e8ff671082e215545f6c4671399d0792.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Surveying the Social Landscape Ontologies, Social Networks, and Analytic Challenges Kimberly Glasgow Senior Technical Engineer, CACI kglasgow@caci. com 1 December 2006 1
Surveying the Social Landscape Ontologies, Social Networks, and Analytic Challenges Kimberly Glasgow Senior Technical Engineer, CACI kglasgow@caci. com 1 December 2006 1
 Overview o Understanding fundamental SNA concepts n n What’s a Network? What do you do with it? p Analytic methods o How might ontology fit in? o How can the two help address intelligence challenges? 1 December 2006 2
Overview o Understanding fundamental SNA concepts n n What’s a Network? What do you do with it? p Analytic methods o How might ontology fit in? o How can the two help address intelligence challenges? 1 December 2006 2
 Hypothetical task o Analysis of an imaginary terrorist group 1 December 2006 3
Hypothetical task o Analysis of an imaginary terrorist group 1 December 2006 3
 Imaginary group - “Sword of Allah Jihadi’s Brigade” o Background n Predominantly Middle Eastern terrorist group n Religious extremism n Loose affiliation with al Qaeda p Training camps n Threat to U. S personnel, business interests throughout region o Goal n Disrupt financial network p Identify key individuals p Confidence p Measure of effectiveness 1 December 2006 4
Imaginary group - “Sword of Allah Jihadi’s Brigade” o Background n Predominantly Middle Eastern terrorist group n Religious extremism n Loose affiliation with al Qaeda p Training camps n Threat to U. S personnel, business interests throughout region o Goal n Disrupt financial network p Identify key individuals p Confidence p Measure of effectiveness 1 December 2006 4
 Imaginary Background on “Sword of Allah Jihadi’s Brigade” Ahmed al-Yemeni, and Yasin al-Yemeni (believed to be brothers, or possibly, cousins) are among those who have supplied currency, in varying amounts of USD to Ahmed Salman, who has also been supported by several others in the SAJB, such as Ahmed Yasin and Salman. Notably, the transfer of funds from Ahmed al-Yemeni may be largest amount (possibly $1400) known to have taken place in SAJB in recent years. Some of this funding may also have been used to enable Ahmed Ali’s activities, probably using Mustafa as a conduit for funds. Support has flowed to Salman Ali, known to have attended a training camp at the same time as both Ahmed Salman, and Salman Said, from a number of sources, including Ahmed Zayman, Salman, and Salman Muhammad, though the amounts or even denominations involved in these activities remains incompletely understood. Yasin has supplied at least $500 to Ahmed Ali, who has in turn funded Salman Hakin, and possibly also provided fraudulent documentation, which he in turn may have gone to Ahmed Yasin, though this cannot be confirmed… 1 December 2006 5
Imaginary Background on “Sword of Allah Jihadi’s Brigade” Ahmed al-Yemeni, and Yasin al-Yemeni (believed to be brothers, or possibly, cousins) are among those who have supplied currency, in varying amounts of USD to Ahmed Salman, who has also been supported by several others in the SAJB, such as Ahmed Yasin and Salman. Notably, the transfer of funds from Ahmed al-Yemeni may be largest amount (possibly $1400) known to have taken place in SAJB in recent years. Some of this funding may also have been used to enable Ahmed Ali’s activities, probably using Mustafa as a conduit for funds. Support has flowed to Salman Ali, known to have attended a training camp at the same time as both Ahmed Salman, and Salman Said, from a number of sources, including Ahmed Zayman, Salman, and Salman Muhammad, though the amounts or even denominations involved in these activities remains incompletely understood. Yasin has supplied at least $500 to Ahmed Ali, who has in turn funded Salman Hakin, and possibly also provided fraudulent documentation, which he in turn may have gone to Ahmed Yasin, though this cannot be confirmed… 1 December 2006 5
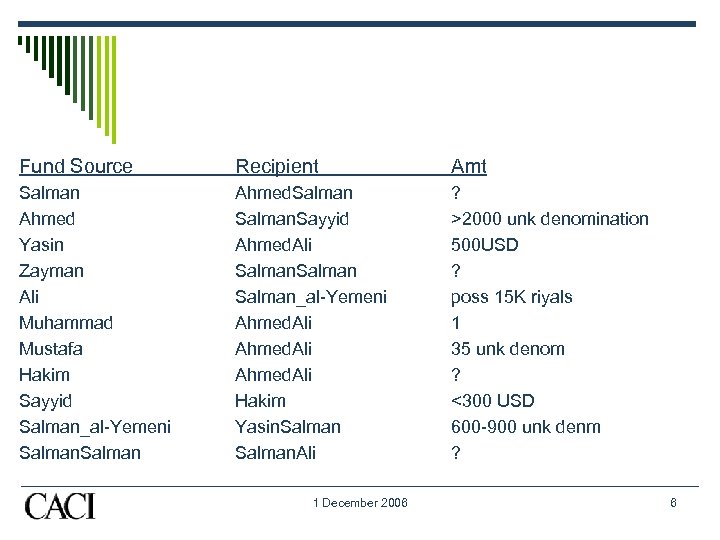 Fund Source Recipient Amt Salman Ahmed Yasin Zayman Ali Muhammad Mustafa Hakim Sayyid Salman_al-Yemeni Salman Ahmed. Salman. Sayyid Ahmed. Ali Salman_al-Yemeni Ahmed. Ali Hakim Yasin. Salman. Ali ? >2000 unk denomination 500 USD ? poss 15 K riyals 1 35 unk denom ? <300 USD 600 -900 unk denm ? 1 December 2006 6
Fund Source Recipient Amt Salman Ahmed Yasin Zayman Ali Muhammad Mustafa Hakim Sayyid Salman_al-Yemeni Salman Ahmed. Salman. Sayyid Ahmed. Ali Salman_al-Yemeni Ahmed. Ali Hakim Yasin. Salman. Ali ? >2000 unk denomination 500 USD ? poss 15 K riyals 1 35 unk denom ? <300 USD 600 -900 unk denm ? 1 December 2006 6
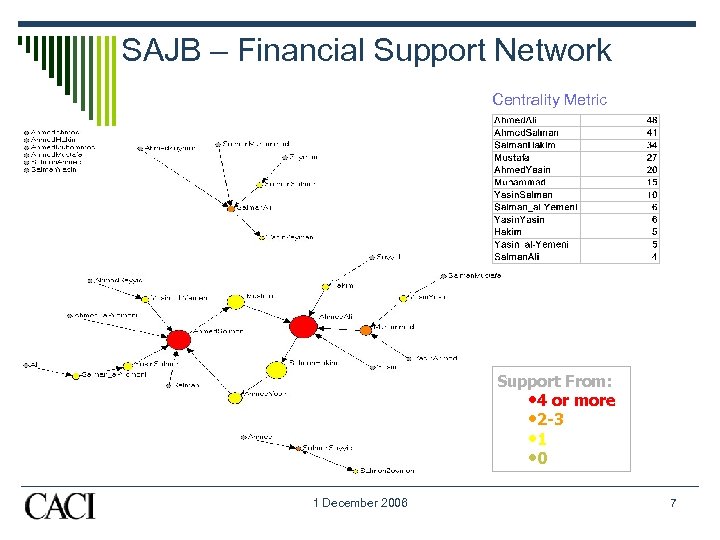 SAJB – Financial Support Network Centrality Metric Support From: • 4 or more • 2 -3 • 1 • 0 1 December 2006 7
SAJB – Financial Support Network Centrality Metric Support From: • 4 or more • 2 -3 • 1 • 0 1 December 2006 7
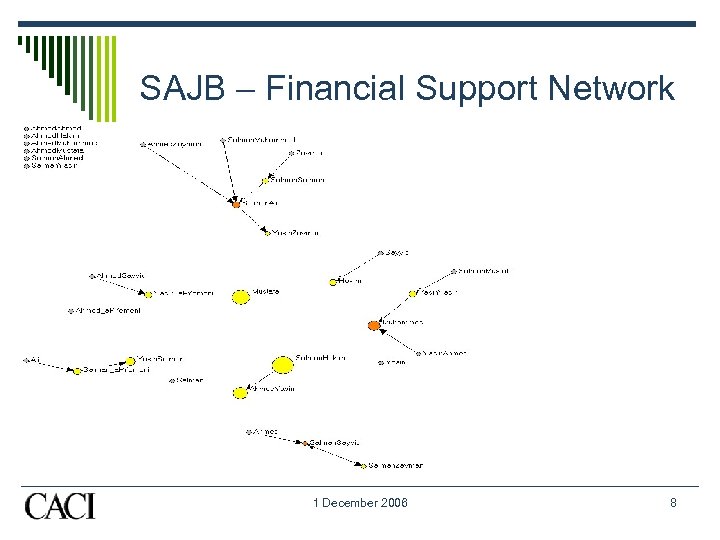 SAJB – Financial Support Network 1 December 2006 8
SAJB – Financial Support Network 1 December 2006 8
 Challenges o Data n n Too much, too fast, too many kinds Bias o Information n Entities p n Representation, normalization, coreference Relations o Analytic n n Methodology Completeness Inference Retrieval 1 December 2006 9
Challenges o Data n n Too much, too fast, too many kinds Bias o Information n Entities p n Representation, normalization, coreference Relations o Analytic n n Methodology Completeness Inference Retrieval 1 December 2006 9
 What’s a network? 1 December 2006 10
What’s a network? 1 December 2006 10
 Another network 1 December 2006 11
Another network 1 December 2006 11
 Another network 1 December 2006 12
Another network 1 December 2006 12
 Last one 1 December 2006 13
Last one 1 December 2006 13
 Global Future of Terrorism. . ”U. S. counterterrorist policies are tailored to combat what we believe to be the shifting trends in terrorism. One trend is the shift from well-organized, local groups supported by state sponsors to loosely organized, international networks of terrorists. . ” Patterns of Global Terrorism, 2000 1 December 2006 14
Global Future of Terrorism. . ”U. S. counterterrorist policies are tailored to combat what we believe to be the shifting trends in terrorism. One trend is the shift from well-organized, local groups supported by state sponsors to loosely organized, international networks of terrorists. . ” Patterns of Global Terrorism, 2000 1 December 2006 14
 The Networked Future of Crime “. . criminal organizations and networks based in North America, Western Europe, China, Columbia, Israel, Japan, Mexico, Nigeria, and Russia will expand the scope and scale of their activities. They will form loose alliances…corrupt leaders. . insinuate themselves into troubled banks and businesses…” Global Trends 2015, Nat’l Intelligence Council 1 December 2006 15
The Networked Future of Crime “. . criminal organizations and networks based in North America, Western Europe, China, Columbia, Israel, Japan, Mexico, Nigeria, and Russia will expand the scope and scale of their activities. They will form loose alliances…corrupt leaders. . insinuate themselves into troubled banks and businesses…” Global Trends 2015, Nat’l Intelligence Council 1 December 2006 15
 A network is. . Anything that can be represented as n Actors (nodes, vertices, entities) joined together by n Relationships (edges, ties, links, arcs) Note: n n Actors are commonly people (groups, organizations, companies, nations) Relationships possess an element of choice (nonrandom) o Work, friendship, kinship, orders, support, communication… Remember the “S” in SNA 1 December 2006 16
A network is. . Anything that can be represented as n Actors (nodes, vertices, entities) joined together by n Relationships (edges, ties, links, arcs) Note: n n Actors are commonly people (groups, organizations, companies, nations) Relationships possess an element of choice (nonrandom) o Work, friendship, kinship, orders, support, communication… Remember the “S” in SNA 1 December 2006 16
 High level view of SNA o Scientific, mathematical means to study networks of connected individuals (or organizations) p Kinship, friendship, exchange, sex p Group survival, individual success, spread of disease o Business consulting- networks and bottom line o Health and Social Policy p AIDS, sex and drug networks, social support, education… o Intelligence, Homeland Security, Law Enforcement 1 December 2006 17
High level view of SNA o Scientific, mathematical means to study networks of connected individuals (or organizations) p Kinship, friendship, exchange, sex p Group survival, individual success, spread of disease o Business consulting- networks and bottom line o Health and Social Policy p AIDS, sex and drug networks, social support, education… o Intelligence, Homeland Security, Law Enforcement 1 December 2006 17
 History o Jacob Moreno (1889 -1974) n n leading psychotherapist, theorist founder of Sociometry pioneer of Group Psychotherapy o Stanley Milgram p “Six Degrees of Separation” o Watts and Strogatz p Network model to generate “small world” graphs o Barabasi n Scale-free, preferential attachment, P(k) =Ak−γ 1 December 2006 18
History o Jacob Moreno (1889 -1974) n n leading psychotherapist, theorist founder of Sociometry pioneer of Group Psychotherapy o Stanley Milgram p “Six Degrees of Separation” o Watts and Strogatz p Network model to generate “small world” graphs o Barabasi n Scale-free, preferential attachment, P(k) =Ak−γ 1 December 2006 18
 SNA Basics n Emerged from p p p n Quantify social relations p p n Sociology Graph Theory Statistics… Data represented as matrices Algorithms (it’s all about the metrics) Properties of networks p p p Structure Position Subgroups 1 December 2006 19
SNA Basics n Emerged from p p p n Quantify social relations p p n Sociology Graph Theory Statistics… Data represented as matrices Algorithms (it’s all about the metrics) Properties of networks p p p Structure Position Subgroups 1 December 2006 19
 What can you do with a matrix? o Add, subtract, multiply, divide o Symmetrize, dichotomize, transpose, reverse In other words, perform any operation that turns your information into a more accurate representation of the phenomenon you’re analyzing = Incredible flexibility Unfortunately, no one can be told what the Matrix is. You have to see it for yourself. -Morpheus 1 December 2006 20
What can you do with a matrix? o Add, subtract, multiply, divide o Symmetrize, dichotomize, transpose, reverse In other words, perform any operation that turns your information into a more accurate representation of the phenomenon you’re analyzing = Incredible flexibility Unfortunately, no one can be told what the Matrix is. You have to see it for yourself. -Morpheus 1 December 2006 20
 How can you analyze a social network? o Network level measures n Basic statistics – how big, how many n Density, distance – how well connected o Subgroup measures n Identify, characterize locally dense regions of the graph o Individual measures n Centrality – prominence, prestige All ways to answer sociologically meaningful questions about networks 1 December 2006 21
How can you analyze a social network? o Network level measures n Basic statistics – how big, how many n Density, distance – how well connected o Subgroup measures n Identify, characterize locally dense regions of the graph o Individual measures n Centrality – prominence, prestige All ways to answer sociologically meaningful questions about networks 1 December 2006 21
 Ontology o Flexible, extensible way to represent knowledge about the world n Can evolve as intelligence needs change o Computationally tractable o Richer than taxonomy o Better suited to modeling social phenomena 1 December 2006 22
Ontology o Flexible, extensible way to represent knowledge about the world n Can evolve as intelligence needs change o Computationally tractable o Richer than taxonomy o Better suited to modeling social phenomena 1 December 2006 22
 How does ontology fit in? o Rigor of creating an ontology for a given domain n clarifies thinking n Exposes knowledge gaps, assumptions o Automation of knowledge creation n Inference new facts from p Existing (individual facts) p Multiple facts o Improved accuracy and completeness of information o Enhanced query and retrieval capabilities n query at a humanly meaningful level 1 December 2006 23
How does ontology fit in? o Rigor of creating an ontology for a given domain n clarifies thinking n Exposes knowledge gaps, assumptions o Automation of knowledge creation n Inference new facts from p Existing (individual facts) p Multiple facts o Improved accuracy and completeness of information o Enhanced query and retrieval capabilities n query at a humanly meaningful level 1 December 2006 23
 An ontology of social relations o Social interactions n What we do with or to each other o Social perception n What we think or feel about others o Social roles n Kinship 1 December 2006 24
An ontology of social relations o Social interactions n What we do with or to each other o Social perception n What we think or feel about others o Social roles n Kinship 1 December 2006 24
 Inner World, Outer World o Behaviors and interactions n Power and authority n Communication n Support n Business n Sexual o Knowledge/beliefs/emotions n Cognitive n Affective 1 December 2006 25
Inner World, Outer World o Behaviors and interactions n Power and authority n Communication n Support n Business n Sexual o Knowledge/beliefs/emotions n Cognitive n Affective 1 December 2006 25
 Is it easy? 1 December 2006 26
Is it easy? 1 December 2006 26
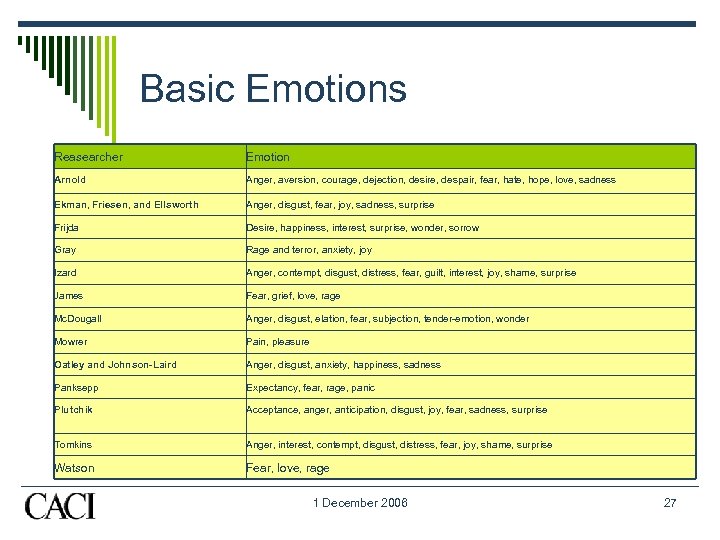 Basic Emotions Reasearcher Emotion Arnold Anger, aversion, courage, dejection, desire, despair, fear, hate, hope, love, sadness Ekman, Friesen, and Ellsworth Anger, disgust, fear, joy, sadness, surprise Frijda Desire, happiness, interest, surprise, wonder, sorrow Gray Rage and terror, anxiety, joy Izard Anger, contempt, disgust, distress, fear, guilt, interest, joy, shame, surprise James Fear, grief, love, rage Mc. Dougall Anger, disgust, elation, fear, subjection, tender-emotion, wonder Mowrer Pain, pleasure Oatley and Johnson-Laird Anger, disgust, anxiety, happiness, sadness Panksepp Expectancy, fear, rage, panic Plutchik Acceptance, anger, anticipation, disgust, joy, fear, sadness, surprise Tomkins Anger, interest, contempt, disgust, distress, fear, joy, shame, surprise Watson Fear, love, rage 1 December 2006 27
Basic Emotions Reasearcher Emotion Arnold Anger, aversion, courage, dejection, desire, despair, fear, hate, hope, love, sadness Ekman, Friesen, and Ellsworth Anger, disgust, fear, joy, sadness, surprise Frijda Desire, happiness, interest, surprise, wonder, sorrow Gray Rage and terror, anxiety, joy Izard Anger, contempt, disgust, distress, fear, guilt, interest, joy, shame, surprise James Fear, grief, love, rage Mc. Dougall Anger, disgust, elation, fear, subjection, tender-emotion, wonder Mowrer Pain, pleasure Oatley and Johnson-Laird Anger, disgust, anxiety, happiness, sadness Panksepp Expectancy, fear, rage, panic Plutchik Acceptance, anger, anticipation, disgust, joy, fear, sadness, surprise Tomkins Anger, interest, contempt, disgust, distress, fear, joy, shame, surprise Watson Fear, love, rage 1 December 2006 27
 Is it easy? . No Organize and prioritize based upon customer’s decision-making needs 1 December 2006 28
Is it easy? . No Organize and prioritize based upon customer’s decision-making needs 1 December 2006 28
 Why care about social networks? n Fundamentally different way of representing and understanding targets p “six n degrees of separation” Enabling unique and powerful kinds of analysis Way to survey, interpret, share information about the social landscape 1 December 2006 29
Why care about social networks? n Fundamentally different way of representing and understanding targets p “six n degrees of separation” Enabling unique and powerful kinds of analysis Way to survey, interpret, share information about the social landscape 1 December 2006 29
 Why care about ontologies wrt social networks? n Way to store structured information about what’s true about the social world we care about p “Knows” n n n what we know In a way that’s useful to humans Integrating different types of data And we can ask them cool questions Way to store, inference, retrieve, share information about the social landscape 1 December 2006 30
Why care about ontologies wrt social networks? n Way to store structured information about what’s true about the social world we care about p “Knows” n n n what we know In a way that’s useful to humans Integrating different types of data And we can ask them cool questions Way to store, inference, retrieve, share information about the social landscape 1 December 2006 30
 In summary o SNA is a fundamentally different way of representing and understanding the world n n n Networks Subgroups Individuals o Enables unique and powerful kinds of analysis to meet intelligence needs o Challenging information demands greatly enabled and enhanced by ontology 1 December 2006 31
In summary o SNA is a fundamentally different way of representing and understanding the world n n n Networks Subgroups Individuals o Enables unique and powerful kinds of analysis to meet intelligence needs o Challenging information demands greatly enabled and enhanced by ontology 1 December 2006 31
 Questions? 1 December 2006 32
Questions? 1 December 2006 32


