4ee57cffbcdc6ddcbad0e7f5193bd120.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 84
 Surgical trauma. Traumatic disease. Multiple injuries. Certain types of damage. L. Yu. Ivashchuk
Surgical trauma. Traumatic disease. Multiple injuries. Certain types of damage. L. Yu. Ivashchuk
 Complex Trauma Priorities
Complex Trauma Priorities
 Overview • Priorities in Multiply Injured Patient – Resuscitation – Fracture Fixation • Pelvic Trauma • Mangled Extremity
Overview • Priorities in Multiply Injured Patient – Resuscitation – Fracture Fixation • Pelvic Trauma • Mangled Extremity
 Resuscitation • ATLS Principles: – Primary survey : emergency/casualty • identify and treat life threatening injuries – Secondary Survey: emergency/casualty • reassess and diagnosis limb and non life threatening injuries – Definitive care: OR, ICU, ward, rehab • treatment of all injuries in logical team approach
Resuscitation • ATLS Principles: – Primary survey : emergency/casualty • identify and treat life threatening injuries – Secondary Survey: emergency/casualty • reassess and diagnosis limb and non life threatening injuries – Definitive care: OR, ICU, ward, rehab • treatment of all injuries in logical team approach
 Primary Survey • Airway: #1 cause of death • Breathing: lungs • Circulation: blood loss • Disability: brain • Expose/Extremities
Primary Survey • Airway: #1 cause of death • Breathing: lungs • Circulation: blood loss • Disability: brain • Expose/Extremities
 Primary Survey • Airway: #1 cause of death • Breathing: lungs • Circulation: blood loss • Disability: brain • Expose/Extremities
Primary Survey • Airway: #1 cause of death • Breathing: lungs • Circulation: blood loss • Disability: brain • Expose/Extremities
 Airway • Rapid assessment - pre-hospital • Intubation • Protect C spine
Airway • Rapid assessment - pre-hospital • Intubation • Protect C spine
 Breathing • Tension pneumothorax: A killer • Flail chest • Pulmonary contusion • Open injuries • Hemothorax • TREATMENT: O 2 and CHEST TUBES
Breathing • Tension pneumothorax: A killer • Flail chest • Pulmonary contusion • Open injuries • Hemothorax • TREATMENT: O 2 and CHEST TUBES
 Circulation • Hypovolemic shock - blood loss – abdomen, chest, fractures, retroperitoneum • Pump failure - rare • TREATMENT: SURGICAL DISEASE – Diagnosis – Stop – Replace
Circulation • Hypovolemic shock - blood loss – abdomen, chest, fractures, retroperitoneum • Pump failure - rare • TREATMENT: SURGICAL DISEASE – Diagnosis – Stop – Replace
 Disability • Head - Brain • Spine • Acute treatment part of resuscitation
Disability • Head - Brain • Spine • Acute treatment part of resuscitation
 Extremities • Pelvis • Open Fractures • Femurs • Crush - Compartment syndromes
Extremities • Pelvis • Open Fractures • Femurs • Crush - Compartment syndromes
 Priorities • Trauma Surgeon -team leader • Neurosurgery • Orthopaedic Surgery • Urology • Plastic Surgery
Priorities • Trauma Surgeon -team leader • Neurosurgery • Orthopaedic Surgery • Urology • Plastic Surgery
 Multiple Trauma Patients • Learn to prioritize/temporize • Haemodynamics • Coagulation Profile • Pulmonary Status • Brain Injury Then, consider orthopaedic needs
Multiple Trauma Patients • Learn to prioritize/temporize • Haemodynamics • Coagulation Profile • Pulmonary Status • Brain Injury Then, consider orthopaedic needs
 Goals not achieved in an “orthopaedic vacuum”
Goals not achieved in an “orthopaedic vacuum”
 Timing of Care Communication/Negotiation • How much care? • How fast? • Continually reassess changing situation
Timing of Care Communication/Negotiation • How much care? • How fast? • Continually reassess changing situation
 Titration • Avoid temptations Too much surgery Too complex reconstructions • Recognize predictable “windows” Plan non-critical procedures KNOW WHEN TO QUIT
Titration • Avoid temptations Too much surgery Too complex reconstructions • Recognize predictable “windows” Plan non-critical procedures KNOW WHEN TO QUIT
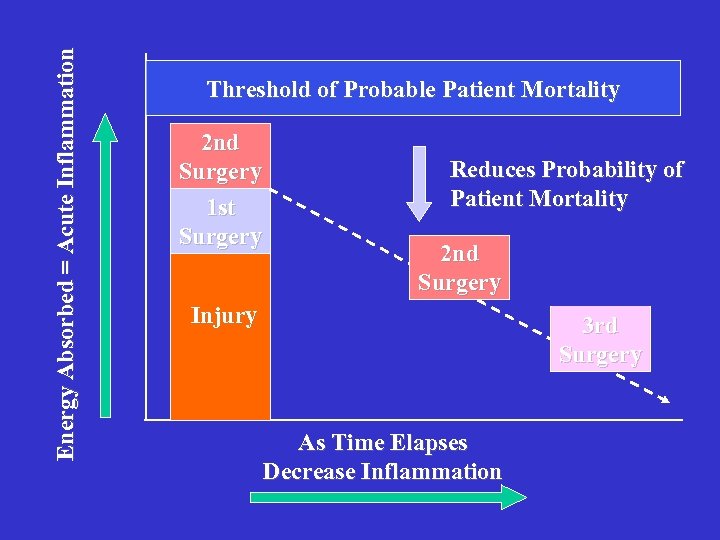 Energy Absorbed = Acute Inflammation Threshold of Probable Patient Mortality 2 nd Surgery 1 st Surgery Reduces Probability of Patient Mortality 2 nd Surgery Injury 3 rd Surgery As Time Elapses Decrease Inflammation
Energy Absorbed = Acute Inflammation Threshold of Probable Patient Mortality 2 nd Surgery 1 st Surgery Reduces Probability of Patient Mortality 2 nd Surgery Injury 3 rd Surgery As Time Elapses Decrease Inflammation
 Virtual Reality Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery • Nothing goes well at night • Anaesthetic support is variable • Double the planned OR time • Triple the estimated blood loss
Virtual Reality Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery • Nothing goes well at night • Anaesthetic support is variable • Double the planned OR time • Triple the estimated blood loss
 Orthopaedic care • Present at bedside • Acknowledge extremity injuries recoverable • Preserve vital organs
Orthopaedic care • Present at bedside • Acknowledge extremity injuries recoverable • Preserve vital organs
 Orthopaedic Care Strategy Goals • Immediate • Intermediate • Long-term
Orthopaedic Care Strategy Goals • Immediate • Intermediate • Long-term
 Immediate/Urgent Care • Priority procedures first • Multiple surgical teams if possible • Quick procedures Optimal fixation is often “sub-optimal plan”
Immediate/Urgent Care • Priority procedures first • Multiple surgical teams if possible • Quick procedures Optimal fixation is often “sub-optimal plan”
 Immediate Goals • Enhance resuscitative effort • Maintain/establish perfusion • Prevent infection • Stabilise major fractures to improve ICU care decrease blood loss decrease pain ? enhance pulmonary recovery
Immediate Goals • Enhance resuscitative effort • Maintain/establish perfusion • Prevent infection • Stabilise major fractures to improve ICU care decrease blood loss decrease pain ? enhance pulmonary recovery
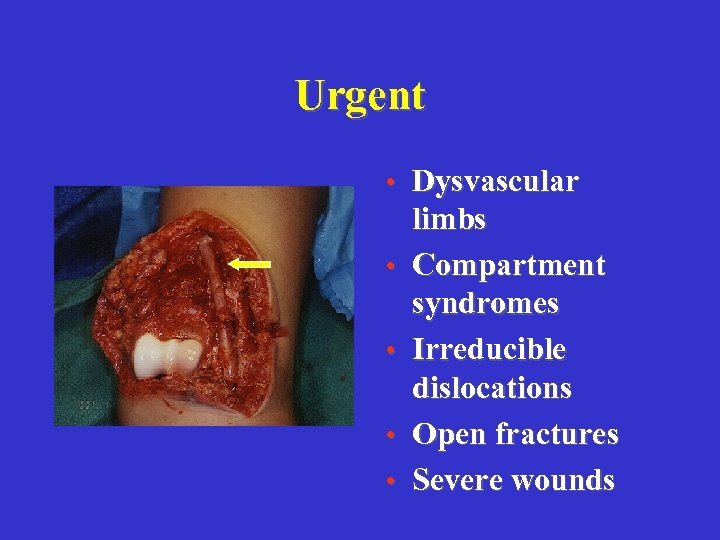 Urgent • Dysvascular • • limbs Compartment syndromes Irreducible dislocations Open fractures Severe wounds
Urgent • Dysvascular • • limbs Compartment syndromes Irreducible dislocations Open fractures Severe wounds
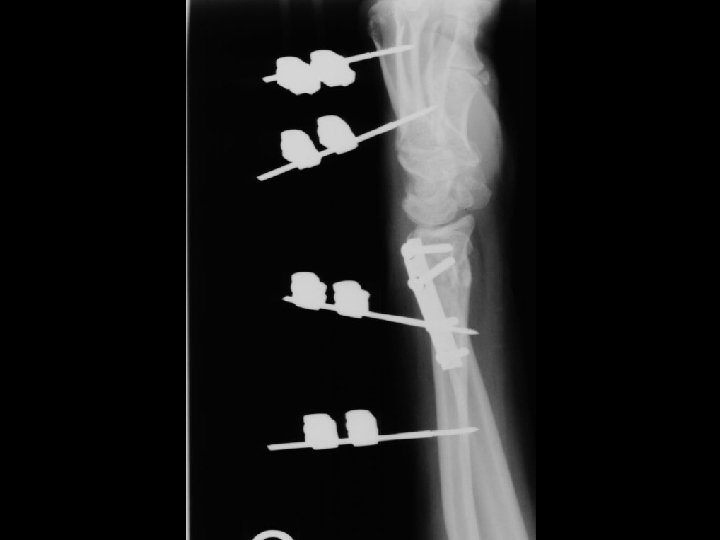
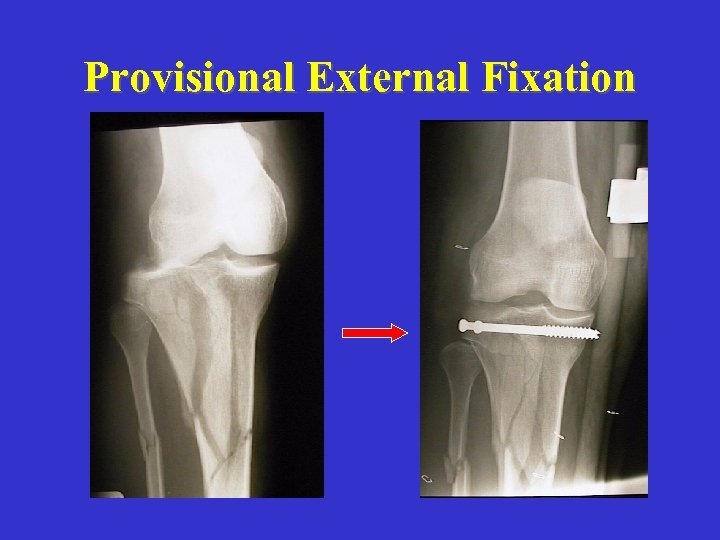 Provisional External Fixation
Provisional External Fixation
 Intermediate Goals • Performed in “windows” once patient • • • stable Convert external fixation to ORIF(long bones) Obtain soft tissue coverage Restore length/alignment of intra-articular fractures
Intermediate Goals • Performed in “windows” once patient • • • stable Convert external fixation to ORIF(long bones) Obtain soft tissue coverage Restore length/alignment of intra-articular fractures
 Non Urgent • Upper extremity fractures • Articular fractures • Foot/ankle fractures
Non Urgent • Upper extremity fractures • Articular fractures • Foot/ankle fractures
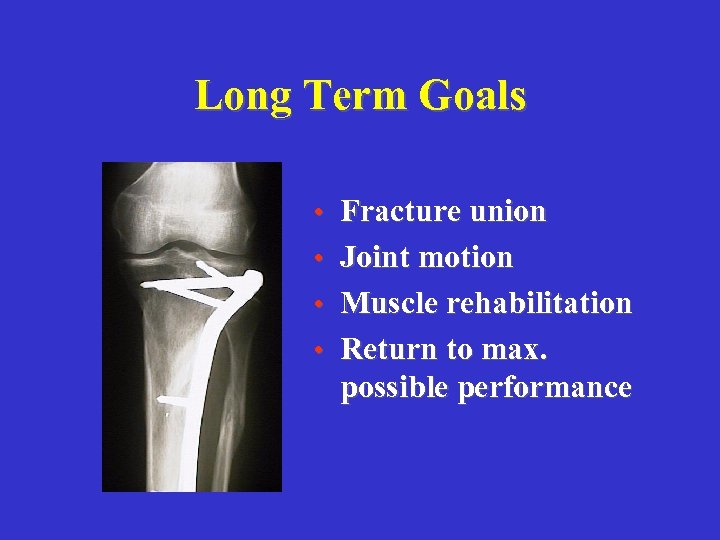 Long Term Goals • Fracture union • Joint motion • Muscle rehabilitation • Return to max. possible performance
Long Term Goals • Fracture union • Joint motion • Muscle rehabilitation • Return to max. possible performance
 Even if the result is a malunion or a non-union, late reconstruction options are available and yield acceptable results Surgery is performed on a stable and healthy patient
Even if the result is a malunion or a non-union, late reconstruction options are available and yield acceptable results Surgery is performed on a stable and healthy patient
 Stabilization of long bone fx’s in the polytraumatized patient
Stabilization of long bone fx’s in the polytraumatized patient
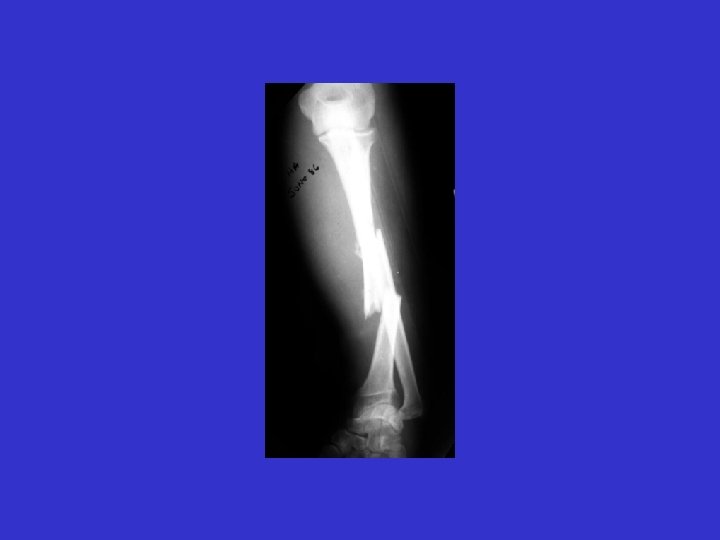
 YOUNG PATIENT HIGH-ENERGY
YOUNG PATIENT HIGH-ENERGY
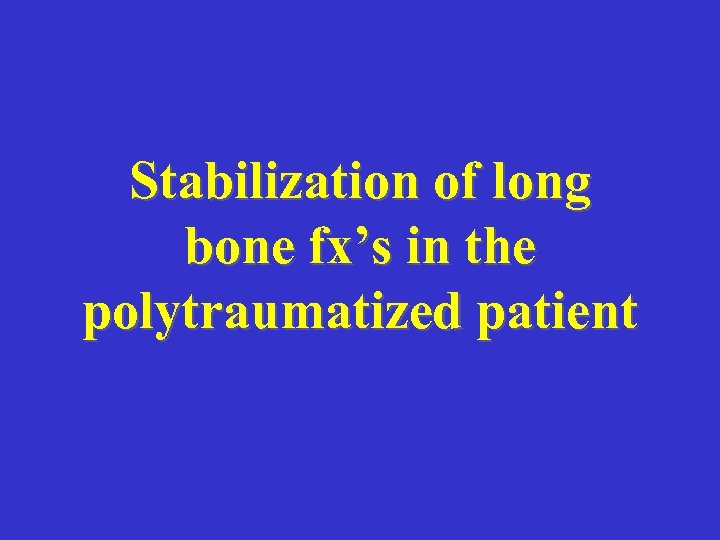
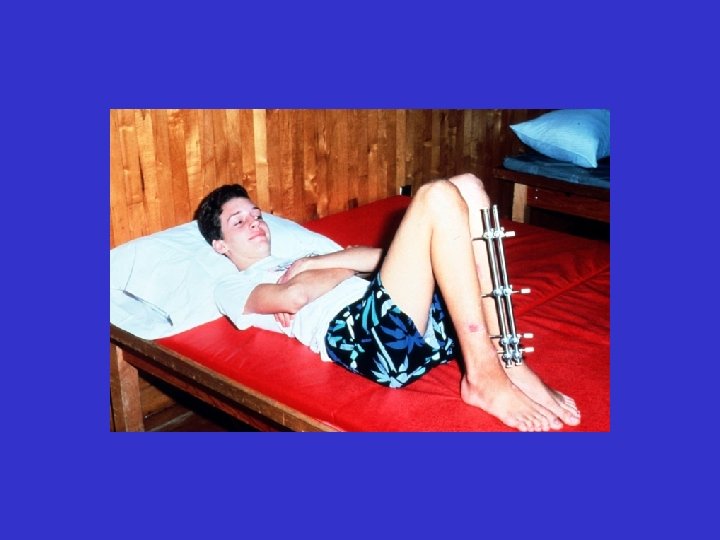
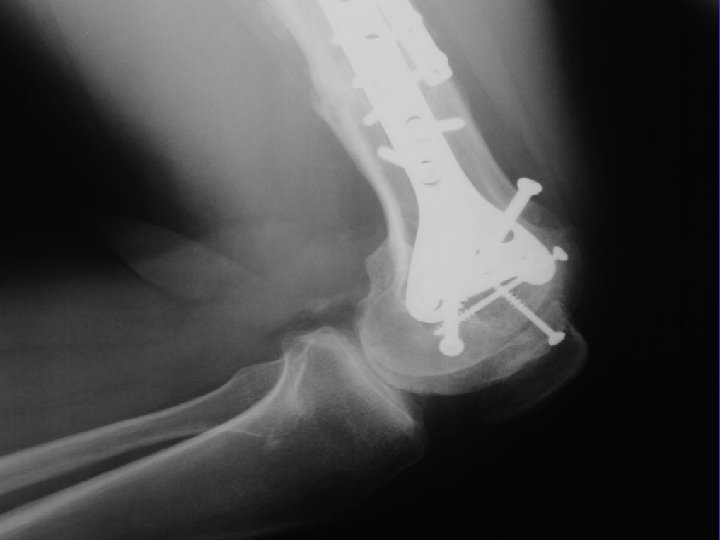
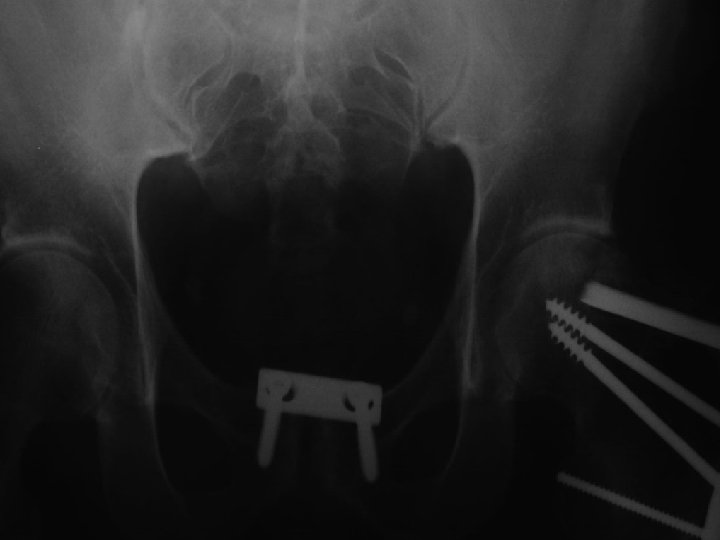
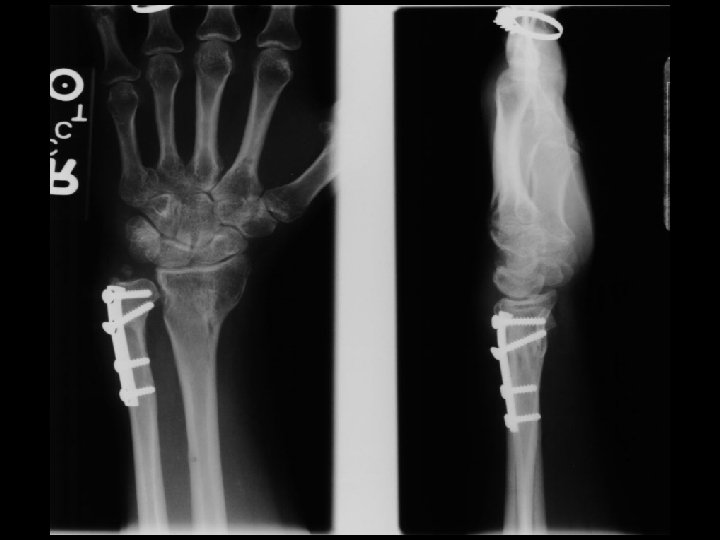
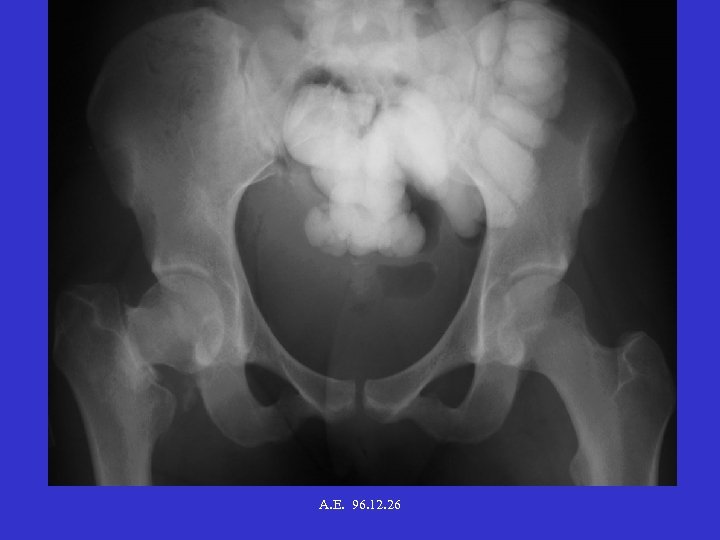 A. E. 96. 12. 26
A. E. 96. 12. 26
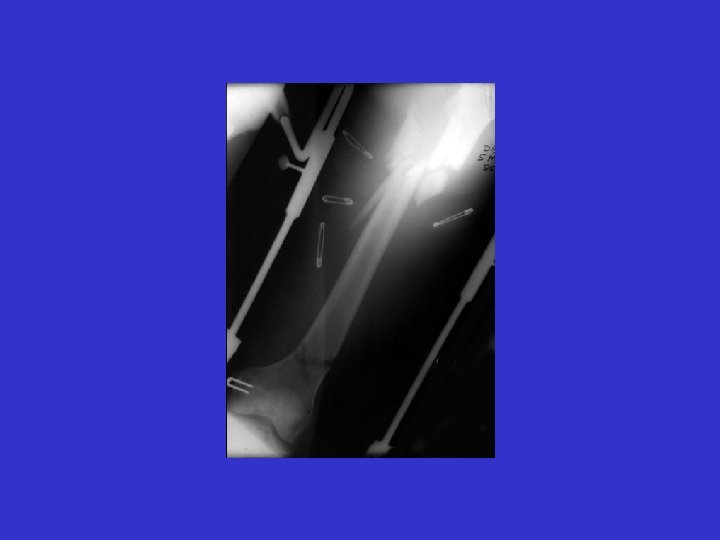
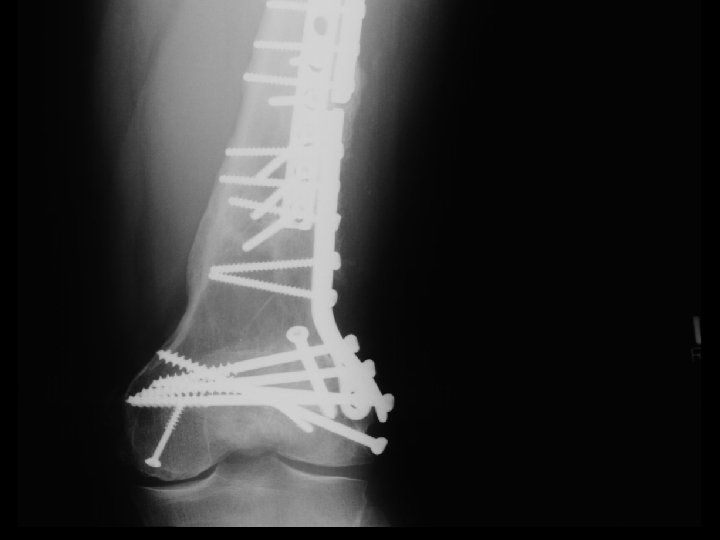
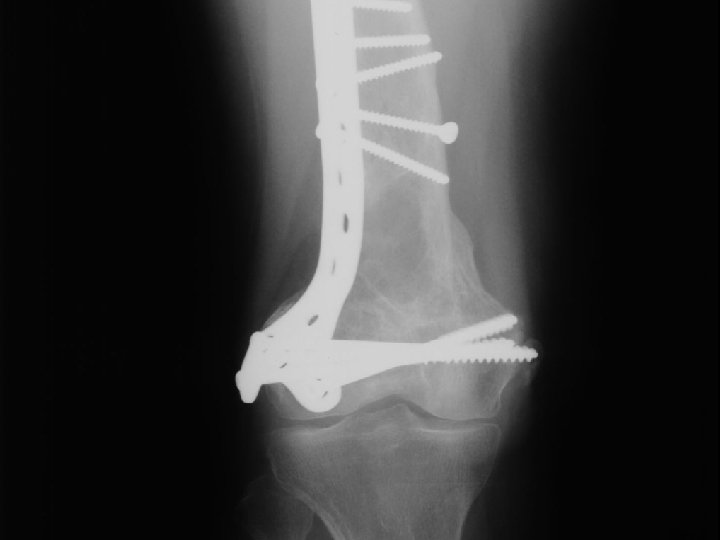
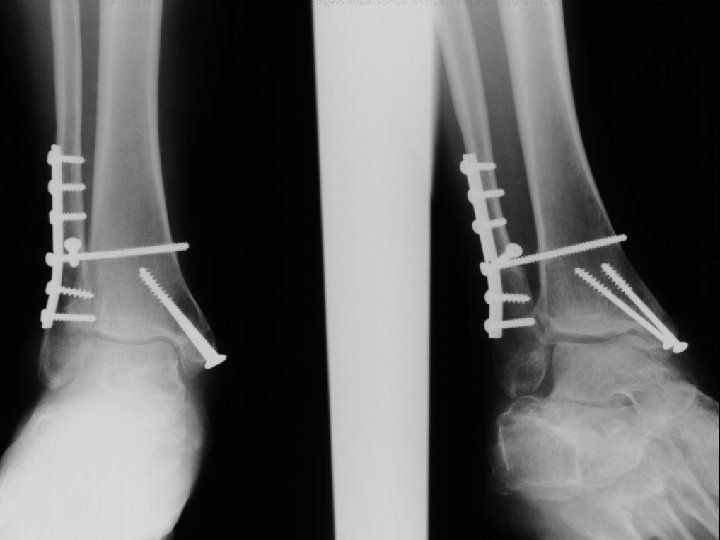
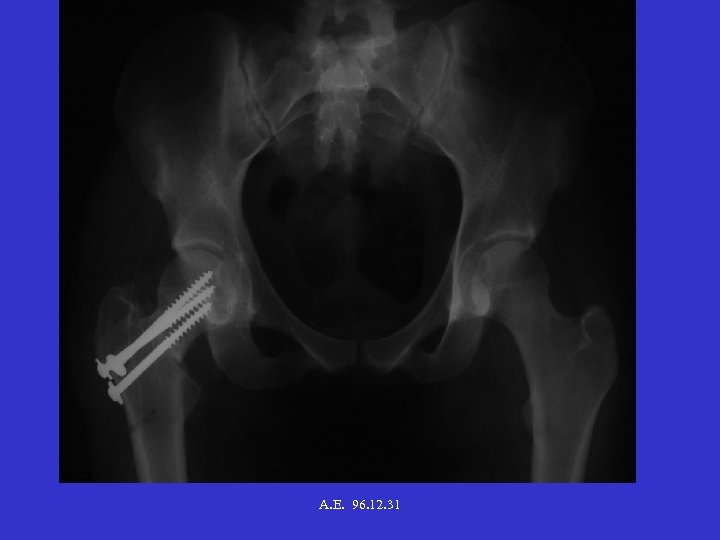 A. E. 96. 12. 31
A. E. 96. 12. 31
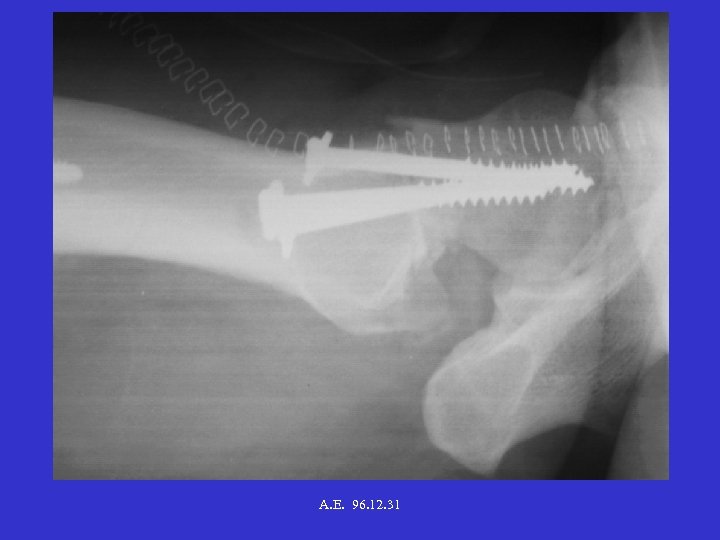 A. E. 96. 12. 31
A. E. 96. 12. 31
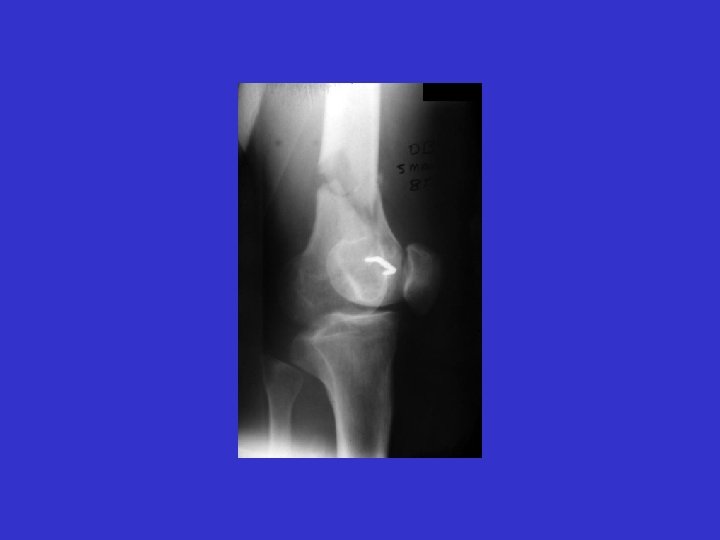
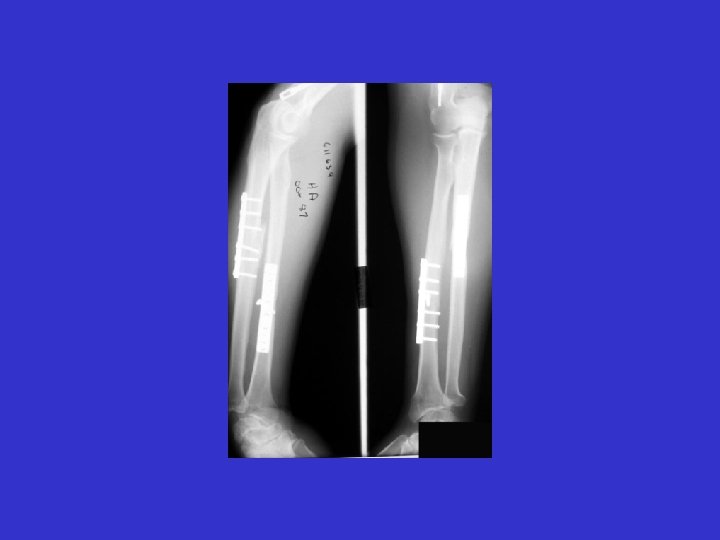
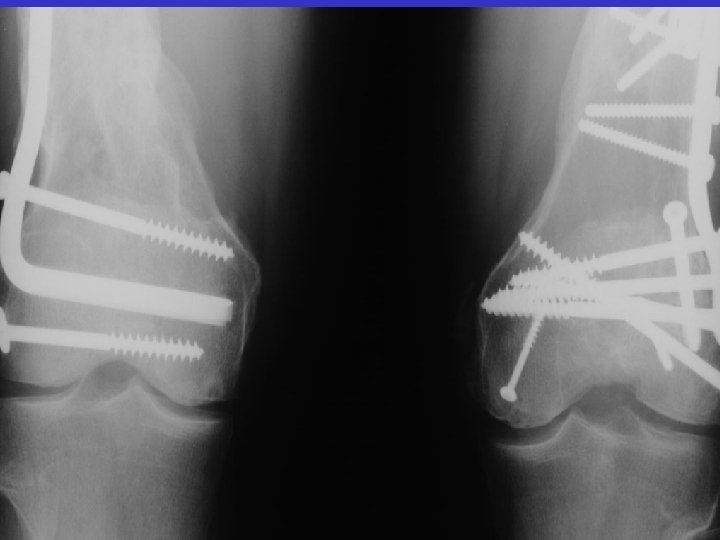
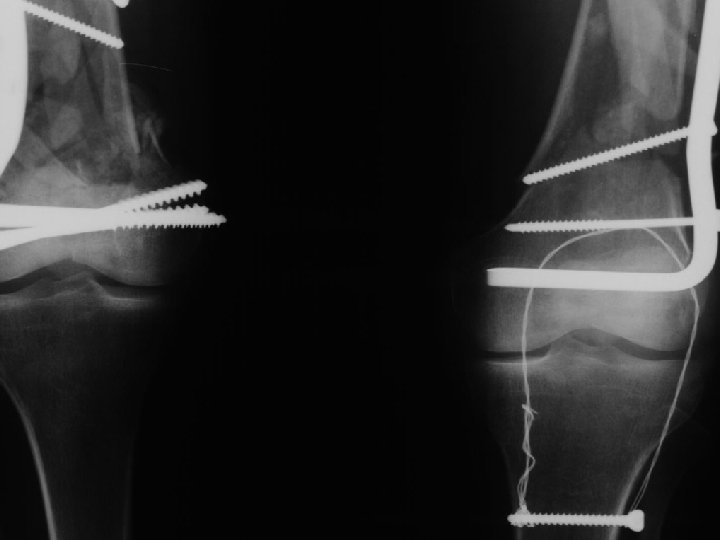
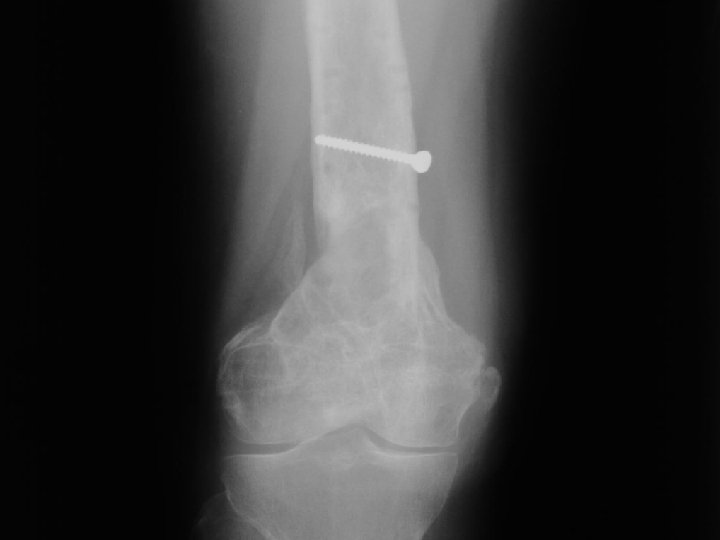
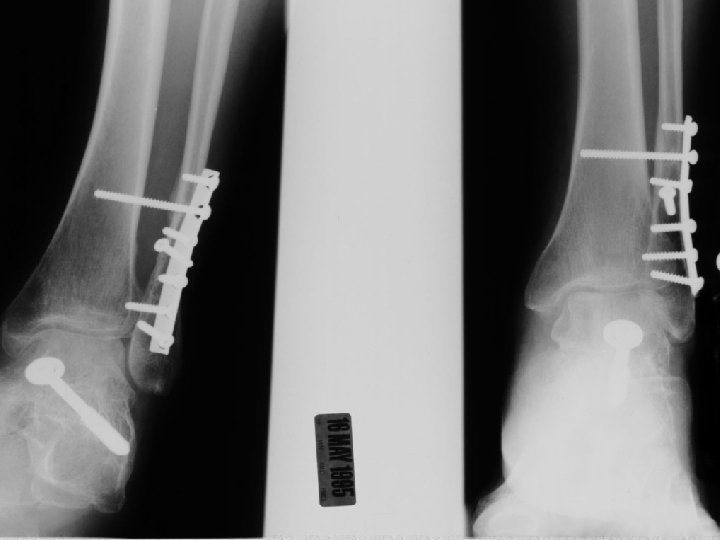
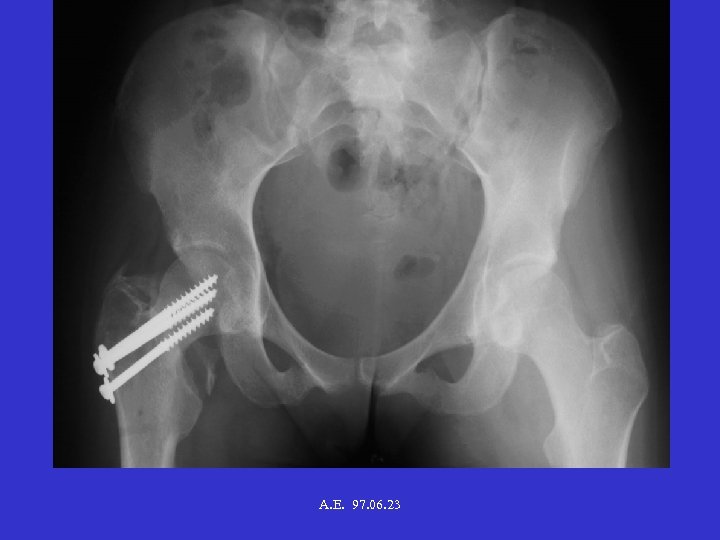 A. E. 97. 06. 23
A. E. 97. 06. 23
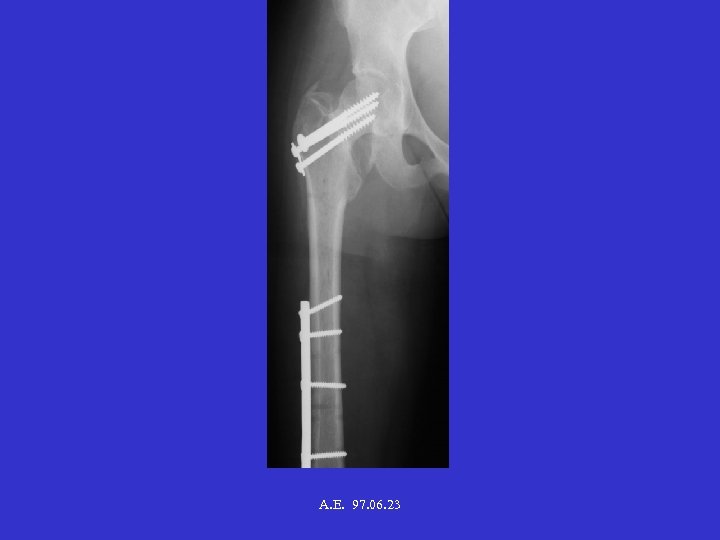 A. E. 97. 06. 23
A. E. 97. 06. 23
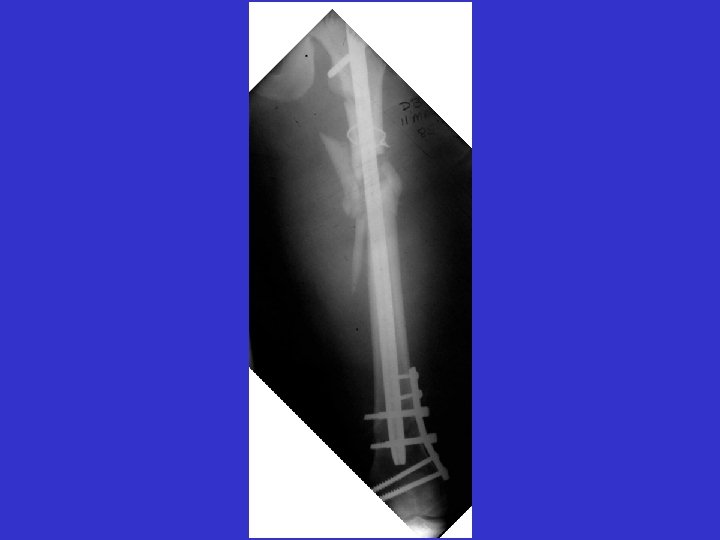
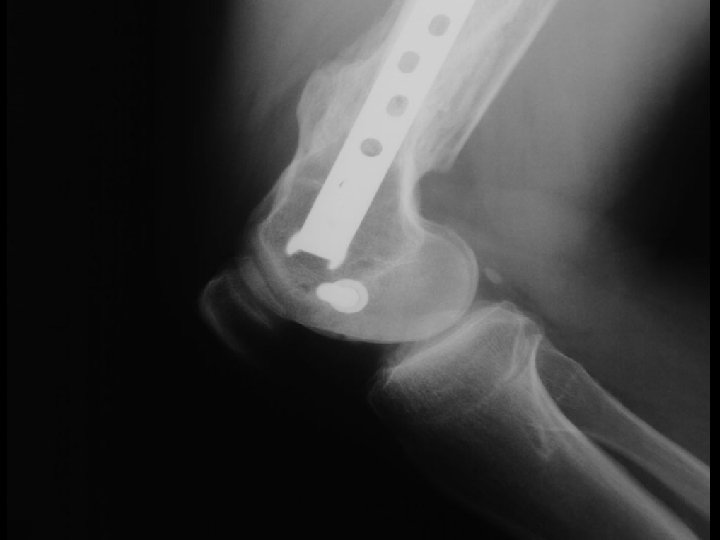
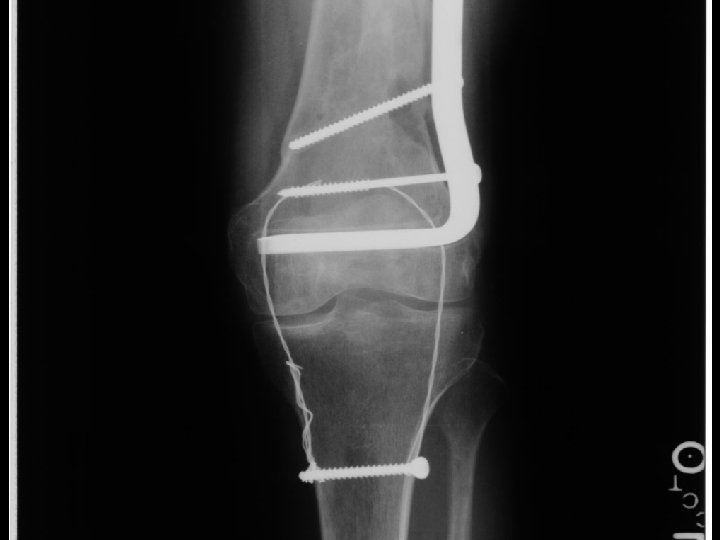
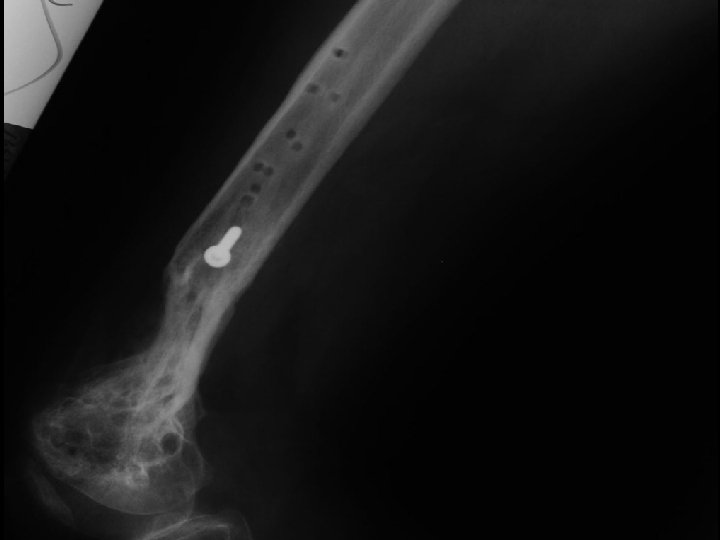
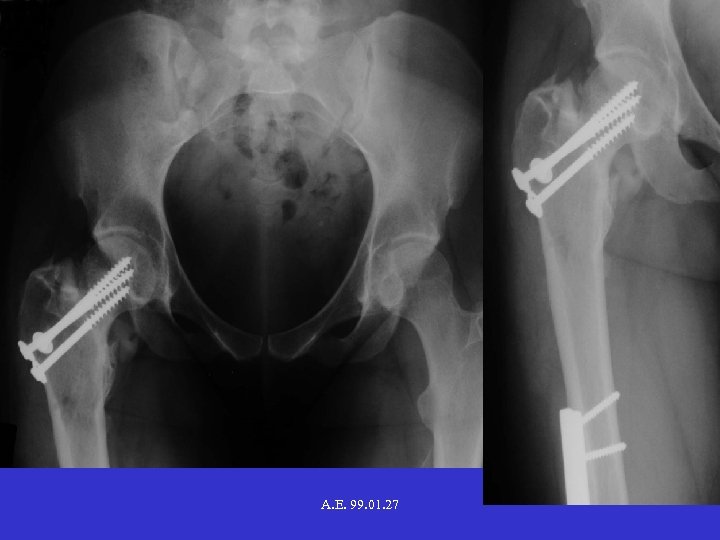 A. E. 99. 01. 27
A. E. 99. 01. 27
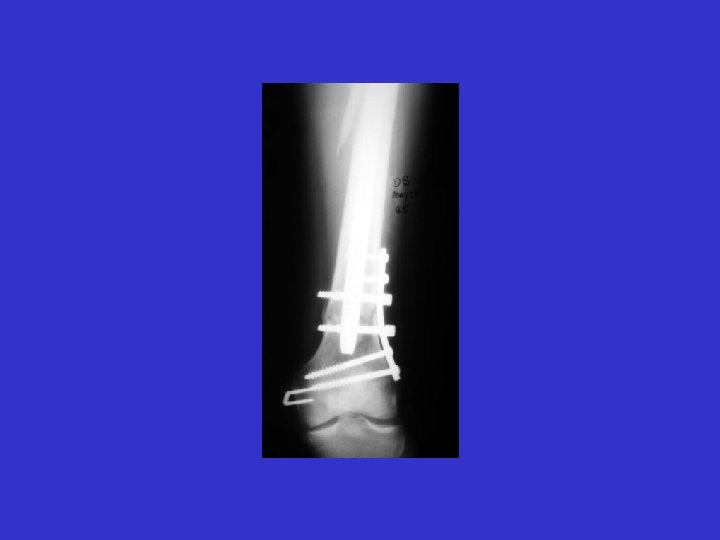
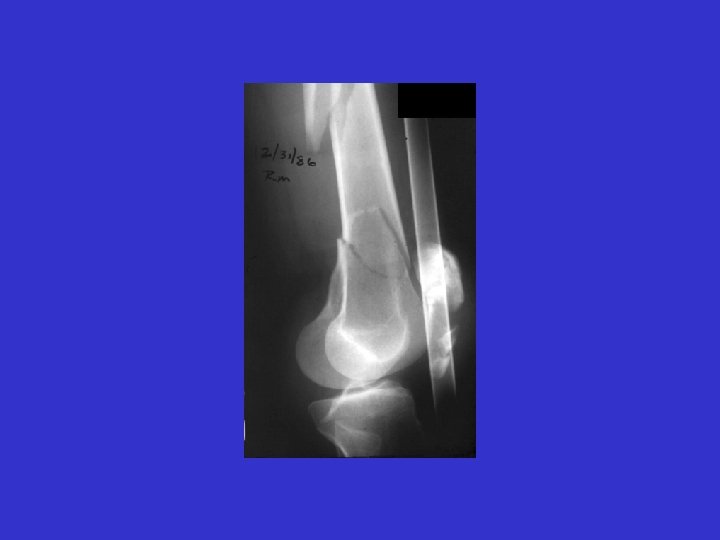
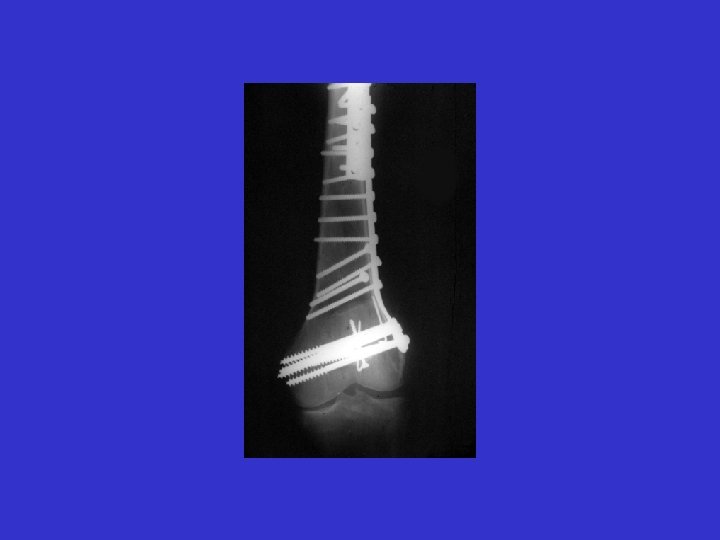
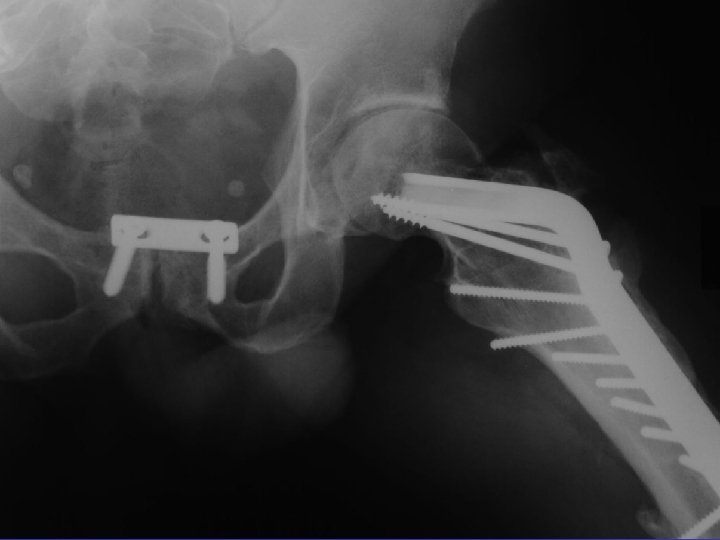
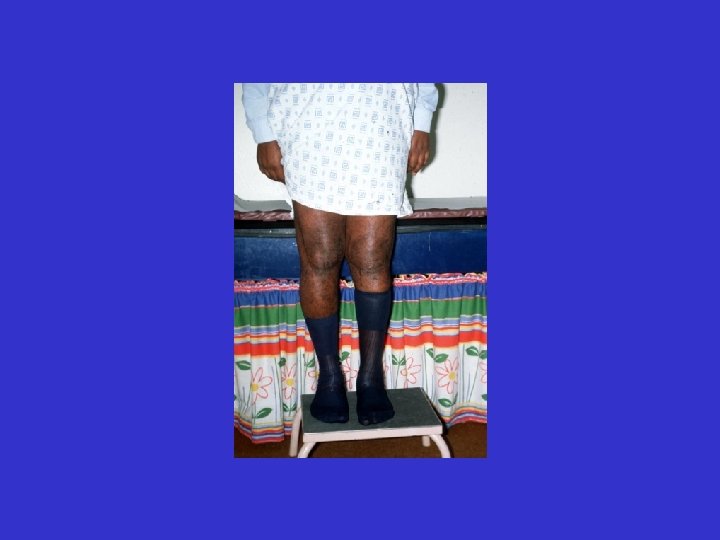
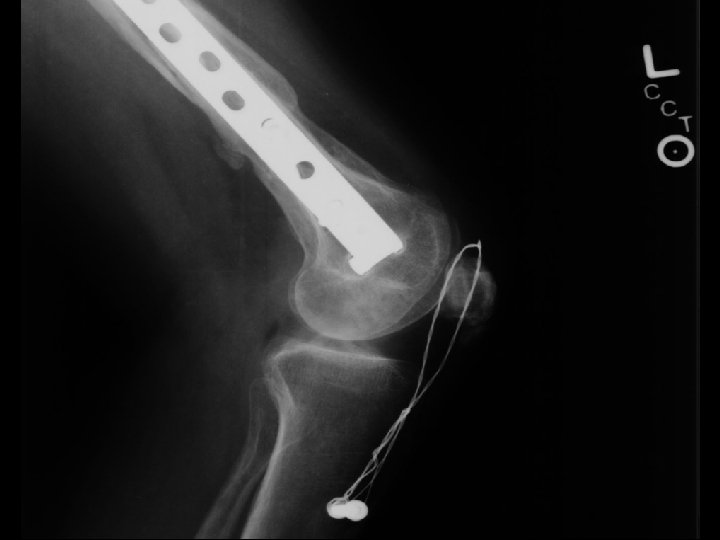
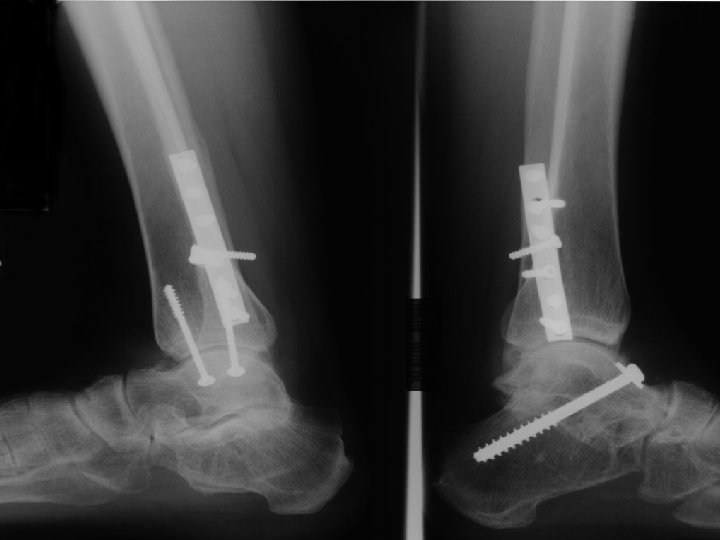
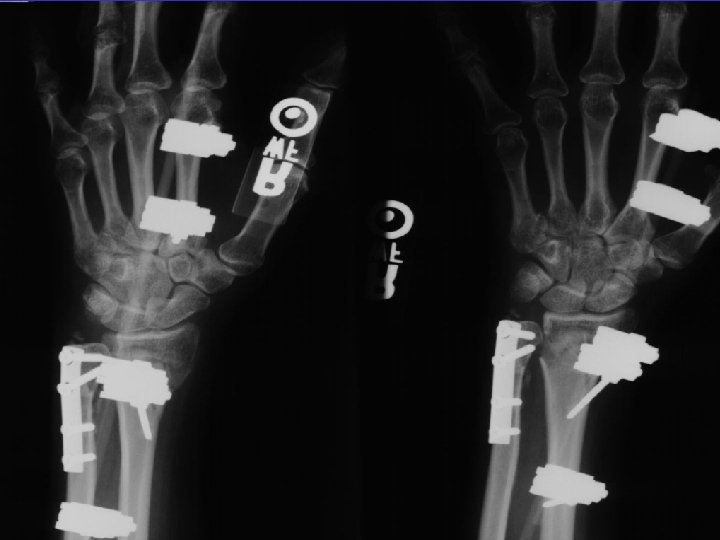
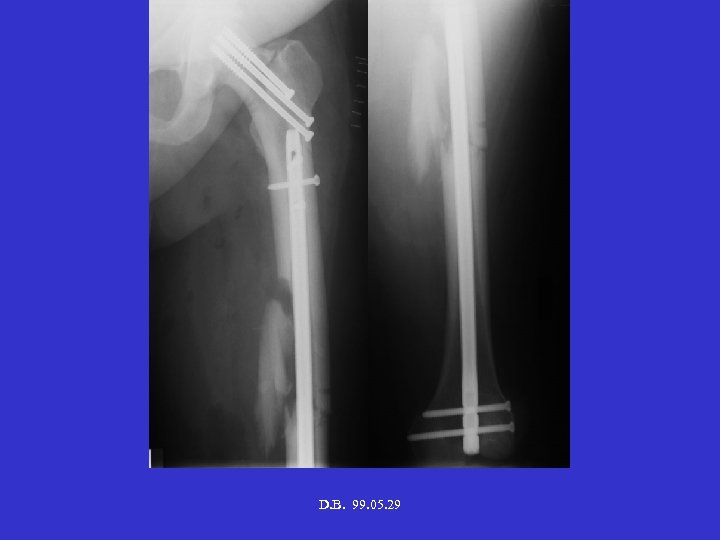 D. B. 99. 05. 29
D. B. 99. 05. 29
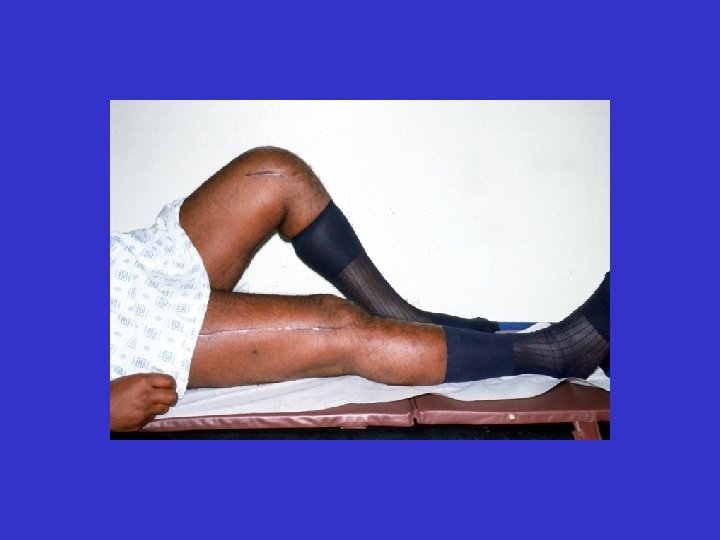
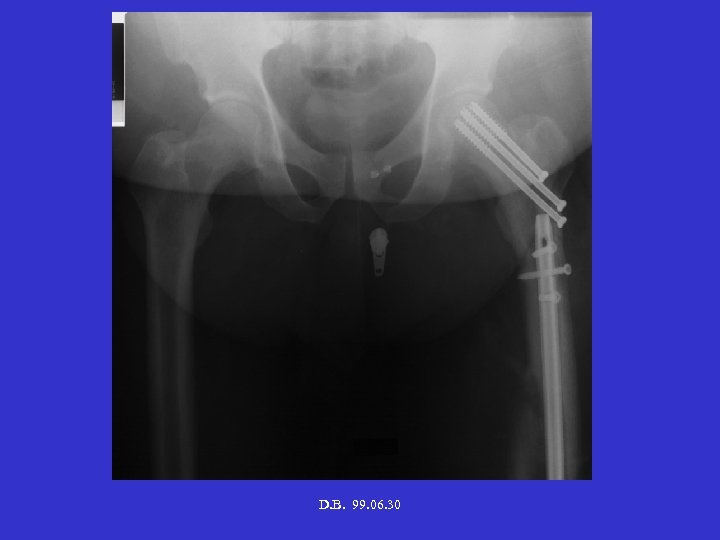 D. B. 99. 06. 30
D. B. 99. 06. 30
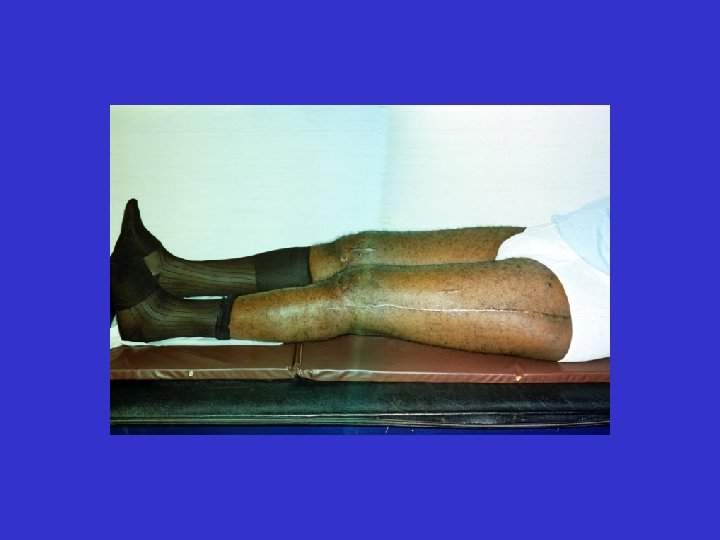
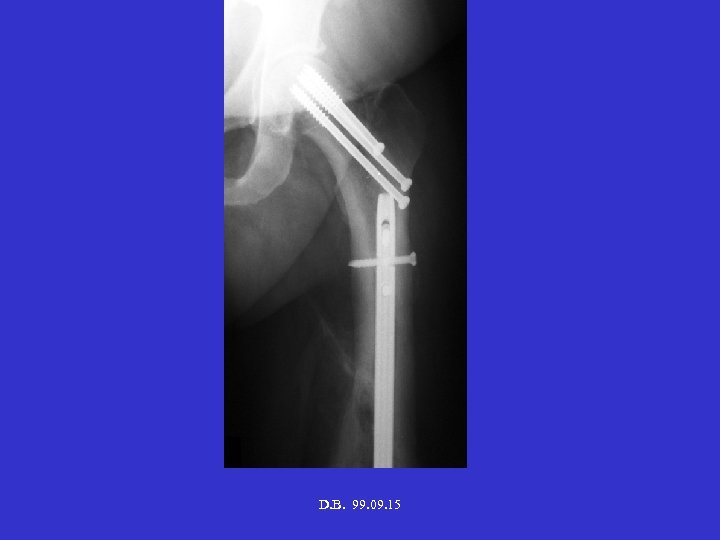 D. B. 99. 09. 15
D. B. 99. 09. 15
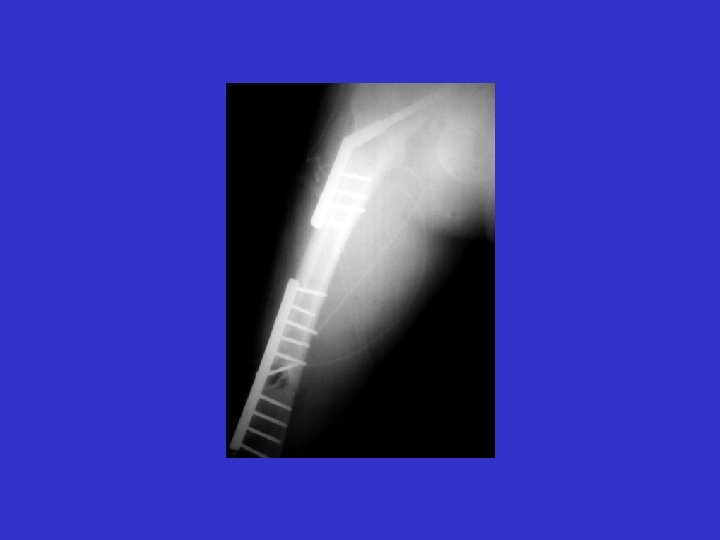
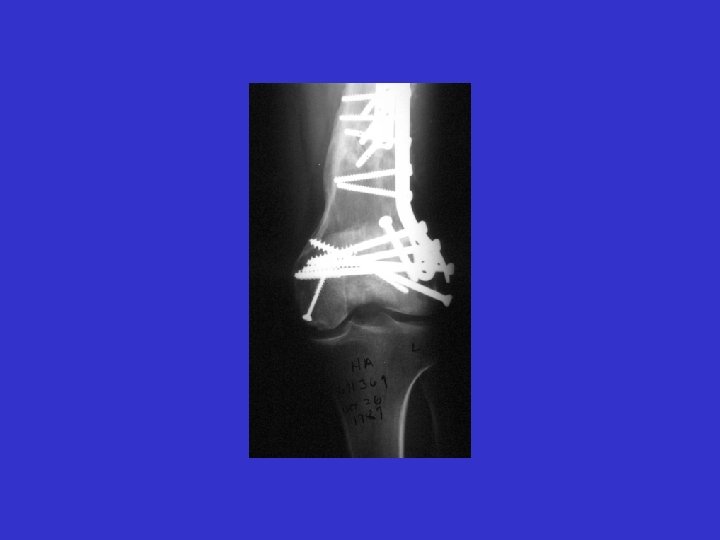
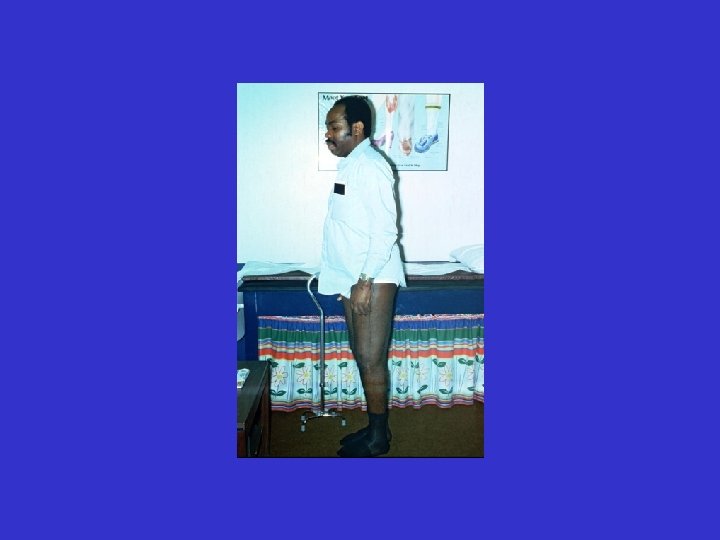
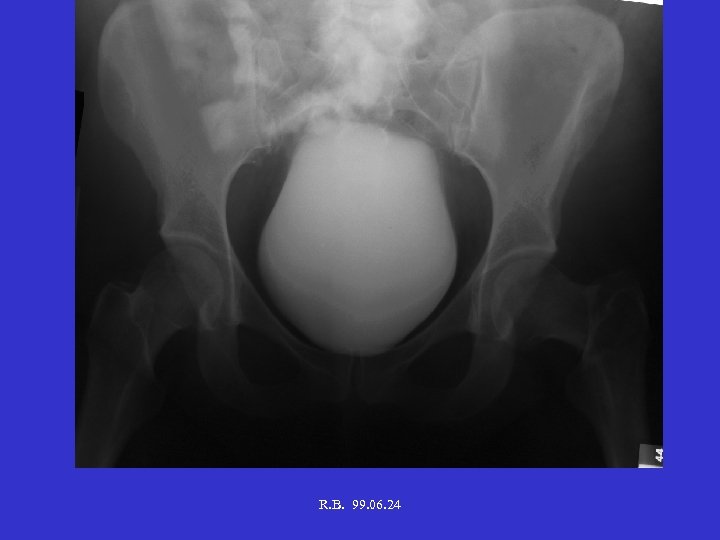 R. B. 99. 06. 24
R. B. 99. 06. 24
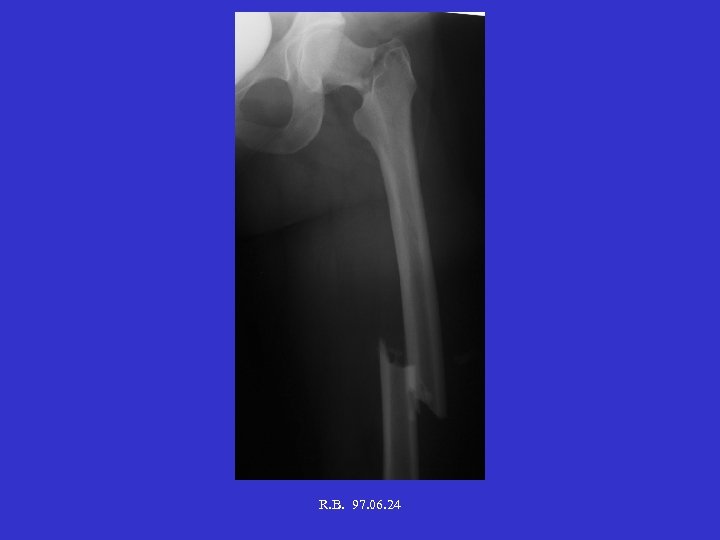 R. B. 97. 06. 24
R. B. 97. 06. 24
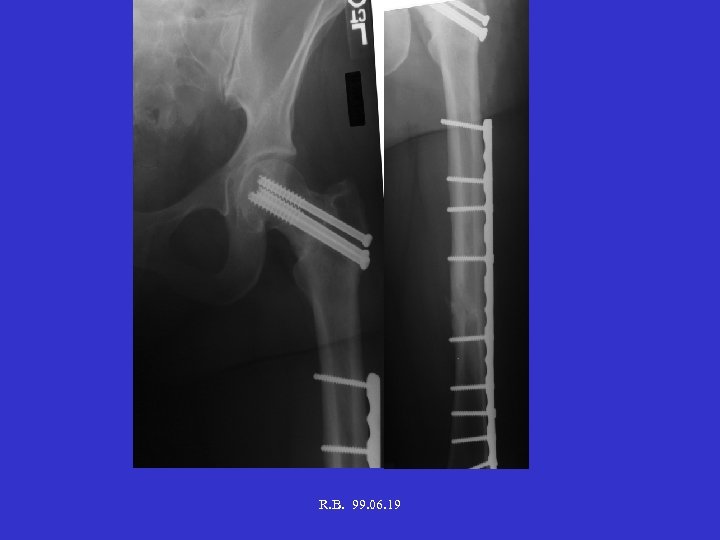 R. B. 99. 06. 19
R. B. 99. 06. 19
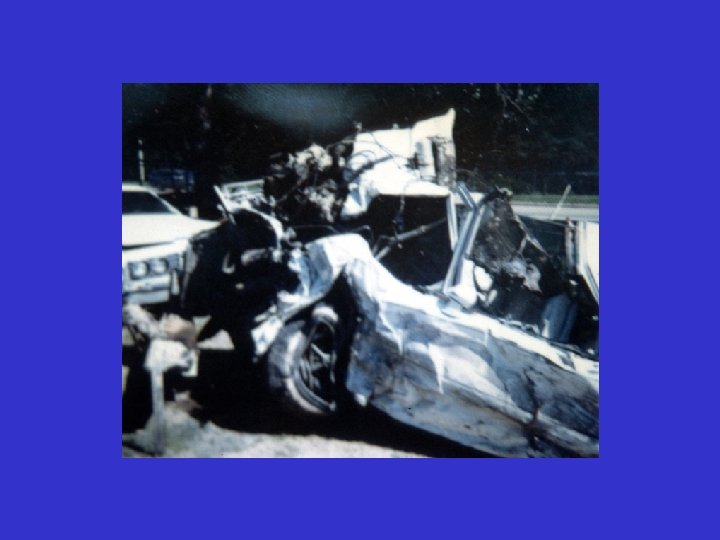
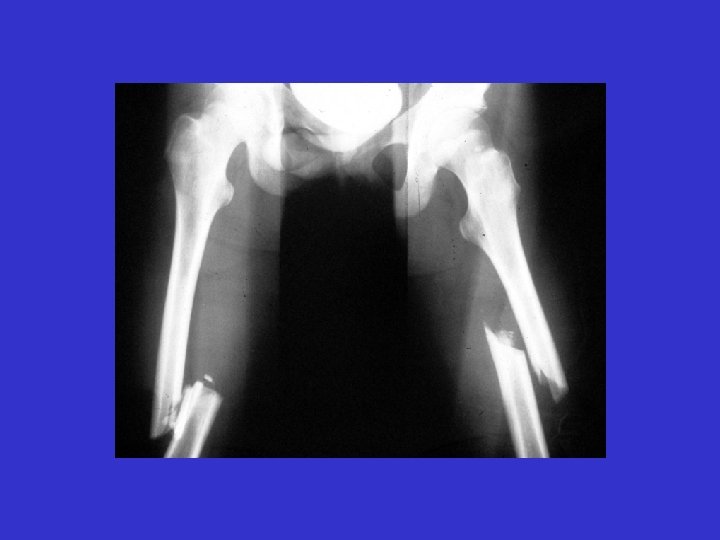
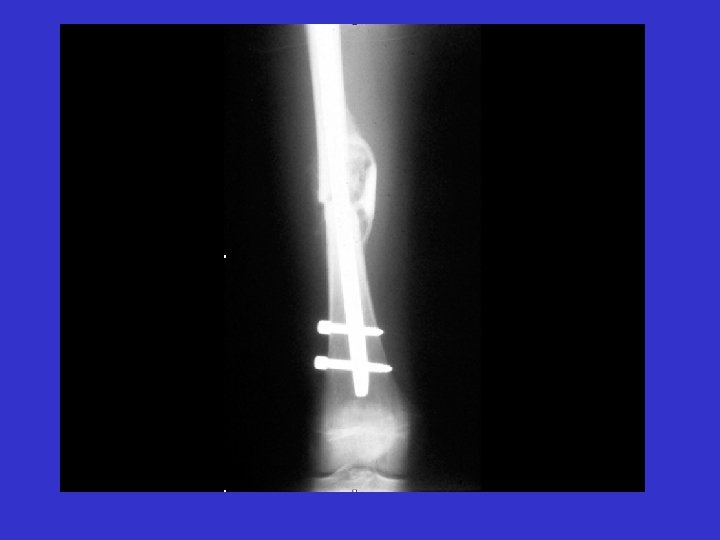
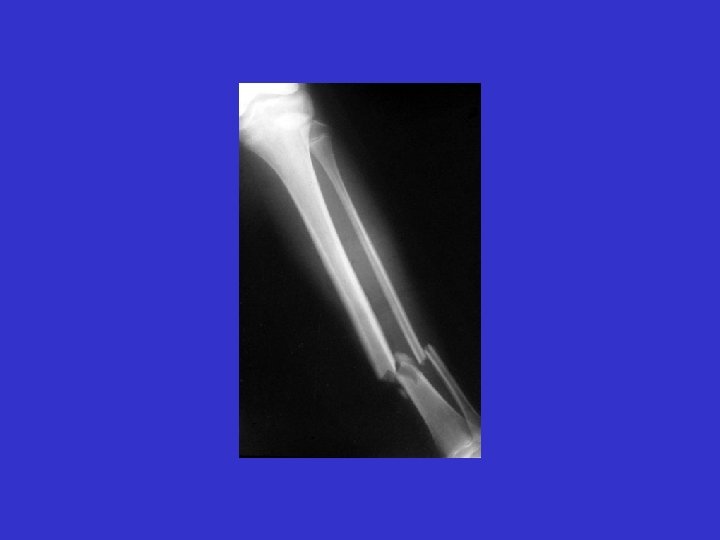




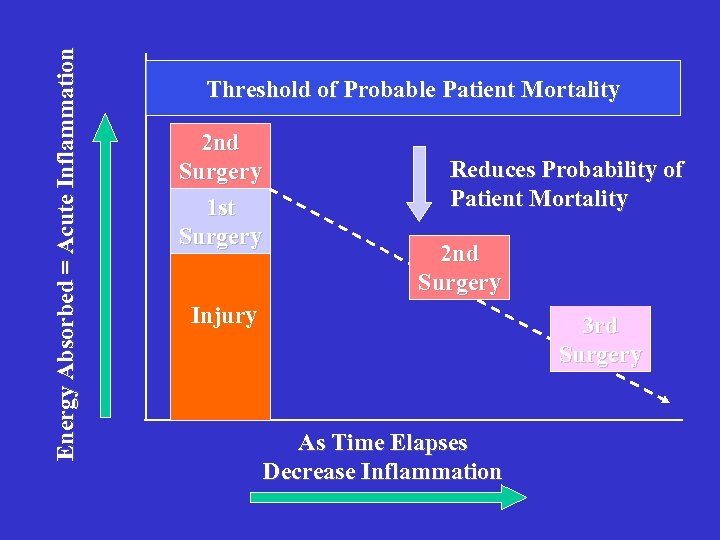 Energy Absorbed = Acute Inflammation Threshold of Probable Patient Mortality 2 nd Surgery 1 st Surgery Reduces Probability of Patient Mortality 2 nd Surgery Injury 3 rd Surgery As Time Elapses Decrease Inflammation
Energy Absorbed = Acute Inflammation Threshold of Probable Patient Mortality 2 nd Surgery 1 st Surgery Reduces Probability of Patient Mortality 2 nd Surgery Injury 3 rd Surgery As Time Elapses Decrease Inflammation
 Summary: • Patient first L ife life • Poly fractured patient M ultiple teams • Poly fractured bone M etaphyseal, joint fx’s first
Summary: • Patient first L ife life • Poly fractured patient M ultiple teams • Poly fractured bone M etaphyseal, joint fx’s first


