2c4719493724e47e82228d37d6f7dd39.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Survival following VAD complications: implications for transplant priority. Todd Dardas, MD, MS May 16, 2015
Survival following VAD complications: implications for transplant priority. Todd Dardas, MD, MS May 16, 2015
 Disclosures • Funding: – American College of Cardiology/Sankyo Daiichi Career Development Grant
Disclosures • Funding: – American College of Cardiology/Sankyo Daiichi Career Development Grant
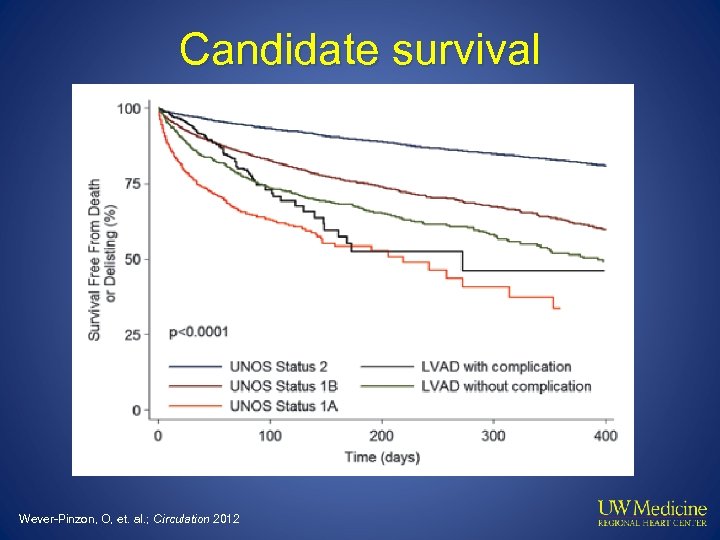 Candidate survival Wever-Pinzon, O, et. al. ; Circulation 2012
Candidate survival Wever-Pinzon, O, et. al. ; Circulation 2012
 Cumulative Mortality Status 1 A: Indexed by “first status” Ventilator Paracorporeal Exception VAD Complication IABP/Dual Inotrope Implanted VAD 0. 4 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 0 0 15 30 45 60 Days from initial listing Dardas T, et al J Am Coll Cardiol 2012 75 90
Cumulative Mortality Status 1 A: Indexed by “first status” Ventilator Paracorporeal Exception VAD Complication IABP/Dual Inotrope Implanted VAD 0. 4 0. 3 0. 2 0. 1 0 0 15 30 45 60 Days from initial listing Dardas T, et al J Am Coll Cardiol 2012 75 90
 Status 1 A exceptions Meyer D, et. al. American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 44– 54
Status 1 A exceptions Meyer D, et. al. American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 44– 54
 UNOS 1 A(b) justifications 4% 15% 11% Thrombosis Infection Device malfunction 18% 52% Arrhythmias Other Unpublished data, UNOS registry
UNOS 1 A(b) justifications 4% 15% 11% Thrombosis Infection Device malfunction 18% 52% Arrhythmias Other Unpublished data, UNOS registry
 Tier Proposals 1. MCS with arrhythmias, non-dischargeable VAD 2. Device malfunction, IABP 3. MCS (infection, thromboembolism, other complications), LVAD 30 days, dual inotropes 4. Inotrope w/o HD monitor, stable VAD 5. Multi-organ transplants 6. Remaining candidates Meyer D, et. al. American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 44– 54
Tier Proposals 1. MCS with arrhythmias, non-dischargeable VAD 2. Device malfunction, IABP 3. MCS (infection, thromboembolism, other complications), LVAD 30 days, dual inotropes 4. Inotrope w/o HD monitor, stable VAD 5. Multi-organ transplants 6. Remaining candidates Meyer D, et. al. American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 44– 54
 Guidance from OPTN 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Aortic insufficiency Hemolysis Pump thrombosis Pump-related local or systemic infection Bleeding Right heart failure Recrudescent arrhythmias Device malfunction Meyer D, et. al. American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 44– 54
Guidance from OPTN 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Aortic insufficiency Hemolysis Pump thrombosis Pump-related local or systemic infection Bleeding Right heart failure Recrudescent arrhythmias Device malfunction Meyer D, et. al. American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 44– 54
 OPTN infection guidance Pump-related or systemic infection with one of: • Symptoms along driveline with leukocytosis AND: + blood culture or + site culture • Surgical debridement of the driveline AND + site culture • + Pump pocket culture • Bacteremia with the same organism 4 weeks following treatment Meyer D, et. al. American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 44– 54; http: //www. uab. edu/medicine/intermacs/appendices-4 -0/appendix-a-4 -0
OPTN infection guidance Pump-related or systemic infection with one of: • Symptoms along driveline with leukocytosis AND: + blood culture or + site culture • Surgical debridement of the driveline AND + site culture • + Pump pocket culture • Bacteremia with the same organism 4 weeks following treatment Meyer D, et. al. American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 44– 54; http: //www. uab. edu/medicine/intermacs/appendices-4 -0/appendix-a-4 -0
 Research aims • Determine mortality for complications following CF VAD placement and compare to non-MCS UNOS candidates. • Evaluate whether subgroups within complications have distinct risks useful for ranking in the tier system.
Research aims • Determine mortality for complications following CF VAD placement and compare to non-MCS UNOS candidates. • Evaluate whether subgroups within complications have distinct risks useful for ranking in the tier system.
 Methods • INTERMACS data for all primary implants of CF devices implanted between 4/2012 and 3/2014 • DT and BTT included unless otherwise specified • Complications: – – – Multiple complications per time point First and isolated complication First infection of any number reported • OPTN/UNOS registry data for patients without MCS
Methods • INTERMACS data for all primary implants of CF devices implanted between 4/2012 and 3/2014 • DT and BTT included unless otherwise specified • Complications: – – – Multiple complications per time point First and isolated complication First infection of any number reported • OPTN/UNOS registry data for patients without MCS
 Sample Complications/ interval Strategy Other 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 BTT BTE DT Total 5 162 53 12 1 1 0 0 151 2, 607 808 118 24 9 1 0 186 4, 320 1, 385 207 44 9 4 4 299 6, 011 2, 052 342 87 17 3 0 641 13, 100 4, 298 679 156 36 8 4
Sample Complications/ interval Strategy Other 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 BTT BTE DT Total 5 162 53 12 1 1 0 0 151 2, 607 808 118 24 9 1 0 186 4, 320 1, 385 207 44 9 4 4 299 6, 011 2, 052 342 87 17 3 0 641 13, 100 4, 298 679 156 36 8 4
 Outcome • Death during VAD support • Censoring at transplant or recovery
Outcome • Death during VAD support • Censoring at transplant or recovery
 Sample • • • 4725 primary CF VAD implants 22, 524 complications 2975 1 st and isolated complications No AE report n=641 Final cohort: n= 3616
Sample • • • 4725 primary CF VAD implants 22, 524 complications 2975 1 st and isolated complications No AE report n=641 Final cohort: n= 3616
 Mortality following first complication N = 3616
Mortality following first complication N = 3616
 Freedom from major complication Major Complications: INTERMACS 1 0. 8 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 0 365 730 1095 Days since implant Kirklin J et. al. , J Heart Lung Transplant 2013 1460
Freedom from major complication Major Complications: INTERMACS 1 0. 8 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 0 365 730 1095 Days since implant Kirklin J et. al. , J Heart Lung Transplant 2013 1460
 INTERMACS AEs Hemolysis Other SAE Respiratory Failure Neurological Dysfunction Right Heart Failure Hepatic Dysfunction Venous Thromboembolism Cardiac Arrhythmias Device Malfunction Hypertension Wound Dehiscence Pericardial Fluid Collection Major Bleeding Myocardial Infarction Arterial Non-CNS embolism Psychiatric Episode Major Infection Renal Dysfunction
INTERMACS AEs Hemolysis Other SAE Respiratory Failure Neurological Dysfunction Right Heart Failure Hepatic Dysfunction Venous Thromboembolism Cardiac Arrhythmias Device Malfunction Hypertension Wound Dehiscence Pericardial Fluid Collection Major Bleeding Myocardial Infarction Arterial Non-CNS embolism Psychiatric Episode Major Infection Renal Dysfunction
 Mortality following first AE reported Adverse Event Cumulative hazard at 90 days following report Std. err. Renal Dysfunction 0. 46 Neurological Dysfunction 0. 45 0. 09 Status 1 A 0. 10 Respiratory Failure 0. 21 0. 04 Device Malfunction 0. 21 0. 10 Right Heart Failure 0. 17 0. 04 Bleeding 0. 15 0. 02 Pericardial Drainage 0. 12 0. 05 Infection 0. 12 Other SAE 0. 10 Status 1 B 0. 02 Venous Thromboemb. 0. 08 0. 06 Hemolysis 0. 07 0. 05 Cardiac Arrhythmia 0. 07 0. 01 Psychiatric Episode 0. 05 0. 03
Mortality following first AE reported Adverse Event Cumulative hazard at 90 days following report Std. err. Renal Dysfunction 0. 46 Neurological Dysfunction 0. 45 0. 09 Status 1 A 0. 10 Respiratory Failure 0. 21 0. 04 Device Malfunction 0. 21 0. 10 Right Heart Failure 0. 17 0. 04 Bleeding 0. 15 0. 02 Pericardial Drainage 0. 12 0. 05 Infection 0. 12 Other SAE 0. 10 Status 1 B 0. 02 Venous Thromboemb. 0. 08 0. 06 Hemolysis 0. 07 0. 05 Cardiac Arrhythmia 0. 07 0. 01 Psychiatric Episode 0. 05 0. 03
 st 1 Infection AE N= 4632
st 1 Infection AE N= 4632
 Adjusting for initial device strategy Variables Hazard ratio P-value AE infection 3. 1 <0. 0001 DT Ref BTT 0. 58 <0. 0001 BTE 0. 67 <0. 0001 Other strategy 0. 97 0. 92
Adjusting for initial device strategy Variables Hazard ratio P-value AE infection 3. 1 <0. 0001 DT Ref BTT 0. 58 <0. 0001 BTE 0. 67 <0. 0001 Other strategy 0. 97 0. 92
 Comparison to OPTN Status 1 A Status 1 B
Comparison to OPTN Status 1 A Status 1 B
 Infection Definition OPTN One of: • Symptoms along driveline with leukocytosis AND: • + blood culture • + site culture • Surgical debridement AND + site culture • + pump pocket culture • Bacteremia 4 wks s/p treatment INTERMACS • Localized non-device • Driveline or pump pocket • Sepsis • Internal pump component Meyer D, et. al. American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 44– 54; http: //www. uab. edu/medicine/intermacs/appendices-4 -0/appendix-a-4 -0
Infection Definition OPTN One of: • Symptoms along driveline with leukocytosis AND: • + blood culture • + site culture • Surgical debridement AND + site culture • + pump pocket culture • Bacteremia 4 wks s/p treatment INTERMACS • Localized non-device • Driveline or pump pocket • Sepsis • Internal pump component Meyer D, et. al. American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 44– 54; http: //www. uab. edu/medicine/intermacs/appendices-4 -0/appendix-a-4 -0
 INTERMACS subgroups All p-values <0. 01 vs. No infection AE
INTERMACS subgroups All p-values <0. 01 vs. No infection AE
 Adjusted for initial device strategy Variable Hazard ratio P-value Infection AE No Inf. AE reported Ref Localized, non-VAD 3. 2 <0. 0001 Perc. lead/pocket 1. 9 <0. 0001 Device component 8. 5 0. 003 Sepsis 3. 8 <0. 0001 DT Ref BTT 0. 58 <0. 0001 BTE 0. 68 <0. 0001 Other 0. 95 0. 86 Strategy
Adjusted for initial device strategy Variable Hazard ratio P-value Infection AE No Inf. AE reported Ref Localized, non-VAD 3. 2 <0. 0001 Perc. lead/pocket 1. 9 <0. 0001 Device component 8. 5 0. 003 Sepsis 3. 8 <0. 0001 DT Ref BTT 0. 58 <0. 0001 BTE 0. 68 <0. 0001 Other 0. 95 0. 86 Strategy
 INTERMACS AEs & OPTN status Driveline vs. No inf. AE p=0. 13 All other p-values <0. 01 Status 1 A Status 1 B
INTERMACS AEs & OPTN status Driveline vs. No inf. AE p=0. 13 All other p-values <0. 01 Status 1 A Status 1 B
 Tier Proposals 1. MCS with arrhythmias, non-dischargeable VAD 2. MCS sepsis OR pump pocket/internal device infection OR localized infection, IABP 3. MCS driveline infection, thromboembolism, LVAD 30 days, dual inotropes 4. Inotrope w/o HD monitor, stable VAD Meyer D, et. al. American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 44– 54
Tier Proposals 1. MCS with arrhythmias, non-dischargeable VAD 2. MCS sepsis OR pump pocket/internal device infection OR localized infection, IABP 3. MCS driveline infection, thromboembolism, LVAD 30 days, dual inotropes 4. Inotrope w/o HD monitor, stable VAD Meyer D, et. al. American Journal of Transplantation 2015; 15: 44– 54
 Considerations • How should continued eligibility be weighted in priority decisions?
Considerations • How should continued eligibility be weighted in priority decisions?
 Changing device strategy Teuteberg J, et. al. J Am Coll Cardiol HF 2013
Changing device strategy Teuteberg J, et. al. J Am Coll Cardiol HF 2013
 BTT vs DT: 90 -day mortality AE type BTT DT DT - BTT Bleeding 0. 12 0. 18 0. 06 Cardiac Arrhythmia 0. 01 0. 12 0. 11 Infection 0. 14 0. 12 -0. 02 Neurological Dysfunction 0. 22 0. 59 0. 37 Other SAE 0. 02 0. 16 0. 13 Psychiatric Episode 0. 07 0. 00 -0. 07 Renal Dysfunction 0. 24 0. 55 0. 30 Respiratory Failure 0. 23 0. 28 0. 05 Right Heart Failure 0. 08 0. 23 0. 15
BTT vs DT: 90 -day mortality AE type BTT DT DT - BTT Bleeding 0. 12 0. 18 0. 06 Cardiac Arrhythmia 0. 01 0. 12 0. 11 Infection 0. 14 0. 12 -0. 02 Neurological Dysfunction 0. 22 0. 59 0. 37 Other SAE 0. 02 0. 16 0. 13 Psychiatric Episode 0. 07 0. 00 -0. 07 Renal Dysfunction 0. 24 0. 55 0. 30 Respiratory Failure 0. 23 0. 28 0. 05 Right Heart Failure 0. 08 0. 23 0. 15
 Considerations • How many subgroups should be identified analyzed?
Considerations • How many subgroups should be identified analyzed?
 Stratified complications? Yes • Infections • Right heart failure • Bleeding • Hemolysis Maybe • Device malfunction No • Ventricular arrhythmias • Thrombosis • Aortic regurg.
Stratified complications? Yes • Infections • Right heart failure • Bleeding • Hemolysis Maybe • Device malfunction No • Ventricular arrhythmias • Thrombosis • Aortic regurg.
 Conclusions Subgroups of patients within broad complication types may warrant further characterization and stratification by INTERMACS definitions
Conclusions Subgroups of patients within broad complication types may warrant further characterization and stratification by INTERMACS definitions
 • • • Susan Meyer Frank Pagani Kent Shively
• • • Susan Meyer Frank Pagani Kent Shively
 Mortality following first AE reported Cumulative hazard at 90 days following report Std. err. At risk Deaths Renal Dysfunction 0. 46 0. 09 53 30 Neurological Dysfunction 0. 45 0. 10 56 24 Respiratory Failure 0. 21 0. 04 95 22 Device Malfunction 0. 21 0. 10 38 5 Right Heart Failure 0. 17 0. 04 170 29 Bleeding 0. 15 0. 02 367 55 Pericardial Drainage 0. 12 0. 05 46 6 Infection 0. 12 0. 02 238 25 Other SAE 0. 10 0. 02 224 22 Venous Thromboemb. 0. 08 0. 06 23 2 Hemolysis 0. 07 0. 05 33 2 Cardiac Arrhythmia 0. 07 0. 01 291 22 Psychiatric Episode 0. 05 0. 03 41 2 Adverse Event
Mortality following first AE reported Cumulative hazard at 90 days following report Std. err. At risk Deaths Renal Dysfunction 0. 46 0. 09 53 30 Neurological Dysfunction 0. 45 0. 10 56 24 Respiratory Failure 0. 21 0. 04 95 22 Device Malfunction 0. 21 0. 10 38 5 Right Heart Failure 0. 17 0. 04 170 29 Bleeding 0. 15 0. 02 367 55 Pericardial Drainage 0. 12 0. 05 46 6 Infection 0. 12 0. 02 238 25 Other SAE 0. 10 0. 02 224 22 Venous Thromboemb. 0. 08 0. 06 23 2 Hemolysis 0. 07 0. 05 33 2 Cardiac Arrhythmia 0. 07 0. 01 291 22 Psychiatric Episode 0. 05 0. 03 41 2 Adverse Event
 Risk of first AE relative to Status 1 A/B Status 1 A Status 1 B
Risk of first AE relative to Status 1 A/B Status 1 A Status 1 B


