9a7df1e9a30c3360da03552a39d491eb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Survival with Cardiac. Resynchronization Therapy in Mild Heart Failure
Survival with Cardiac. Resynchronization Therapy in Mild Heart Failure
 Abstract • Background: MADIT-CRT showed CRT-D in patients with LBBB reduced HF events over 2. 4 years compared with defibrillator alone. • Methods: Eval of long term survival of MADITCRT over median period of 5. 6 years. • Results: At 7 yrs, CRD of LBBB patients with CRT-D was 18% compared to 29% of defib only • Conclusions: mild HF, LV dysfx, LBBB, CRT-D associated with long term survival benefit
Abstract • Background: MADIT-CRT showed CRT-D in patients with LBBB reduced HF events over 2. 4 years compared with defibrillator alone. • Methods: Eval of long term survival of MADITCRT over median period of 5. 6 years. • Results: At 7 yrs, CRD of LBBB patients with CRT-D was 18% compared to 29% of defib only • Conclusions: mild HF, LV dysfx, LBBB, CRT-D associated with long term survival benefit
 MADIT-CRT • 1820 pts with cardiomyopathy, EF <= 30%, QRS of >= 130 msec, NYHA I or II symptoms followed for 2. 4 years, Dec 2004 – June 2009 • Either CRT-D or ICD alone, 3: 2 ratio • End point = death or nonfatal HF event • No difference in risk of death • 41% reduction in HF events in CRT-D group
MADIT-CRT • 1820 pts with cardiomyopathy, EF <= 30%, QRS of >= 130 msec, NYHA I or II symptoms followed for 2. 4 years, Dec 2004 – June 2009 • Either CRT-D or ICD alone, 3: 2 ratio • End point = death or nonfatal HF event • No difference in risk of death • 41% reduction in HF events in CRT-D group
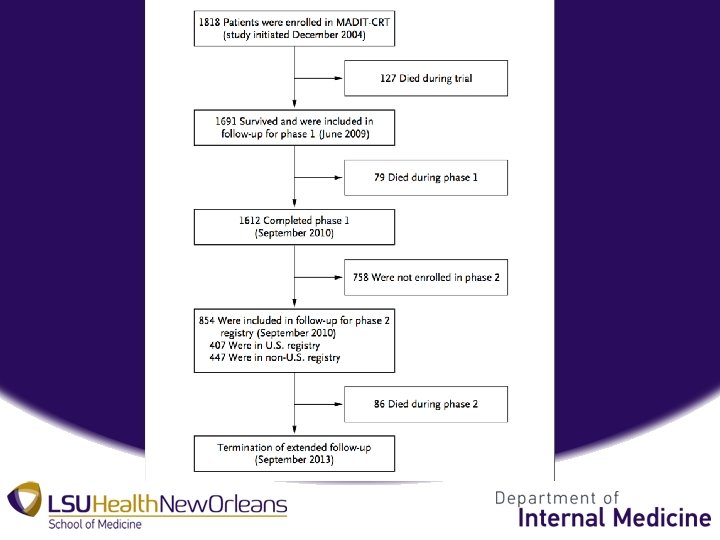
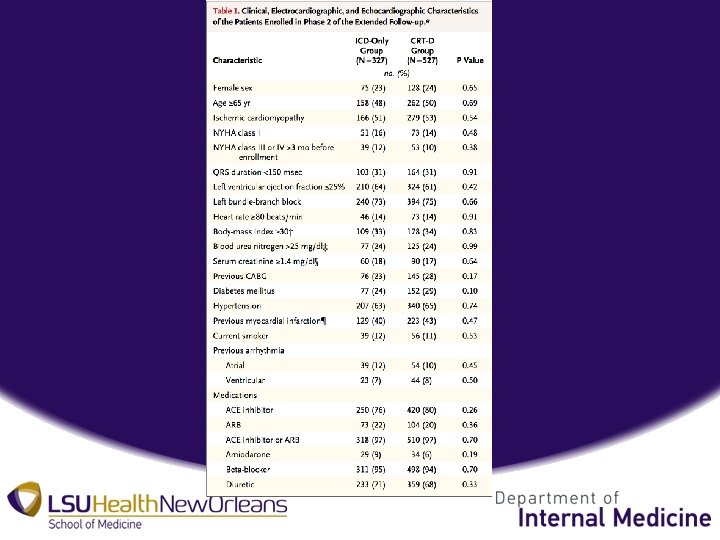
 Methods • Data Acquisition and Patient Follow-up – Phase 1: 1691 surviving pts from MADIT-CRT from US (88), Canada, Israel, and Europe (24) 6/22/09 – 9/10/10 – Phase 2: 854 surviving pts from MADIT-CRT from 9/10/10 – 9/2013 (48 US, 23 Non-US) – Phase 2 patient characteristics remained similar to phase 1.
Methods • Data Acquisition and Patient Follow-up – Phase 1: 1691 surviving pts from MADIT-CRT from US (88), Canada, Israel, and Europe (24) 6/22/09 – 9/10/10 – Phase 2: 854 surviving pts from MADIT-CRT from 9/10/10 – 9/2013 (48 US, 23 Non-US) – Phase 2 patient characteristics remained similar to phase 1.
 • Definitions and End Points – Death from any cause (primary), Non-Fatal HF event, either/or, whichever occurred first – Evaluated effects of CRT-D according to baseline QRS morphology, LBBB (70%) or non-LBBB (30%) • Original MADIT-CRT didn’t account for QRS morphology at onset of trial.
• Definitions and End Points – Death from any cause (primary), Non-Fatal HF event, either/or, whichever occurred first – Evaluated effects of CRT-D according to baseline QRS morphology, LBBB (70%) or non-LBBB (30%) • Original MADIT-CRT didn’t account for QRS morphology at onset of trial.
 Statistical Analysis • Analyses performed on intent-to-treat basis • Variables expressed as +/- SD • Categorical data summarized as freq and percentages • P-value of <0. 05 used as statistical significance
Statistical Analysis • Analyses performed on intent-to-treat basis • Variables expressed as +/- SD • Categorical data summarized as freq and percentages • P-value of <0. 05 used as statistical significance
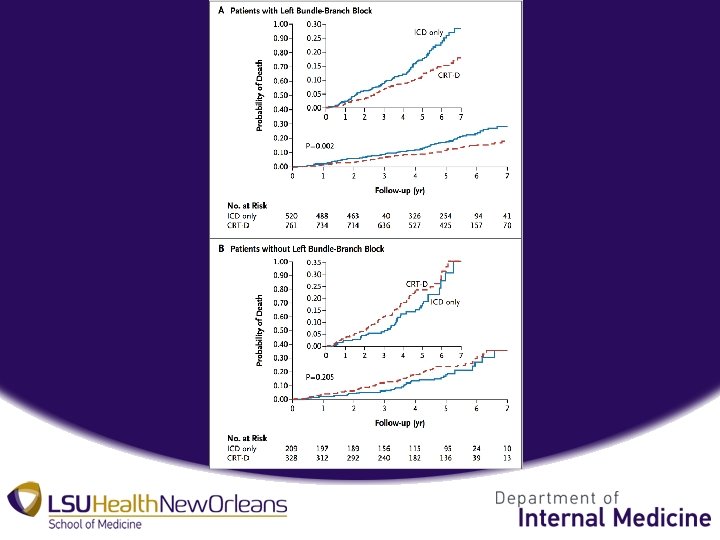
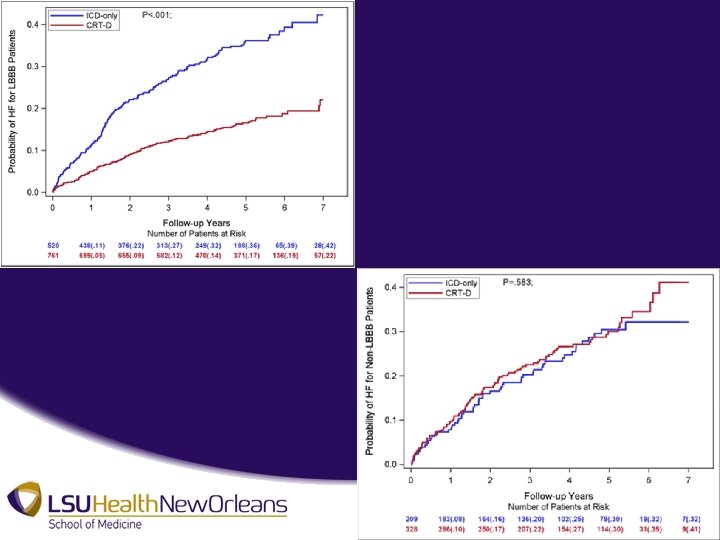
 Results • CRT-D in Patients with LBBB – At 7 years, cumulative rate of death of 29% in ICD only group compared to 18% in CRT-D group • P value = 0. 002 • NNT = 9 over 7 years • 41% reduction in long term risk of death, HR 0. 59 – At 7 years, probability of non-fatal HF event significantly lower in CRT-D group • P value < 0. 001 • 62% reduction in long term risk on HF event, HR 0. 38
Results • CRT-D in Patients with LBBB – At 7 years, cumulative rate of death of 29% in ICD only group compared to 18% in CRT-D group • P value = 0. 002 • NNT = 9 over 7 years • 41% reduction in long term risk of death, HR 0. 59 – At 7 years, probability of non-fatal HF event significantly lower in CRT-D group • P value < 0. 001 • 62% reduction in long term risk on HF event, HR 0. 38
 • CRT-D in Patients Without LBBB – At 7 years, no significant difference in cumulative rate of death between CRT-D and ICD only • P value = 0. 21 – At 7 years, no significant difference in rate of HF events • P value = 0. 58 • Trend toward increased risk of death and HF events >7 years
• CRT-D in Patients Without LBBB – At 7 years, no significant difference in cumulative rate of death between CRT-D and ICD only • P value = 0. 21 – At 7 years, no significant difference in rate of HF events • P value = 0. 58 • Trend toward increased risk of death and HF events >7 years
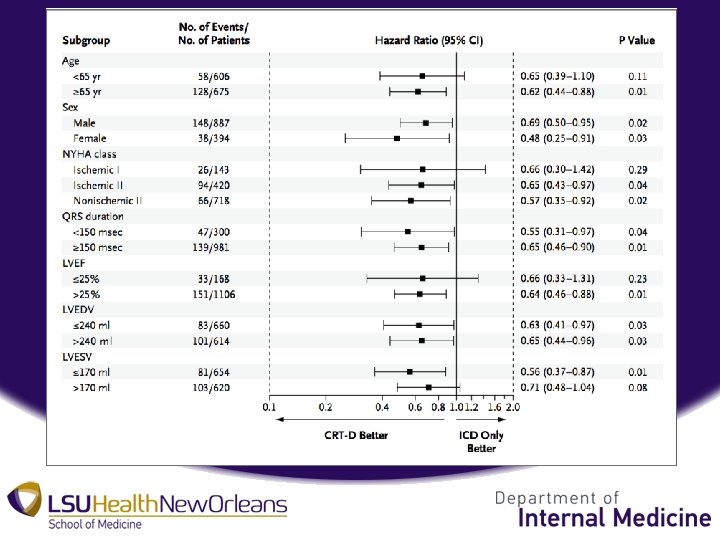
 Discussion • Early CRT-D has significant long term survival benefit in pts with mild HF, LV dys, and LBBB – Consistent across subgroups, sex, QRS, cause of cardiomyopathy – Associated with reverse remodeling • No benefit in long term outcomes without LBBB – Data doesn’t support early intervention in any subset.
Discussion • Early CRT-D has significant long term survival benefit in pts with mild HF, LV dys, and LBBB – Consistent across subgroups, sex, QRS, cause of cardiomyopathy – Associated with reverse remodeling • No benefit in long term outcomes without LBBB – Data doesn’t support early intervention in any subset.
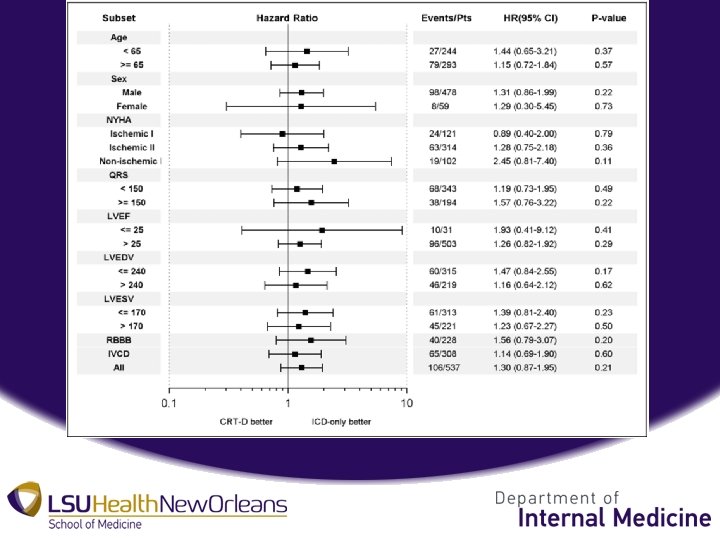
 Discussion • Mechanism of lack of benefit in non-LBBB uncertain • Possible disruption of electrical activation in LV – LV depolarization more heterogeneous – Pacing induced discrepancy of wave front – Increase in tachyarrhythmias – Poorer prognosis
Discussion • Mechanism of lack of benefit in non-LBBB uncertain • Possible disruption of electrical activation in LV – LV depolarization more heterogeneous – Pacing induced discrepancy of wave front – Increase in tachyarrhythmias – Poorer prognosis
 Discussion • Minimal survival bias – Analysis performed on an intention-to-treat basis – Negates cross-overs occurring during/after trial • Possible selection bias – 758 lost to follow up after phase 1 because of institutions that declined to participate – Study population characteristics comparable – Limited individual patient bias
Discussion • Minimal survival bias – Analysis performed on an intention-to-treat basis – Negates cross-overs occurring during/after trial • Possible selection bias – 758 lost to follow up after phase 1 because of institutions that declined to participate – Study population characteristics comparable – Limited individual patient bias
 Discussion • Possible Covariate Selection – Applies to harmful effects of CRT-D in non-LBBB population – No statistical significance – Data obtained after multivariate adjustment – Interpret with caution
Discussion • Possible Covariate Selection – Applies to harmful effects of CRT-D in non-LBBB population – No statistical significance – Data obtained after multivariate adjustment – Interpret with caution


