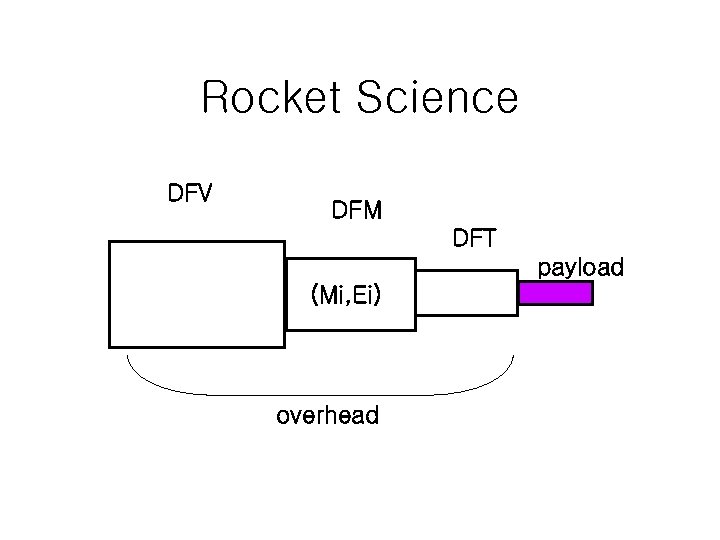 Rocket Science DFV DFM DFT payload (Mi, Ei) overhead
Rocket Science DFV DFM DFT payload (Mi, Ei) overhead
 Overhead of DFX DFV DFM DFT
Overhead of DFX DFV DFM DFT
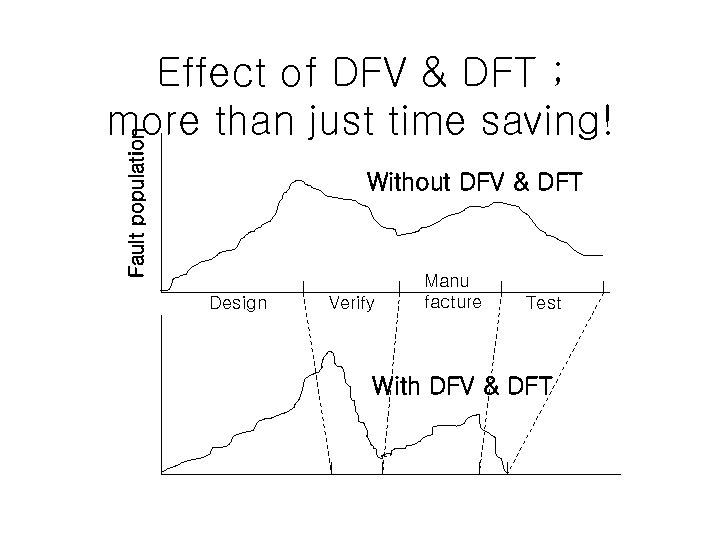 Fault population Effect of DFV & DFT ; more than just time saving! Without DFV & DFT Design Verify Manu facture Test With DFV & DFT
Fault population Effect of DFV & DFT ; more than just time saving! Without DFV & DFT Design Verify Manu facture Test With DFV & DFT
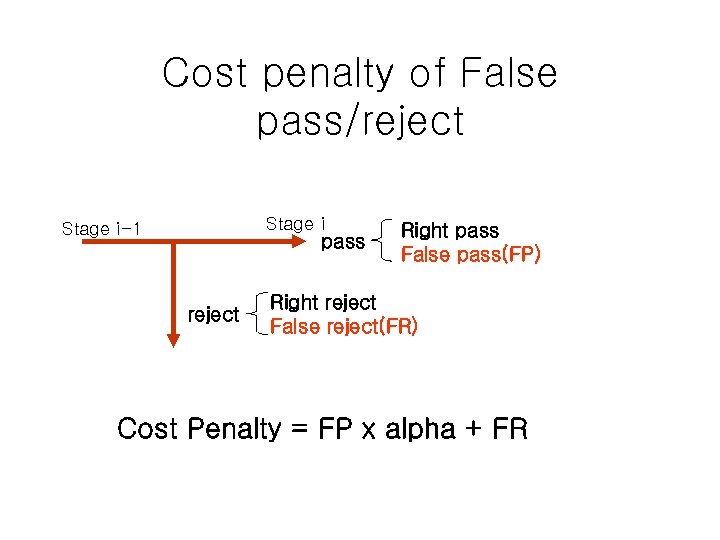 Cost penalty of False pass/reject Stage i-1 pass reject Right pass False pass(FP) Right reject False reject(FR) Cost Penalty = FP x alpha + FR
Cost penalty of False pass/reject Stage i-1 pass reject Right pass False pass(FP) Right reject False reject(FR) Cost Penalty = FP x alpha + FR
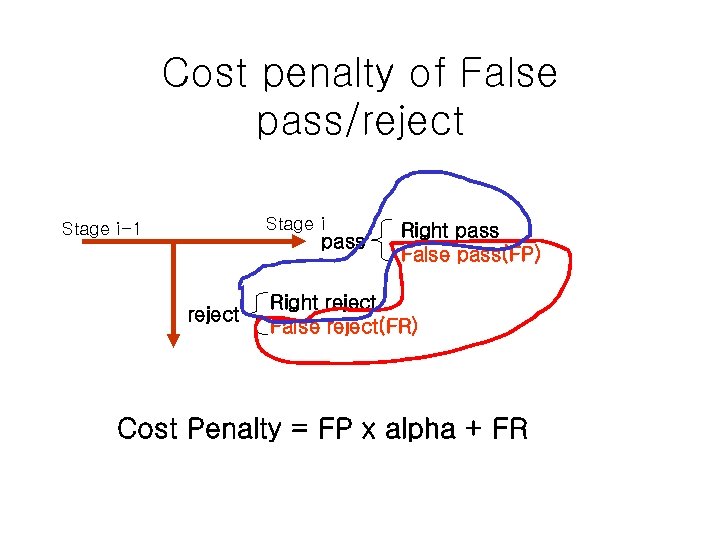 Cost penalty of False pass/reject Stage i-1 pass reject Right pass False pass(FP) Right reject False reject(FR) Cost Penalty = FP x alpha + FR
Cost penalty of False pass/reject Stage i-1 pass reject Right pass False pass(FP) Right reject False reject(FR) Cost Penalty = FP x alpha + FR
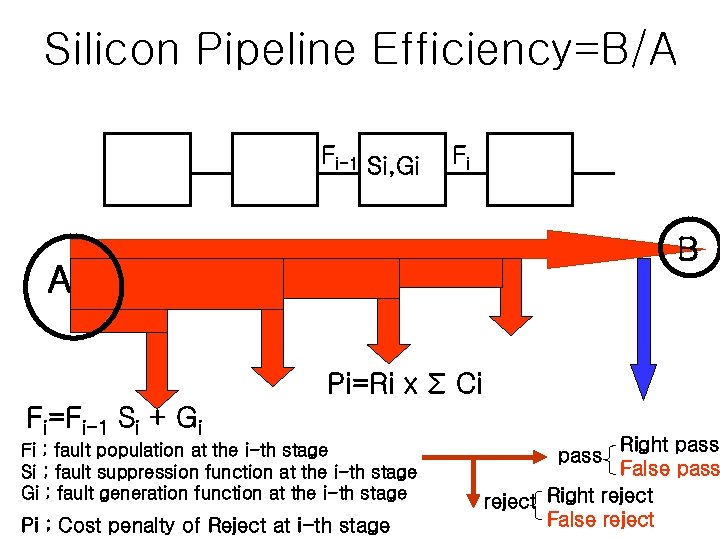 Silicon Pipeline Efficiency=B/A Fi-1 Si, Gi Fi B A Pi=Ri x Σ Ci Fi=Fi-1 Si + Gi Fi ; fault population at the i-th stage Si ; fault suppression function at the i-th stage Gi ; fault generation function at the i-th stage Pi ; Cost penalty of Reject at i-th stage Right pass False pass reject Right reject False reject pass
Silicon Pipeline Efficiency=B/A Fi-1 Si, Gi Fi B A Pi=Ri x Σ Ci Fi=Fi-1 Si + Gi Fi ; fault population at the i-th stage Si ; fault suppression function at the i-th stage Gi ; fault generation function at the i-th stage Pi ; Cost penalty of Reject at i-th stage Right pass False pass reject Right reject False reject pass
 Conclusion ; Silicon Pipeline Modeling • Silicon Pipeline Modeling is useful tool because – It Maximizes silicon pipeline efficiency. • Proper early investment of time & area for early detect & cure of faults – It maximizes resource (designer time, silicon area, expensive equipment time) utilization (Minimize resource conflicts)
Conclusion ; Silicon Pipeline Modeling • Silicon Pipeline Modeling is useful tool because – It Maximizes silicon pipeline efficiency. • Proper early investment of time & area for early detect & cure of faults – It maximizes resource (designer time, silicon area, expensive equipment time) utilization (Minimize resource conflicts)


